ELK介绍与Spring Boot集成使用
ELK单机部署(docker-compose)#
docker-compose.yml
version : "3.5"
services:
elasticsearch:
image: elasticsearch:7.13.4
container_name: elasticsearch
environment:
- "ES_JAVA_OPTS=-Xms2g -Xmx2g"
- "discovery.type=single-node"
- "xpack.security.enabled=true"
- "ELASTIC_PASSWORD=mypassword"
volumes:
- ./elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml:/usr/share/elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml
ports:
- "9200:9200"
logstash:
image: logstash:7.13.4
container_name: logstash
environment:
- "LS_JAVA_OPTS=-Xms512m -Xmx512m"
- "LOGSTASH_SETTINGS={\"pipeline.workers\": 1,\"pipeline.batch.size\": 125}"
depends_on:
- elasticsearch
ports:
- "5066:5066"
- "5044:5044"
- "9600:9600"
volumes:
- ./logstash/pipeline/tcp.conf:/usr/share/logstash/pipeline/tcp.conf
kibana:
image: kibana:7.13.4
container_name: kibana
depends_on:
- elasticsearch
ports:
- "5601:5601"
volumes:
- ./kibana/kibana.yml:/usr/share/kibana/config/kibana.yml
elasticsearch.yml配置:
cluster.name: "docker-cluster"
network.host: 0.0.0.0
kibana.yml配置:
server.name: kibana
server.host: "0"
elasticsearch.hosts: [ "http://elasticsearch:9200" ]
monitoring.ui.container.elasticsearch.enabled: true
elasticsearch.username: "elastic"
elasticsearch.password: "mypassword"
xpack.security.enabled: true
基于docker-compose.yml部署,报错:
elasticsearch | {"type": "server", "timestamp": "2024-08-29T08:20:43,188Z", "level": "INFO", "component": "o.e.t.TransportService", "cluster.name": "es-cluster", "node.name": "node1", "message": "publish_address {172.22.0.2:9300}, bound_addresses {0.0.0.0:9300}" }
elasticsearch | {"type": "server", "timestamp": "2024-08-29T08:20:43,355Z", "level": "INFO", "component": "o.e.b.BootstrapChecks", "cluster.name": "es-cluster", "node.name": "node1", "message": "bound or publishing to a non-loopback address, enforcing bootstrap checks" }
elasticsearch | ERROR: [1] bootstrap checks failed. You must address the points described in the following [1] lines before starting Elasticsearch.
elasticsearch | bootstrap check failure [1] of [1]: max virtual memory areas vm.max_map_count [65530] is too low, increase to at least [262144]elasticsearch | ERROR: Elasticsearch did not exit normally - check the logs at /usr/share/elasticsearch/logs/es-cluster.log
elasticsearch | {"type": "server", "timestamp": "2024-08-29T08:20:43,365Z", "level": "INFO", "component": "o.e.n.Node", "cluster.name": "es-cluster", "node.name": "node1", "message": "stopping ..." }
elasticsearch | {"type": "server", "timestamp": "2024-08-29T08:20:43,384Z", "level": "INFO", "component": "o.e.n.Node", "cluster.name": "es-cluster", "node.name": "node1", "message": "stopped" }
elasticsearch | {"type": "server", "timestamp": "2024-08-29T08:20:43,384Z", "level": "INFO", "component": "o.e.n.Node", "cluster.name": "es-cluster", "node.name": "node1", "message": "closing ..." }
elasticsearch | {"type": "server", "timestamp": "2024-08-29T08:20:43,409Z", "level": "INFO", "component": "o.e.n.Node", "cluster.name": "es-cluster", "node.name": "node1", "message": "closed" }
elasticsearch | {"type": "server", "timestamp": "2024-08-29T08:20:43,411Z", "level": "INFO", "component": "o.e.x.m.p.NativeController", "cluster.name": "es-cluster", "node.name": "node1", "message": "Native controller process has stopped - no new native processes can be started" }
解决办法:
方法一,使用特权模式启动容器
version : "3.5"services:
elasticsearch: ... ports: - "9200:9200" - "9300:9300" privileged: true
command: /bin/sh -c "sysctl -w vm.max_map_count=262144 && /usr/local/bin/docker-entrypoint.sh" logstash:....
