对第二次—文献摘要热词统计及进阶需求
格式描述
- 课程名称: 软件工程实践
- 作业要求: 结对第二次—文献摘要热词统计及进阶需求
- 结对学号: 221600412 | 221600411
- Fork同名仓库的GitHub项目地址: GitHub地址
- GitHub代码签入记录:
作业开发过程
- 团队分工
- 221600411工作
- 需求分析
- 代码开发(单元测试、微信小程序)
- 代码测试
- 博客撰写
- 设计函数流程图
- 设计类图极其关系
- 辅助开发
- 独立完成附加小程序的编码工作
- 221600412工作
- 需求讨论
- 代码编写
- 基本需求和进阶需求的功能实现
- 代码测试
- 博客撰写
- 代码压力测试
- 代码优化
- 附加题的数据分析与制图
- 221600411工作
- 效能分析和PSP
PSP是卡耐基梅隆大学(CMU)的专家们针对软件工程师所提出的一套模型:Personal Software Process (PSP, 个人开发流程,或称个体软件过程)。
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 0 | 0 |
| Estimate | 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 900 | 1600 |
| Development | 开发 | 350 | 500 |
| Analysis | 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 60 | 230 |
| Design Spec | 生成设计文档 | 10 | 60 |
| Design Review | 设计复审 | 10 | 10 |
| Coding Standard | 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | 20 | 30 |
| Design | 具体设计 | 20 | 20 |
| Coding | 具体编码 | 270 | 450 |
| Code Review | 代码复审 | 10 | 20 |
| Test | 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 40 | 60 |
| Reporting | 报告 | 60 | 120 |
| Test Report | 测试报告 | 20 | 40 |
| Size Measurement | 计算工作量 | 10 | 20 |
| Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 20 | 40 |
| 合计 | 900 | 1600 | |
解题思路
-
需求分析
- 首先大概阅读整个作业文档,大致了解这次作业的主要任务。
- 将整个作业根据要求分成基础和进阶,首先考虑完成基础部分。两人共同对作业文档的基础作业部分进行精细阅读,归纳出每部分的要求,便于后续的功能设计
- 对于作业文档中感觉有争议的要求或理解,去群里寻找助教的热情解答,私下与班级同学共同探讨对这个争议的理解,结合百度查阅相关的资料
-
代码实现与测试
- 对分析后的功能要求点,对代码开发进行初步的设计(比如包的设计,团队两人约定同意的代码规范等),便于后续对代码的管理
- 按照对代码的设计进行代码开发,开发过程中碰到某个知识点忘记了,就进行百度查找答案
- 每开发一个功能就进行该功能的测试,防止后续测试寻找bug的工作量太大
- 基本功能实现后,进行各类数据和各项指标的测试
- 对代码进行复查,补上开发过程漏掉的注释等,方便后期的维护
代码设计过程
-
基本需求
- 项目结构
221600412&221600411
|- src
|- Main.java(主程序,可以从命令行接收参数)
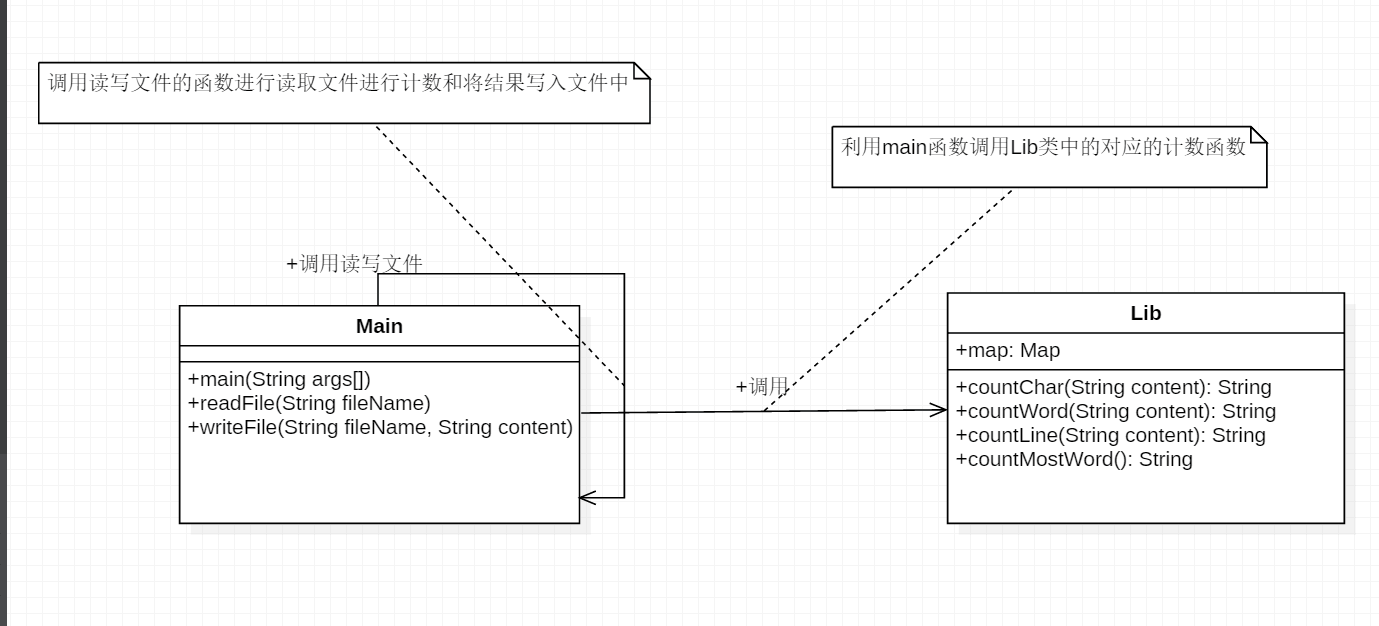
|- lib.java(包含其它自定义函数,可以有多个) - 函数关系与流程:
- 主要有两个类 Main.java 和 Lib.java 为了方便维护和修改 函数拆成四个 主要函数countChar,countWord,countLine,countMostWord,分别为计算字符数,单词数,行数,和输出词频,通过主函数依次调用countChar,countWord,countLine,countMostWord去进行计算并输出
- 项目结构
-
进阶需求:
- 项目结构
- 221600412&221600411
|- src
|- Main.java(主程序,可以从命令行接收参数)
|- lib.java(包含其它自定义函数,可以有多个)
|- Main.class(编译生成的可运行程序)
|- lib.class(编译生成的可运行程序)
|- cvpr
|- result.txt(爬虫结果)
