用JavaScript实现链表
什么是链表
链表是一种动态的数据结构,用来存储一系列有序的元素。每个元素由一个存储元素本身的节点和一个指向下一个元素的指针构成。
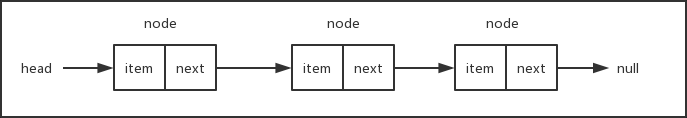
与数组的区别在于
- 链表分配内存空间灵活,并非保存在连续的存储空间中。
- 且链表不提供利用特定索引进行访问。因此,如果需要链表表中的第三个元素,则必须遍历第一个和第二个节点才能到得到它。
- 当要移动或删除元素时,只需要修改相应元素上的指针就可以了。对链表元素的操作要比对数组元素的操作效率更高。

要实现链表数据结构,关键在于保存head元素(即链表的头元素)以及每一个元素的next指针,有这两部分我们就可以很方便地遍历链表从而操作所有的元素。
(详见JavaScript数据结构——链表的实现与应用 )
单向链表具体实现
- 创建一个辅助类,来描述链表中的节点
let Node = function(element){
this.element = element; // 属性1:保存节点值
this.next = null; // 属性2:next指针
}
或者写成这样
class Node {
constructor(element) {
this.element = element;
this.next = null;
}
}
- 搭链表类的骨架/属性+方法
class LinkedList{
constructor(){
this.length = 0;
this.head = null;
}
append(element){} // 向链表尾部中添加新节点
insert(position, element){} // 向链表的指定位置插入节点
removeAt(position){} // 删除链表中指定位置的元素,并返回这个元素的值
remove(element){} // 删除链表中对应的元素
indexOf(element){} // 在链表中查找给定元素的索引
getElementAt(position){} // 返回链表中索引对应的元素
isEmpty(){} //判断链表是否为空
size(){} // 返回链表的长度
getHead(){} // 返回链表的头元素
clear(){} // 清空链表
toString(){} // 辅助方法,按指定格式输出链表中的所有元素,方便验证结果
}
- getElementAt()方法,返回链表中索引对应的元素
getElementAt(position){
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length)
return null;
let current = this.head;
for(let i=0; i<position; i++){
current = current.next; // next()获得匹配元素集合中每个元素紧邻的同胞元素。(jQuery)
}
return current;
}
- append()方法,向链表尾部中添加新节点
append(element){
let node = new Node(element);
// 如果当前链表为空,则将head指向node
if (this.head === null){
this.head = node;
}else{
// 否则在链表尾部元素后添加新元素
let current = this.getElementAt(this.length - 1);
current.next = node;
}
this.length++;
}
- insert()方法,向链表的指定位置插入节点
insert(position, element){ // 向链表的指定位置插入节点
// 判断position是否超出边界
if (position < 0 || position > this.length)
return false;
let node = new Node(element);
if (position === 0){
node.next = this.head;
this.head = node;
}else{
let previous = this.getElementAt(position - 1);
node.next = previous.next;
previous.next = node;
}
this.length++;
return true;
}
- removeAt()方法,删除链表中指定位置的元素,并返回这个元素的值
removeAt(position){
// 判断position合法
if (position < 0 || position > this.length)
return null; // 找不到
let current = this.head;
if (position === 0){
this.head = current.next;
}else{
let previous = this.getElementAt(position - 1);
current = previous.next;
previous.next = current.next;
}
this.length--;
return current.element;
}
如果当前链表只有一个节点,那么下一个节点为null,此时将head指向下一个节点等同于将head设置成null,删除之后链表为空。被删除的节点由于再也没有其它部分的引用而被丢弃在内存中,等待垃圾回收器来清除。
- indexOf()方法,查找并返回给定元素在链表中的索引位置
indexOf(element){
let current = this.head;
for(let i=0; i<this.length; i++){
if(current.element === element)
return i;
current = current.next;
}
return -1; // 找不到
}
- remove()方法,删除并返回链表中对应的元素
remove(element){
let index = this.indexOf(element);
return this.removeAt(index);
}
- isEmpty()方法,判断链表是否为空
isEmpty(){
return this.length === 0; // 也可用head===null
}
- clear()方法,清空链表
clear(){
this.head = null;
this.length = 0;
}
- 一些测试用例
let linkedList = new LinkedList();
// 测试用例1
linkedList.append(10);
linkedList.append(15);