方法二,修改宿主主机,在宿主机上直接设置vm.max_map_count,这样就不需要在容器内部设置
echo "vm.max_map_count=262144" | sudo tee -a /etc/sysctl.conf
sudo sysctl -p
es集群部署#
参考: https://blog.csdn.net/ren9436/article/details/138705378
下载安装包
curl -O hhttps://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-7.17.23-linux-aarch64.tar.gz
tar -xzf elasticsearch-7.17.23-linux-aarch64.tar.gz
cd elasticsearch-7.17.23/
设置ssl
cd ./elasticsearch-7.17.23/bin/
# 执行下面的命令,根据提示信息创建CA证书
# 创建时需要设置密码和文件名,可以直接回车
./elasticsearch-certutil ca
./elasticsearch-certutil cert --ca elastic-stack-ca.p12
# 生成的文件位于ES目录下(与bin目录平级)
# 如果在生成证书时设置了密码,还需要执行下面的步骤 参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/djd66/p/16828001.html
./elasticsearch-keystore add xpack.security.transport.ssl.keystore.secure_password
./elasticsearch-keystore add xpack.security.transport.ssl.truststore.secure_password
./elasticsearch-keystore add xpack.security.http.ssl.keystore.secure_password
./elasticsearch-keystore add xpack.security.http.ssl.truststore.secure_password
注意将生产的elastic-certificates.p12、elastic-stack-ca.p12文件放置到目录中:
./elasticsearch/config/certs/
修改配置
# ======================== Elasticsearch Configuration =========================
#
# NOTE: Elasticsearch comes with reasonable defaults for most settings.
# Before you set out to tweak and tune the configuration, make sure you
# understand what are you trying to accomplish and the consequences.
#
# The primary way of configuring a node is via this file. This template lists
# the most important settings you may want to configure for a production cluster.
#
# Please consult the documentation for further information on configuration options:
# https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/index.html
#
# ---------------------------------- Cluster -----------------------------------
#
# Use a descriptive name for your cluster:
#
cluster.name: my-es
#
# ------------------------------------ Node ------------------------------------
#
# Use a descriptive name for the node:
#
node.name: node-1
#
# Add custom attributes to the node:
#
#node.attr.rack: r1
#
# ----------------------------------- Paths ------------------------------------
#
# Path to directory where to store the data (separate multiple locations by comma):
#
#path.data: /path/to/data
#
# Path to log files:
#
#path.logs: /path/to/logs
#
# ----------------------------------- Memory -----------------------------------
#
# Lock the memory on startup:
#
#bootstrap.memory_lock: true
#
# Make sure that the heap size is set to about half the memory available
# on the system and that the owner of the process is allowed to use this
# limit.
#
# Elasticsearch performs poorly when the system is swapping the memory.
#
# ---------------------------------- Network -----------------------------------
#
# By default Elasticsearch is only accessible on localhost. Set a different
# address here to expose this node on the network:
#
network.host: 10.xxx.xxx.192
#
# By default Elasticsearch listens for HTTP traffic on the first free port it
# finds starting at 9200. Set a specific HTTP port here:
#
http.port: 9200
#
# For more information, consult the network module documentation.
#
# --------------------------------- Discovery ----------------------------------
#
# Pass an initial list of hosts to perform discovery when this node is started:
# The default list of hosts is ["127.0.0.1", "[::1]"]
#
discovery.seed_hosts: ["10.xxx.xxx.192", "10.xxx.xxx.193","10.xxx.xxx.194","10.xxx.xxx.195","10.xxx.xxx.196","10.xxx.xxx.197"]
#
# Bootstrap the cluster using an initial set of master-eligible nodes:
#
cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["node-1", "node-2","node-3","node-4","node-5","node-6"]
