使用DQN 来优化车间排产JSP探索
首先感谢莫烦大神的python 强化学习的教程让我能快速了解强化学习
自从几年前从事智能工厂建设工作,对于APS 听到最多的就是APS 上线失败的案例。让自己开始思考APS上线的难度到底在哪里?
可能主要原因是APS 动态性问题待解决,信息化孤岛的问题。动态性主要是客户订单变化、现场生产干预排产等等 这些问题有机会再深入研究下。所以自己最近一直在想计划排产的算法的问题。
算法问题如果通过寻找排产规则我相信这个问题还是没有彻底解决,这个方法毕竟是静态的。因为环境一直在变化不可能规则一成不变。强化学习给了一个解决问题的思路,所以开始尝试在网上找了一篇通过q_learning 方式来解决。
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qianyushenlan/article/details/130303987
我使用了DQN DeepQNetwork 网络来在q_learning基础上导入DQN试了下,感觉还不错
import numpy as np import pandas as pd import tensorflow as tf np.random.seed(1) tf.random.set_seed(1) class DeepQNetwork: def __init__(self, n_actions, n_features, learning_rate=0.01, reward_decay=0.9, e_greedy=0.9, replace_target_iter=300, memory_size=500, batch_size=32, e_greedy_increment=None, output_graph=False, ): self.n_actions=n_actions self.n_features=n_features self.lr=learning_rate self.gamma=reward_decay self.epsilon_max=e_greedy self.replace_target_iter=replace_target_iter self.memory_size=memory_size self.batch_size=batch_size self.epsilon_increment=e_greedy_increment self.epsilon=0 if e_greedy_increment is not None else self.epsilon_max self.learn_step_counter=0 # [s,a,r,s_] self.memory=np.zeros((self.memory_size,n_features*2+2)) self._build_net() t_params=tf.compat.v1.get_collection('target_net_params') e_params=tf.compat.v1.get_collection('eval_net_params') self.replace_target_op=[tf.compat.v1.assign(t,e) for t,e in zip(t_params,e_params)] self.sess=tf.compat.v1.Session() if output_graph: tf.compat.v1.summary.FileWriter("logs/",self.sess.graph) self.sess.run(tf.compat.v1.global_variables_initializer()) self.cost_his=[] def _build_net(self): tf.compat.v1.disable_eager_execution() self.s=tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,self.n_features],name='s') self.q_target=tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,self.n_actions],name='Q_target') with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope('eval_net'): c_names,n_l1,w_initializer,b_initializer=\ ['eval_net_params',tf.compat.v1.GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLES],10,\ tf.random_normal_initializer(0.,0.3),tf.constant_initializer(0.1) with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope('l1'): w1= tf.compat.v1.get_variable('w1',[self.n_features,n_l1],initializer=w_initializer,collections=c_names) b1=tf.compat.v1.get_variable('b1',[1,n_l1],initializer=b_initializer,collections=c_names) l1=tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(self.s,w1)+b1) with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope('l2'): w2=tf.compat.v1.get_variable('w2',[n_l1,self.n_actions],initializer=w_initializer,collections=c_names) b2=tf.compat.v1.get_variable('b2',[1,self.n_actions],initializer=b_initializer,collections=c_names) self.q_eval=tf.matmul(l1,w2)+b2 