find命令查询实例
[weihu1@localhost ~]$ find ./ -type l -exec ls -l {} \;
lrwxrwxrwx 1 weihu1 weihu1 10 Oct 17 13:50 ./xunjian.txt -> xunjian.sh
按size大小查找
[weihu1@localhost ~]$ find ./ -type f -size +4k -exec du -sh {} \;
316K ./.bash_history
8.0K ./.ssh/known_hosts
40K ./xunjian_172.18.136.11report.tar.gz
12K ./172.18.136.11_property.log
8.0K ./.viminfo
16K ./xunjian/172.18.136.11-2023060720.txt
16K ./xunjian/172.18.136.11-2023060814.txt
16K ./xunjian/172.18.136.11-2023060816.txt
[weihu1@localhost ~]$ find ./ -type f -size 4k -exec du -sh {} \;
4.0K ./.ssh/known_hosts.old
4.0K ./xunjian.sh
查5分钟之前创建的链接文件:(按分钟查找)
[weihu1@localhost ~]$ find ./ -type l -mmin -5 -exec ls -l {} \;
lrwxrwxrwx 1 weihu1 weihu1 10 Oct 17 13:50 ./xunjian.txt -> xunjian.sh

查目录:
find ./xunjian -type d -exec ls -lh {} \;

查普通文件

Linux系统下查找文件 命令总结
1、根据文件名或正则表达式查找文件
find . -name nginx-1.12.2.tar.gz
[root@master ~]# find / -name nginx-1.12.2.tar.gz
/root/nginx-1.12.2.tar.gz
[root@master ~]#
如何找到所有格式为 png 的图像?使用正则表达式:
find /home/linuxmi/linuxmi.com -name "*.png"默认情况下,find 命令搜索常规文件,但最好指定类型以使一切更清晰:
find /home/linuxmi/linuxmi.com -type f -name "*.png"
[root@master tmp]# find . -type d -name "test*"
./test1
./test2
./test3
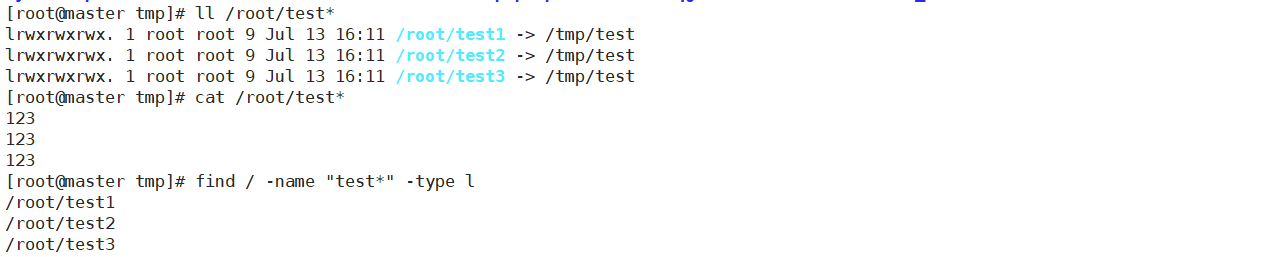
例如文件:
[root@master tmp]# find . -type f -name "test*"
./test
例如快捷键文件:
[root@master tmp]# ln -s /tmp/test /root/test1
