学习ASP.NET Core Blazor编程系列二十六——登录(5)
九、模拟登录
登录的本质原理同网页应用是一样的,一般的流程是:
用户打开登页--》输入账号密码后提交表单--》服务端验证成功后生成cookie信息写入浏览器--》之后用户访问页面时浏览器会带上此cookie信息作为用户标识--》服务端解析此cookie信息就能识别这个用户了。
在webapi出现之后,出现了JWT这样的认证方式,原理大同小异,相同的是, 认证信息都是保存在请求头中传递的,不同是JWT中的认证信息需要编码写入请求头之后再发送请求,不像浏览器,发送请求时会自动带上cookie信息,不需要编码。
Blazor中的登录流程可以分成几下几个步骤:
- 启用验证
- 制作自定义AuthenticationStateProvider
- 修改App.razor
- 使用AuthorizeView和进行登录验证和角色授权
自定义AuthenticationStateProvider
首先来理解一下什么是AuthenticationStateProvider。AuthenticationStateProvider是一个抽象类,由Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components.Authorization类库提供,主要用来提供当前用户的认证状态信息。既然是抽象类,我们需要自定义一个它的子类,由于是模拟登录,进行登录流程的验证,因此我们先来做一个测试的Provider来试试。
1. 在Visual Studio 2022的解决方案资源管理器中,在项目名称“BlazorAppDemo”上单击鼠标右键,在弹出菜单中选择“添加—>新建文件夹”,并将之命名为“Auth”。如下图。
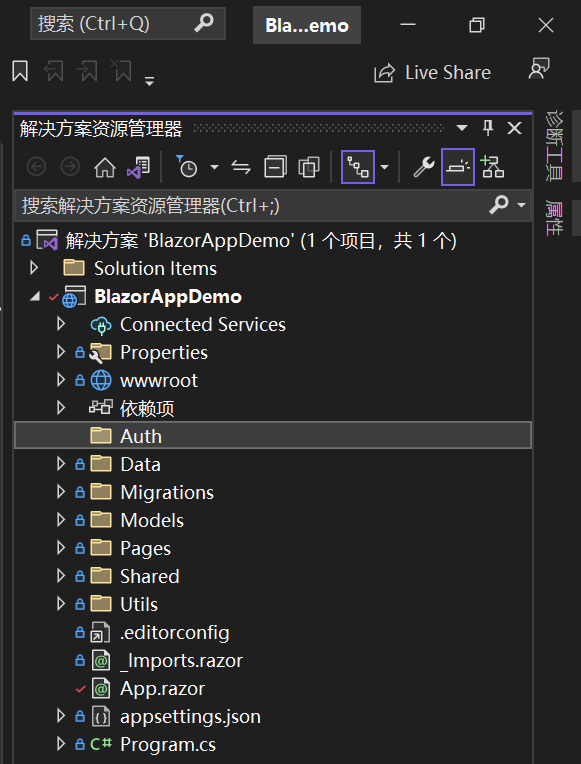
2. 在Visual Studio 2022的解决方案资源管理器中,鼠标左键选中“Auth”文件夹,右键单击,在弹出菜单中选择“添加—>类”,并将类命名为“ImitateAuthStateProvider”。 AuthStateProvider类的最核心方法是 Task<AuthenticationState> GetAuthenticationStateAsync()。基于最简单的登录机制,我们的扩展提供程序如下。具体代码如下:
using BlazorAppDemo.Models;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components.Authorization;
using System.Security.Claims;
namespace BlazorAppDemo.Auth
{
public class ImitateAuthStateProvider : AuthenticationStateProvider
{
bool isLogin = false;
public override Task<AuthenticationState> GetAuthenticationStateAsync()
{
if (isLogin)
{
var claims = new List<Claim>()
{
new Claim(ClaimTypes.Name,"user"),
new Claim(ClaimTypes.Role, "admin")
};
var anonymous = new ClaimsIdentity(claims, "testAuthType");
return Task.FromResult(new AuthenticationState(new ClaimsPrincipal(anonymous)));
}
else
{
var anonymous = new ClaimsIdentity();
return Task.FromResult(new AuthenticationState(new ClaimsPrincipal(anonymous)));
}
}
public void Login(UserInfo request)
{
if (request.UserName == "user" && request.Password == "111111")
isLogin = true;
NotifyAuthenticationStateChanged(GetAuthenticationStateAsync());
}
}
}
- var anonymous = new ClaimsIdentity();:我们现在进行模拟登录,先做一个匿名的使用者,所以ClaimsIdentity的构造方法中不传参数。
- 返回AuthenticationState。
- 我们给ClaimsIdentity一个List<Claim>属性,其中有使用者的名字和角色,表示我们已登录成功。
3. 在Visual Studio 2022的解决方案资源管理器中,使用鼠标双击在文本编辑器中打开Program.cs文件,使用
builder.Services.AddScoped<ImitateAuthStateProvider>();
builder.Services.AddScoped<AuthenticationStateProvider>(implementationFactory =>
implementationFactory.GetRequiredService<ImitateAuthStateProvider>());
;这二行代码使用DI方式注入ImitateAuthStateProvider。具体代码如下:
using BlazorAppDemo.Data;
using BlazorAppDemo.Models;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components.Web;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components.Authorization;
using BlazorAppDemo.Auth;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
builder.Services.AddRazorPages();
builder.Services.AddServerSideBlazor();
builder.Services.AddSingleton<WeatherForecastService>();
System.Console.WriteLine(ConfigHelper.Configuration["ConnectionStrings:BookContext"]);
builder.Services.AddDbContextFactory<BookContext>(opt =>
opt.UseSqlServer(ConfigHelper.Configuration["ConnectionStrings:BookContext"]));
//builder.Services.AddScoped<AuthenticationStateProvider, ImitateAuthStateProvider>();
builder.Services.AddScoped<ImitateAuthStateProvider>();
builder.Services.AddScoped<AuthenticationStateProvider>(implementationFactory =>
implementationFactory.GetRequiredService<ImitateAuthStateProvider>());
var app = builder.Build();
// Configure the HTTP request pipeline.
if (!app.Environment.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Error");
