Next Permutation
原题地址:https://leetcode.com/submissions/detail/48922153/
所谓一个排列的下一个排列的意思就是 这一个排列与下一个排列之间没有其他的排列。这就要求这一个排列与下一个排列有尽可能长的共同前缀,也即变化限制在尽可能短的后缀上。这句话的意思我一直没弄明白!
对于数字序列:
先看前面2排的话,可以看出来第二排是比第一排要大的,参考字符串比较大小的问题。那么第2个排列是不是第一个排列的下一个排列呢。很明显不是,第3个排列才是, 那么如何获取到下一个排列呢。步骤比较简单:假设数组大小为 n
1.从后往前,找到第一个 A[i-1] < A[i]的。也就是第一个排列中的 6那个位置,可以看到A[i]到A[n-1]这些都是单调递减序列。
2.从 A[n-1]到A[i]中找到一个比A[i-1]大的值(也就是说在A[n-1]到A[i]的值中找到比A[i-1]大的集合中的最小的一个值)
3.交换 这两个值,并且把A[n-1]到A[i]排序,从小到大。
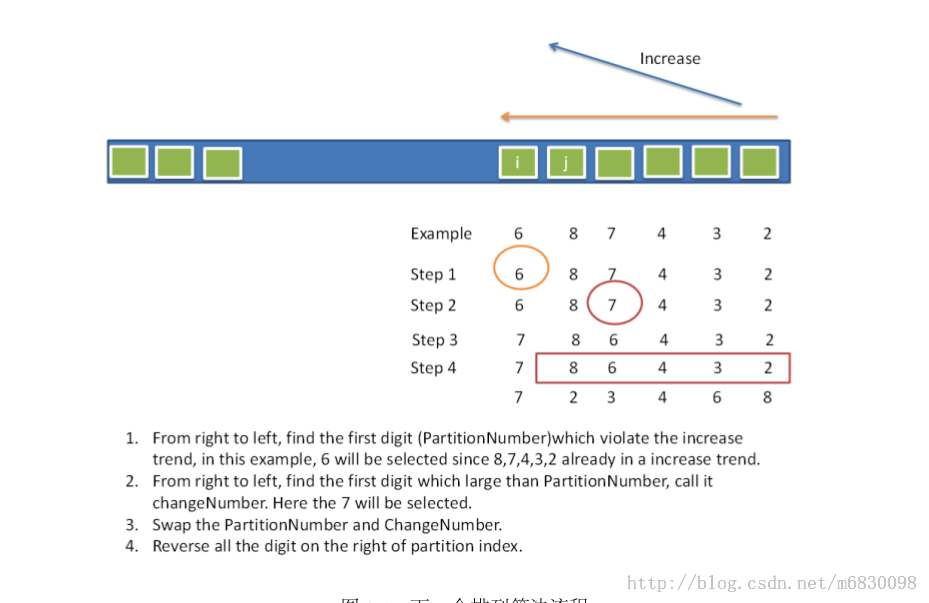
Well, in fact the problem of next permutation has been studied long ago. From the Wikipedia page, in the 14th century, a man named Narayana Pandita gives the following classic and yet quite simple algorithm (with minor modifications in notations to fit the problem statement):
- Find the largest index
ksuch thatnums[k] < nums[k + 1]. If no such index exists, the permutation is sorted in descending order, just reverse it to ascending order and we are done. For example, the next permutation of[3, 2, 1]is[1, 2, 3]. - Find the largest index
lgreater thanksuch thatnums[k] < nums[l]. - Swap the value of
nums[k]with that ofnums[l]. - Reverse the sequence from
nums[k + 1]up to and including the final elementnums[nums.size() - 1].
Quite simple, yeah? Now comes the following code, which is barely a translation.这就是上面图片的另外一种表述!!
就看第一个算法就好了:
1 class Solution {
2 public:
3 void nextPermutation(vector<int>& nums) //注意,这里传进来的可是引用
4 {
5 int index1,index2;
6 for(int i=nums.size()-1;i>=0;i--)
7 {
8 if(i>=1 && nums[i-1]<nums[i])
9 {
10 index1=i-1;
11 break;
12 }
13 if(i==0)
14 {
15 reverse(nums,0,nums.size()-1);
16 return;
17 }
18 }
19 for(int j=nums.size()-1;j>=0;j--)
20 {
21 if(nums[j]>nums[index1])
22 {
23 index2=j;
24 break;
25 }
26 }
27 int temp=nums[index1];
28 nums[index1]=nums[index2];
29 nums[index2]=temp;
30 reverse(nums,index1+1,nums.size()-1);
31 }
32 void reverse(vector<int>&nums,int begin,int end)
33 {
34 while(begin<end)
35 {
36 int temp=nums[begin];
37 nums[begin]=nums[end];
38 nums[end]=temp;
39 begin++;
40 end--;
41 }
42 }
43 };
#include<iostream> #include<string> #include<vector> using namespace std; class Solution { public: void nextPermutation(vector<int>& nums) { int index1,index2; for(int i=nums.size()-1;i>=0;i--) { if(i>=1 && nums[i-1]<nums[i]) { index1=i-1; break; } if(i==0) { reverse(nums,0,nums.size()-1); return; } } for(int j=nums.size()-1;j>=0;j--) { if(nums[j]>nums[index1]) { index2=j; break; } } int temp=nums[index1]; nums[index1]=nums[index2]; nums[index2]=temp; reverse(nums,index1+1,nums.size()-1); } void reverse(vector<int>&nums,int begin,int end) { while(begin<end) { int temp=nums[begin]; nums[begin]=nums[end]; nums[end]=temp; begin++; end--; } } }; int main() { Solution test; vector<int> arr; arr.push_back(1); arr.push_back(3); arr.push_back(2); for(int i=0;i<arr.size();i++) cout<<arr[i]<<endl; cout<<"after:"<<endl; test.nextPermutation(arr); for(int i=0;i<arr.size();i++) cout<<arr[i]<<endl; }
手里拿着一把锤子,看什么都像钉子,编程界的锤子应该就是算法了吧!


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号