#
# For more information, consult the discovery and cluster formation module documentation.
#
# ---------------------------------- Various -----------------------------------
#
# Require explicit names when deleting indices:
#
#action.destructive_requires_name: true
#
# ---------------------------------- Security ----------------------------------
#
# *** WARNING ***
#
# Elasticsearch security features are not enabled by default.
# These features are free, but require configuration changes to enable them.
# This means that users don't have to provide credentials and can get full access
# to the cluster. Network connections are also not encrypted.
#
# To protect your data, we strongly encourage you to enable the Elasticsearch security features.
# Refer to the following documentation for instructions.
#
# https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/7.16/configuring-stack-security.html
# ssl
xpack.security.enabled: true
xpack.license.self_generated.type: basic
xpack.security.transport.ssl.enabled: true
xpack.security.transport.ssl.verification_mode: certificate
xpack.security.transport.ssl.keystore.path: certs/elastic-certificates.p12
xpack.security.transport.ssl.truststore.path: certs/elastic-certificates.p12
修改jvm.options文件,设置内存占用大小
-Xms2g
-Xmx2g
启动命令
./bin/elasticsearch -d -p pid
设置密码
$ ./bin/elasticsearch-setup-passwords interactive
Initiating the setup of passwords for reserved users elastic,apm_system,kibana,kibana_system,logstash_system,beats_system,remote_monitoring_user.
You will be prompted to enter passwords as the process progresses.
Please confirm that you would like to continue [y/N]y
Enter password for [elastic]:
Reenter password for [elastic]:
Enter password for [apm_system]:
Reenter password for [apm_system]:
Enter password for [kibana_system]:
Reenter password for [kibana_system]:
Enter password for [logstash_system]:
Reenter password for [logstash_system]:
Enter password for [beats_system]:
Reenter password for [beats_system]:
Enter password for [remote_monitoring_user]:
Reenter password for [remote_monitoring_user]:
Changed password for user [apm_system]
Changed password for user [kibana_system]
Changed password for user [kibana]
Changed password for user [logstash_system]
Changed password for user [beats_system]
Changed password for user [remote_monitoring_user]
Changed password for user [elastic]
查看es集群健康情况
curl -u elastic:23ddecd2dscaaf -X GET "http://10.xxx.xxx.192:9200/_cluster/health"
# 查看节点信息
curl -u elastic:23ddecd2dscaaf "http://10.167.65.192:9200/_cat/nodes?v"
Logstash#
Logstash 是一个具有实时管道功能的开源数据收集引擎。 Logstash 可以动态地统一来自不同来源的数据,并将数据规范化到您选择的目的地。清理和民主化您的所有数据,以实现各种高级下游分析和可视化用例。
一般Logstash与Elasticsearch和Kibanan协同使用,扩展数据处理
官方介绍:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/logstash/7.10/introduction.html
安装Logstash#
sudo rpm --import https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch
cd /etc/yum.repos.d/
vi logstash.repo
接着输入如下内容到logstash.repo
[logstash-7.x]
name=Elastic repository for 7.x packages
baseurl=https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/7.x/yum
