使用Supervisord管理进程
1. Supervisor简介
Supervisord 是用 Python 实现的一款的进程管理工具,supervisord 要求管理的程序是非 daemon 程序,supervisord 会帮你把它转成 daemon 程序,因此如果用 supervisord 来管理进程,进程需要以非daemon的方式启动。
例如:管理nginx 的话,必须在 nginx 的配置文件里添加一行设置 daemon off 让 nginx 以非 daemon 方式启动。
2. Supervisor安装
以centos系统为例,以下两种方式选择其一。
# yum install 的方式
yum install -y supervisor
# easy_install的方式
yum install -y python-setuptools
easy_install supervisor
echo_supervisord_conf >/etc/supervisord.conf3. Supervisor的配置
3.1. supervisord.conf的配置
如果使用yum install -y supervisor的命令安装,会生成默认配置/etc/supervisord.conf和目录/etc/supervisord.d,如果没有则自行创建。
在/etc/supervisord.d的目录下创建conf和log两个目录,conf用于存放管理进程的配置,log用于存放管理进程的日志。
cd /etc/supervisord.d
mkdir conf log修改/etc/supervisord.conf的[include]部分,即载入/etc/supervisord.d/conf目录下的所有配置。
vi /etc/supervisord.conf
...
[include]
files = supervisord.d/conf/*.conf
...也可以修改supervisor应用日志的目录,默认日志路径为/var/log/supervisor/supervisord.log。
vi /etc/supervisord.conf
...
[supervisord]
logfile=/var/log/supervisor/supervisord.log ; (main log file;default $CWD/supervisord.log)
logfile_maxbytes=50MB ; (max main logfile bytes b4 rotation;default 50MB)
logfile_backups=10 ; (num of main logfile rotation backups;default 10)
loglevel=info ; (log level;default info; others: debug,warn,trace)
pidfile=/var/run/supervisord.pid ; (supervisord pidfile;default supervisord.pid)
...3.2. 管理应用的配置
进入到/etc/supervisord.d/conf目录,创建管理应用的配置,可以创建多个应用配置。
例如,创建confd.conf配置。
[program:confd]
directory = /usr/local/bin ; 程序的启动目录
command = /usr/local/bin/confd -config-file /etc/confd/confd.toml ; 启动命令,与命令行启动的命令是一样的
autostart = true ; 在 supervisord 启动的时候也自动启动
startsecs = 5 ; 启动 5 秒后没有异常退出,就当作已经正常启动了
autorestart = true ; 程序异常退出后自动重启
startretries = 3 ; 启动失败自动重试次数,默认是 3
user = root ; 用哪个用户启动
redirect_stderr = true ; 把 stderr 重定向到 stdout,默认 false
stdout_logfile_maxbytes = 20MB ; stdout 日志文件大小,默认 50MB
stdout_logfile_backups = 20 ; stdout 日志文件备份数
; stdout 日志文件,需要注意当指定目录不存在时无法正常启动,所以需要手动创建目录(supervisord 会自动创建日志文件)
