「学习笔记」AC 自动机
一. 概述
AC 自动机是一种多模式匹配算法。
AC 自动机构建在 Trie 的结构基础上,结合了 Kmp 算法的失配指针思想。
在进行多模式串匹配前,只有两个步骤需要去实现:
\(1.\) 将所有模式串扔进一颗 Trie 中。
\(2.\) 对于 Trie 上的所有节点构建失配指针。
二.构建 Trie 树
只需要按照 Trie 树的基本构建方法搭建即可。
请注意,Trie 树节点的含义十分重要:
它表示的是某个模式串的前缀,也就是一个状态。
而 Trie 的边就是状态的转移。
对于概念理解不够透彻的同学可以看这里。
代码如下:
void insert (char *s) {
int slen = strlen (s), u = 0, c;
for (int i = 0; i < slen; i ++) {
c = s[i] - 'a';
if (!trie[u][c]) {//无节点就添加节点。
trie[u][c] = ++ tot;
}
u = trie[u][c];
}
tag[u] ++;
}
三.Fail 指针
这是 AC 自动机的核心。
什么是 Fail 指针呢?
如果一个 Trie 树上的节点 u 的 Fail 指针指向 节点 v,那么这就表示根节点到节点 v 的字符串是 根节点到节点 u 的字符串的一个后缀。
如下图:
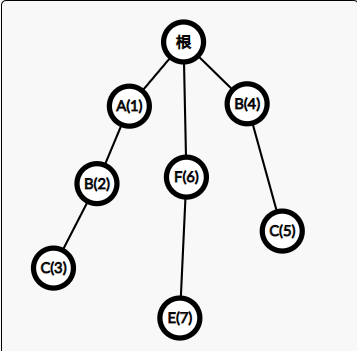
\(3\) 号节点的 Fail 指针就指向 \(5\) 号节点。
因为根节点到 \(3\) 号节点的字符串为 \(ABC\),
根节点到 \(5\) 号节点的字符串为 \(BC\),
由于 \(BC\) 是 \(ABC\) 的一个后缀,所以 \(3\) 号节点的 Fail 指针指向 \(5\) 号节点。
四.构建 Fail 指针
对于一个 Trie 树上的节点 u,设它的父节点为 v,两个节点通过字符 c 连接,也就是说 \(trie_{v,c} = u\)。
那么求 Fail 指针的有两个,如下:
\(1.\) 如果 \(trie_{fail_p,c}\) 不是空节点,那么就将节点 u 的 Fail 指针指向 \(trie_{fail_p,c}\)。
\(2.\) 如果 \(trie_{fail_p,c}\) 是空节点,那么继续向上寻找 \(trie_{fail_{fail_p}, c}\),继续重复第 \(1\) 个操作的判断。
注意:如果找寻到了根节点,那么就将节点 u 的 Fail 指针指向根节点。
代码如下:
queue<int> q;
inline void GetFail () {
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i ++) {
if (trie[0][i]) {//非空节点入队。
q.push (trie[0][i]);
}
}
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i ++) {
if (trie[u][i]) {
q.push (trie[u][i]);//非空节点入队。
fail[trie[u][i]] = trie[fail[u]][i];
}
else {
trie[u][i] = trie[fail[u]][i];
}
}
}
}
稍微对于代码做一个解释:
这里的 GetFail 函数将 Trie 树上所有节点按照 BFS 的顺序入队,最后依次求 Fail 指针。
首先我们单独处理根节点,代码中编号为 \(0\),将其非空的子节点入队。
然后每次取出队首处理 Fail 指针,遍历 \(26\) 个字符(根据题目判断)。
\(Fail_u\) 就表示节点 u 的 Fail 指针指向的节点。
五.查询出现个数
问题如下:
关于许多模式串,求有多少个模式串在文本串中出现。
根据 Fail 指针的定义,如果当前字符串匹配成功,那么它的 Fail 指针指向的字符串也可以成功匹配。
因为 Fail 指针指向的字符串与其后缀匹配。
这样就启发我们一直跳 Fail 指针,累计其答案。
代码如下:
int query (char *s) {
int slen = strlen (s), u = 0, res = 0, c;
for (int i = 0; i < slen; i ++) {
c = s[i] - 'a';
u = trie[u][c];
for (int j = u; j && ~tag[j]; j = fail[j]) {
res += tag[j];
tag[j] = -1;//标记,重复的不累计答案。
}
}
return res;
}
六.查询最大出现次数
给出若干个模式串和一个文本串,求某个模式串在文本串中出现的最大次数和该模式。
我们考虑如何查询最大出现次数。
由于会出现文本串中可能会出现多次模式串,所以将 \(tag\) 数组转化为存储该字符串的顺序,在统计答案时用一个 \(vis\) 数组存储出现的次数,取最大值。
然后遍历 \(vis\) 数组,当 \(vis_i\) 与最大值相同时,就输出第 \(i\) 个模式串。
多测记得清空。
代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 333333;
int n, vis[N];
struct AC_automaton {
int trie[N][26], fail[N], tag[N], tot = 0;
inline void Clear() {
memset (trie, 0, sizeof (trie));
memset (tag, 0, sizeof (tag));
memset (fail, 0, sizeof (fail));
memset (vis, 0, sizeof (vis));
tot = 0;
}
inline void Insert (char *s, int v) {
int slen = strlen (s), u = 0, c;
for (int i = 0; i < slen; i ++) {
c = s[i] - 'a';
if (!trie[u][c]) {
trie[u][c] = ++ tot;
}
u = trie[u][c];
}
tag[u] = v;
}
queue<int> q;
inline void GetFail () {
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i ++) {
if (trie[0][i]) {
q.push (trie[0][i]);
}
}
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i ++) {
if (trie[u][i]) {
q.push (trie[u][i]);
fail[trie[u][i]] = trie[fail[u]][i];
}
else {
trie[u][i] = trie[fail[u]][i];
}
}
}
}
inline int Query(char *s) {
int slen = strlen (s), u = 0, ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < slen; i ++) {
int c = s[i] - 'a';
u = trie[u][c];
for (int j = u; j; j = fail[j]) {
if (!tag[j]) {
//没有该节点,往下一个 Fail 指针跳。
continue;
}
vis[tag[j]] ++;
//统计出现次数。
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
ans = max (ans, vis[i]);
//取最大值。
}
return ans;
}
}AC;
char c[200][90];
char TXT[1919810];
int main() {
while (scanf ("%d", &n) && n != 0) {
AC.Clear();//多测清空!!!!!
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
scanf ("%s", c[i]);
AC.Insert (c[i], i);
}
AC.Build ();
scanf ("%s", TXT);
int mx = AC.Query (TXT);
printf ("%d\n", mx);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
if (vis[i] == mx) {
printf ("%s\n", c[i]);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
七.基础例题
这两道题就是以上模块的基本操作。
给定文本串和若干个模式串,求出有多少个不同的模式串在文本串中出现。
代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 5e5 + 7;
char a[N * 20];
int n;
struct AC_automaton {
int tag[N], trie[N][26], fail[N], tot;
void insert (char *s) {
int slen = strlen (s), u = 0, c;
for (int i = 0; i < slen; i ++) {
c = s[i] - 'a';
if (!trie[u][c]) {
trie[u][c] = ++ tot;
}
u = trie[u][c];
}
tag[u] ++;
}
queue<int> q;
void build () {
int u;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i ++) {
if (trie[0][i]) {
fail[trie[0][i]] = 0;
q.push (trie[0][i]);
}
}
while (!q.empty()) {
u = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i ++) {
if (trie[u][i]) {
fail[trie[u][i]] = trie[fail[u]][i];
q.push (trie[u][i]);
}
else {
trie[u][i] = trie[fail[u]][i];
}
}
}
}
int query (char *s) {
int slen = strlen (s), u = 0, res = 0, c;
for (int i = 0; i < slen; i ++) {
c = s[i] - 'a';
u = trie[u][c];
for (int j = u; j && ~tag[j]; j = fail[j]) {
res += tag[j];
tag[j] = -1;
}
}
return res;
}
}AC;
int main() {
scanf ("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
scanf ("%s", a);
AC.insert (a);
}
AC.build();
scanf ("%s", a);
int ans = AC.query(a);
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
首先,定义一个节点的权值为该节点属于的字符串个数。
那么,一个节点表示的字符串,在整个字典树中出现的次数就是子树的权值和。
代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1222222;
char c[N];
int n, ans[N], tot = 0;
struct AC_automaton {
int tag[N], trie[N][26], fail[N], q[N], siz[N];
//手写队列方便。
inline void Insert (char *s, int k) {
int slen = strlen (s), u = 0, c;
for (int i = 0; i < slen; i ++) {
c = s[i] - 'a';
if (!trie[u][c]) {
trie[u][c] = ++ tot;
}
u = trie[u][c];
siz[u] ++;
}
tag[k] = u;//记录第k个字符串的最后状态。
}
inline void GetFail () {
int head = 0, tail = 0, u = 0, c;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i ++) {
if (trie[0][i]) {
q[++ tail] = trie[0][i];
}
}
while (head < tail) {
u = q[++ head];
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i ++) {
if (trie[u][i]) {
q[++ tail] = trie[u][i];
fail[trie[u][i]] = trie[fail[u]][i];
}
else {
trie[u][i] = trie[fail[u]][i];
}
}
}
}
inline void Query () {
for (int i = tot; i >= 0; i --) {
siz[fail[q[i]]] += siz[q[i]];//倒推计算子树和。
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
printf ("%d\n", siz[tag[i]]);
}
}
}AC;
int main() {
scanf ("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {
scanf ("%s", c);
AC.Insert (c, i);
}
AC.GetFail ();
AC.Query ();
return 0;
}
要求对于每一个模式串,求出其最长的前缀 \(p\),满足 \(p\) 是文本串的子串。
题目稍有变化,思维难度还是比较低的。
我们可以设 \(tag_i\) 表示 Trie 树上的 \(i\) 节点状态是文本串的前缀。
那么我们就可以匹配出 \(tag\) 数组,最后对于每一个模式串进行匹配即可。
代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <queue>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
const int N = 10000007;
const int M = 100007;
const int T = 107;
int n, m;
char TXT[N];
char p[M][T];
struct AC_automaton {
int trie[N][4], tag[N], fail[N], tot = 0;
inline int Change (char c) {
if (c == 'E') {
return 0;
}
else if (c == 'S') {
return 1;
}
else if (c == 'W') {
return 2;
}
else if (c == 'N') {
return 3;
}
}
inline void Insert (char *s) {
int slen = strlen (s), u = 0, c;
for (int i = 0; i < slen; i ++) {
c = Change (s[i]);
if (!trie[u][c]) {
trie[u][c] = ++ tot;
}
u = trie[u][c];
}
}
queue<int> q;
inline void GetFail () {
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++) {
if (trie[0][i]) {
q.push (trie[0][i]);
}
}
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front();
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++) {
if (trie[u][i]) {
q.push (trie[u][i]);
fail[trie[u][i]] = trie[fail[u]][i];
}
else {
trie[u][i] = trie[fail[u]][i];
}
}
}
}
inline void Find (char *T) {
int Tlen = strlen (T), u = 0, ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < Tlen; i ++) {
int c = Change (T[i]);
u = trie[u][c];
for (int j = u; j && !tag[j]; j = fail[j]) {
tag[j] = 1;
//求tag。
}
}
}
inline int Query (char *T) {
int u = 0, ans = 0, Tlen = strlen (T);
for (int i = 0; i < Tlen; i ++) {
int cc = Change (T[i]);
u = trie[u][cc];
if (tag[u]) {
ans = i + 1;//下标从0开始,要+1。
}
else {
break;
}
}
return ans;
}
}AC;
int main() {
scanf ("%d%d", &n, &m);
scanf ("%s", TXT);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++) {
scanf ("%s", p[i]);
AC.Insert (p[i]);
}
AC.GetFail ();
AC.Find (TXT);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i ++) {
printf ("%d\n", AC.Query (p[i]));
}
return 0;
}