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch
enabled=1
autorefresh=1
type=rpm-md
之后就可以安装logstash
sudo yum install logstash
Logstash目录布局#
以最新的7.17.19版本为例:
$ whereis logstash
logstash: /etc/logstash /usr/share/logstash
$ cd /usr/share/logstash/
$ ls
bin CONTRIBUTORS data Gemfile Gemfile.lock jdk lib LICENSE.txt logstash-core logstash-core-plugin-api modules NOTICE.TXT tools vendor x-pack
$ cd /etc/logstash/
$ ls
conf.d jvm.options log4j2.properties logstash-sample.conf logstash.yml pipelines.yml startup.options
总的来说,可以归纳为:
| 类型 | 描述 | 默认位置 | 设置 |
|---|---|---|---|
| home | Logstash 安装的主目录 | /usr/share/logstash | |
| bin | 二进制脚本,包括用于启动 Logstash 的 logstash 和用于安装插件的 logstash-plugin |
/usr/share/logstash/bin | |
| settings | 配置文件,包括 logstash.yml 、 jvm.options 和 startup.options |
/etc/logstash | path.settings |
| conf | Logstash 管道配置文件 | /etc/logstash/conf.d/*.conf | /etc/logstash/pipelines.yml定义conf文件路径 |
| logs | Log files 日志文件 | /var/log/logstash | path.logs参数可以修改logs文件路径 |
| plugins | 本地、非 Ruby-Gem 插件文件。每个插件都包含在一个子目录中。仅推荐用于开发。 | /usr/share/logstash/plugins | path.plugins可以指定插件 |
| data | Logstash 及其插件使用的数据文件可满足任何持久性需求。 | /var/lib/logstash | path.data |
Logstash启动测试#
我们通过运行最简单的Logstash管道来测试您的Logstash安装。
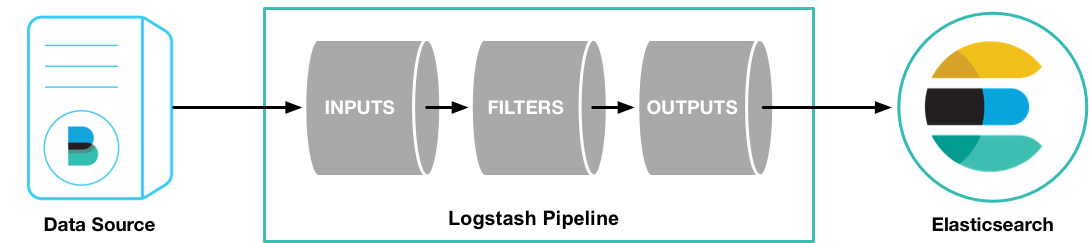
Logstash管道有两个必需元素input和output,以及一个可选元素filter。输入插件使用来自源的数据,过滤器插件根据您的指定修改数据,输出插件将数据写入目标
要测试 Logstash 安装,请运行最基本的 Logstash 管道。例如:
cd /usr/share/logstash
bin/logstash -e 'input { stdin { } } output { stdout {} }'
之后,logstash启动就可以在当前控制台输入字符,接着控制台打印输出信息:
使用filebeat+Logstash解析日志#
在上面案例中,创建了一个基本的Logstash管道来测试您的Logstash设置。但实际上,Logstash管道有点复杂: 它通常具有一个或多个输入、过滤器和输出插件。例如,某服务器A安装了Logstash\ES\Kibana,但需要收集的日志文件(nginx日志文件、apache日志文件)存放在服务器B、C、D等不同服务器,这种情况可以配置Filebeat将日志行发送到Logstash,相比Logstash,Filebeat从服务器收集日志、转发日志在主机上资源占用很少,Beats input(Logstash上也同样需要配置使用的一种插件)插件最大限度减少了Logstash实例的资源需求。
安装filebeat#
要在数据源计算机上安装Filebeat,以centos为例:
$ curl -L -O https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/beats/filebeat/filebeat-8.13.0-x86_64.rpm
$ sudo rpm -vi filebeat-8.13.0-x86_64.rpm
# 查看模块
$ filebeat modules list
安装Filebeat后,需要对其进行配置。打开位于 Filebeat 安装目录中的 filebeat.yml (/etc/filebeat目录中)文件,并将内容替换为以下行。确保 paths 指向您之前下载的示例 Apache 日志文件 logstash-tutorial.log :
filebeat.inputs:
- type: log
paths:
- /path/to/file/logstash-tutorial.log
output.logstash:
hosts: ["localhost:5044"]
切换到filebeat主目录,运行Filebeat:
cd /usr/share/filebeat/bin
sudo ./filebeat -e -c /etc/filebeat/filebeat.yml -d "publish"
此时,Logstash还没有配置和运行,因此Filebeat报错可以先忽略。如何后面Logstash配置好之后,可以重启Filebeat测试,强制 Filebeat 从头开始读取日志文件,请关闭 Filebeat(按 Ctrl+C),删除注册表文件,然后使用以下命令重新启动 Filebeat:
$ cd /usr/share/filebeat/bin
$ sudo rm -rf data/registry
$ sudo ./filebeat -e -c /etc/filebeat/filebeat.yml -d "publish"
为Filebeat输入配置Logstash#
接下来,创建一个Logstash配置管道,该管道使用Beats插件从Beats接受事件。
$ cd /usr/share/logstash
$ vi first-pipeline.conf
粘贴以下内容到first-pipeline.conf,注意如果es配置地址不是同一台主机,则可以修改为对应的IP:Port,
input {
beats {
port => "5044"
}
}
filter {
grok {
match => { "message" => "%{COMBINEDAPACHELOG}"}
}
geoip {
source => "clientip"
}
}
output {