stdout_logfile = /etc/supervisord.d/log/confd.log ;日志统一放在log目录下
; 可以通过 environment 来添加需要的环境变量,一种常见的用法是修改 PYTHONPATH
; environment=PYTHONPATH=$PYTHONPATH:/path/to/somewhere4. Surpervisor的启动
# supervisord二进制启动
supervisord -c /etc/supervisord.conf
# 检查进程
ps aux | grep supervisord或者以systemd的方式管理
vi /etc/rc.d/init.d/supervisord
#!/bin/sh
#
# /etc/rc.d/init.d/supervisord
#
# Supervisor is a client/server system that
# allows its users to monitor and control a
# number of processes on UNIX-like operating
# systems.
#
# chkconfig: - 64 36
# description: Supervisor Server
# processname: supervisord
# Source init functions
. /etc/rc.d/init.d/functions
prog="supervisord"
prefix="/usr"
exec_prefix="${prefix}"
prog_bin="${exec_prefix}/bin/supervisord"
PIDFILE="/var/run/$prog.pid"
start()
{
echo -n $"Starting $prog: "
daemon $prog_bin --pidfile $PIDFILE -c /etc/supervisord.conf
[ -f $PIDFILE ] && success $"$prog startup" || failure $"$prog startup"
echo
}
stop()
{
echo -n $"Shutting down $prog: "
[ -f $PIDFILE ] && killproc $prog || success $"$prog shutdown"
echo
}
case "$1" in
start)
start
;;
stop)
stop
;;
status)
status $prog
;;
restart)
stop
start
;;
*)
echo "Usage: $0 {start|stop|restart|status}"
;;
esac设置开机启动及systemd方式启动。
sudo chmod +x /etc/rc.d/init.d/supervisord
sudo chkconfig --add supervisord
sudo chkconfig supervisord on
sudo service supervisord start
5. supervisorctl&supervisord
Supervisord 安装完成后有两个可用的命令行 supervisord 和 supervisorctl,命令使用解释如下:
5.1. supervisorctl
supervisorctl stop programxxx,停止某一个进程(programxxx),programxxx 为 [program:beepkg] 里配置的值,这个示例就是 beepkg。supervisorctl start programxxx,启动某个进程。supervisorctl restart programxxx,重启某个进程。supervisorctl status,查看进程状态。supervisorctl stop groupworker,重启所有属于名为 groupworker 这个分组的进程(start,restart 同理)。supervisorctl stop all,停止全部进程,注:start、restart、stop 都不会载入最新的配置文件。supervisorctl reload,载入最新的配置文件,停止原有进程并按新的配置启动、管理所有进程。supervisorctl update,根据最新的配置文件,启动新配置或有改动的进程,配置没有改动的进程不会受影响而重启。
更多参考:
$ supervisorctl --help
supervisorctl -- control applications run by supervisord from the cmd line.
Usage: /usr/bin/supervisorctl [options] [action [arguments]]
Options:
-c/--configuration -- configuration file path (default /etc/supervisord.conf)
-h/--help -- print usage message and exit
-i/--interactive -- start an interactive shell after executing commands
-s/--serverurl URL -- URL on which supervisord server is listening
(default "http://localhost:9001").
-u/--username -- username to use for authentication with server
-p/--password -- password to use for authentication with server
-r/--history-file -- keep a readline history (if readline is available)
action [arguments] -- see below
Actions are commands like "tail" or "stop". If -i is specified or no action is
specified on the command line, a "shell" interpreting actions typed
interactively is started. Use the action "help" to find out about available
actions.例如:
# supervisorctl status
confd RUNNING pid 31256, uptime 0:11:24
twemproxy RUNNING pid 31255, uptime 0:11:245.2. supervisord
- supervisord,初始启动 Supervisord,启动、管理配置中设置的进程。
$ supervisord --help
supervisord -- run a set of applications as daemons.
Usage: /usr/bin/supervisord [options]
Options:
-c/--configuration FILENAME -- configuration file
-n/--nodaemon -- run in the foreground (same as 'nodaemon true' in config file)
-h/--help -- print this usage message and exit
-v/--version -- print supervisord version number and exit
-u/--user USER -- run supervisord as this user (or numeric uid)
-m/--umask UMASK -- use this umask for daemon subprocess (default is 022)
-d/--directory DIRECTORY -- directory to chdir to when daemonized
-l/--logfile FILENAME -- use FILENAME as logfile path
-y/--logfile_maxbytes BYTES -- use BYTES to limit the max size of logfile
-z/--logfile_backups NUM -- number of backups to keep when max bytes reached
-e/--loglevel LEVEL -- use LEVEL as log level (debug,info,warn,error,critical)
-j/--pidfile FILENAME -- write a pid file for the daemon process to FILENAME
-i/--identifier STR -- identifier used for this instance of supervisord
-q/--childlogdir DIRECTORY -- the log directory for child process logs
-k/--nocleanup -- prevent the process from performing cleanup (removal of
old automatic child log files) at startup.
-a/--minfds NUM -- the minimum number of file descriptors for start success
-t/--strip_ansi -- strip ansi escape codes from process output
--minprocs NUM -- the minimum number of processes available for start success
--profile_options OPTIONS -- run supervisord under profiler and output
results based on OPTIONS, which is a comma-sep'd
list of 'cumulative', 'calls', and/or 'callers',
e.g. 'cumulative,callers')6. Supervisor控制台
在/etc/supervisord.conf中修改[inet_http_server]的参数,具体如下:
[inet_http_server] ; inet (TCP) server disabled by default
port=*:9001 ; ip_address:port specifier, *:port for all iface
username=root ; default is no username (open server)
password=xxxx ; default is no password (open server)修改后重启supervisor进程,在浏览器访问 http://<host-ip>:9001。
具体如下: 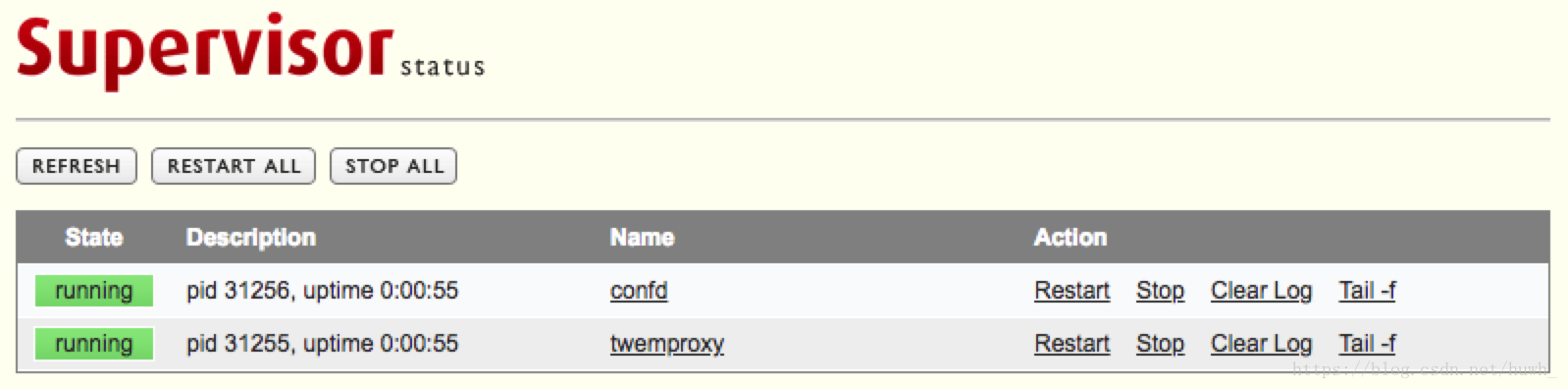
7. supervisor.conf详细配置
cat /etc/supervisord.conf
; Sample supervisor config file.
[unix_http_server]
file=/var/run/supervisor/supervisor.sock ; (the path to the socket file)
;chmod=0700 ; sockef file mode (default 0700)
;chown=nobody:nogroup ; socket file uid:gid owner
;username=user ; (default is no username (open server))
;password=123 ; (default is no password (open server))
;[inet_http_server] ; inet (TCP) server disabled by default
;port=127.0.0.1:9001 ; (ip_address:port specifier, *:port for all iface)
;username=user ; (default is no username (open server))
;password=123 ; (default is no password (open server))
[supervisord]
logfile=/var/log/supervisor/supervisord.log ; (main log file;default $CWD/supervisord.log)
logfile_maxbytes=50MB ; (max main logfile bytes b4 rotation;default 50MB)
logfile_backups=10 ; (num of main logfile rotation backups;default 10)
loglevel=info ; (log level;default info; others: debug,warn,trace)
pidfile=/var/run/supervisord.pid ; (supervisord pidfile;default supervisord.pid)
nodaemon=false ; (start in foreground if true;default false)
minfds=1024 ; (min. avail startup file descriptors;default 1024)
minprocs=200 ; (min. avail process descriptors;default 200)
;umask=022 ; (process file creation umask;default 022)
;user=chrism ; (default is current user, required if root)
;identifier=supervisor ; (supervisord identifier, default is 'supervisor')
;directory=/tmp ; (default is not to cd during start)
;nocleanup=true ; (don't clean up tempfiles at start;default false)
;childlogdir=/tmp ; ('AUTO' child log dir, default $TEMP)
;environment=KEY=value ; (key value pairs to add to environment)
;strip_ansi=false ; (strip ansi escape codes in logs; def. false)
; the below section must remain in the config file for RPC
; (supervisorctl/web interface) to work, additional interfaces may be
; added by defining them in separate rpcinterface: sections
[rpcinterface:supervisor]
supervisor.rpcinterface_factory = supervisor.rpcinterface:make_main_rpcinterface
[supervisorctl]
serverurl=unix:///var/run/supervisor/supervisor.sock ; use a unix:// URL for a unix socket
;serverurl=http://127.0.0.1:9001 ; use an http:// url to specify an inet socket
;username=chris ; should be same as http_username if set
;password=123 ; should be same as http_password if set
;prompt=mysupervisor ; cmd line prompt (default "supervisor")
;history_file=~/.sc_history ; use readline history if available
; The below sample program section shows all possible program subsection values,
; create one or more 'real' program: sections to be able to control them under
; supervisor.