[root@master tmp]# ln -s /tmp/test /root/test2
[root@master tmp]# ln -s /tmp/test /root/test3
3、按特定的时间戳查找文件

要按特定的时间戳搜索文件,我们需要了解Linux系统中的3种不同时间戳:
访问时间戳(atime):文件上次被读取的时间。
修改时间戳(mtime):文件内容上次被修改的时间。
更改时间戳(ctime):文件的元数据,例如所有权、位置、文件类型和权限设置等上次更改的时间。
所以,就像开始时提到的面试问题一样,要搜索那些atime超过一年前的文件,我们可以编写以下命令:
find . -type f -atime +365
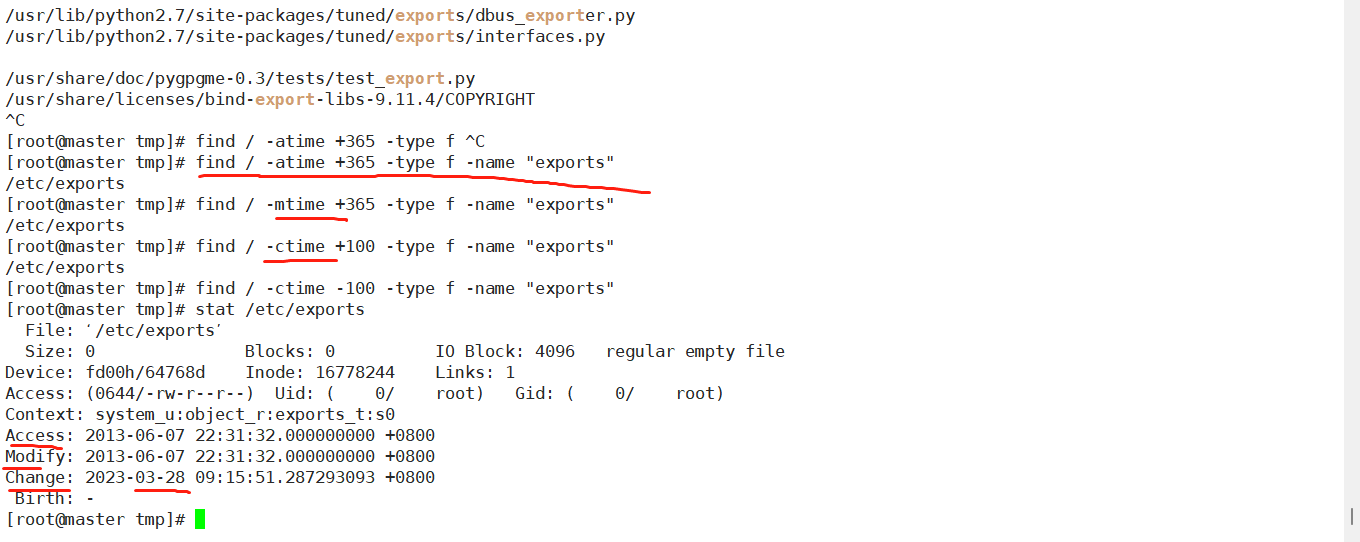
如果我们需要找到 mtime 恰好是 5 天前的文件,请不要包含 + 号,因为它表示“大于”。刚好是5天
linuxmi@linuxmi:~$ find . -type f -mtime 5

显然,+号表示“大于”,-号表示“小于”。因此,我们可以搜索 ctime 在 5 到 10 天之间的文件:5-10天
linuxmi@linuxmi:~$ find . -type f -ctime +5 -ctime -10

[root@master ~]# find . -type f -atime -1 |wc -l
14
[root@master ~]# find . -type f -atime -2 |wc -l
15
4、按文件大小查找文件
-size选项使我们能够按特定大小查找文件。我们可以使用以下约定指定其计量单位:b:512字节块(默认)c:字节w:两字节单词k:千字节M:兆字节G:千兆字节
find . -type f -size +10M -size -1G5、按权限查找文件
适当控制文件的权限是Linux管理员的重要任务。find命令的-perm选项可以帮助我们按特定权限搜索文件:find . -type f -perm 7776、按文件所有者查找文件
这个任务很简单。我们只需要在-user选项中指定一个用户名。例如,以下命令将找到所有属于 linuxmi 的文件:find -type f -user linuxmi7、在查找文件后执行命令
在大多数情况下,我们希望在找到所需文件后执行一些后续操作,例如删除它们、检查它们的详细信息等等。-exec命令使所有这些操作变得更加简单。现在,为了理解如何使用它,让我们回到之前提到的面试问题:find . -type f -atime +365 -exec rm -rf {} ;find . -type f -atime +5 -exec ls {} ;find . -type f -atime +5 -exec ls ;总结
阅读完find命令的7个用途后,之前提到的面试问题现在看起来非常简单了。现在你能直接写出答案并清楚地解释吗?find . -type f -atime 1 -exec ls {} \;
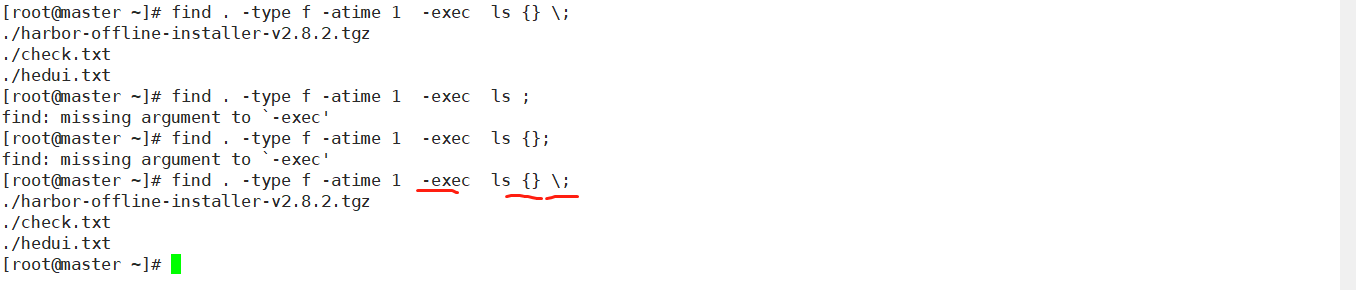