elasticsearch {
hosts => [ "localhost:9200" ]
}
}
要验证配置是否生效,可以运行以下命令测试:
$ cd /usr/share/logstash
$ bin/logstash -f first-pipeline.conf --config.test_and_exit
之后看到以下测试结果,最后显示Config Validation Result: OK. 说明测试成功:
...
[WARN ] 2024-03-28 15:30:38.715 [LogStash::Runner] beats - Relying on default value of `pipeline.ecs_compatibility`, which may change in a future major release of Logstash. To avoid unexpected changes when upgrading Logstash, please explicitly declare your desired ECS Compatibility mode.
Configuration OK
[INFO ] 2024-03-28 15:30:38.862 [LogStash::Runner] runner - Using config.test_and_exit mode. Config Validation Result: OK. Exiting Logstash
配置文件测试通过之后,则使用以下命令启动Logstash:
$ bin/logstash -f first-pipeline.conf --config.reload.automatic
--config.reload.automatic 选项启用自动配置重新加载,这样您就不必在每次修改配置文件时停止并重新启动 Logstash。
最后,留意控制台可以查看Logstash一些启动信息:
[root@node01 logstash]# bin/logstash -f first-pipeline.conf --config.reload.automatic
Using bundled JDK: /usr/share/logstash/jdk
OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM warning: Option UseConcMarkSweepGC was deprecated in version 9.0 and will likely be removed in a future release.
WARNING: Could not find logstash.yml which is typically located in $LS_HOME/config or /etc/logstash. You can specify the path using --path.settings. Continuing using the defaults
Could not find log4j2 configuration at path /usr/share/logstash/config/log4j2.properties. Using default config which logs errors to the console
[INFO ] 2024-03-28 15:52:14.821 [main] runner - Starting Logstash {"logstash.version"=>"7.17.19", "jruby.version"=>"jruby 9.2.20.1 (2.5.8) 2021-11-30 2a2962fbd1 OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM 11.0.22+7 on 11.0.22+7 +indy +jit [linux-x86_64]"}
[INFO ] 2024-03-28 15:52:14.828 [main] runner - JVM bootstrap flags: [-Xms1g, -Xmx1g, -XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC, -XX:CMSInitiatingOccupancyFraction=75, -XX:+UseCMSInitiatingOccupancyOnly, -Djava.awt.headless=true, -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8, -Djdk.io.File.enableADS=true, -Djruby.compile.invokedynamic=true, -Djruby.jit.threshold=0, -Djruby.regexp.interruptible=true, -XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError, -Djava.security.egd=file:/dev/urandom, -Dlog4j2.isThreadContextMapInheritable=true]
[WARN ] 2024-03-28 15:52:15.055 [LogStash::Runner] multilocal - Ignoring the 'pipelines.yml' file because modules or command line options are specified
[INFO ] 2024-03-28 15:52:15.878 [Api Webserver] agent - Successfully started Logstash API endpoint {:port=>9600, :ssl_enabled=>false}
[INFO ] 2024-03-28 15:52:16.621 [Converge PipelineAction::Create<main>] Reflections - Reflections took 52 ms to scan 1 urls, producing 119 keys and 419 values
[WARN ] 2024-03-28 15:52:17.152 [Converge PipelineAction::Create<main>] plain - Relying on default value of `pipeline.ecs_compatibility`, which may change in a future major release of Logstash. To avoid unexpected changes when upgrading Logstash, please explicitly declare your desired ECS Compatibility mode.