|- Main.java - 爬虫使用工具 :Java
- 爬虫思路:首先进入CVPR官网对html文档进行分析发现每篇论文都在的div.class="ptitle"中,所以程序先class选择器(getElementByClass("ptitle"))获取所有的div,接着使用元素选择器(select("a"))获取其中的a标签,最后分别用(attr("href")),和(text())获取href和文本的值,把获取的链接和基础的url拼接成论文的访问地址,接着进入论文的详情页,ID选择器getElementById("abstract"),获取Div的id属性为abstract的元素并用text()获取对应摘要的文本内容,然后依照格式输出到指定的文件中。如下图
- 标题和链接部分

- 摘要部分

- 主要有两个类 Main.java 和 Lib.java,主函数接收命令行参数后,设置完变量并传递给Lib类,Lib类通过参数控制调用哪个函数。主要函数countWordOrWordGroupAndFrequency,countWord,countWordGroup,printCountMostWord,通过函数countWordOrWordGroupAndFrequency进行控制调用那个函数和输出
-
单元测试
- 每完成一项功能比如单词数的统计,然后根据作业文档尽可能设计各种可能出现的输入情况进行测试统计,尽量确保每项功能在开发完成后是没有bug存在
- 对总的输出进行测试并比对输出的数据格式
- 最后对要上传的代码,先删掉代码中的中文字符和一些无用代码注解 并用javac 和 java 进行编译运行确保程序在提交后能正确编译运行
- 单元测试图

-
代码组织与内部实现设计
- 基本需求类图
- 进阶需求类图
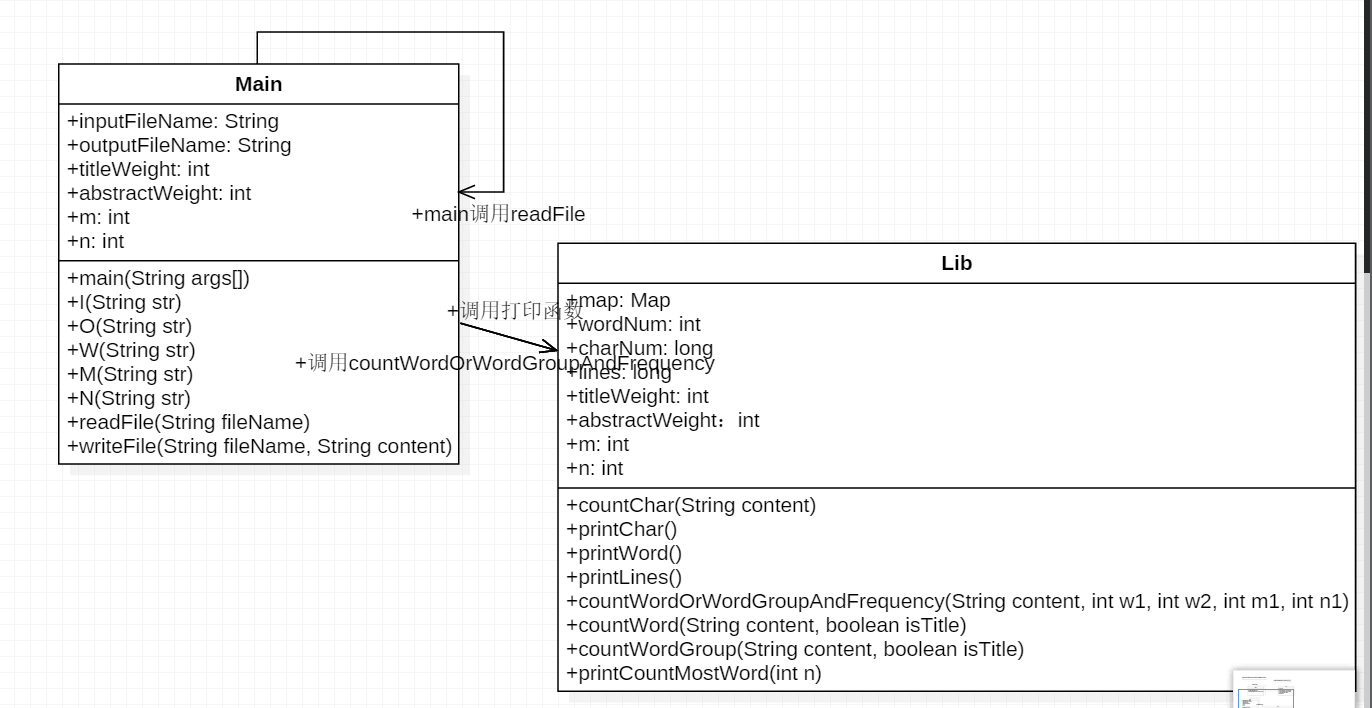
- 基本需求类图
-
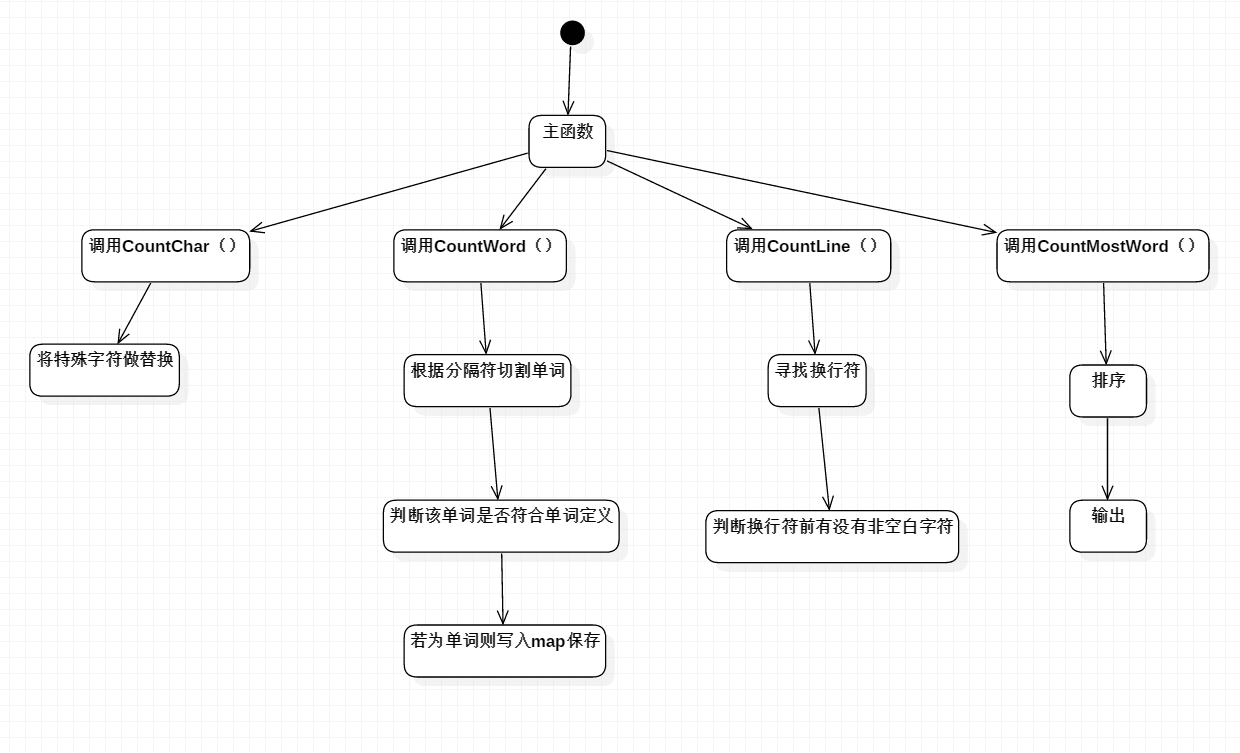
算法的关键与关键实现部分流程图
- 基本需求算法的关键主要是countChar,countWord,countLine,countMostWord
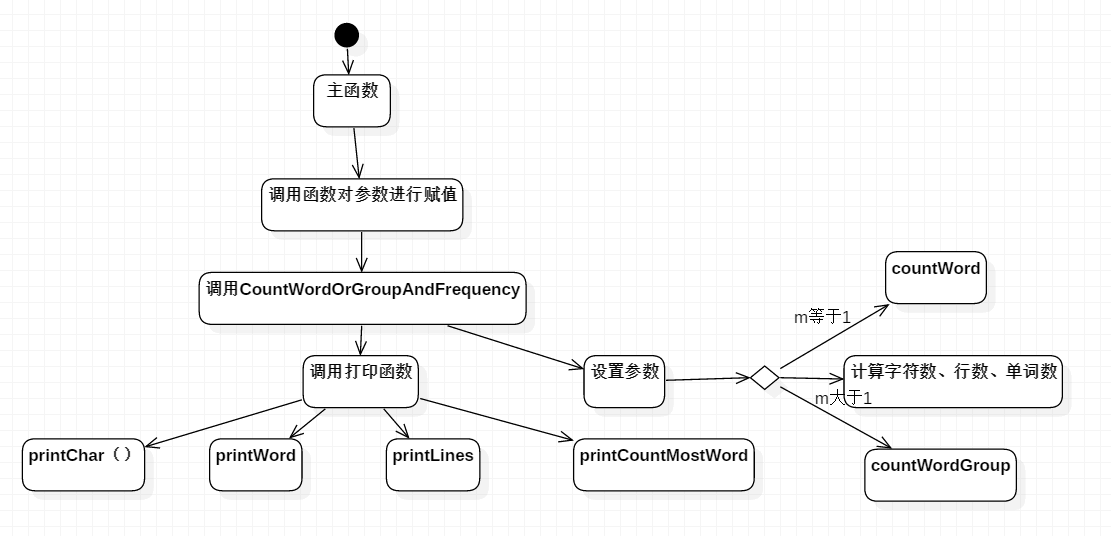
- 进阶需求算法的关键主要是countWordOrWordGroupAndFrequency,countWord,countWordGroup,printCountMostWord
- 具体算法思路在 下面的代码说明
- 基本需求流程图如下
- 进阶需求的流程图如下
改进程序性能
-
花费的时间:120分钟
-
改进思路 :
- 对文件的读取一开始分成计算char,word,line分成三个函数分别然后三个函数互相独立,计算的时候分别读取三次的文件IO,导致程序跑得慢,之后改进文件的读取次数,主函数从文件读取数据之后把数据存在内存中,然后在对内存中的数据进行操作,这样只进行了一遍IO操作,节省了两次IO。
- 把字符串切割成单词,首先是最简单的想法,直接double for 进行遍历把分割符位置全部标出来,并进行切割。改进后:用单重for循环进行遍历用标识符标识单词的首尾,接着进行切割单词并判断是否为题目所要求的单词。改进后的结构为O(n)
- 对于进阶需求,虽然把功能也才成三个函数,但在处理数据的时候,只进行一遍的处理,也就是程序只进行一次IO和一次for循环,时间复杂度达到O(n)。思路就是创建几个保存数据的字段,我的处理论文的方式,先把数据读入到内存中,之后对论文进行切分,切分后一篇论文包含,编号,标题,和摘要,之后对这些数据分开处理,同时计算字符,单词,行数,和词组,对每篇论文处理的结果和字段中的结果累加,达到了只对数据处理一遍就能完成计算。
-
性能分析图:
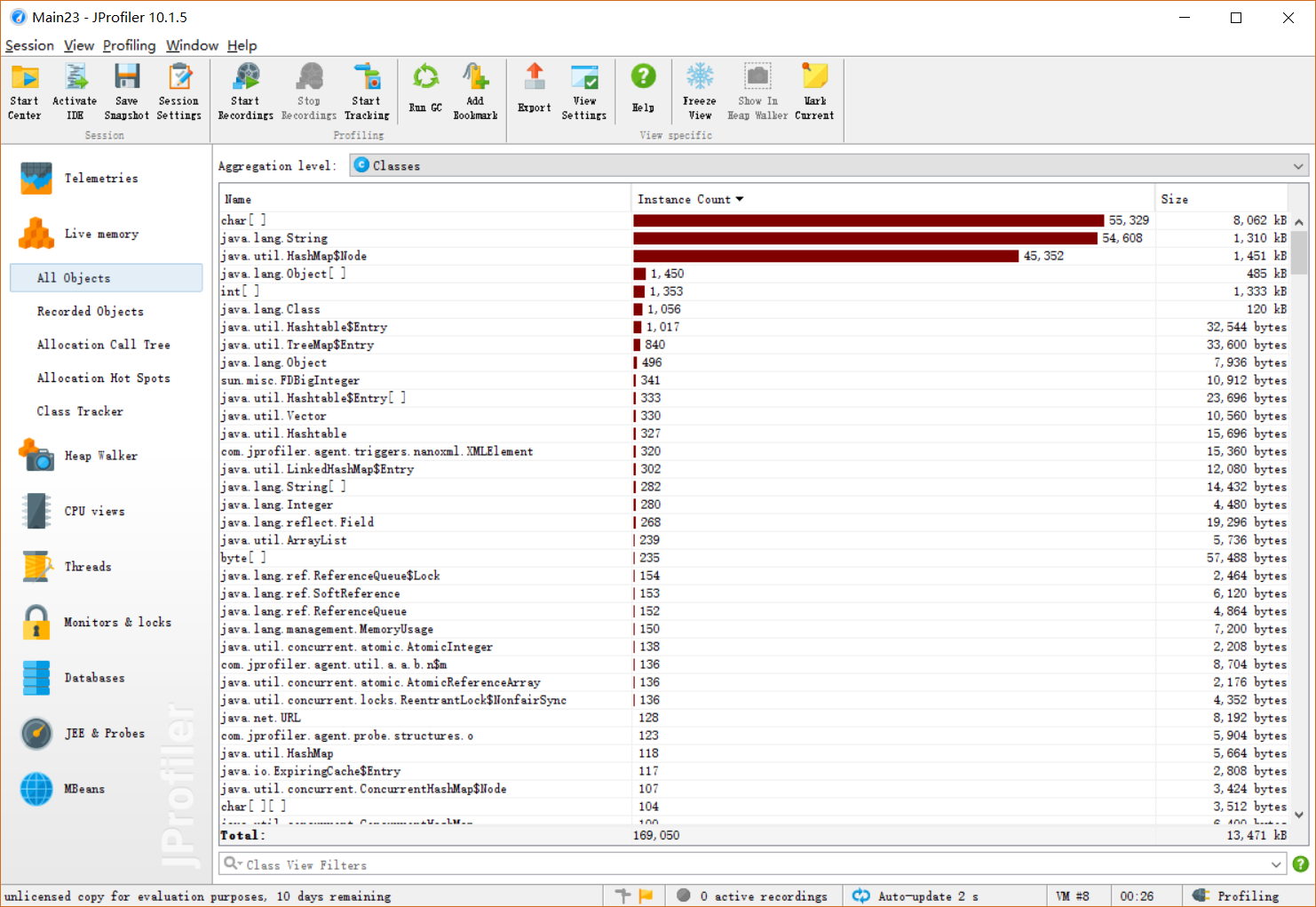
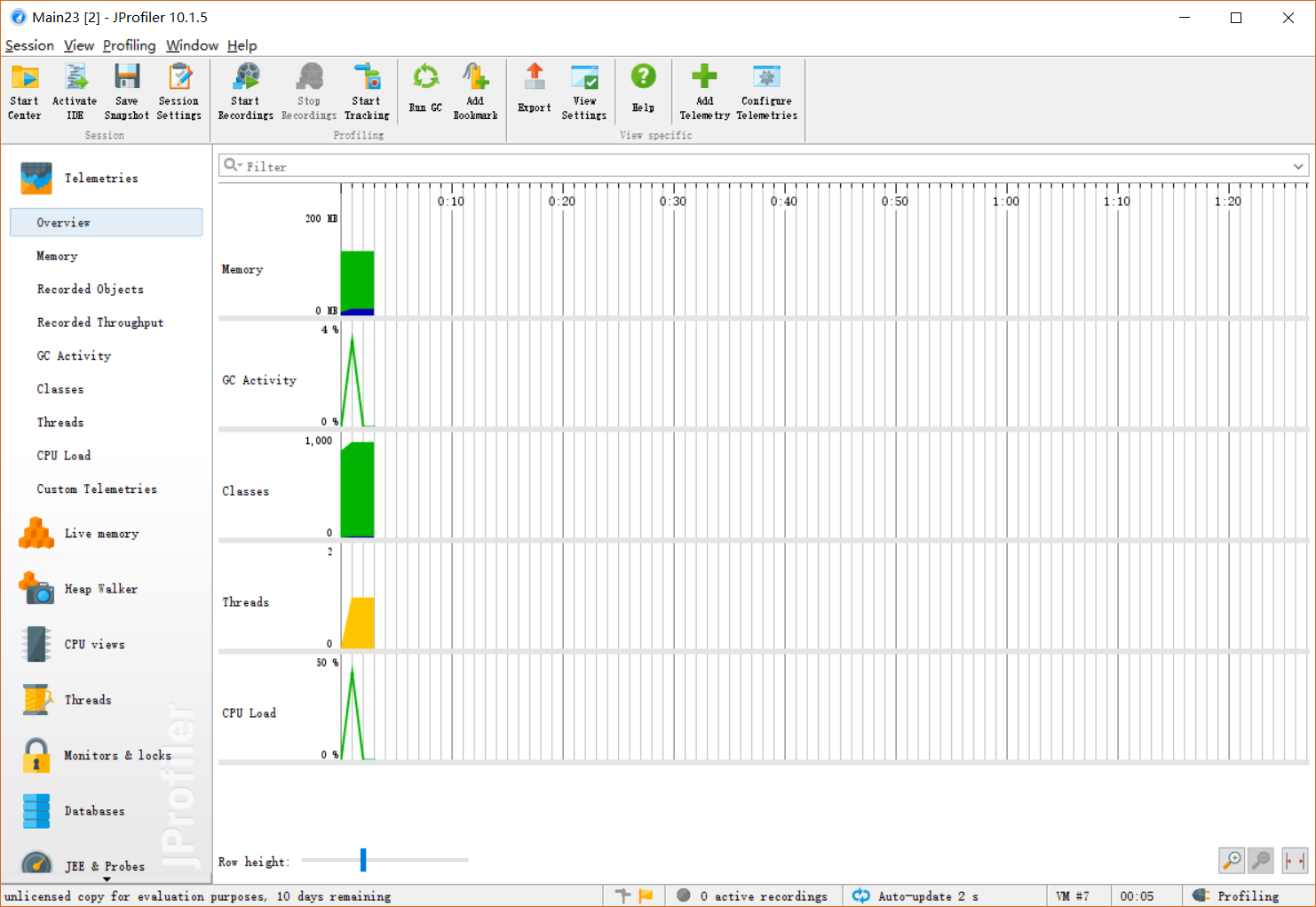
-
消耗最大的函数countWord()和 countGroupWord()
- 复杂度为均为 O(n) 都对数据进行一次遍历 得到计算结果
代码说明
- 基本需求
- 思路与说明:首先程序从命令行读取文件明,然后通过文件名对文件的内容进行读取到字符串中,然后分别对这个字符串进行countChar,countWord,countLine,countMostWord,分别为计算字符数,单词数,行数,和输出词频,通过主函数依次调用countChar,countWord,countLine,countMostWord去进行计算并输出
- 主函数流程,依此调用函数并输出到指定文件中
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
String content = readFile(args[0]);
Lib lib = new Lib();
String str1 = lib.countChar(content);
String str2 = lib.countWord(content);
String str3 = lib.countLine(content);
String str4 = lib.countMostWord();
writeFile("result.txt", str1 + "\r\n" + str2 + "\r\n" + str3 + "\r\n" + str4);
}
- countChar,对计算字符 一个特例 \r\n 这个原本ascii码为13,10算做两个字符,作业要求只算一个字符所以关键代码如下
public String countChar(String content) {
return "characters: " + content.replaceAll("\r\n", " ").toCharArray().length;
}
- countWord,对计算单词,通过单层for循环进行遍历,先找到两个分隔符,然后用函数substring切出单词并用toLowerCase全部转成小写,然后对这个单词判断是否为 题目需求定义的单词,是的话存放到Map中,不是的话继续循环。
public String countWord(String content) {
int wordNum = 0;
char[] ch = content.toCharArray();
int begin = 0, end = 0, len = content.toCharArray().length;
String str = null;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
boolean flag = !((ch[i] >= 65 && ch[i] <= 90) || (ch[i] >= 97 && ch[i] <= 122) || (ch[i] >= 48 && ch[i] <= 57));
if (flag || i == 0) { // If it is a delimiter or the beginning of the calculation
if (flag) {
begin = end = i + 1;
} else {
begin = end = i;
}
// Find two delimiters
while (end < len && ((ch[end] >= 65 && ch[end] <= 90) ||
(ch[end] >= 97 && ch[end] <= 122) || (ch[end] >= 48 && ch[end] <= 57))) {
end++;
}
if (begin != end) {
i = end - 1;
if (end - begin >= 4) {
str = content.substring(begin, end).toLowerCase();
boolean isWord = true;
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) { // If the first four are letters
if (str.charAt(j) >= 48 && str.charAt(j) <= 57) {
isWord = false;
break;
}
}
if (isWord) {
wordNum++;
if (map.containsKey(str)) {
map.put(str, map.get(str) + 1);
} else {
map.put(str, 1);
}
}
}
}
} else {
continue;
}
}
return "words: " + wordNum;
}
- 对于计算行数,通过循环先判断有没有非空白字符,有非空白字符的话进行标记,直到找到回车换行符然后,结束
public String countLine(String content) {
int len = content.toCharArray().length;
char[] ch = content.toCharArray();
int line = 0;
boolean flag = false;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
while (i + 1 < len) { // /r/n Text wrap skips calculations
if ((ch[i] == 13 && ch[i + 1] == 10)) {
break;
}
if ((ch[i] >= 0 && ch[i] <= 32) || ch[i] == 127) { // Is a blank character
i++;
continue;
} else {
i++;
flag = true;
}
}
if( i + 1 == len && ! ((ch[i] >= 0 && ch[i] <= 32) || ch[i] == 127)){
flag = true;
}
i = i + 1;
if (flag) {
line++;
flag = false;
}
}
return "lines: " + line;
}
- 输出词频,上面把所有的单词存放到map中,通过这个函数对mao进行排序之后输出
// Computing word frequency
public String countMostWord() {
// Sort the keys in the HashMap and display the sorted results
List<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> infoIds = new ArrayList<Map.Entry<String, Integer>>(map.entrySet());
// Sort the keys in the HashMap
Collections.sort(infoIds, new Comparator<Map.Entry<String, Integer>>() {
public int compare(Map.Entry<String, Integer> o1,
Map.Entry<String, Integer> o2) {
if (o1.getValue() == o2.getValue()) {
return o1.getKey().compareTo(o2.getKey());
}
return -(o1.getValue() - o2.getValue());
}
});
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
// The output frequency
for (int i = 0; i < infoIds.size() && i < 10; i++) {
sb.append("<" + infoIds.get(i).getKey() + ">: " + infoIds.get(i).getValue() + "\r\n");
}
return sb.toString();
}
- 进阶需求
- 思路与说明
- 爬虫思路在上面已提到
- 主函数通过接收命令行参数,并调用相对应的函数,对一些字段进行设置值,然后通过调用Lib类中的countWordOrWordGroupAndFrequency函数进行计算,最后输出到指定的文件中
- 思路与说明
public String inputFileName = null; // The file name to read
public String outputFileName = null; // The file name to output
public int titleWeight = 10; // title weight
public int abstractWeight = 1; // abstract weight
public int m = 1; // The length of the phrase
public int n = 10; // Output the number of words
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
Main instance = new Main();
for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) {
switch (args[i]) {
case "-i":
instance.I(args[i + 1]);
break;
case "-o":
instance.O(args[i + 1]);
break;
case "-w":
instance.W(args[i + 1]);
break;
case "-m":
instance.M(args[i + 1]);
break;
case "-n":
instance.N(args[i + 1]);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
String content = instance.readFile(instance.inputFileName);
Lib lib = new Lib();
lib.countWordOrWordGroupAndFrequency(content, instance.titleWeight, instance.abstractWeight, instance.m, instance.n); // 计算单词总数
String str1 = lib.printChar(); // calculate Number of characters
String str2 = lib.printWord(); // Count words
String str3 = lib.printLines(); // Calculate number of lines
String str4 = lib.printCountMostWord(instance.n);// Computing word frequency
instance.writeFile(instance.outputFileName,str1 + "\r\n" + str2 + "\r\n" + str3 + "\r\n" + str4);
}
public void I(String str) {
inputFileName = str;
}
public void O(String str) {
outputFileName = str;
}
public void W(String str) {
if (Integer.valueOf(str) == 0) {
titleWeight = abstractWeight = 1;
} else if (Integer.valueOf(str) == 1) {
titleWeight = 10;
abstractWeight = 1;
}
}
public void M(String str) {
m = Integer.valueOf(str);
}
public void N(String str) {
n = Integer.valueOf(str);
}
- countWordOrWordGroupAndFrequency接收一系列的参数( content, int w1, int w2, int m1, int n1),然后分别对content进行论文切分,通过论文之间的两个回车换行符把论文分开,对每篇论文也用回车换行进行切分,分成编号,标题和摘要。之后对标题和摘要分别进行统计,统计后存放在字段中,之后调用printChar,printWord,printLines,printCountMostWord输出到指定文件中
public void countWordOrWordGroupAndFrequency(String content, int w1, int w2, int m1, int n1) {
titleWeight = w1;
abstractWeight = w2;
m = m1;
n = n1;
boolean isWordGroup = false;
if (m >= 2) {
isWordGroup = true;
}
String[] attr = content.split("\r\n\r\n");
String[] str = null;
String t1 = null;
String t2 = null;
for (int i = 0; i < attr.length; i++) {
if (attr[i] != null && !attr[i].equals("")) {
if (i == 0) {
str = attr[i].split("\r\n");
} else {
str = attr[i].replaceFirst("\r\n", "").split("\r\n");
}
if (str.length == 3) {
t1 = str[1].substring(7);
t2 = str[2].substring(10);
lines += 2; // add line
charNum += 2; // add line
countChar(t1 + t2);
if (isWordGroup) {
countWordGroup(t1, true); // Calculate the title
countWordGroup(t2, false); // Calculated in this paper,
} else {
countWord(t1, true); // Calculate the title
countWord(t2, false); // Calculated in this paper
}
}
}
}
}
- countWord,countWordGroup 两个算法思路很相似,都是先进行切分单词,对于countWordGroup切分后的第一个单词标记起始位置如果连续m个都为单词,切出起始位置和末尾的位置,然后存到map中,存放的时候因为上面已经把title和摘要进行了分开计算所以在存放的时候,能知道当处理的是摘要还是标题,然后用正确的权重去加权,最后调用排序算法后输出。
public void countWordOrWordGroupAndFrequency(String content, int w1, int w2, int m1, int n1) {
titleWeight = w1;
abstractWeight = w2;
m = m1;
n = n1;
boolean isWordGroup = false;
if (m >= 2) {
isWordGroup = true;
}
String[] attr = content.split("\r\n\r\n");
String[] str = null;
String t1 = null;
String t2 = null;
for (int i = 0; i < attr.length; i++) {
if (attr[i] != null && !attr[i].equals("")) {
if (i == 0) {
str = attr[i].split("\r\n");
} else {
str = attr[i].replaceFirst("\r\n", "").split("\r\n");
}
if (str.length == 3) {
t1 = str[1].substring(7);
t2 = str[2].substring(10);
lines += 2; // add line
charNum += 2; // add line
countChar(t1 + t2);
if (isWordGroup) {
countWordGroup(t1, true); // Calculate the title
countWordGroup(t2, false); // Calculated in this paper,
} else {
countWord(t1, true); // Calculate the title
countWord(t2, false); // Calculated in this paper
}
}
}
}
}
// Count words
public void countWord(String content, boolean isTitle) {
char[] ch = content.toCharArray();
int begin = 0, end = 0, len = content.toCharArray().length;
String str = null;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
boolean flag = !((ch[i] >= 65 && ch[i] <= 90) || (ch[i] >= 97 && ch[i] <= 122) || (ch[i] >= 48 && ch[i] <= 57)); // 判断是否是分隔符
if (flag || i == 0) { // If it is a delimiter or the beginning of the calculation
if (flag) {
begin = end = i + 1;
} else {
begin = end = i;
}
// Find two delimiters
while (end < len && ((ch[end] >= 65 && ch[end] <= 90) ||
(ch[end] >= 97 && ch[end] <= 122) || (ch[end] >= 48 && ch[end] <= 57))) {
end++;
}
if (begin != end) {
i = end - 1;
if (end - begin >= 4) {
str = content.substring(begin, end).toLowerCase();
boolean isWord = true;
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) { // If the first four are letters
if (str.charAt(j) >= 48 && str.charAt(j) <= 57) {
isWord = false;
break;
}
}
if (isWord) {
wordNum++;
if (map.containsKey(str)) {
if (isTitle) {
map.put(str, map.get(str) + titleWeight);
} else {
map.put(str, map.get(str) + abstractWeight);
}
} else {
if (isTitle) {
map.put(str,titleWeight);
} else {
map.put(str,abstractWeight);
}
}
}
}
}
} else {
continue;
}
}
}
// Computing phrase
public void countWordGroup(String content, boolean isTitle) {
char[] ch = content.toCharArray();
int wordGroupBegin = 0, wordGroupEnd = 0;
int firstWordEnd = 0;
int begin = 0, end = 0, len = content.toCharArray().length;
String str = null;
int wordGroupNum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
boolean flag = !((ch[i] >= 65 && ch[i] <= 90) || (ch[i] >= 97 && ch[i] <= 122) || (ch[i] >= 48 && ch[i] <= 57)); // Determines if it is a delimiter
if (flag || i == 0) { // If it is a delimiter or the beginning of the calculation
if (flag) {
begin = end = i + 1;
} else {
begin = end = i;
}
// Find two delimiters
while (end < len && ((ch[end] >= 65 && ch[end] <= 90) ||
(ch[end] >= 97 && ch[end] <= 122) || (ch[end] >= 48 && ch[end] <= 57))) {
end++;
}
if (begin != end) {
i = end - 1;
if (end - begin < 4) {
wordGroupNum = 0;
}
if (end - begin >= 4) {
str = content.substring(begin, end).toLowerCase();
boolean isWord = true;
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) { // If the first four are letters
if (str.charAt(j) >= 48 && str.charAt(j) <= 57) {
isWord = false;
wordGroupNum = 0;
break;
}
}
if (isWord) {
wordNum++;
wordGroupNum++;
if (wordGroupNum == 1) {
wordGroupBegin = begin;
firstWordEnd = end;
}
if (wordGroupNum == m) {
wordGroupEnd = end;
str = content.substring(wordGroupBegin, wordGroupEnd).toLowerCase();
if (map.containsKey(str)) {
if (isTitle) {
map.put(str, map.get(str) + titleWeight);
} else {
map.put(str, map.get(str) + abstractWeight);
}
} else {
if (isTitle) {
map.put(str,titleWeight);
} else {
map.put(str,abstractWeight);
}
}
wordGroupNum = 0;
i = firstWordEnd - 1;
wordNum = wordNum - m +1 ;
}
} else {
wordGroupNum = 0;
}
}
}
} else {
continue;
}
}
}
单元测试代码
- 测试代码
@org.junit.Test
public void Test10() throws IOException {
String arg = "H:\\javaweb代码\\qqqqq\\src\\main\\java\\软工实践_test\\input.txt";
String content = readFile(arg);
Lib lib = new Lib();
String str1 = lib.countChar(content); // 计算 字符数
String str2 = lib.countWord(content); // 计算单词总数
String str3 = lib.countLine(content); // 计算行数
String str4 = lib.countMostWord();// 计算词频
String test1="characters: 99";
String test2="words: 20";
String test3="lines: 20";
String test4="<aaaa>: 4\n" +
"<bbbb>: 1\n" +
"<cccc>: 1\n" +
"<dddd>: 1\n" +
"<eeee>: 1\n" +
"<ffff>: 1\n" +
"<gggg>: 1\n" +
"<hhhh>: 1\n" +
"<iiii>: 1\n" +
"<jjjj>: 1\n";
Assert.assertEquals(str1,test1);
Assert.assertEquals(str2,test2);
Assert.assertEquals(str3,test3);
Assert.assertEquals(str4,test4);
}
- 部分测试数据
qq q qqq qqq.qqq
q www w www
结果
characters: 35
words: 0
lines: 2
a
b
c
d
结果
characters: 11
words: 0
lines: 4
abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz
1234567890
,./;'[]\<>?:"{}|`-=~!@#$%^&*()_+
结果
characters: 76
words: 1
lines: 3
<abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz>: 1
- 测试的思路与想法
- 测试的思路与想法主要在于对各种不满足条件的情形进行测试,特别是在临界条件,测试程序能否正确统计各种特殊情况
- 开头带有空格、tab的情形
- 整个文档只有空白字符的情形
- 对于单词的检查,根据要求设计各种不满足的情况,观察是否可以正确统计
- 针对空白字符,设计多种情况进行测试
- 对回车换行做独立的测试
- 对\r\n的特殊输入进行测试
- 对各类边界条件进行多次反复的测试
- 测试的思路与想法主要在于对各种不满足条件的情形进行测试,特别是在临界条件,测试程序能否正确统计各种特殊情况
困难及解决和评价队友
- 评价221600411
- 值得学习的地方:对作业一丝不苟,对程序的测试非常严谨,流程图和类图制作得很好
- 需要改进的地方:需要加强时间的管理,平衡好作业和其他的时间。
- 评价221600412
- 值得学习的地方:动手实践能力较强,独自完成了大部分的编码工作,尽自己最大的能力完成作业。
- 需要改进的地方:需平衡好时间的,加强理论的学习
- 所遇困难
- 需求理解花了许多时间去理解,有些需求理解错误导致程序多次变动
- 一些程序软件没有安装,比如性能测试工具
- 解决办法
- 查找助教的解答,与同学探讨
- 通过百度查阅相关资料进行安装和操作
附加题设计与展示
- 数据分析使用python 库
- 数据分析
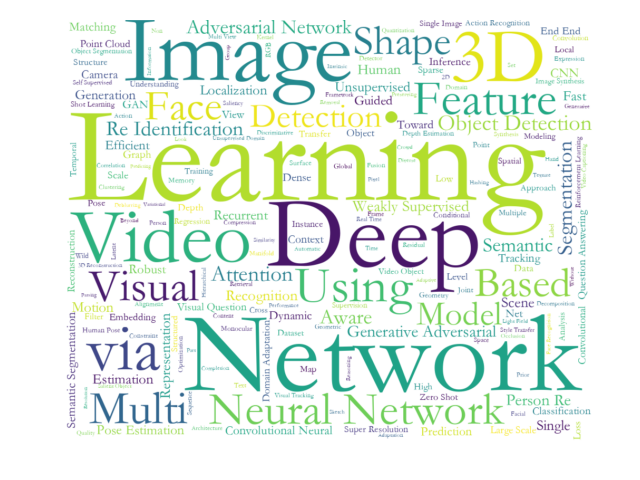
- 分别对标题和摘要进行了词频统计并输出成 词云
- 标题词云

- 摘要词云
- 下图为对作者发表论文的svg图显示前30位 链接 点击链接可以在网站上查看svg图下图只有静态效果
-
设计的创意
- 针对进阶要求所爬取的数据繁多,在控制台的查看较为费劲,便开发论文列表的界面,便于用户对爬取的论文进行浏览;考虑到提高用户的简便程度,决定使用微信小程序进行简单的界面显示
-
实现思路
- 后端使用java开发接口,将爬取的数据存取在数据库,通过接口与微信小程序对接,传递数据,实现论文列表的界面显示与浏览
-
实现成果的展示

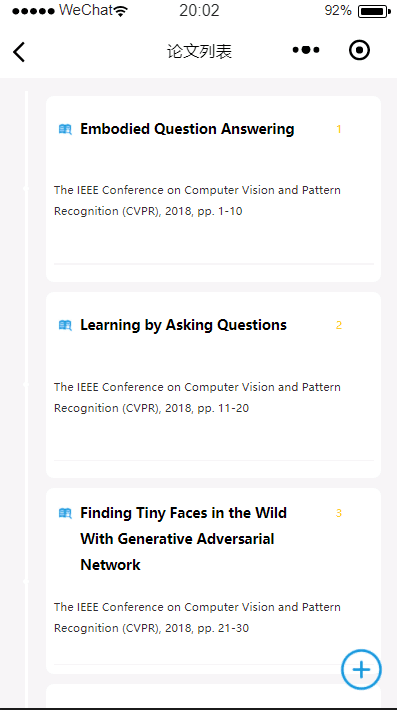

-
词频分析 代码下载
-
心得体会
陈迎仁
- 心得与总结
通过这次作业学会了许多除了编写代码外的知识,比如GitHub的上传,单元测试的含义,以及测试数据的设计,等各种非代码类的技能。当然在代码这方面也提升不少,主要在于测试阶段,设计各类流程图以及类图还有微信小程序的界面开发以及博客文档的撰写,辅助队友进行代码开发。通过这次团队作业,我进一步对团队协作有了深的理解,一个人完成代码开发以及测试真的工作量大,而且在对于测试,客观性不够强,团队配合测试,所使用的测试用例可能更加的全面以及更能够保证测试结果的正确性。总之在这次软工实践作业中,虽然花费的时间较多,但是也学到了许多新的技能。累但值得哈哈哈!
陈宇
- 心得与总结
这次作业的作业量虽然很大,但是通过这次作业我学到了很多东西,比如一个明确的需求有多重要,这个作业的需求研究了好几天,最后还是通过微信群里的同学进行了讨论,还有助教的回答。之后就是编码和测试,在编码的过程中,一开始对需求的不明确导致一直修改代码,后面等确定了需求后在写之后进度快了好多,编写完代码之后就和队友一起测试代码,调试代码,知道程序的运行的结果和周围队友的结果一致,虽然这次作业花了很多的时间,也学到了很多的东西,也学到了很多和团队配合的东西。


