图的遍历——BFS
原创
裸一篇图的BFS遍历,直接来图:
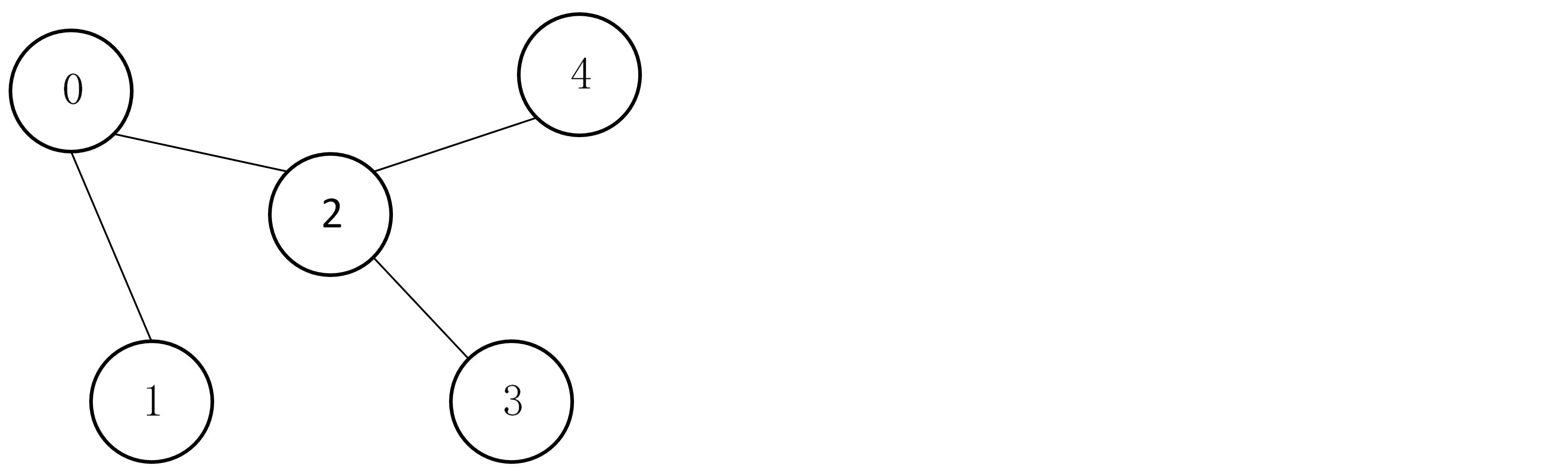
简单介绍一下BFS遍历的过程:
以上图为例子,从0开始遍历,访问0,按大小顺序访问与0相邻的所有顶点,即先访问1,再访问2;
至此顶点0已经没有作用了,因为其本身和与其所有相邻的顶点都已被访问,将其出队列,我们用队列
存储已访问过的顶点;然后顺着队列,访问顶点1和所有与顶点1相邻的顶点,这里没有,所有访问顶点
2和所有与顶点2相邻的结点,即3和4,注意,是先访问3,再访问4,因为采用邻接矩阵来存储图。
Java:
import java.util.*; public class 图的遍历_bfs { static int v; //顶点数 static int e; //边数 static int array[][]; //邻接矩阵 static int book[]; //标记 static int que[]; //队列 static int max=99999; //无穷 public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner reader=new Scanner(System.in); v=reader.nextInt(); e=reader.nextInt(); array=new int[v][v]; book=new int[v]; que=new int[v]; //矩阵初始化 for(int i=0;i<v;i++) { for(int j=0;j<v;j++) { if(i==j) { array[i][j]=0; } else { array[i][j]=max; } } } //读入边 for(int i=0;i<e;i++) { int first_One=reader.nextInt(); int second_Two=reader.nextInt(); array[first_One][second_Two]=1; array[second_Two][first_One]=1; } int head=0; //头指针 int tail=0; //尾指针 que[tail]=0; //从顶点0开始遍历 book[0]=1; tail++; while(head<tail) { for(int i=0;i<v;i++) { if(array[ que[head] ][i]==1 && book[i]==0) { que[tail]=i; //加入队列 tail++; book[i]=1; } if(tail>v-1) { break; } } head++; } for(int i=0;i<v;i++) { System.out.print(que[i]+" "); } } }
测试用例:
输入:
6 5
0 1
1 2
2 3
0 4
4 5
输出:
0 1 4 2 5 3
22:34:03
2018-07-22



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号