[WARN ] 2024-03-28 15:52:17.182 [Converge PipelineAction::Create<main>] beats - Relying on default value of `pipeline.ecs_compatibility`, which may change in a future major release of Logstash. To avoid unexpected changes when upgrading Logstash, please explicitly declare your desired ECS Compatibility mode.
[WARN ] 2024-03-28 15:52:17.276 [Converge PipelineAction::Create<main>] geoip - Relying on default value of `pipeline.ecs_compatibility`, which may change in a future major release of Logstash. To avoid unexpected changes when upgrading Logstash, please explicitly declare your desired ECS Compatibility mode.
[WARN ] 2024-03-28 15:52:17.293 [Converge PipelineAction::Create<main>] plain - Relying on default value of `pipeline.ecs_compatibility`, which may change in a future major release of Logstash. To avoid unexpected changes when upgrading Logstash, please explicitly declare your desired ECS Compatibility mode.
[WARN ] 2024-03-28 15:52:17.326 [Converge PipelineAction::Create<main>] elasticsearch - Relying on default value of `pipeline.ecs_compatibility`, which may change in a future major release of Logstash. To avoid unexpected changes when upgrading Logstash, please explicitly declare your desired ECS Compatibility mode.
[INFO ] 2024-03-28 15:52:17.379 [[main]-pipeline-manager] elasticsearch - New Elasticsearch output {:class=>"LogStash::Outputs::ElasticSearch", :hosts=>["//localhost:9200"]}
[INFO ] 2024-03-28 15:52:17.570 [[main]-pipeline-manager] elasticsearch - Elasticsearch pool URLs updated {:changes=>{:removed=>[], :added=>[http://localhost:9200/]}}
[WARN ] 2024-03-28 15:52:17.724 [[main]-pipeline-manager] elasticsearch - Restored connection to ES instance {:url=>"http://localhost:9200/"}
[INFO ] 2024-03-28 15:52:17.739 [[main]-pipeline-manager] elasticsearch - Elasticsearch version determined (7.10.0) {:es_version=>7}
[WARN ] 2024-03-28 15:52:17.742 [[main]-pipeline-manager] elasticsearch - Detected a 6.x and above cluster: the `type` event field won't be used to determine the document _type {:es_version=>7}
[INFO ] 2024-03-28 15:52:17.807 [Ruby-0-Thread-10: :1] elasticsearch - Config is not compliant with data streams. `data_stream => auto` resolved to `false`
[INFO ] 2024-03-28 15:52:17.810 [[main]-pipeline-manager] elasticsearch - Config is not compliant with data streams. `data_stream => auto` resolved to `false`
[INFO ] 2024-03-28 15:52:17.865 [Ruby-0-Thread-10: :1] elasticsearch - Using a default mapping template {:es_version=>7, :ecs_compatibility=>:disabled}
[INFO ] 2024-03-28 15:52:17.923 [Ruby-0-Thread-10: :1] elasticsearch - Installing Elasticsearch template {:name=>"logstash"}
[INFO ] 2024-03-28 15:52:18.403 [Ruby-0-Thread-10: :1] elasticsearch - Created rollover alias {:name=>"<logstash-{now/d}-000001>"}
[INFO ] 2024-03-28 15:52:18.422 [Ruby-0-Thread-10: :1] elasticsearch - Installing ILM policy {"policy"=>{"phases"=>{"hot"=>{"actions"=>{"rollover"=>{"max_size"=>"50gb", "max_age"=>"30d"}}}}}} {:name=>"logstash-policy"}
[INFO ] 2024-03-28 15:52:18.956 [[main]-pipeline-manager] downloadmanager - new database version detected? false
[INFO ] 2024-03-28 15:52:19.056 [[main]-pipeline-manager] databasemanager - By not manually configuring a database path with `database =>`, you accepted and agreed MaxMind EULA. For more details please visit https://www.maxmind.com/en/geolite2/eula
[INFO ] 2024-03-28 15:52:19.056 [[main]-pipeline-manager] geoip - Using geoip database {:path=>"/usr/share/logstash/data/plugins/filters/geoip/1711611578/GeoLite2-City.mmdb"}
[WARN ] 2024-03-28 15:52:19.078 [[main]-pipeline-manager] grok - Relying on default value of `pipeline.ecs_compatibility`, which may change in a future major release of Logstash. To avoid unexpected changes when upgrading Logstash, please explicitly declare your desired ECS Compatibility mode.
