Python实现二分法和黄金分割法
运筹学课上,首先介绍了非线性规划算法中的无约束规划算法。二分法和黄金分割法是属于无约束规划算法的一维搜索法中的代表。
二分法:$$x_{1}^{(k+1)}=\frac{1}{2}(x_{R}^{(k)}+x_{L}^{(k)}-\Delta)$$$$x_{2}^{(k+1)}=\frac{1}{2}(x_{R}^{(k)}+x_{L}^{(k)}+\Delta)$$
黄金分割法:$$x_{1}^{(k+1)}=x_{R}^{(k)}-(\frac{\sqrt{5}-1}{2})(x_{R}^{(k)}-x_{L}^{(k)})$$$$x_{2}^{(k+1)}=x_{L}^{(k)}+(\frac{\sqrt{5}-1}{2})(x_{R}^{(k)}-x_{L}^{(k)})$$
选择的$x_{1}^{(k+1)}$和$x_{2}^{(k+1)}$一定满足$$x_{L}^{(k)}<x_{1}^{(k+1)}<x_{2}^{(k+1)}<x_{R}^{(k)}$$
下面确定新的不确定空间$I^{(k+1)}$
情况1:若$f(x_{1}^{(k+1)})>f(x_{2}^{(k+1)})$,则$I^{(k+1)}=\left[x_{L}^{(k)},x_{2}^{(k+1)}\right]$
情况2:若$f(x_{1}^{(k+1)})<f(x_{2}^{(k+1)})$,则$I^{(k+1)}=\left[x_{1}^{(k+1)},x_{R}^{(k)}\right]$
情况3:若$f(x_{1}^{(k+1)})=f(x_{2}^{(k+1)})$,则$I^{(k+1)}=\left[x_{1}^{(k+1)},x_{2}^{(k+1)}\right]$
下面记录下用Python实现二分法和黄金分割法的代码。
二分法:
1 import math 2 import numpy as np 3 4 5 def anyfunction(x): # 在这里我们定义任意一个指定初始区间内的单峰函数,以x*cos(x)为例 6 return x*math.cos(x) 7 8 9 Low = float(input("Please enter the lowbound: ")) 10 High = float(input("Please enter the highbound: ")) 11 High = np.pi # 在这里我们取初始上界为π,如果可以输入则注释掉这一行 12 echos = int(input("Please enter the echos: ")) # 迭代次数 13 small = float(input("Please enter the smallvalue: ")) # 公式中的Delta 14 15 for i in range(1, echos + 1): 16 Lowvalue = anyfunction(0.5*(Low + High - small)) 17 Highvalue = anyfunction(0.5*(Low + High + small)) 18 print("echos: " + str(i)) 19 print('before ' + "Lowbound: " + str(0.5*(Low + High - small)) + " Highbound: " + str(0.5*(Low + High + small))) 20 print('Lowvalue: ' + str(Lowvalue) + ' ' + 'Highvalue: ' + str(Highvalue)) 21 if(Lowvalue == Highvalue): 22 Low = 0.5*(Low + High - small) 23 High = 0.5*(Low + High + small) 24 elif(Lowvalue < Highvalue): 25 Low = 0.5*(Low + High - small) 26 else: 27 High = 0.5*(Low + High + small) 28 print("Lowbound: " + str(Low) + " Highbound: " + str(High))
