elasticsearch mapping映射属性_source、_all、store和index
Elasticsearch中有几个关键属性容易混淆,很多人搞不清楚_source字段里存储的是什么?store属性的true或false和_source字段有什么关系?store属性设置为true和_all有什么关系?index属性又起到什么作用?什么时候设置store属性为true?什么时候应该开启_all字段?本文通过图解的方式,深入理解Elasticsearch中的_source、_all、store和index属性。
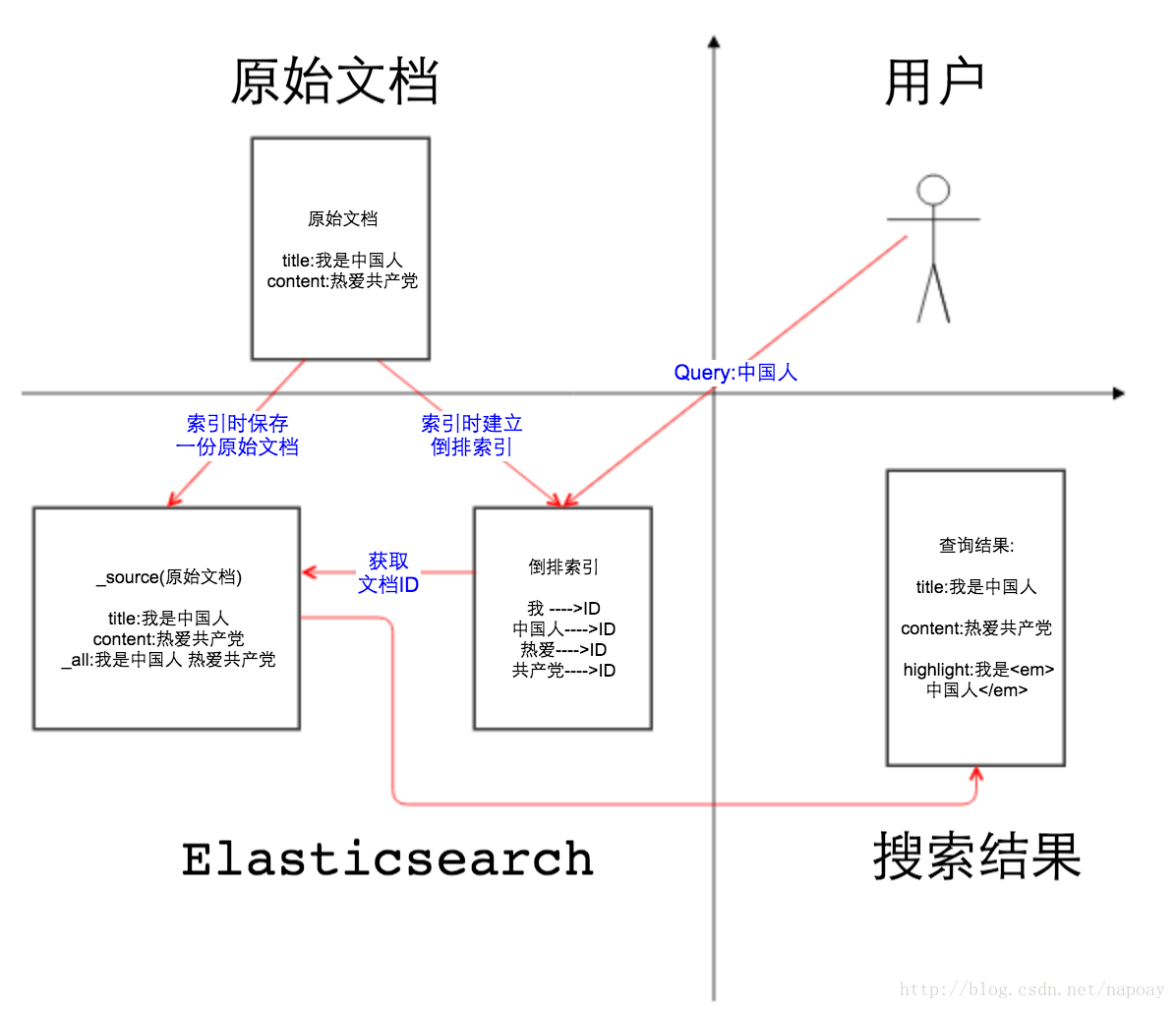
如 图1所示, 第二象限是一份原始文档,有title和content2个字段,字段取值分别为”我是中国人”和” 热爱***”,这一点没什么可解释的。我们把原始文档写入Elasticsearch,默认情况下,Elasticsearch里面有2份内容,一份是原始文档,也就是_source字段里的内容,我们在Elasticsearch中搜索文档,查看的文档内容就是_source中的内容,如图2,相信大家一定非常熟悉这个界面。

另一份是倒排索引,倒排索引中的数据结构是倒排记录表,记录了词项和文档之间的对应关系,比如关键词”中国人”包含在文档ID为1的文档中,倒排记录表中存储的就是这种对应关系,当然也包括词频等更多信息。Elasticsearch底层用的是Lucene的API,Elasticsearch之所以能完成全文搜索的功能就是因为存储的有倒排索引。如果把倒排索引拿掉,Elasticsearch是不是和mongoDB很像?
