MySQL - 死锁的产生及解决方案
MySQL - 死锁的产生及解决方案
大家好,我是一安~
简介
死锁指两个或多个事务相互等待对方释放锁,从而导致进程无法继续执行的一种情况。当一个事务需要锁定一些资源时,如果这些资源已经被其他事务锁定,则该事务必须等待其他事务释放锁,才能继续执行。如果多个事务同时等待对方释放锁,就会发生死锁。
总结:
- 互斥条件:一个资源每次只能被一个进程使用。
- 请求和保持条件:一个进程因请求资源而阻塞时,对已获得的资源保持不放。
- 不剥夺条件:进程已获得的资源,在未使用完之前,不能被其他进程强行剥夺,只能由该进程自己释放。
- 循环等待条件:若干进程之间形成一种头尾相接的循环等待资源关系。
产生死锁的必要满足以上4个条件,缺一不可。
案例分析
表锁
用户A访问表A(锁住了表A),然后又访问表B;另一个用户B访问表B(锁住了表B),然后企图访问表A;这时用户A由于用户B已经锁住表B,它必须等待用户B释放表B才能继续,同样用户B要等用户A释放表A才能继续,死锁就这样产生了。
行锁
如果在事务中执行了一条没有索引条件的查询,引发全表扫描,把行级锁上升为全表记录锁定(等价于表级锁),多个这样的事务执行后,就很容易产生死锁和阻塞。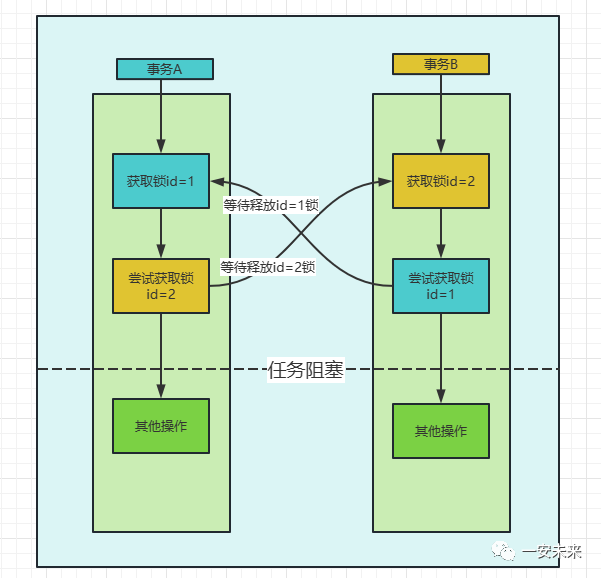
如何解决
以上死锁基本是由于程序的BUG产生的,在对数据库的多表或单表操作时,尽量按照相同的顺序进行处理且避免同时锁定两个资源。
必须同时锁定两个资源时,要保证在任何时刻都应该按照相同的顺序来锁定资源。
select for update:
- 如果有唯一索引,命中了唯一记录:行锁,互斥锁;
- 如果有唯一索引,没命中:
gap锁,另一个事务也可以获得这个gap锁,但是不能插入数据;(后续有死锁可能)- 如果有普通索引,命中了记录:行锁+
gap锁;(后续有死锁可能)- 如果有普通索引,没有命中记录:
gap锁,和情况2相同;(后续有死锁可能)- 如果没有索引,直接锁全表,互斥,直接阻塞别的事务
演示
说明:
共享锁(S):允许多个事务同时读取同一份数据,但不允许对数据进行修改。当一个事务获得共享锁时,其他事务只能获得共享锁,不能获得排他锁。排他锁(X):只允许一个事务对数据进行修改,其他事务不能读取或修改该数据。当一个事务获得排他锁时,其他事务不能获得任何类型的锁。意向共享锁(IS):表示事务想要在某个数据上获得共享锁,但并不是真正的共享锁,只是一个辅助锁。当一个事务获得意向共享锁时,其他事务可以获得共享锁或意向共享锁,但不能获得排他锁。意向排他锁(IX):表示事务想要在某个数据上获得排他锁,但并不是真正的排他锁,只是一个辅助锁。当一个事务获得意向排他锁时,其他事务只能获得意向共享锁,不能获得任何类型的锁。
CREATE TABLE `test_lock` (
`id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`user_name` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`age` int DEFAULT NULL,
`city` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY `idx_user_name` (`user_name`),
KEY `idx_city` (`city`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=0 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
insert into test_lock(id,user_name,age,city) values(1,'杰伦',20,'深圳');
insert into test_lock(id,user_name,age,city) values(5,'奕迅',25,'湛江');
insert into test_lock(id,user_name,age,city) values (9,'俊杰',29,'广州');
案例1(主键索引):
BEGIN;
select * from test_lock where id = 1 for update;
select * from performance_schema.data_locks;
ROLLBACK;