find . -type f -atime +365 -exec rm -rf {};【Linux250个常用命令速查手册】关注【入门小站】,后台回复 「1001」 自取。
http://u6.gg/kq67b
查命令绝对路径:
which 用于查找并显示给定命令的绝对路径, 环境变量中 PATH 参数也可以被查出来。
[root@localhost ~]# which bash
/usr/bin/bash
[root@localhost ~]# which ls
alias ls='ls --color=auto'
/usr/bin/ls
寻找特定文件:
whereis 命令用来定位指令的二进制程序、源代码文件和 man 手册页等相关文件的路径, 该命令只能用于程序名的搜索
[root@localhost ~]# whereis --help
语法格式:[ whereis [选项] 文件名 ]
-b #只找二进制文件
-m #只找man文档
-s #只找源代码
使用 whereis -b 命令找二进制文件,与帮助手册。
[root@localhost ~]# whereis -b ifconfig
ifconfig: /usr/sbin/ifconfig
[root@localhost ~]# whereis -m ifconfig
ifconfig: /usr/share/man/man8/ifconfig.8.gz
缓存查找文件:
locate 搜索一个数据库 / var/lib/mlocatedb, 这个数据库中含有本地所有文件信息, Linux 系统自动创建这个数据库, 并且每天自动更新一次, 所以使用 locate 命令查不到最新变动过的文件, 为了避免这种情况, 可以在使用 locate 之前, 先使用 updatedb 命令, 手动更新数据库, updatedb 命令会根据 / etc/updatedb.conf 来更新文件.
[root@localhost ~]# yum install -y mlocate
[root@localhost ~]# locate --help
语法格式:[ locate [选项] 文件名 ]
-d 目录 #指定数据库所在的目录
-i #忽略大小写差异
-r #后面接正则表达式
使用 locate 命令查询一个文件.
[root@localhost ~]# updatedb
[root@localhost ~]# locate /etc/passwd
/etc/passwd
/etc/passwd-
遍历文件查找:
find 命令可以说是最重要的查找命令了,该命令参数较多。
[root@localhost ~]# find --help
语法格式:[ find [目录] [属性] 文件名 ]
-name #按文件名查找
-size #根据大小查找
-user #根据属主查找
-perm #根据权限查找
-type #根据类型查找
-time #按时间查找
-inum #根据i节点查询
-exec #查找后执行命令
-name 按文件名查找:
常用查询通配符
\* #匹配任意一个或多个字符
? #匹配任意一个字符
[] #指定范围,外侧加引号
查找 / var / 目录下, 以. log 结尾的文件.