那么文档索引到Elasticsearch的时候,默认情况下是对所有字段创建倒排索引的(动态mapping解析出来为数字类型、布尔类型的字段除外),某个字段是否生成倒排索引是由字段的index属性控制的,在Elasticsearch 5之前,index属性的取值有三个:
- analyzed:字段被索引,会做分词,可搜索。反过来,如果需要根据某个字段进搜索,index属性就应该设置为analyzed。
- not_analyzed:字段值不分词,会被原样写入索引。反过来,如果某些字段需要完全匹配,比如人名、地名,index属性设置为not_analyzed为佳。
- no:字段不写入索引,当然也就不能搜索。反过来,有些业务要求某些字段不能被搜索,那么index属性设置为no即可。
再说_all字段,顾名思义,_all字段里面包含了一个文档里面的所有信息,是一个超级字段。以图中的文档为例,如果开启_all字段,那么title+content会组成一个超级字段,这个字段包含了其他字段的所有内容,当然也可以设置只存储某几个字段到_all属性里面或者排除某些字段。
回到图一的第一象限,用户输入关键词" 中国人",分词以后,Elasticsearch从倒排记录表中查找哪些文档包含词项"中国人 ",注意变化,分词之前" 中国人"是用户查询(query),分词之后在倒排索引中" 中国人"是词项(term)。Elasticsearch根据文档ID(通常是文档ID的集合)返回文档内容给用户,如图一第四象限所示。
通常情况下,对于用户查询的关键字要做高亮处理,如图3所示:
关键字高亮实质上是根据倒排记录中的词项偏移位置,找到关键词,加上前端的高亮代码。这里就要说到store属性,store属性用于指定是否将原始字段写入索引,默认取值为no。如果在Lucene中,高亮功能和store属性是否存储息息相关,因为需要根据偏移位置到原始文档中找到关键字才能加上高亮的片段。在Elasticsearch,因为_source中已经存储了一份原始文档,可以根据_source中的原始文档实现高亮,在索引中再存储原始文档就多余了,所以Elasticsearch默认是把store属性设置为no。
注意:如果想要对某个字段实现高亮功能,_source和store至少保留一个。下面会给出测试代码。
至此,文章开头提出的几个问题都给出了答案。下面给出这几个字段常用配置的代码。
1. _source配置
_source字段默认是存储的, 什么情况下不用保留_source字段?如果某个字段内容非常多,业务里面只需要能对该字段进行搜索,最后返回文档id,查看文档内容会再次到mysql或者hbase中取数据,把大字段的内容存在Elasticsearch中只会增大索引,这一点文档数量越大结果越明显,如果一条文档节省几KB,放大到亿万级的量结果也是非常可观的。
如果想要关闭_source字段,在mapping中的设置如下:
{ "yourtype":{ "_source":{ "enabled":false }, "properties": { ... } } }
如果只想存储某几个字段的原始值到Elasticsearch,可以通过incudes参数来设置,在mapping中的设置如下:
{ "yourtype":{ "_source":{ "includes":["field1","field2"] }, "properties": { ... } } }
同样,可以通过excludes参数排除某些字段:
{ "yourtype":{ "_source":{ "excludes":["field1","field2"] }, "properties": { ... } } }
示例:
# 首先创建一个索引 PUT test # 设置mapping,禁用_source: PUT test/test/_mapping { "test": { "_source": { "enabled": false } } } # 写入一条文档: POST test/test/1 { "title":"我是中国人", "content":"热爱***" #敏感词 } # 搜索关键词”中国人”: GET test/_search { "query": { "match": { "title": "中国人" } } } { "took": 9, "timed_out": false, "_shards": { "total": 5, "successful": 5, "failed": 0 }, "hits": { "total": 1, "max_score": 0.30685282, "hits": [ { "_index": "test", "_type": "test", "_id": "1", "_score": 0.30685282 } ] } }
从返回结果中可以看到,搜到了一条文档,但是禁用_source以后查询结果中不会再返回文档原始内容。(注,测试基于ELasticsearch 2.3.3,配置文件中已默认指定ik分词。)