查询条件是主键索引,命中数据库表记录时,一共会加两把锁:一把
IX意向排他锁(表锁,不影响插入),一把对应主键的X排他锁(行锁,影响对应主键那一行的插入)。
案例2(唯一索引):
BEGIN;
select * from test_lock where user_name ='杰伦' for update;
select * from performance_schema.data_locks;
ROLLBACK;

查询条件是唯一索引,命中数据库表记录时,一共会加三把锁:一把
IX意向排他锁 (表锁,不影响插入),一把对应主键的X排他锁(行锁),一把对应唯一索引的X排他锁 (行锁)。
案例3(普通索引):
BEGIN;
select * from test_lock where city ='深圳' for update;
select * from performance_schema.data_locks;
ROLLBACK;

查询条件是普通索引,命中数据库表记录时,一共会加四把锁:一把
IX意向排他锁 (表锁,不影响插入),一把对应主键的X排他锁(行锁),一把对应普通索引的X排他锁 (行锁),一把对应普通索引的Gap间隙锁 (锁住一个范围,会影响插入)。
案例4(非索引):
BEGIN;
select * from test_lock where age =20 for update;
select * from performance_schema.data_locks;
ROLLBACK;

查询条件不是索引,命中或非命中数据库表记录时,都会加一个
IX锁(表锁,不影响插入),每一行实际记录行的X锁,还有对应于supremum pseudo-record的虚拟全表行锁(通俗点讲,其实就是锁表了)
案例5(索引未命中):
BEGIN;
select * from test_lock where id = 4 for update;
select * from performance_schema.data_locks;
ROLLBACK;

查询条件是主键,未命中数据库表记录时,查询条件是中间值,会加一个
IX锁(表锁,不影响插入),一把对应主键索引的X排他锁 (行锁),一把对应主键索引的Gap间隙锁 (锁住一个范围,会影响插入)
BEGIN;
select * from test_lock where id = 10 for update;
select * from performance_schema.data_locks;
ROLLBACK;

