打印更多的用户态段错误信息
在调试上层程序时,经常会遇到的错误是段错误,当出现段错误时,系统往往只会给出一个 segmention error,而在没有更多的信息(默认不产生core dump),在这种情况下,可以通过修改内核启动参数来使能调试模式,让用户态出现段错误时,打印出更多的提示信息,有助于定位错误。
分析流程:
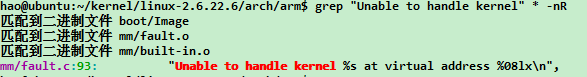
先从在内核态的段错误出发,当产生内核态的段错误时,通常会打印出如下字段:
Unable to handle kernel paging request at virtual address 56000050
鉴于主流的体系结构为arm,我们可以在内核目录 arch/arm/ 目录下面,通过如下方式来定位:
找到对于代码所在的文件:
1: static void
2: __do_kernel_fault(struct mm_struct *mm, unsigned long addr, unsigned int fsr,
3: struct pt_regs *regs)
4: {
5: /*
6: * Are we prepared to handle this kernel fault?
7: */
8: if (fixup_exception(regs))
9: return;
10:
11: /*
12: * No handler, we'll have to terminate things with extreme prejudice.
13: */
14: bust_spinlocks(1);
15: printk(KERN_ALERT
16: "Unable to handle kernel %s at virtual address %08lx\n",
17: (addr < PAGE_SIZE) ? "NULL pointer dereference" :
18: "paging request", addr);
19:
20: show_pte(mm, addr);
21: die("Oops", regs, fsr);
22: bust_spinlocks(0);
23: do_exit(SIGKILL);
24: }
此函数在这里被调用:
1: void do_bad_area(unsigned long addr, unsigned int fsr, struct pt_regs *regs)
2: {
3: struct task_struct *tsk = current;
4: struct mm_struct *mm = tsk->active_mm;
5:
6: /*
7: * If we are in kernel mode at this point, we
8: * have no context to handle this fault with.
9: */
10: if (user_mode(regs))
11: __do_user_fault(tsk, addr, fsr, SIGSEGV, SEGV_MAPERR, regs);
12: else
13: __do_kernel_fault(mm, addr, fsr, regs);
14: }
从上面可以看出,如果是在用户态访问了非法区域,会调用__do_user_fault函数,在内核态的话,会调用__do_kernel_fault函数。
我们进入__do_user_fault来查看:
1: static void
2: __do_user_fault(struct task_struct *tsk, unsigned long addr,
3: unsigned int fsr, unsigned int sig, int code,
4: struct pt_regs *regs)
5: {
6: struct siginfo si;
7:
8: #ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_USER
9: if (user_debug & UDBG_SEGV) {
10: printk(KERN_DEBUG "%s: unhandled page fault (%d) at 0x%08lx, code 0x%03x\n",
11: tsk->comm, sig, addr, fsr);
12: show_pte(tsk->mm, addr);
13: show_regs(regs);
14: }
15: #endif
16: .....
17:
18: }
从上述可以看出,要想在用户态打印更多的调试信息,需要
1. 内核配置 CONFIG_DEBUG_USER 宏
2. user_debug & UDBG_SEGV 为真 ,其中 UDBG_SEGV = (1 << 3) ,而全局变量user_debug初始化为0,
#define UDBG_UNDEFINED (1 << 0) //产生未定义指令信息
#define UDBG_SYSCALL (1 << 1) //产生非法的系统调用
#define UDBG_BADABORT (1 << 2)
#define UDBG_SEGV (1 << 3) //产生段错误信息
#define UDBG_BUS (1 << 4)
1:
2: #ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_USER
3: unsigned int user_debug;
4:
5: static int __init user_debug_setup(char *str)
6: {
7: get_option(&str, &user_debug);
8: return 1;
9: }
10: __setup("user_debug=", user_debug_setup);
11: #endif
分析到这里,我们就知道了,可以通过Uboot传递给内核的启动参数 bootargs,设置 user_debug = 0xFF,开启所有用户态调试信息
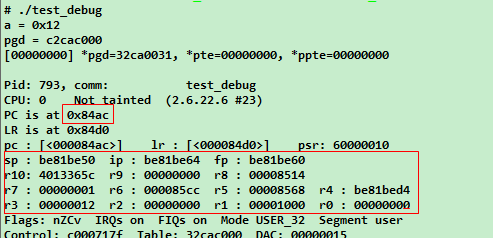
此后,在执行用户态程序时,当出现段错误,会显示许多信息,在这里,有用的值是pc值。
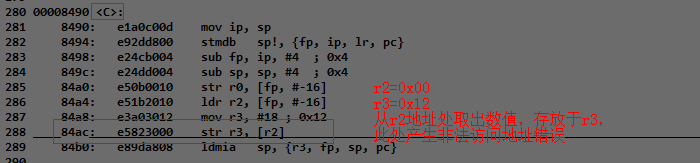
我们可以通过反汇编应用程序来分析此pc值对于的具体哪一句汇编指令:
arm-linux-objdump –D test_debug > test_debug.dis , 在test_debug.dis中搜索 PC值:84ac,对比发生错误时的寄存器信息。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号