[INFO ] 2024-03-28 15:52:19.227 [[main]-pipeline-manager] javapipeline - Starting pipeline {:pipeline_id=>"main", "pipeline.workers"=>8, "pipeline.batch.size"=>125, "pipeline.batch.delay"=>50, "pipeline.max_inflight"=>1000, "pipeline.sources"=>["/usr/share/logstash/first-pipeline.conf"], :thread=>"#<Thread:0x169d9587 run>"}
[INFO ] 2024-03-28 15:52:19.834 [[main]-pipeline-manager] javapipeline - Pipeline Java execution initialization time {"seconds"=>0.61}
[INFO ] 2024-03-28 15:52:19.860 [[main]-pipeline-manager] beats - Starting input listener {:address=>"0.0.0.0:5044"}
[INFO ] 2024-03-28 15:52:19.881 [[main]-pipeline-manager] javapipeline - Pipeline started {"pipeline.id"=>"main"}
[INFO ] 2024-03-28 15:52:19.974 [Agent thread] agent - Pipelines running {:count=>1, :running_pipelines=>[:main], :non_running_pipelines=>[]}
[INFO ] 2024-03-28 15:52:19.984 [[main]<beats] Server - Starting server on port: 5044
查看es索引情况,可以看到类似 logstash-2024.03.28-000001,说明Logstash已经采集到日志并发送到ES中:
$ curl 'localhost:9200/_cat/indices?v'
health status index uuid pri rep docs.count docs.deleted store.size pri.store.size
yellow open logstash-2024.03.28-000001 hdm0BRwcR1meto90wLe20g 1 1 0 0 208b 208b
green open .apm-custom-link SrBPEdFBRvik8_DK9NJoQQ 1 0 0 0 208b 208b
green open .kibana_task_manager_1 9z9EfaY2QF2VN6UD5HXFJA 1 0 5 4144 904.6kb 904.6kb
green open kibana_sample_data_ecommerce g5A2oEGuS4KYJKuG1y6C2g 1 0 4675 0 4mb 4mb
green open .apm-agent-configuration HqI3PsIVSqyUT-o_Qb-q6w 1 0 0 0 208b 208b
green open .kibana-event-log-7.10.0-000001 Ihcvnmq4RBycyEP1TnVFmg 1 0 2 0 11kb 11kb
green open .async-search b0h1k_JST7GSCKphozwgkQ 1 0 0 0 228b 228b
green open .kibana_1 b2qz4UxyQt6rMrHsG_BO3Q 1 0 84 8 11.3mb 11.3mb
查看日志内容:
curl -XGET 'localhost:9200/logstash-2024.03.28-000001/_search'
curl -XGET 'localhost:9200/logstash-2024.03.28-000001/_search?pretty&q=xxx'
Logstash的TCP输入插件#
通过 TCP 套接字读取事件,与标准输入和文件输入一样,每个事件都被假定为一行文本。可以接受来自客户端的连接或连接到服务器,具体取决于 mode 。Log4j2 可以通过套接字发送 JSON,我们可以将其与 TCP 输入结合使用来接受日志。
配置如下:
$ cd /etc/logstash/conf.d
$ vi tcp-logstash.conf
input{
tcp {
mode => "server"
host => "0.0.0.0"
port => 5000
codec => json_lines
}
}
output{
stdout{
codec => rubydebug
}
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["localhost:9200"]
}
}
之后,可以重启Logstash进行测试
$ service logstash restart
# 通过向Logstash的监听端口5000发送json数据,之后就可以到es中查看
$ echo '{"message": "Hello, Logstash!", "level": "INFO"}' | nc localhost 5000
查看验证数据
$ curl -XGET 'localhost:9200/logstash-2024.03.28-000001/_search?pretty&q=connecting'
{
"took" : 4,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 2,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 10.967979,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "logstash-2024.03.28-000001",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "R352hI4Bz5Eh2WrJgx5n",
"_score" : 10.967979,
"_source" : {
"@version" : "1",
"host" : "localhost",
"@timestamp" : "2024-03-28T09:49:05.523Z",
