eigen之三维旋转运动表达
简介
用于表示三维刚体旋转运动的方法主要有:
- 旋转向量
- 旋转矩阵
- 欧拉角
- 四元数
旋转向量
#include <iostream>
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <Eigen/Geometry>
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
/**** 1. 旋转向量 ****/ 欧拉角的实际范围是: roll-[-pi:pi], pitch-[-pi/2:pi/2], yaw-[-pi:pi], 但是Eigen库中函数的范围是[0:pi], pitch-[-pi:pi], yaw-[-pi:pi].
std::cout << "\n ********** AngleAxis **********" << std::endl;
Eigen::AngleAxisd rotation_vector1(M_PI/4, Eigen::Vector3d(0, 0, 1));
std::cout << "rotation vector1: " << "angle is: " << rotation_vector1.angle() * (180 / M_PI)
<< " axis is: " << rotation_vector1.axis().transpose() << std::endl;
// 旋转向量 -> 旋转矩阵
Eigen::Matrix3d rotation_matrix1 = rotation_vector1.matrix(); //用matrix()转换成旋转矩阵
std::cout << "rotation matrix1 : \n" << rotation_matrix1 << std::endl;
Eigen::Matrix3d rotation_matrix1_1 = rotation_vector1.toRotationMatrix(); // 由罗德里格公式进行转换
std::cout << "rotation matrix1_1 : \n" << rotation_matrix1_1 << std::endl;
// 旋转向量 -> 欧拉角
Eigen::Vector3d euler_angle1 = rotation_vector1.matrix().eulerAngles(2, 1, 0); // 先转为旋转矩阵, 然后转为欧拉角
std::cout << "euler angle: " << euler_angle1.transpose() << std::endl;
// 旋转向量 -> 四元数
Eigen::Quaterniond quaternion1(rotation_vector1); // 直接初始化
Eigen::Quaterniond quaternion1_1;
quaternion1_1 = rotation_vector1; // 通过赋值
std::cout << "quaternion1: " << quaternion1.coeffs().transpose() << std::endl; // x y z w
std::cout << "quaternion1_1: " << quaternion1_1.coeffs().transpose() << std::endl;
return 0;
}
结果:
********** AngleAxis **********
rotation vector1: angle is: 45 axis is: 0 0 1
rotation matrix1 :
0.707107 -0.707107 0
0.707107 0.707107 0
0 0 1
rotation matrix1_1 :
0.707107 -0.707107 0
0.707107 0.707107 0
0 0 1
euler angle: 0.785398 -0 0
quaternion1: 0 0 0.382683 0.92388
quaternion1_1: 0 0 0.382683 0.92388
旋转矩阵
#include <iostream>
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <Eigen/Geometry>
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
/**** 2. 旋转矩阵 *****/
std::cout << "\n ********** RotationMatrix **********" << std::endl;
Eigen::Matrix3d rotation_matrix2;
rotation_matrix2 << 0.707107, -0.707107, 0, 0.707107, 0.707107, 0, 0, 0, 1;
std::cout << "rotation matrix2 : \n" << rotation_matrix2 << std::endl;
// 旋转矩阵 -> 旋转向量
Eigen::AngleAxisd rotation_vector2;
rotation_vector2.fromRotationMatrix(rotation_matrix2); // fromRotationMatrix
Eigen::AngleAxisd rotation_vector2_1(rotation_matrix2); // 直接初始化
std::cout << "rotation vector2: " << "angle is: " << rotation_vector2.angle() * (180 / M_PI)
<< " axis is: " << rotation_vector2.axis().transpose() << std::endl;
std::cout << "rotation vector2_1: " << "angle is: " << rotation_vector2_1.angle() * (180 / M_PI)
<< " axis is: " << rotation_vector2_1.axis().transpose() << std::endl;
// 旋转矩阵 -> 欧拉角
Eigen::Vector3d euler_angle2 = rotation_matrix2.eulerAngles(2, 1, 0); // ZYX顺序, 即先绕x轴roll,再绕y轴pitch,最后绕z轴yaw
std::cout << "euler angle2: " << euler_angle2.transpose() << std::endl; // // row pitch yaw
// 旋转矩阵 -> 四元数
Eigen::Quaterniond quaternion2(rotation_matrix2);
Eigen::Quaterniond quaternion2_1;
quaternion2_1 = rotation_matrix2;
std::cout << "quaternion2: " << quaternion2.coeffs().transpose() << std::endl; // x y z w
std::cout << "quaternion2_1: " << quaternion2_1.coeffs().transpose() << std::endl;
return 0;
}
结果:
********** RotationMatrix **********
rotation matrix2 :
0.707107 -0.707107 0
0.707107 0.707107 0
0 0 1
rotation vector2: angle is: 45 axis is: 0 0 1
rotation vector2_1: angle is: 45 axis is: 0 0 1
euler angle2: 0.785398 -0 0
quaternion2: 0 0 0.382684 0.92388
quaternion2_1: 0 0 0.382684 0.92388
注: 单位旋转矩阵的旋转向量为(0, 0, 0)
欧拉角
#include <iostream>
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <Eigen/Geometry>