with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope('loss'): self.loss=tf.reduce_mean(tf.compat.v1.squared_difference(self.q_target,self.q_eval)) with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope('train'): self.train_op=tf.compat.v1.train.RMSPropOptimizer(self.lr).minimize(self.loss) self.s_=tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,self.n_features],name='s_') with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope('target_net'): # c_names(collections_names) are the collections to store variables c_names = ['target_net_params', tf.compat.v1.GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLES] # first layer. collections is used later when assign to target net with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope('l1'): w1 = tf.compat.v1.get_variable('w1', [self.n_features, n_l1], initializer=w_initializer, collections=c_names) b1 = tf.compat.v1.get_variable('b1', [1, n_l1], initializer=b_initializer, collections=c_names) l1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(self.s_, w1) + b1) # second layer. collections is used later when assign to target net with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope('l2'): w2 = tf.compat.v1.get_variable('w2', [n_l1, self.n_actions], initializer=w_initializer, collections=c_names) b2 = tf.compat.v1.get_variable('b2', [1, self.n_actions], initializer=b_initializer, collections=c_names) self.q_next = tf.matmul(l1, w2) + b2 def store_transition(self,s,a,r,s_): if not hasattr(self,'memory_counter'): self.memory_counter=0 transition=np.hstack((s,[a,r],s_)) index=self.memory_counter%self.memory_size self.memory[index,:]=transition self.memory_counter+=1 def choose_action(self,observation): observation=np.array(observation)[np.newaxis,:] if np.random.uniform()<self.epsilon: actions_value=self.sess.run(self.q_eval,feed_dict={self.s:observation}) action=np.argmax(actions_value) else: action=np.random.randint(0,self.n_actions) return action def learn(self): if self.learn_step_counter % self.replace_target_iter==0: self.sess.run(self.replace_target_op) print('\ntarget_params_replaced\n') if self.memory_counter > self.memory_size: sample_index=np.random.choice(self.memory_size,size=self.batch_size) else: sample_index=np.random.choice(self.memory_counter,size=self.batch_size) batch_memory=self.memory[sample_index,:] q_next,q_eval=self.sess.run( [self.q_next,self.q_eval], feed_dict={ self.s_:batch_memory[:,-self.n_features:],# fixed params self.s:batch_memory[:,:self.n_features], #newest params } ) q_target=q_eval.copy() batch_index=np.arange(self.batch_size,dtype=np.int32) eval_act_index=batch_memory[:,self.n_features].astype(int) reward=batch_memory[:,self.n_features+1] q_target[batch_index,eval_act_index]=reward+self.gamma*np.max(q_next,axis=1) _,self.cost=self.sess.run([self.train_op,self.loss], feed_dict={self.s:batch_memory[:,:self.n_features], self.q_target:q_target}) self.cost_his.append(self.cost) self.epsilon=self.epsilon+self.epsilon_increment if self.epsilon < self.epsilon_max else self.epsilon_max self.learn_step_counter+=1 def plot_cost(self): import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.plot(np.arange(len(self.cost_his)), self.cost_his) plt.ylabel('Cost') plt.xlabel('training steps') plt.show()