// The default HSTS value is 30 days. You may want to change this for production scenarios, see https://aka.ms/aspnetcore-hsts.
app.UseHsts();
}
using (var scope = app.Services.CreateScope())
{
var services = scope.ServiceProvider;
try
{
Console.WriteLine("数据库开始初始化。");
var context = services.GetRequiredService<BookContext>();
// requires using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
context.Database.Migrate();
// Requires using RazorPagesMovie.Models;
SeedData.Initialize(services);
Console.WriteLine("数据库初始化结束。");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
var logger = services.GetRequiredService<ILogger<Program>>();
logger.LogError(ex, "数据库数据初始化错误.");
}
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.MapBlazorHub();
app.MapFallbackToPage("/_Host");
app.Run();
修改App.razor
现在我们已经完成了登录认证的Provider了,接下來要做的事情,就是让我们的页面上的组件,可以获取登录信息,来决定是登录用户是否已经授权。这一步请参数之前的文章学习ASP.NET Core Blazor编程系列二十三——登录(3)之中的“七、修改路由与启动页面”。
修改Login.razor页面进行登录
在Visual Studio 2022的文本编辑器中打开Login.razor组件文件,我们将鼠标定位到@code中的SubmitHandler方法 ,写上我们登录成功的代码。具体代码如下:
@page "/Login"
@using BlazorAppDemo.Auth;
@using BlazorAppDemo.Models
@using BlazorAppDemo.Utils
@layout LoginLayout
@inject NavigationManager NavigationManager
@inject ImitateAuthStateProvider AuthStateProvider;
<div class="card align-items-center">
<div class="card-body my-2">
<h3>Login</h3>
<hr />
<EditForm Model="loginModel" OnValidSubmit="SubmitHandler" OnInvalidSubmit="InvalidHandler">
<DataAnnotationsValidator />
<div class="form-group">
<label for="userName"> @HtmlHelper.GetDisplayName(loginModel ,m=> m.UserName)</label>
<InputText @bind-Value="loginModel.UserName" class="form-control" id="userName" />
<ValidationMessage For="()=>loginModel.UserName" />
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="pwd"> @HtmlHelper.GetDisplayName(loginModel ,m=> m.Password)</label>
<InputPassword @bind-Value="loginModel.Password" class="form-control" id="pwd" />
<ValidationMessage For="()=>loginModel.Password" />
</div>
<span class="form-control-plaintext"></span>
<div class="form-group row">
<div class="col-sm-10">
<button class="btn btn-primary">登录</button>
</div>
</div>
</EditForm>
</div>
</div>
@code {
private UserInfo loginModel = new UserInfo();
bool isAuthLoading = false;
private void SubmitHandler()
{
Console.WriteLine($"用户名:{loginModel.UserName} ,密码:{loginModel.Password}");
isAuthLoading = true;
try {
AuthStateProvider.Login(new UserInfo() {
UserName = loginModel.UserName,
Password =loginModel.Password
});
NavigationManager.NavigateTo("/Index");
} catch (Exception ex) {
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
} finally {
isAuthLoading = false;
}
}
private void InvalidHandler()
{
Console.WriteLine($"用户名: {loginModel.UserName} ,密码:{loginModel.Password}");
}
}
登录并显示当前用户
1.在Visual Studio 2022的文本编辑器中打开MainLayout.razor组件文件,在AuthorizeView中显示当前登录用户,具体代码如下:
2.在Visual Studio 2022的菜单栏上,找到“调试-->开始调试”或是按F5键,Visual Studio 2022会生成BlazorAppDemo应用程序,浏览器中会Login登录页面。@using BlazorAppDemo.Pages @inherits LayoutComponentBase <PageTitle>BlazorAppDemo</PageTitle> <div class="page"> <div class="sidebar"> <NavMenu /> </div> <main> <AuthorizeView> <Authorized> <div class="top-row px-4"> <a href="https://docs.microsoft.com/aspnet/" target="_blank">About</a> <p> 你好, @context.User.Identity.Name! </p> </div> <article class="content px-4"> @Body </article> </Authorized> <NotAuthorized> <div style="margin: 120px 0; width:100%; text-align: center; color: red;"> <span style="font-size:20px">检测到登录超时,请重新<a href="/login" style="text-decoration:underline">登录</a>!