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
/**** 3. 欧拉角 ****/
std::cout << "\n ********** EulerAngle **********" << std::endl;
Eigen::Vector3d euler_angle3(0.785398, -0, 0); // row pitch yaw
std::cout << "euler angle3: " << euler_angle3.transpose() << std::endl;
// 欧拉角 -> 旋转矩阵
Eigen::Matrix3d rotation_matrix3;
rotation_matrix3 = Eigen::AngleAxisd(euler_angle3[0], Eigen::Vector3d::UnitZ()) *
Eigen::AngleAxisd(euler_angle3[1], Eigen::Vector3d::UnitY()) *
Eigen::AngleAxisd(euler_angle3[2], Eigen::Vector3d::UnitX());
std::cout << "rotation matrix3 : \n" << rotation_matrix3 << std::endl;
// 欧拉角 -> 旋转向量
Eigen::AngleAxisd rotation_vector3;
rotation_vector3 = Eigen::AngleAxisd(euler_angle3[0], Eigen::Vector3d::UnitZ()) *
Eigen::AngleAxisd(euler_angle3[1], Eigen::Vector3d::UnitY()) *
Eigen::AngleAxisd(euler_angle3[2], Eigen::Vector3d::UnitX());
std::cout << "rotation vector3: " << "angle is: " << rotation_vector3.angle() * (180 / M_PI)
<< " axis is: " << rotation_vector3.axis().transpose() << std::endl;
// 欧拉角 -> 四元数
Eigen::Quaterniond quaternion3;
quaternion3 = Eigen::AngleAxisd(euler_angle3[0], Eigen::Vector3d::UnitZ()) *
Eigen::AngleAxisd(euler_angle3[1], Eigen::Vector3d::UnitY()) *
Eigen::AngleAxisd(euler_angle3[2], Eigen::Vector3d::UnitX());
std::cout << "quaternion2: " << quaternion3.coeffs().transpose() << std::endl; // x y z w
return 0;
}
结果:
********** EulerAngle **********
euler angle3: 0.785398 0 0
rotation matrix3 :
0.707107 -0.707107 0
0.707107 0.707107 0
0 0 1
rotation vector3: angle is: 45 axis is: 0 0 1
quaternion2: 0 0 0.382683 0.92388
注: 欧拉角转为旋转向量的顺序
四元数
#include <iostream>
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <Eigen/Geometry>
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
/**** 4.四元数 ****/
std::cout << "\n ********** Quaternion **********" << std::endl;
Eigen::Quaterniond quaternion4(0.92388, 0, 0, 0.382683); // w, x, y, z
// 四元数 -> 旋转矩阵
Eigen::Matrix3d rotation_matrix4;
rotation_matrix4 = quaternion4.matrix();
Eigen::Matrix3d rotation_matrix4_1;
rotation_matrix4_1 = quaternion4.toRotationMatrix();
std::cout << "rotation matrix4 : \n" << rotation_matrix4 << std::endl;
std::cout << "rotation matrix4_1 : \n" << rotation_matrix4_1 << std::endl;
// 四元数 -> 旋转向量
Eigen::AngleAxisd rotation_vector4(quaternion4);
Eigen::AngleAxisd rotation_vector4_1;
rotation_vector4_1 = quaternion4;
std::cout << "rotation vector4: " << "angle is: " << rotation_vector4.angle() * (180 / M_PI)
<< " axis is: " << rotation_vector4.axis().transpose() << std::endl;
std::cout << "rotation vector4_1: " << "angle is: " << rotation_vector4_1.angle() * (180 / M_PI)
<< " axis is: " << rotation_vector4_1.axis().transpose() << std::endl;
// 四元数 -> 欧拉角
Eigen::Vector3d euler_angle4 = quaternion4.matrix().eulerAngles(2, 1, 0);
std::cout << "euler angle4: " << euler_angle4.transpose() << std::endl;
return 0;
}
结果
********** Quaternion **********
rotation matrix4 :
0.707107 -0.707106 0
0.707106 0.707107 0
0 0 1
rotation matrix4_1 :
0.707107 -0.707106 0
0.707106 0.707107 0
0 0 1
rotation vector4: angle is: 44.9999 axis is: 0 0 1
rotation vector4_1: angle is: 44.9999 axis is: 0 0 1
euler angle4: 0.785397 -0 0
注: 四元数到欧拉角有时会错.
笔记
二维旋转公式
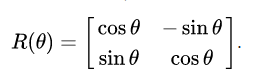
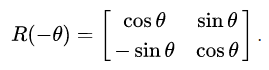
三维旋转公式
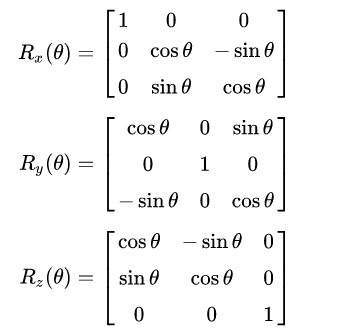
欧拉角
在Eigen库中, 其他运动表达转欧拉角都是通过rotation.eulerAngles(2, 1, 0)函数, 即先转为旋转矩阵然后再转为欧拉角. 这个函数有个问题就是出来欧拉角的范围不对.
- 欧拉角的实际范围是: roll-[-pi:pi], pitch-[-pi/2:pi/2], yaw-[-pi:pi]
- Eigen库中函数的范围是:roll-[0:pi], pitch-[-pi:pi], yaw-[-pi:pi].

所以推荐使用ros中的tf函数得到欧拉角,而不是eigen或者pcl中的函数
参考
chrislzy: 如有疑惑,错误或者建议,请在评论区留下您宝贵的文字; 转载请注明作者和出处,未经允许请勿用于商业用途!