"message" : "Hello,this is tcp connecting to Logstash!",
"level" : "INFO",
"port" : 36786,
"tags" : [
"_grokparsefailure",
"_geoip_lookup_failure"
]
}
},
{
"_index" : "logstash-2024.03.28-000001",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "SH52hI4Bz5Eh2WrJgx5w",
"_score" : 10.967979,
"_source" : {
"@version" : "1",
"host" : "localhost",
"@timestamp" : "2024-03-28T09:49:05.523Z",
"message" : "Hello,this is tcp connecting to Logstash!",
"level" : "INFO",
"port" : 36786,
"tags" : [
"_grokparsefailure",
"_geoip_lookup_failure"
]
}
}
]
}
}
Spring Boot日志输出es#
Spring Boot通过TCP与logstash组件链接,此时只需要搭建ELK环境(不需要filebeat),配置logstash如下:
[root@node01 conf.d]# cat tcp-logstash.conf
input{
tcp {
mode => "server"
host => "0.0.0.0"
port => 5000
codec => json_lines
}
}
output{
stdout{
codec => rubydebug
}
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["localhost:9200"]
}
}
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.7.18</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>demo-logstash</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>demo-logstash</name>
<description>demo-logstash</description>
<properties>
<java.version>8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- Logstash Appender for Logback -->
<dependency>
<groupId>net.logstash.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logstash-logback-encoder</artifactId>
<version>5.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<image>
<builder>paketobuildpacks/builder-jammy-base:latest</builder>
</image>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
logback-spring.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration>
<include resource="org/springframework/boot/logging/logback/base.xml" />
<property name="LOGSTASH_HOST" value="${LOGSTASH_HOST:-${DOCKER_HOST:-192.168.137.21}}" />
<property name="LOGSTASH_PORT" value="${LOGSTASH_PORT:-5000}" />
<appender name="LOGSTASH" class="net.logstash.logback.appender.LogstashTcpSocketAppender">
<destination>${LOGSTASH_HOST}:${LOGSTASH_PORT}</destination>
<encoder charset="UTF-8" class="net.logstash.logback.encoder.LogstashEncoder" />
</appender>
<root level="INFO">
<appender-ref ref="LOGSTASH" />
<appender-ref ref="CONSOLE" />
</root>
</configuration>
application.properties
# Logstash appender 配置
logging.config=classpath:logback-spring.xml
BasicController
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class BasicController {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(BasicController.class);
@RequestMapping("/hello")
@ResponseBody
public String hello(@RequestParam(name= "name", defaultValue = "unknow user") String name) {
logger.info("This is a sample log message sent to Logstash, " + name);
return "Hello " + name;
}
}
之后访问接口hello就可以看到es有日志



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 物流快递公司核心技术能力-地址解析分单基础技术分享
· .NET 10首个预览版发布:重大改进与新特性概览!
· 单线程的Redis速度为什么快?
· 展开说说关于C#中ORM框架的用法!
· Pantheons:用 TypeScript 打造主流大模型对话的一站式集成库