D. Madoka and The Corruption Scheme -- (贪心,组合数学,构造)
题目链接:Problem - D - Codeforces
题目大意:
一共n轮比赛,有
大,求Madoka在主办方任意修改之后可能获得的胜利者的最小编号
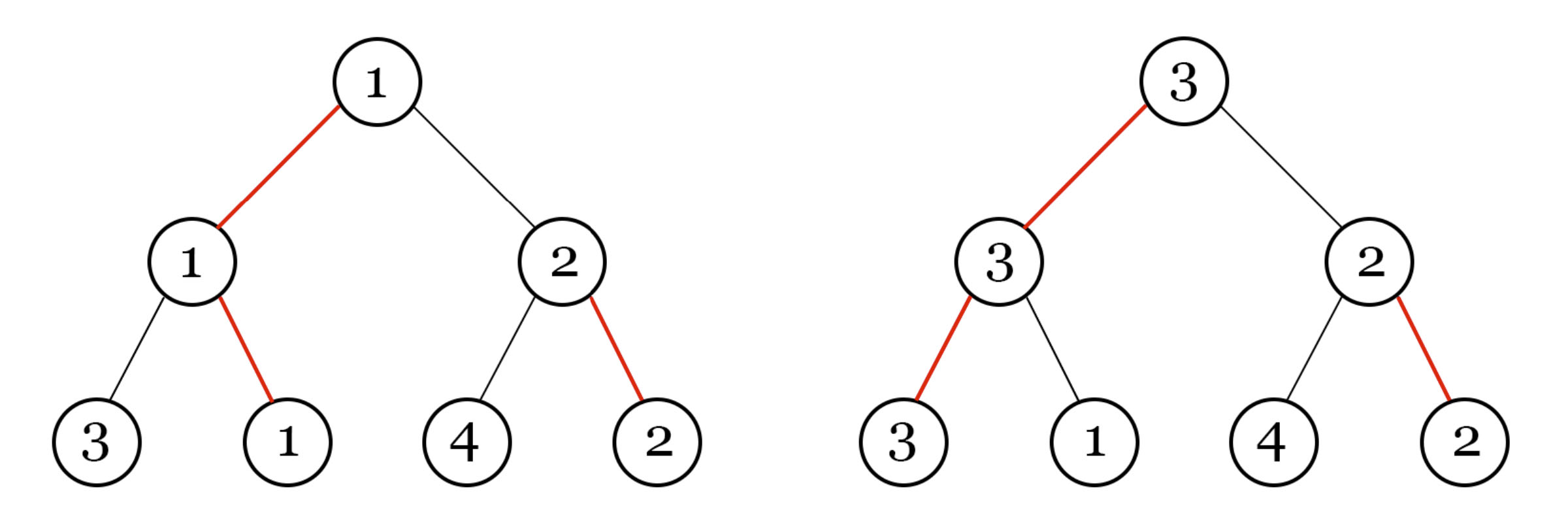
比如上面就是整个比赛,Madoka安排的第一局的顺序是 3 - 1 4 - 2,最终的结果是1获胜,但是第二个图是主办方修改之后的,导致3获胜了
算法过程
首先,我们可以让这个二叉树的左节点是获胜的那一方,右节点是输的那一方,然后我们看k次操作最多把第一局的那几个节点变成最终赢家,那么这就得满足从二叉树的根节点,到这个节点输的边得少于等于k,那么我求所有输的边有1个,输的边有2个......输的边有k个就一定能把这个点变成最终赢家,那么,主办方最多能变这么多,Madoka就能按照这个来安排开始的顺序,最小的编号就是能除去这么多一定能变成最终节点的节点,我们只需要求所有小于k个输边的数量就行,要用到组合数学,因为每个节点到最终节点的路上一共n条边,求
代码
// Problem: D. Madoka and The Corruption Scheme
// Contest: Codeforces - Codeforces Round 818 (Div. 2)
// URL: https://codeforces.com/contest/1717/problem/D
// Memory Limit: 256 MB
// Time Limit: 1000 ms
//
// Powered by CP Editor (https://cpeditor.org)
//by codeforcer ——
// ____ _ _ _ _ _ _ ____ _
// / ___|| | | || | | || | | | |___ \ | |
//| | | |_| || |_| || |_| | __) | | |
//| | | _ || _ || _ | |__ < | |
//| |___ | | | || | | || | | | ___) | | |
// \____||_| |_||_| |_||_| |_| |____ / |_|
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef int E;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef tuple<int, int, int> PIII;
typedef tuple<LL, LL, LL> PLLL;
typedef pair<long long, long long> PLL;
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
#define int long long
#define lowbit(x) (x & (-x))
#define mod(x) (x % MOD + MOD) % MOD
#define ls(x) (x << 1)
#define rs(x) (x << 1 | 1)
#define endl '\n'
#define vec vector
#define pb push_back
#define pob pop_back
#define fir first
#define sec second
#define INT 0x3f3f3f3f
#define LLONG 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3fLL
#define lower lower_bound
#define upper upper_bound
#define umap unordered_map
#define uset unordered_set
#define maxheap priority_queue<E, vector<E>, less<E>>
#define minheap priority_queue<E, vector<E>, greater<E>>
#define prvec(a) \
for (int i = 0; i < (a).size(); i++) { \
cout << (a)[i] << " "; \
} \
cout << endl;
#define debug0(a) \
cout << #a << ": "; \
for (int k = 0; k < (a).size(); k++) { \
cout << (a)[k] << " "; \
} \
cout << endl;
#define debug1(a) \
cout << #a << ": "; \
for (int k = 1; k <= (a).size(); k++) { \
cout << (a)[k] << " "; \
} \
cout << endl;
LL gcd(LL a, LL b) { return (b) ? gcd(b, a % b) : a; }
LL exgcd(LL a, LL b, LL &x, LL &y) {if (b == 0) { x = 1, y = 0; return a; }LL gcd = exgcd(b, a % b, y, x);y -= a / b * x;return gcd;}
LL qmi(LL a, LL b, LL mod) {LL res = 1;while (b) {if (b & 1) res = res * a % mod;a = a * a % mod;b >>= 1;}return res;}
const int N = 100010,MOD = 1e9 + 7;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
int fact[N], infact[N];
int pmod(int a,int b){
int res=1;
while(b){
if(b&1) res=res*a%mod;
b>>=1;
a=a*a%mod;
}
return res;
}
void init()
{
fact[0] = 1, infact[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
fact[i] = fact[i - 1] * i % mod;
infact[i] = infact[i - 1] * pmod(i,mod - 2) % mod;
}
}
int C(int a,int b)
{
return fact[a] * infact[a - b] % mod * infact[b] % mod;
}
void solve() {
int n,k;
cin>>n>>k;
init();
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 0;i <= min(k,n);i ++)
{
ans = (ans + C(n,i)) % mod;
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
signed main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
//i//nt n;cin>>n;while(n --)
solve();
return 0;
}



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构