2. _all配置
_all字段默认是关闭的,如果要开启_all字段,索引增大是不言而喻的。_all字段开启适用于不指定搜索某一个字段,根据关键词,搜索整个文档内容。
开启_all字段的方法和_source类似,mapping中的配置如下:
{ "yourtype": { "_all": { "enabled": true }, "properties": { ... } } }
也可以通过在字段中指定某个字段是否包含在_all中:
{ "yourtype": { "properties": { "field1": { "type": "string", "include_in_all": false }, "field2": { "type": "string", "include_in_all": true } } } }
如果要把字段原始值保存,要设置store属性为true,这样索引会更大,需要根据需求使用。下面给出测试代码。
创建test索引:
DELETE test
PUT test
设置mapping,这里设置所有字段都保存在_all中并且存储原始值:
PUT test/test/_mapping { "test": { "_all": { "enabled": true, "store": true } } }
插入文档:
POST test/test/1 { "title":"我是中国人", "content":"热爱***" }
对_all字段进行搜索并高亮:
POST test/_search { "fields": ["_all"], "query": { "match": { "_all": "中国人" } }, "highlight": { "fields": { "_all": {} } } } # 查询结果 { "took": 3, "timed_out": false, "_shards": { "total": 5, "successful": 5, "failed": 0 }, "hits": { "total": 1, "max_score": 0.15342641, "hits": [ { "_index": "test", "_type": "test", "_id": "1", "_score": 0.15342641, "_all": "我是中国人 热爱*** ", "highlight": { "_all": [ "我是<em>中国人</em> 热爱*** " ] } } ] } }
Elasticsearch中的query_string和simple_query_string默认就是查询_all字段,示例如下:
GET test/_search { "query": { "query_string": { "query": "***" } } }
3. index和store配置
index和store属性实在字段内进行设置的,下面给出一个例子,设置test索引不保存_source,title字段索引但不分析,字段原始值写入索引,content字段为默认属性,代码如下:
DELETE test PUT test PUT test/test/_mapping { "test": { "_source": { "enabled": false }, "properties": { "title": { "type": "string", "index": "not_analyzed", "store": "true" }, "content": { "type": "string" } } } }
对title字段进行搜索并高亮,代码如下:
GET test/_search { "query": { "match": { "title": "我是中国人" } }, "highlight": { "fields": { "title": {} } } } # 查询结果 { "took": 6, "timed_out": false, "_shards": { "total": 5, "successful": 5, "failed": 0 }, "hits": { "total": 1, "max_score": 0.30685282, "hits": [ { "_index": "test", "_type": "test", "_id": "1", "_score": 0.30685282, "highlight": { "title": [ "<em>我是中国人</em>" ] } } ] } }
从返回结果中可以看到,虽然没有保存title字段到_source, 但是依然可以实现搜索高亮。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/napoay/article/details/62233031





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)