查询条件是主键,未命中数据库表记录时,查询条件非中间值,会加一个
IX锁(表锁,不影响插入),每一行实际记录行的X锁,还有对应于supremum pseudo-record的虚拟全表行锁(通俗点讲,其实就是锁表了)
死锁排查
查看死锁日志
通过 show engine innodb status命令查看近期死锁日志信息,主要关注日志中的 LATEST DETECTED DEADLOCK部分:
=====================================
2023-04-19 15:27:25 0x9b1c INNODB MONITOR OUTPUT
=====================================
Per second averages calculated from the last 31 seconds
-----------------
BACKGROUND THREAD
-----------------
srv_master_thread loops: 147 srv_active, 0 srv_shutdown, 587314 srv_idle
srv_master_thread log flush and writes: 0
----------
SEMAPHORES
----------
OS WAIT ARRAY INFO: reservation count 3596
OS WAIT ARRAY INFO: signal count 3509
RW-shared spins 0, rounds 0, OS waits 0
RW-excl spins 0, rounds 0, OS waits 0
RW-sx spins 0, rounds 0, OS waits 0
Spin rounds per wait: 0.00 RW-shared, 0.00 RW-excl, 0.00 RW-sx
------------------------
LATEST DETECTED DEADLOCK
------------------------
2023-04-19 15:27:18 0x121c
*** (1) TRANSACTION:
TRANSACTION 39296, ACTIVE 26 sec starting index read
mysql tables in use 1, locked 1
LOCK WAIT 3 lock struct(s), heap size 1128, 2 row lock(s)
MySQL thread id 383, OS thread handle 37880, query id 9857 localhost 127.0.0.1 root statistics
select * from test_lock where id = 5 for update
*** (1) HOLDS THE LOCK(S):
RECORD LOCKS space id 899 page no 4 n bits 72 index PRIMARY of table `springcloud_test`.`test_lock` trx id 39296 lock_mode X locks rec but not gap
Record lock, heap no 6 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 6; compact format; info bits 0
0: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;;
1: len 6; hex 000000009974; asc t;;
2: len 7; hex 81000000b00110; asc ;;
3: len 6; hex e69db0e4bca6; asc ;;
4: len 4; hex 80000014; asc ;;
5: len 6; hex e6b7b1e59cb3; asc ;;
*** (1) WAITING FOR THIS LOCK TO BE GRANTED:
RECORD LOCKS space id 899 page no 4 n bits 72 index PRIMARY of table `springcloud_test`.`test_lock` trx id 39296 lock_mode X locks rec but not gap waiting
Record lock, heap no 3 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 6; compact format; info bits 0
0: len 4; hex 80000005; asc ;;
1: len 6; hex 00000000993a; asc :;;
2: len 7; hex 81000000990110; asc ;;
3: len 6; hex e5a595e8bf85; asc ;;
4: len 4; hex 80000019; asc ;;
5: len 6; hex e6b99be6b19f; asc ;;
*** (2) TRANSACTION:
TRANSACTION 39297, ACTIVE 14 sec starting index read
mysql tables in use 1, locked 1
LOCK WAIT 3 lock struct(s), heap size 1128, 2 row lock(s)
MySQL thread id 384, OS thread handle 38372, query id 9861 localhost 127.0.0.1 root statistics
select * from test_lock where id = 1 for update
*** (2) HOLDS THE LOCK(S):
RECORD LOCKS space id 899 page no 4 n bits 72 index PRIMARY of table `springcloud_test`.`test_lock` trx id 39297 lock_mode X locks rec but not gap
Record lock, heap no 3 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 6; compact format; info bits 0
0: len 4; hex 80000005; asc ;;
1: len 6; hex 00000000993a; asc :;;
2: len 7; hex 81000000990110; asc ;;
3: len 6; hex e5a595e8bf85; asc ;;
4: len 4; hex 80000019; asc ;;
5: len 6; hex e6b99be6b19f; asc ;;
*** (2) WAITING FOR THIS LOCK TO BE GRANTED:
RECORD LOCKS space id 899 page no 4 n bits 72 index PRIMARY of table `springcloud_test`.`test_lock` trx id 39297 lock_mode X locks rec but not gap waiting
Record lock, heap no 6 PHYSICAL RECORD: n_fields 6; compact format; info bits 0
0: len 4; hex 80000001; asc ;;
1: len 6; hex 000000009974; asc t;;
2: len 7; hex 81000000b00110; asc ;;
3: len 6; hex e69db0e4bca6; asc ;;
4: len 4; hex 80000014; asc ;;
5: len 6; hex e6b7b1e59cb3; asc ;;
从上面日志可以看出,存在两个事务,分别在执行这两条sql时发生了死锁:
select * from test_lock where id = 1 for update
select * from test_lock where id = 5 for update
死锁的本质原因还是由加锁顺序不同所导致,如上面事务1先给id=1加锁,事务2给id=5加锁,然后事务1再给id=5加锁,事务2再给id=1加锁。
死锁记录只记录最近一个死锁信息,若要将每个死锁信息都保存到错误日志,启用以下参数
show variables like 'innodb_print_all_deadlocks';
查当前正在运行的InnoDB事务的信息,可以kill长期占用锁的事务对应的线程id
select * from information_schema.INNODB_TRX;
解决死锁
- 可以设置
innodb_deadlock_detect=on来开启死锁检测。死锁检测在发生死锁的时候,能够快速发现并进行处理,回滚并重新启动。但是死锁检测会比较耗资源。
show VARIABLES like 'innodb_deadlock_detect' -- 查看当前死锁检测是否开启
set global innodb_deadlock_detect = OFF; --设置死锁检测关闭
set global innodb_deadlock_detect = ON; --设置死锁检测开启
- 保证资源的加锁顺序,避免循环等待的产生。
- 减少对资源的占用时间和占用范围,避免长事务,锁粒度变大的情况,可以大大减少死锁产生的概率。
- 使用乐观锁
mvcc机制,读取数据不上锁,在读情况下共享资源。
如果这篇文章对你有所帮助,或者有所启发的话,帮忙 分享、收藏、点赞、在看,你的支持就是我坚持下去的最大动力!

基于Shrio的分布式微服务权限控制和会话管理的详细设计与实现