</span> </div> <RedirectToLogin></RedirectToLogin> </NotAuthorized> </AuthorizeView> </main> </div>
3.我们在用户名输入框中输入用户名,在密码输入框中输入密码,点击“登录”按钮,进行模拟登录。我们进入了系统。如下图。 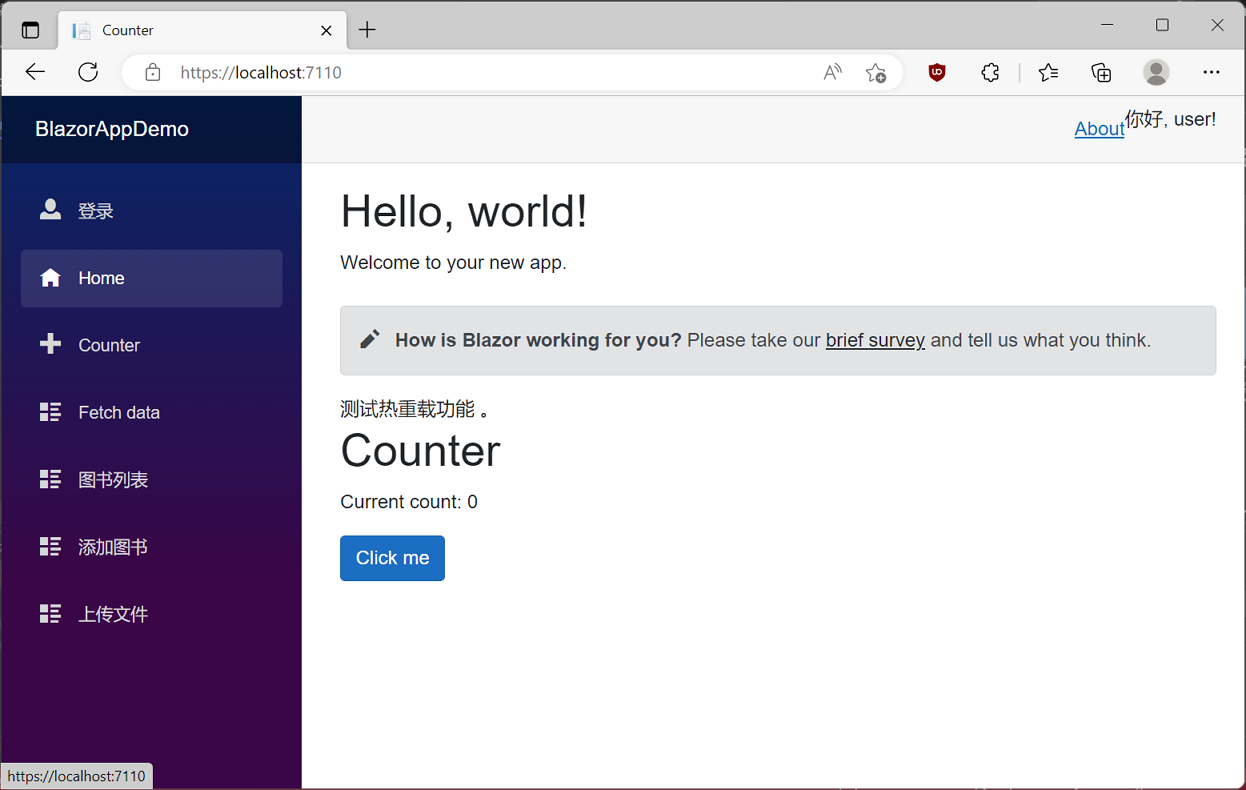
到此为止,我们已经实现了Blazor的登录认证流程,接下来我们要来实现通过jwt进行登录。