;[program:theprogramname]
;command=/bin/cat ; the program (relative uses PATH, can take args)
;process_name=%(program_name)s ; process_name expr (default %(program_name)s)
;numprocs=1 ; number of processes copies to start (def 1)
;directory=/tmp ; directory to cwd to before exec (def no cwd)
;umask=022 ; umask for process (default None)
;priority=999 ; the relative start priority (default 999)
;autostart=true ; start at supervisord start (default: true)
;autorestart=true ; retstart at unexpected quit (default: true)
;startsecs=10 ; number of secs prog must stay running (def. 1)
;startretries=3 ; max # of serial start failures (default 3)
;exitcodes=0,2 ; 'expected' exit codes for process (default 0,2)
;stopsignal=QUIT ; signal used to kill process (default TERM)
;stopwaitsecs=10 ; max num secs to wait b4 SIGKILL (default 10)
;user=chrism ; setuid to this UNIX account to run the program
;redirect_stderr=true ; redirect proc stderr to stdout (default false)
;stdout_logfile=/a/path ; stdout log path, NONE for none; default AUTO
;stdout_logfile_maxbytes=1MB ; max # logfile bytes b4 rotation (default 50MB)
;stdout_logfile_backups=10 ; # of stdout logfile backups (default 10)
;stdout_capture_maxbytes=1MB ; number of bytes in 'capturemode' (default 0)
;stdout_events_enabled=false ; emit events on stdout writes (default false)
;stderr_logfile=/a/path ; stderr log path, NONE for none; default AUTO
;stderr_logfile_maxbytes=1MB ; max # logfile bytes b4 rotation (default 50MB)
;stderr_logfile_backups=10 ; # of stderr logfile backups (default 10)
;stderr_capture_maxbytes=1MB ; number of bytes in 'capturemode' (default 0)
;stderr_events_enabled=false ; emit events on stderr writes (default false)
;environment=A=1,B=2 ; process environment additions (def no adds)
;serverurl=AUTO ; override serverurl computation (childutils)
; The below sample eventlistener section shows all possible
; eventlistener subsection values, create one or more 'real'
; eventlistener: sections to be able to handle event notifications
; sent by supervisor.
;[eventlistener:theeventlistenername]
;command=/bin/eventlistener ; the program (relative uses PATH, can take args)
;process_name=%(program_name)s ; process_name expr (default %(program_name)s)
;numprocs=1 ; number of processes copies to start (def 1)
;events=EVENT ; event notif. types to subscribe to (req'd)
;buffer_size=10 ; event buffer queue size (default 10)
;directory=/tmp ; directory to cwd to before exec (def no cwd)
;umask=022 ; umask for process (default None)
;priority=-1 ; the relative start priority (default -1)
;autostart=true ; start at supervisord start (default: true)
;autorestart=unexpected ; restart at unexpected quit (default: unexpected)
;startsecs=10 ; number of secs prog must stay running (def. 1)
;startretries=3 ; max # of serial start failures (default 3)
;exitcodes=0,2 ; 'expected' exit codes for process (default 0,2)
;stopsignal=QUIT ; signal used to kill process (default TERM)
;stopwaitsecs=10 ; max num secs to wait b4 SIGKILL (default 10)
;user=chrism ; setuid to this UNIX account to run the program
;redirect_stderr=true ; redirect proc stderr to stdout (default false)
;stdout_logfile=/a/path ; stdout log path, NONE for none; default AUTO
;stdout_logfile_maxbytes=1MB ; max # logfile bytes b4 rotation (default 50MB)
;stdout_logfile_backups=10 ; # of stdout logfile backups (default 10)
;stdout_events_enabled=false ; emit events on stdout writes (default false)
;stderr_logfile=/a/path ; stderr log path, NONE for none; default AUTO
;stderr_logfile_maxbytes=1MB ; max # logfile bytes b4 rotation (default 50MB)
;stderr_logfile_backups ; # of stderr logfile backups (default 10)
;stderr_events_enabled=false ; emit events on stderr writes (default false)
;environment=A=1,B=2 ; process environment additions
;serverurl=AUTO ; override serverurl computation (childutils)
; The below sample group section shows all possible group values,
; create one or more 'real' group: sections to create "heterogeneous"
; process groups.
;[group:thegroupname]
;programs=progname1,progname2 ; each refers to 'x' in [program:x] definitions
;priority=999 ; the relative start priority (default 999)
; The [include] section can just contain the "files" setting. This
; setting can list multiple files (separated by whitespace or
; newlines). It can also contain wildcards. The filenames are
; interpreted as relative to this file. Included files *cannot*
; include files themselves.
[include]
files = supervisord.d/conf/*.conf





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)