[root@localhost ~]# find /var/ -name "*.log"
/var/log/tuned/tuned.log
/var/log/audit/audit.log
/var/log/anaconda/X.log
/var/log/anaconda/program.log
....省略....
查找 / root / 目录下, 以 [1-3 之间], 结尾是. txt 的文件
[root@localhost ~]# ls
1.txt 2.txt 3.txt Catalog File
[root@localhost ~]# find /root/ -name "[1-3].txt"
/root/1.txt
/root/2.txt
/root/3.txt
查找 / etc / 目录下, 开头是 6 个任意字符的文件
[root@localhost ~]# find /etc/ -name "??????"
/etc/grub.d
/etc/grub.d/README
/etc/shells
/etc/init.d
....省略....
-size 根据大小查找
单位是 block 数据块 一块是512字节
1M -> 1024k -> 2048 块 (1块是0.5k 也就是512字节)
100M -> 102400k -> 204800块
查找 / etc / 目录下, 小于 10k 的文件
root@localhost ~]# find /etc/ -size -10k
/etc/crypttab
/etc/.pwd.lock
/etc/environment
....省略....
查找 / etc / 目录下, 大于 1M 的文件
[root@localhost ~]# find /etc/ -size +1M #查询大于1M的文件
/etc/udev/hwdb.bin
/etc/selinux/targeted/active/policy.kern
/etc/selinux/targeted/contexts/files/file_contexts.bin
/etc/selinux/targeted/policy/policy.31
....省略....
#注意:+-号如果没有,是精确到这么大,通常都会带上+或-号表示一个范围.公众号:入门小站
-user 根据属主与权限查找
在 / root 目录中查找属于 wang 用户的文件
[root@localhost ~]# find /root/ -user wang
/root/1.txt
/root/2.txt
/root/3.txt
#注意:系统中要存在该用户,否则会报错误.
查找 / boot / 目录中权限是 644 的文件
[root@localhost ~]# find /boot/ -perm 0644
/boot/grub2/device.map
/boot/grub2/i386-pc/gcry_rmd160.mod
/boot/grub2/i386-pc/acpi.mod
/boot/grub2/i386-pc/gcry_rsa.mod
....省略....
-type 根据类型查找
-type f 二进制文件(普通文件)
-type l 软链接文件
-type d 目录
查找 / usr/bin / 目录下, 类型是二进制文件.
[root@localhost ~]# find /usr/bin/ -type f
/usr/bin/cp
/usr/bin/gzip
/usr/bin/alias
/usr/bin/csplit
/usr/bin/bash
....省略....
-time 按时间查找
按天数 ctime atime mtime
按分钟 cmin amin mmin
c change #表示属性被修改过:所有者、所属组、权限
a access #被访问过(被查看过)
m modify #表示内容被修改过
查找 / etc / 目录下, 在 120 分钟以内, 内容被修改过的文件
[root@localhost ~]# find /etc/ -mmin -120
/etc/
/etc/resolv.conf
/etc/group-
/etc/gshadow-
/etc/group
/etc/gshadow
....省略....
查找 / etc / 目录下, 在 7 天之前, 属性被修改过的文件
[root@localhost ~]# find /etc/ -ctime +7
/etc/resolv.conf
/etc/group-
/etc/gshadow-
....省略....