linkedList.append(20);
console.log(linkedList.toString());
// 测试用例2
linkedList.insert(0, 9);
linkedList.insert(2, 11);
linkedList.insert(5, 25);
console.log(linkedList.toString());
// 测试用例3
console.log(linkedList.removeAt(0));
console.log(linkedList.removeAt(1));
console.log(linkedList.removeAt(3));
console.log(linkedList.toString());
// 测试用例4
console.log(linkedList.indexOf(20));
// 测试用例5
linkedList.remove(20);
// 测试用例6
console.log(linkedList.toString());
// 测试用例7
linkedList.clear();
console.log(linkedList.size());
双向链表具体实现
单向链表中每一个元素只有一个next指针,用来指向下一个节点,我们只能从链表的头部开始遍历整个链表,任何一个节点只能找到它的下一个节点,而不能找到它的上一个节点。
双向链表中的每一个元素拥有两个指针,一个用来指向下一个节点,一个用来指向上一个节点。在双向链表中,除了可以像单向链表一样从头部开始遍历之外,还可以从尾部进行遍历。下面是双向链表的数据结构示意图:
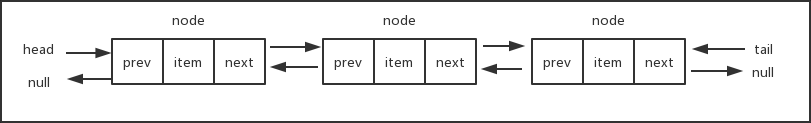
- 由于双向链表具有单向链表的所有特性,因此我们的双向链表类可以继承自前面的单向链表类,不过辅助类Node需要添加一个prev属性,用来指向前一个节点。
class Node {
constructor(element) {
this.element = element; // 属性1:保存节点值
this.next = null; // 属性2:next指针,指向后一个节点
this.prev = null; // 属性3:prev指针,指向前一个节点
}
}
- 双向链表类的基本骨架
继承了LinkedList类,其中的一些方法需要重定义
class DoubleLinkedList extends LinkedList{
constructor(){
super();
this.tail = null;
}
getTail(){}
}
- append()方法
append(element){
let node = new Node(element);
// 如果链表为空,则将head和tail都指向当前添加的节点
if (this.head === null){
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
}else{
// 否则将当前节点添加到链表的尾部
this.tail.next = node;
node.prev = this.tail;
this.tail = node;
}
this.length++;
}
- getElementAt()方法,如果要查找的元素的索引号大于链表长度的一半,则从链表的尾部开始遍历
getElementAt(position){ // 如果要查找的元素的索引号大于链表长度的一半,则从链表的尾部开始遍历
if (position < 0 || position >= this.length)
return null;
if (position > Math.floor(this.length /2)){
let current = this.tail;
for(let i=this.length-1; i>position; i--){
current = current.prev;
}
return current;
}else{
return super.getElementAt(position);
}
}
- insert()方法
insert(position, element){
if (position < 0 || position > this.length)
return false;
if(position === this.length){
this.append(element);
}else{
let node = new Node(element);
// 插到头部
if(position === 0){
if(this.head === null){
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
}else{
node.next = this.head;
this.head.prev = node;
this.head = node;
}
}else{
// 插到中间
let current = this.getElementAt(position);
let previous = current.prev;
node.next = current;
node.prev = previous;
previous.next = node;
current.prev = node;
}
}
this.length++;
return true;
}
- removeA()方法
removeAt(position){
if (position < 0 || position > this.length)
return null;
let current = this.head;
let previous;
// 移除头部元素
if(position === 0){
this.head = current.next;
this.head.prev = null;
if (this.length ===1)
this.tail = null;
}else if(position === this.length -1){
// 移除尾部元素
current = this.tail;
this.tail = current.prev;
this.tail.next = null;
}else{
// 移除中间元素
current = this.getElementAt(position);
previous = current.prev;
previous.next = current.next;
current.next.prev = previous;
}
this.length--;
return current.element;
}
循环链表
循环链表的尾部指向它自己的头部。循环链表可以有单向循环链表,也可以有双向循环链表。下面是单向循环链表和双向循环链表的数据结构示意图:



