tensorflow的gpu和cpu计算时间对比的小例子
例子1
参数设置
NVIDIA3070, cuda11.2 cudnn8.1.0 tensorfow2.5.0,tensorflow-gpu2.5.0
cpu约80 s计算1代epoch, 而 gpu却约3 s计算一代epoch
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # @Time : 2022/6/11 16:03 # @Author : chuqianyu # @FileName: testtt2tt.py # @Software: PyCharm # @Blog :https://home.cnblogs.com/u/chuqianyu # # 指定GPU训练 # import os # os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"]="/gpu:0" ##表示使用GPU编号为0的GPU进行计算 import numpy as np from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential # 采用贯序模型 from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Dropout, Conv2D, MaxPool2D, Flatten from tensorflow.keras.datasets import mnist from tensorflow.keras.utils import to_categorical from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import TensorBoard import time def create_model(): model = Sequential() model.add(Conv2D(32, (5, 5), activation='relu', input_shape=[28, 28, 1])) # 第一卷积层 model.add(Conv2D(64, (5, 5), activation='relu')) # 第二卷积层 model.add(MaxPool2D(pool_size=(2, 2))) # 池化层 model.add(Flatten()) # 平铺层 model.add(Dropout(0.5)) model.add(Dense(128, activation='relu')) model.add(Dropout(0.5)) model.add(Dense(10, activation='softmax')) return model def compile_model(model): model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer="adam", metrics=['acc']) return model def train_model(model, x_train, y_train, batch_size=128, epochs=10): tbCallBack = TensorBoard(log_dir="model", histogram_freq=1, write_grads=True) history = model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=batch_size, epochs=epochs, shuffle=True, verbose=2, validation_split=0.2, callbacks=[tbCallBack]) return history, model if __name__ == "__main__": import tensorflow as tf print(tf.__version__) # NVIDIA3070, cuda11.2 cudnn8.1.0 tensorfow2.5.0,tensorflow-gpu2.5.0 # cpu约80 s计算1代epoch, 而 gpu却约3 s计算一代epoch with tf.device("/gpu:0"): from tensorflow.python.client import device_lib print(device_lib.list_local_devices()) (x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data() # mnist的数据我自己已经下载好了的 print(np.shape(x_train), np.shape(y_train), np.shape(x_test), np.shape(y_test)) x_train = np.expand_dims(x_train, axis=3) x_test = np.expand_dims(x_test, axis=3) y_train = to_categorical(y_train, num_classes=10) y_test = to_categorical(y_test, num_classes=10) print(np.shape(x_train), np.shape(y_train), np.shape(x_test), np.shape(y_test)) model = create_model() model = compile_model(model) print("start training") ts = time.time() history, model = train_model(model, x_train, y_train, epochs=20) print("start training", time.time() - ts)
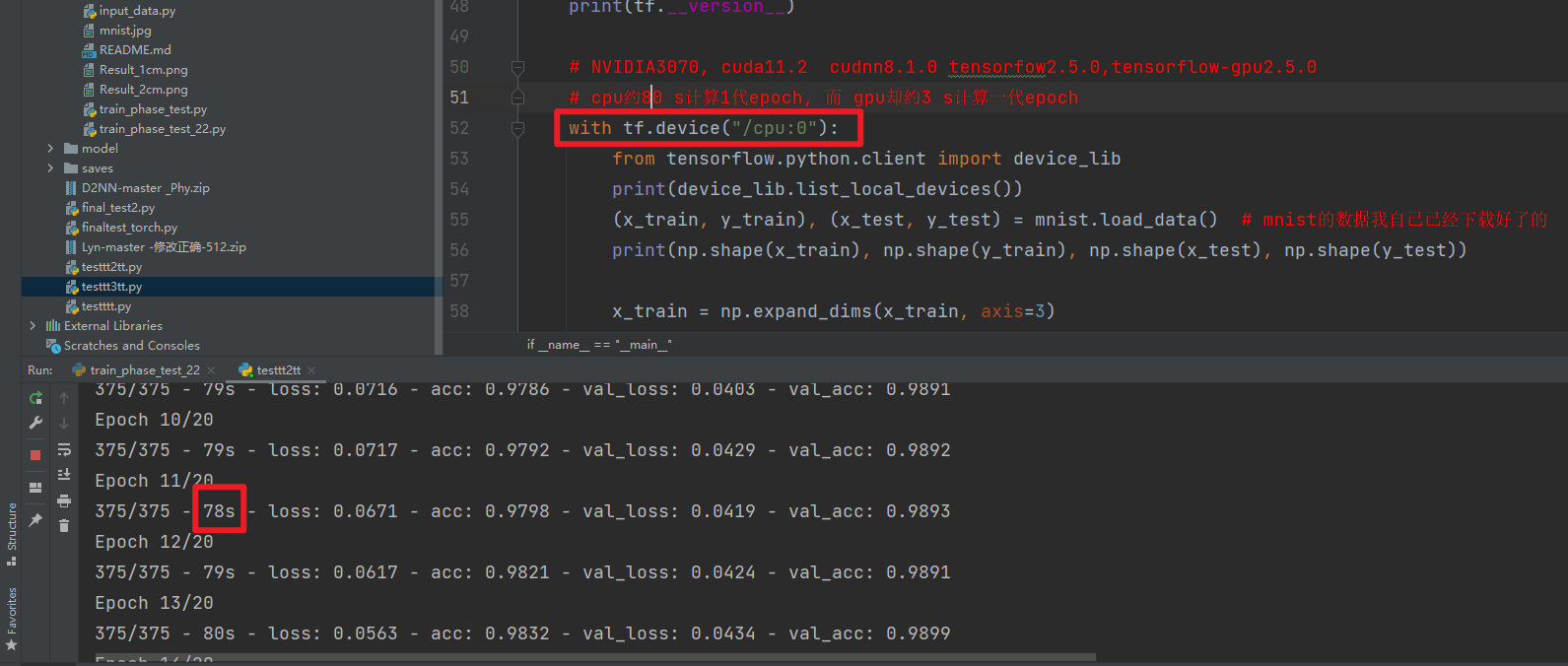
gpu约3 s计算一代epoch
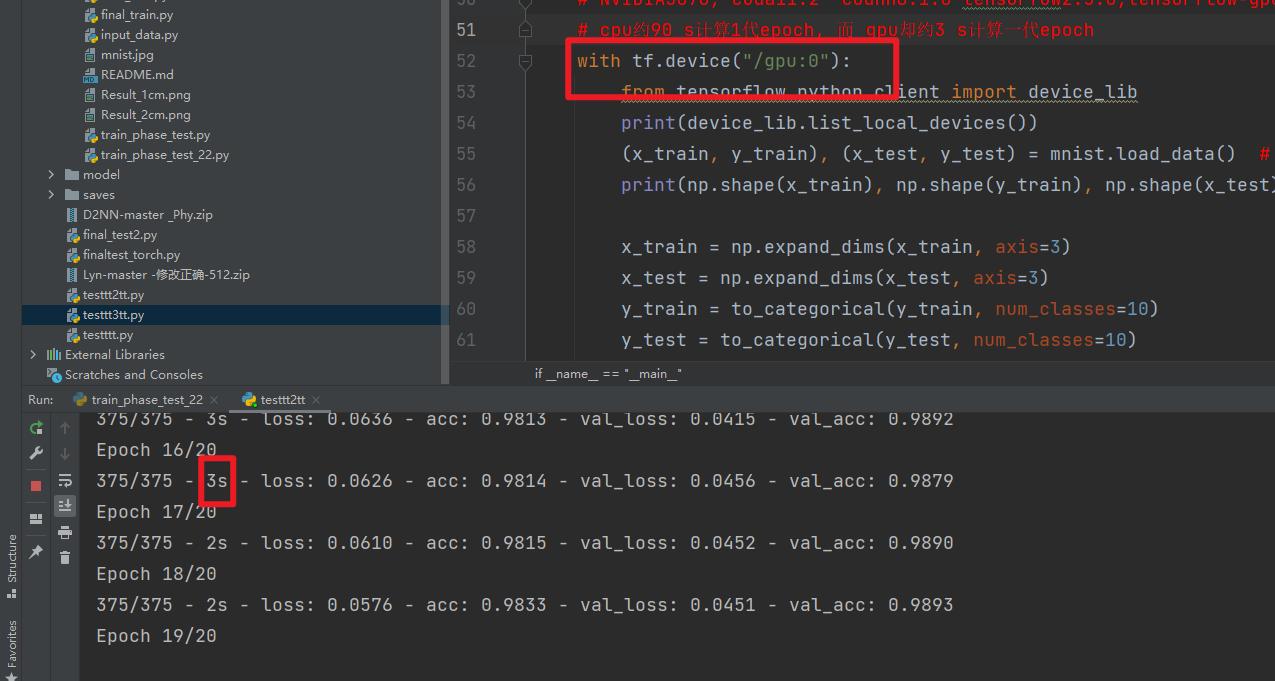
cpu约80 s计算一代epoch
例子2
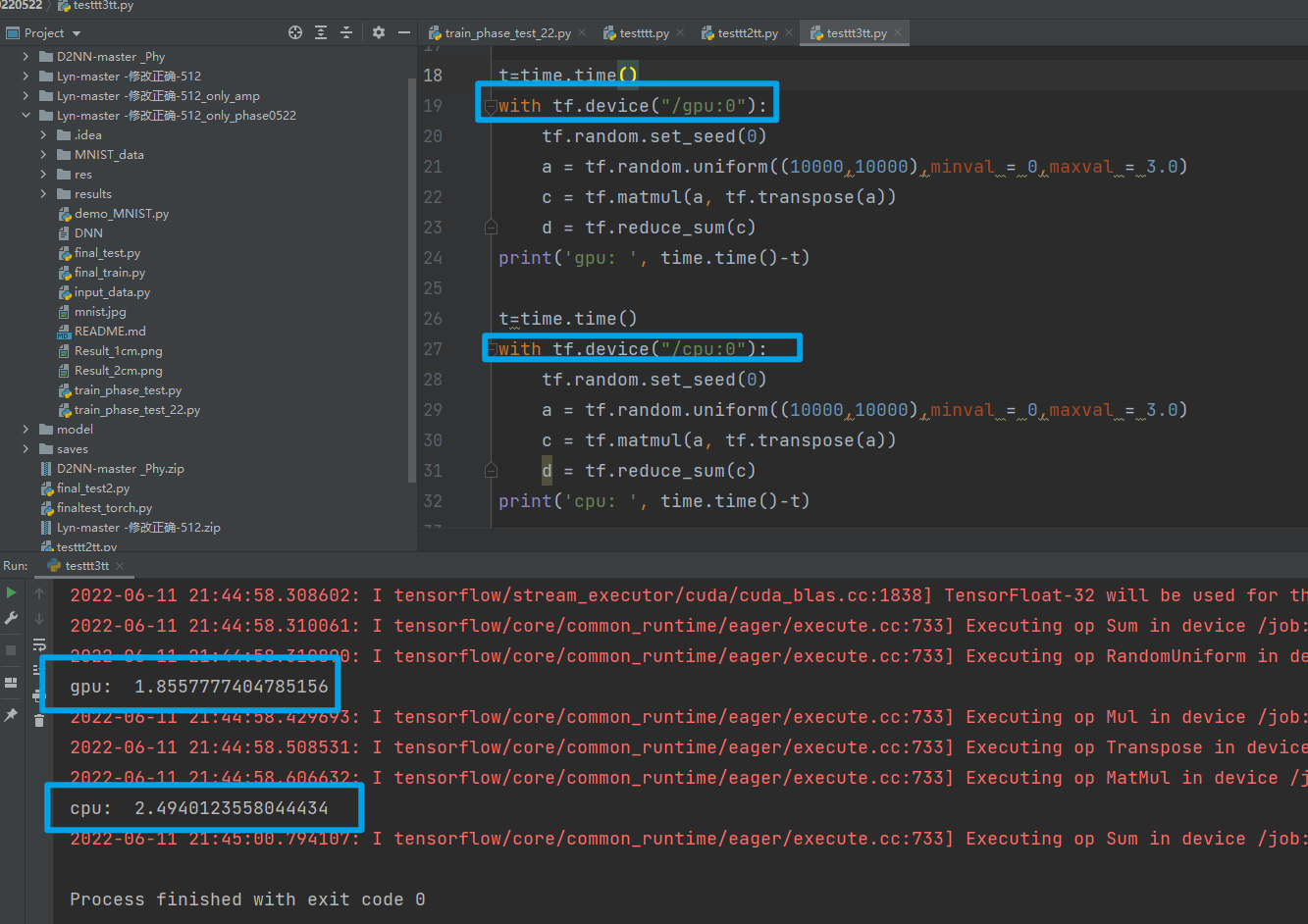
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # @Time : 2022/6/11 20:32 # @Author : chuqianyu # @FileName: testtt3tt.py # @Software: PyCharm # @Blog :https://home.cnblogs.com/u/chuqianyu import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.keras import * import time tf.config.set_soft_device_placement(True) tf.debugging.set_log_device_placement(True) gpus = tf.config.experimental.list_physical_devices('GPU') print(gpus) tf.config.experimental.set_visible_devices(gpus[0], 'GPU') tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth(gpus[0], True) t=time.time() with tf.device("/gpu:0"): tf.random.set_seed(0) a = tf.random.uniform((10000,10000),minval = 0,maxval = 3.0) c = tf.matmul(a, tf.transpose(a)) d = tf.reduce_sum(c) print('gpu: ', time.time()-t) t=time.time() with tf.device("/cpu:0"): tf.random.set_seed(0) a = tf.random.uniform((10000,10000),minval = 0,maxval = 3.0) c = tf.matmul(a, tf.transpose(a)) d = tf.reduce_sum(c) print('cpu: ', time.time()-t)
作者:楚千羽
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/chuqianyu/
本文来自博客园,本文作者:楚千羽,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/chuqianyu/p/16366889.html
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须在文章页面给出原文连接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利!
















【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 从HTTP原因短语缺失研究HTTP/2和HTTP/3的设计差异
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~