输出结果如下:
5次循环后极值点被限制在[0.7828981633974482,0.8907604338221292]内。
黄金分割法:
1 from math import sqrt, cos 2 import numpy as np 3 4 5 def anyfunction(x): # 同上以函数x*cos(x)为例 6 return x*cos(x) 7 8 9 Low = float(input("Please enter the lowbound: ")) 10 High = float(input("Please enter the highbound: ")) 11 High = np.pi # 同上,使用时应该注释掉 12 echos = int(input("Please enter the echos: ")) 13 14 # 初始化,第一次运算不存在运算简化 15 uniquevalue = ((sqrt(5)-1)/2)*(High-Low) 16 value1 = anyfunction(High - uniquevalue) 17 value2 = anyfunction(Low + uniquevalue) 18 19 for i in range(1, echos + 1): 20 print("echos: " + str(i)) 21 print('before ' + "Lowbound: " + str(High - uniquevalue) + " Highbound: " + str(Low + uniquevalue)) 22 print('value1: ' + str(value1) + ' ' + 'value2: ' + str(value2)) 23 # 利用黄金分割法的性质减少一半的运算量 24 if(value1 == value2): 25 Low = High - uniquevalue 26 High = Low + uniquevalue 27 uniquevalue = ((sqrt(5)-1)/2)*(High-Low) 28 value1 = anyfunction(High - uniquevalue) 29 value2 = anyfunction(Low + uniquevalue) 30 elif(value1 < value2): 31 Low = High - uniquevalue 32 uniquevalue = ((sqrt(5)-1)/2)*(High-Low) 33 value1 = value2 34 value2 = anyfunction(Low + uniquevalue) 35 else: 36 High = Low + uniquevalue 37 uniquevalue = ((sqrt(5)-1)/2)*(High-Low) 38 value2 = value1 39 value1 = anyfunction(High - uniquevalue) 40 print("Lowbound: " + str(Low) + " Highbound: " + str(High))
输出结果如下: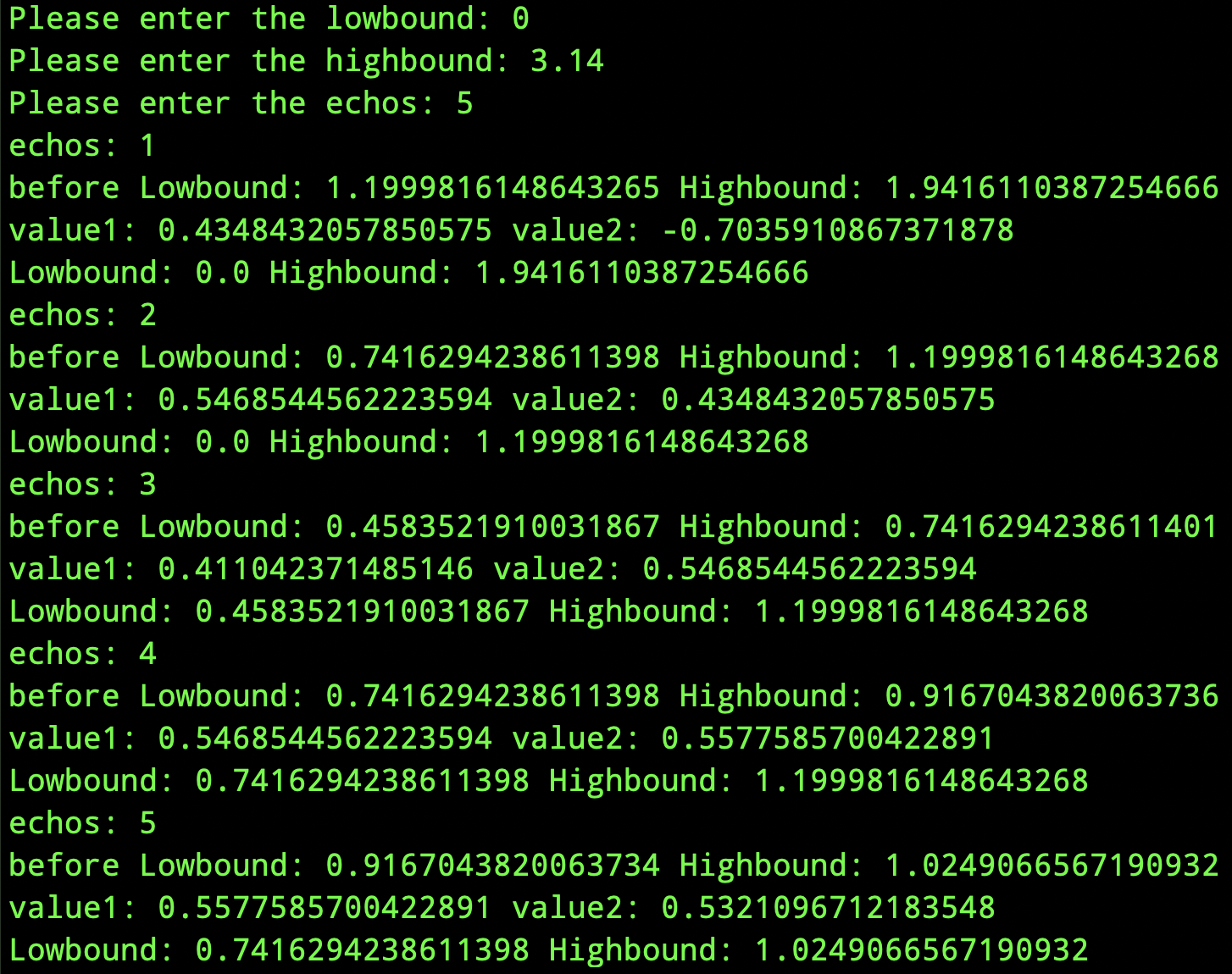
5次循环后极值点被限制在[0.7416294238611398,1.0249066567190932]



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号