-inum 根据 i 节点查询
有一些文件的硬链接数量很多,有相同的 i 节点,查找其中一个文件的 i 节点号,一次性删除。
[root@localhost ~]# find ./ -inum 1024 -exec rm{} \; #删除相同I节点的数据
-and or 逻辑连接符
-a (and 逻辑与)
-o (or 逻辑或)
在 / etc / 目录下, 查找大于 1k, 并且小于 10k 的文件
[root@localhost ~]# find /etc/ -size +1k -a -size -10k
/etc/
/etc/grub.d/00_header
/etc/grub.d/20_ppc_terminfo
/etc/grub.d/00_tuned
/etc/rc.d/init.d/README
/etc/rc.d/init.d/netconsole
/etc/rc.d/init.d/network
/etc/pam.d
....省略....
-exec 命令执行连接符
[查询格式] find ... -exec 命令 {} \;
{} #表示find查询的结果集
\ #是转义符,不使用命令别名,直接使用命令本身
; #分号是表示语句的结束.
#注意:固定格式,只能这样写.注意中间的空格.
(公众号:入门小站)-----------------------------------------------------------------
说明: 转义符的作用是什么?
在linux中有一个别名机制,如rm删除文件,执行的却是rm -i(用which rm 可以查看命令别名),
使用rm删除文件前会提示,就是因为rm -i这个参数。如果想使用命令原意,可以在加\转义,
如:\rm test.txt 则不会提示,直接删除
查找 / var/log / 目录下名字以. log 结尾的文件, 找到后执行 ls -l 显示详细信息. 公众号:入门小站
[root@localhost ~]# find /var/log/ *.log -exec ls -l {} \;
total 1176
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 204 Sep 18 09:12 anaconda
drwx------. 2 root root 23 Sep 18 09:12 audit
-rw-------. 1 root root 53001 Sep 19 00:57 boot.log
-rw-------. 1 root utmp 384 Sep 18 09:22 btmp
drwxr-xr-x. 2 chrony chrony 6 Apr 12 13:37 chrony
-rw-------. 1 root root 3523 Sep 19 01:01 cron
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 119414 Sep 19 00:57 dmesg
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 119599 Sep 18 23:35 dmesg.old
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1320 Sep 19 00:23 firewalld
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 193 Sep 18 09:05 grubby_prune_debug
....
查找 / etc / 目录下名字以 "init*" 开头的文件, 找到后, 只列出文件, 过滤掉目录, 并执行 ls -l 显示详细信息.
[root@localhost ~]# find /etc/ -name "init*" -a -type f -exec ls -l {} \;
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 511 Apr 11 01:09 /etc/inittab
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 798 Apr 11 01:09 /etc/sysconfig/init
-rwxr-xr-x. 1 root root 5419 Jan 2 2018 /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/init.ipv6-global
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 30 Apr 11 14:12 /etc/selinux/targeted/contexts/initrc_context
查找 / tmp / 下, 的 yum.log 文件, 找到后直接删除.
[root@localhost tmp]# find /tmp/ -name yum.log -exec rm {} \;
[root@localhost tmp]#
查找根下, 找关于 lyshark 用户的所有文件, 找到后直接删除.
[root@localhost ~]# find / -user lyshark -exec rm -r {} \;
find: ‘/proc/1465/task/1465/fd/6’: No such file or directory
find: ‘/proc/1465/task/1465/fdinfo/6’: No such file or directory
find: ‘/proc/1465/fd/5’: No such file or directory
find: ‘/proc/1465/fdinfo/5’: No such file or directory
find: ‘/root/Catalog’: No such file or directory
find: ‘/home/lyshark’: No such file or directory
#rm -r 连带目录一起删除.报错原因:-exec 不适合大量传输,速率慢导致.
在根下, 查找 lyshark 用户的文件, 找到后删除, 删除前会提示是否删除.
[root@localhost ~]# find / -user lyshark -ok rm -r {} \;
find: ‘/proc/1777/task/1777/fd/6’: No such file or directory
find: ‘/proc/1777/task/1777/fdinfo/6’: No such file or directory
< rm ... /root/LyShark > ? y
# -ok的使用和-exec是一样的,区别是-ok,执行时会提示你是否进行下一步操作.
【Linux250个常用命令速查手册】关注【入门小站】,后台回复 「1001」 自取。