DQN_JSP.py
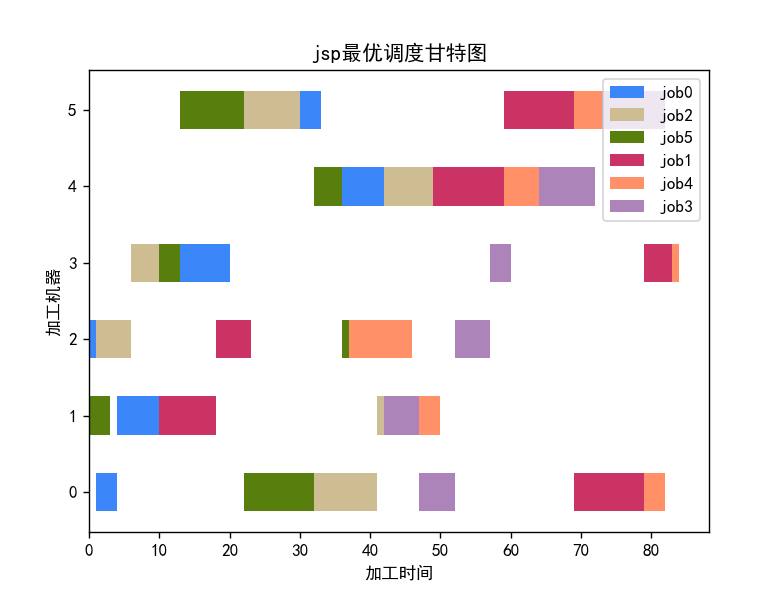
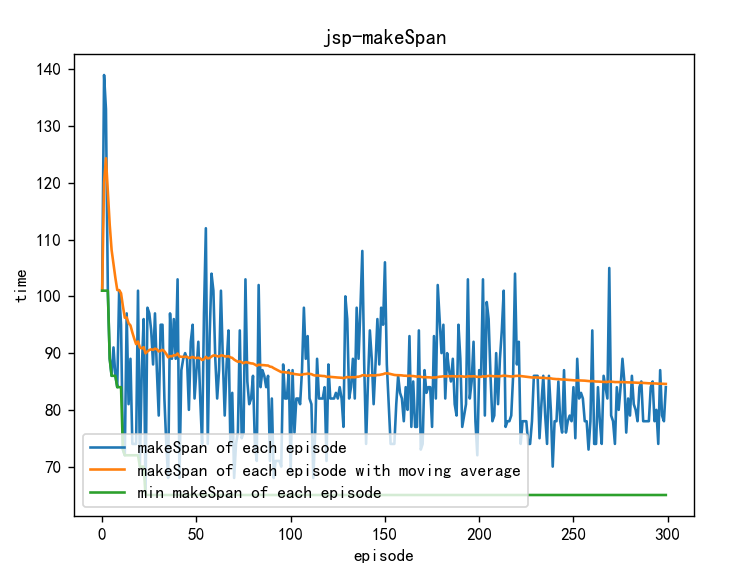
import numpy as np from DQN import DeepQNetwork from JSP import JspEnv import copy import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from draw_gantt import GanttChart from data_extract import load_txt _,_,PT,Ma=load_txt("./lft06.txt"," ") gantt_chart=GanttChart(PT,Ma) env = JspEnv(PT, Ma) State_init, State_term = env.state_initial() dimension = copy.copy(env.O_num) # 各工件工序数集 for i in range(env.J_num): dimension[i] += 1 # +1 是考虑S_next的时候会越界 dimension.append(env.J_num) episode_num = 300 C_plot = [] C_mean = [] min_C = [] RL = DeepQNetwork(env.J_num,len(Ma), learning_rate=0.01, reward_decay=0.9, e_greedy=0.9, replace_target_iter=200, memory_size=2000, output_graph=True ) step=0 for e in range(episode_num): observation=State_init #初始化s O_list=[] C=[] env.reset() start_list=[] while True: reward=0 # RL choose action based on observation action = RL.choose_action(observation) if O_list.count(action)<6: O_list.append(action) O_sum=O_list.count(action) if O_sum==1: Start=env.C_m[Ma[action][O_sum-1]-1] else: Start=max(env.C_m[Ma[action][O_sum-1]-1],env.C_J[action][O_sum-2]) start_list.append(Start) C.append(env.scheduling(Start,action,O_sum-1)) observation_=copy.copy(observation) if observation_[action]<6: observation_[action]+=1 if len(C) > 1 and C[-1] - C[-2] > 0: # C[-1] - C[-2] > 0 最后一个最大完工时间比倒数第二个大,得到的奖励少 reward = 1 / (C[-1] - C[-2]) else: reward = 10 else: reward=0 # RL take action and get next observation and reward #observation_, reward, done = env.step(action) RL.store_transition(observation, action, reward, observation_) if (step > 200) and (step % 5 == 0): RL.learn() # swap observation observation = observation_ # break while loop when end of this episode if observation==State_term: break step += 1 if e==episode_num-1: plt.figure(1) C_J=env.C_J print("工件顺序列表:", O_list) # 工件顺序列表 print("各工序完工时间:", C_J) # 各工序完工时间 print("开始时间列表:", start_list) gantt_chart.draw_gantt(start_list, O_list, C_J) if e % 100 == 0: print("episode: {}/{}".format(episode_num, e)) C_plot.append(C[-1]) C_mean.append(np.mean(C_plot)) min_C.append(np.min(C_plot)) plt.figure(2) plt.plot(C_plot[:], label="makeSpan of each episode") plt.plot(C_mean[:], label="makeSpan of each episode with moving average") plt.plot(min_C[:], label="min makeSpan of each episode") plt.legend(loc="lower left") plt.title('jsp-makeSpan') plt.xlabel('episode') plt.ylabel('time') plt.show()
跑了下效果: