使用DataSourceUtils进行Connection的管理 由上节代码可知,JdbcTemplate在获取Connection的时候,并不是直接调用DataSource的getConnection(),而是调用了如下的代码: 1 | Connection con = DataSourceUtils.getConnection(getDataSource()); |
1 | Connection con = dataSource.getConnection(); |
org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceUtils所提供的方法,用来从指定的DataSource中获取或者释放连接,它会将取得的Connection绑定到当前的线程,以便在使用Spring所提供的统一事务抽象层进行事务管理的时候使用。
为什么要使用NativeJdbcExtractor
在execute()方法中可以看到:
1 | if (this.nativeJdbcExtractor != null && |
2 | this.nativeJdbcExtractor.isNativeConnectionNecessaryForNativeStatements()) { |
3 | conToUse = this.nativeJdbcExtractor.getNativeConnection(con); |
1 | if (this.nativeJdbcExtractor != null) { |
2 | stmtToUse = this.nativeJdbcExtractor.getNativeStatement(stmt); |
1 | /** Custom NativeJdbcExtractor */ |
2 | private NativeJdbcExtractor nativeJdbcExtractor; |
1 | public void setNativeJdbcExtractor(NativeJdbcExtractor extractor) { |
2 | this.nativeJdbcExtractor = extractor; |
spring默认提供面向Commons DBCP、C3P0、Weblogic、Websphere等数据源的NativeJdbcExtractor的实现类: CommonsDbcpNativeJdbcExtractor:为Jakarta Commons DBCP数据库连接池所提供的NativeJdbcExtractor实现类 C3P0NativeJdbcExtractor:为C3P0数据库连接池所提供的NativeJdbcExtractor实现类 WebLogicNativeJdbcExtractor:为Weblogic所准备的NativeJdbcExtractor实现类
WebSphereNativeJdbcExtractor:为WebSphere所准备的NativeJdbcExtractor实现类
控制JdbcTemplate的行为 JdbcTemplate在使用Statement或者PreparedStatement等进行具体的数据操作之前,会调用如下的代码:
01 | protected void applyStatementSettings(Statement stmt) throws SQLException { |
02 | int fetchSize = getFetchSize(); |
04 | stmt.setFetchSize(fetchSize); |
06 | int maxRows = getMaxRows(); |
08 | stmt.setMaxRows(maxRows); |
10 | DataSourceUtils.applyTimeout(stmt, getDataSource(), getQueryTimeout()); |
这样便可以设置Statement每次抓取的行数 等等。
SQLException到DataAccessException的转译 因为JdbcTemplate直接操作的是JDBC API,所以它需要捕获在此期间可能发生的SQLException,处理的宗旨是将SQLException 转译到spring的数据访问异常层次体系,以统一数据访问异常的处理方式,这个工作主要是交给了SQLExceptionTranslator,该 接口的定义如下:
01 | package org.springframework.jdbc.support; |
03 | import java.sql.SQLException; |
05 | import org.springframework.dao.DataAccessException; |
11 | * @author Juergen Hoeller |
12 | * @see org.springframework.dao.DataAccessException |
14 | public interface SQLExceptionTranslator { |
17 | DataAccessException translate(String task, String sql, SQLException ex); |
该接口有两个主要的实现类,SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator和SQLStateSQLExceptionTranslator,如下所示: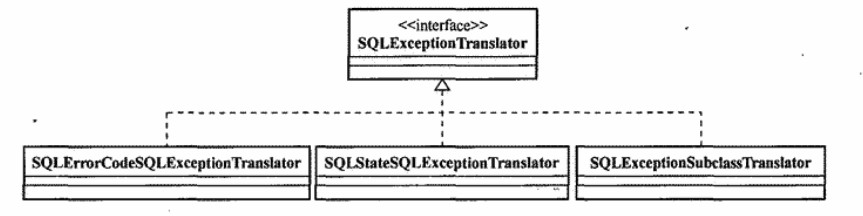
SQLExceptionSubclassTranslator是Spring2.5新加的实现类,主要用于JDK6发布的将JDBC4版本中新定义的异常体系转化为spring的异常体系,对于之前的版本,该类派不上用场。
SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator会基于SQLExcpetion所返回的ErrorCode进行异常转译。通常情况下,根据各个数据库提供商所提供的ErrorCode进行分析要比基于SqlState的方式要准确的多。默认情况下,JdbcTemplate会采用SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator进行SQLException的转译,当ErrorCode无法提供足够的信息的时候,会转而求助SQLStateSQLExceptionTranslator。
如果JdbcTemplate默认的SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator无法满足当前异常转译的需要,我们可以扩展SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator,使其支持更多的情况,有两种方法进行扩展:提供其子类或者在classpath下提供相应的配置文件,
我们先大致看一下SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator的大致调用规则,然后再从代码层面上研究下,r进行转译的大致的流程如下:
1、SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator定义了如下的自定义异常转译的方法:
1 | protected DataAccessException customTranslate(String task, String sql, SQLException sqlEx) { |
3、如果基于ErrorCode的异常转译还是没法搞定的话,SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator只能求助于SQLStateSQLExceptionTranslator或者SQLExceptionSubclassTranslator
下面从代码层面上剖析之:
假若JdbcTemplate的如下模板方法在执行的过程中发生了异常:
01 | public Object execute(StatementCallback action) throws DataAccessException { |
02 | Assert.notNull(action, "Callback object must not be null"); |
04 | Connection con = DataSourceUtils.getConnection(getDataSource()); |
05 | Statement stmt = null; |
07 | Connection conToUse = con; |
08 | if (this.nativeJdbcExtractor != null && |
09 | this.nativeJdbcExtractor.isNativeConnectionNecessaryForNativeStatements()) { |
10 | conToUse = this.nativeJdbcExtractor.getNativeConnection(con); |
12 | stmt = conToUse.createStatement(); |
13 | applyStatementSettings(stmt); |
14 | Statement stmtToUse = stmt; |
15 | if (this.nativeJdbcExtractor != null) { |
16 | stmtToUse = this.nativeJdbcExtractor.getNativeStatement(stmt); |
18 | Object result = action.doInStatement(stmtToUse); |
22 | catch (SQLException ex) { |
23 | // Release Connection early, to avoid potential connection pool deadlock |
24 | // in the case when the exception translator hasn't been initialized yet. |
25 | JdbcUtils.closeStatement(stmt); |
27 | DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, getDataSource()); |
29 | throw getExceptionTranslator().translate("StatementCallback", getSql(action), ex); |
32 | JdbcUtils.closeStatement(stmt); |
33 | DataSourceUtils.releaseConnection(con, getDataSource()); |
1 | throw getExceptionTranslator().translate("StatementCallback", getSql(action), ex); |
01 | public synchronized SQLExceptionTranslator getExceptionTranslator() { |
02 | if (this.exceptionTranslator == null) { |
03 | DataSource dataSource = getDataSource(); |
04 | if (dataSource != null) { |
05 | this.exceptionTranslator = newSQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator(dataSource); |
08 | this.exceptionTranslator = new SQLStateSQLExceptionTranslator(); |
11 | return this.exceptionTranslator; |
1 | public SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator(DataSource dataSource) { |
3 | setDataSource(dataSource); |
1 | public SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator() { |
2 | if (JdkVersion.getMajorJavaVersion() >= JdkVersion.JAVA_16) { |
3 | setFallbackTranslator(new SQLExceptionSubclassTranslator()); |
6 | setFallbackTranslator(new SQLStateSQLExceptionTranslator()); |
1 | public void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) { |
2 | this.sqlErrorCodes = SQLErrorCodesFactory.getInstance().getErrorCodes(dataSource); |
01 | protected SQLErrorCodesFactory() { |
02 | Map errorCodes = null; |
05 | DefaultListableBeanFactory lbf = new DefaultListableBeanFactory(); |
06 | XmlBeanDefinitionReader bdr = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(lbf); |
08 | // Load default SQL error codes. |
09 | Resource resource = loadResource(SQL_ERROR_CODE_DEFAULT_PATH); |
10 | if (resource != null && resource.exists()) { |
11 | bdr.loadBeanDefinitions(resource); |
14 | logger.warn("Default sql-error-codes.xml not found (should be included in spring.jar)"); |
17 | // Load custom SQL error codes, overriding defaults. |
18 | resource = loadResource(SQL_ERROR_CODE_OVERRIDE_PATH); |
19 | if (resource != null && resource.exists()) { |
20 | bdr.loadBeanDefinitions(resource); |
21 | logger.info("Found custom sql-error-codes.xml file at the root of the classpath"); |
24 | // Check all beans of type SQLErrorCodes. |
25 | errorCodes = lbf.getBeansOfType(SQLErrorCodes.class, true, false); |
26 | if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { |
27 | logger.info("SQLErrorCodes loaded: " + errorCodes.keySet()); |
30 | catch (BeansException ex) { |
31 | logger.warn("Error loading SQL error codes from config file", ex); |
32 | errorCodes = Collections.EMPTY_MAP; |
35 | this.errorCodesMap = errorCodes; |
可知首先会读取org.springframework.jdbc.support下的sql-error-codes.xml文件,如果classpath下也有该文件,则覆盖之,
这样便生成了sqlErrorCodes
getExceptionTranslator().translate("StatementCallback", getSql(action), ex)的方法如下所示:
01 | public DataAccessException translate(String task, String sql, SQLException ex) { |
02 | Assert.notNull(ex, "Cannot translate a null SQLException"); |
10 | DataAccessException dex = doTranslate(task, sql, ex); |
12 | // Specific exception match found. |
15 | // Looking for a fallback... |
16 | SQLExceptionTranslator fallback = getFallbackTranslator(); |
17 | if (fallback != null) { |
18 | return fallback.translate(task, sql, ex); |
20 | // We couldn't identify it more precisely. |
21 | return new UncategorizedSQLException(task, sql, ex); |
01 | protected DataAccessException doTranslate(String task, String sql, SQLException ex) { |
02 | SQLException sqlEx = ex; |
03 | if (sqlEx instanceof BatchUpdateException && sqlEx.getNextException() != null) { |
04 | SQLException nestedSqlEx = sqlEx.getNextException(); |
05 | if (nestedSqlEx.getErrorCode() > 0 || nestedSqlEx.getSQLState() != null) { |
06 | logger.debug("Using nested SQLException from the BatchUpdateException"); |
11 | // First, try custom translation from overridden method. |
12 | DataAccessException dex = customTranslate(task, sql, sqlEx); |
17 | // Check SQLErrorCodes with corresponding error code, if available. |
18 | if (this.sqlErrorCodes != null) { |
19 | String errorCode = null; |
20 | if (this.sqlErrorCodes.isUseSqlStateForTranslation()) { |
21 | errorCode = sqlEx.getSQLState(); |
24 | errorCode = Integer.toString(sqlEx.getErrorCode()); |
27 | if (errorCode != null) { |
28 | // Look for defined custom translations first. |
29 | CustomSQLErrorCodesTranslation[] customTranslations =this.sqlErrorCodes.getCustomTranslations(); |
30 | if (customTranslations != null) { |
31 | for (int i = 0; i < customTranslations.length; i++) { |
32 | CustomSQLErrorCodesTranslation customTranslation = customTranslations[i]; |
33 | if (Arrays.binarySearch(customTranslation.getErrorCodes(), errorCode) >= 0) { |
34 | if (customTranslation.getExceptionClass() != null) { |
35 | DataAccessException customException = createCustomException( |
36 | task, sql, sqlEx, customTranslation.getExceptionClass()); |
37 | if (customException != null) { |
38 | logTranslation(task, sql, sqlEx, true); |
39 | return customException; |
45 | // Next, look for grouped error codes. |
46 | if (Arrays.binarySearch(this.sqlErrorCodes.getBadSqlGrammarCodes(), errorCode) >= 0) { |
47 | logTranslation(task, sql, sqlEx, false); |
48 | return new BadSqlGrammarException(task, sql, sqlEx); |
50 | else if(Arrays.binarySearch(this.sqlErrorCodes.getInvalidResultSetAccessCodes(), errorCode) >= 0) { |
51 | logTranslation(task, sql, sqlEx, false); |
52 | return new InvalidResultSetAccessException(task, sql, sqlEx); |
54 | else if(Arrays.binarySearch(this.sqlErrorCodes.getDataIntegrityViolationCodes(), errorCode) >= 0) { |
55 | logTranslation(task, sql, sqlEx, false); |
56 | return new DataIntegrityViolationException(buildMessage(task, sql, sqlEx), sqlEx); |
58 | else if(Arrays.binarySearch(this.sqlErrorCodes.getPermissionDeniedCodes(), errorCode) >=0) { |
59 | logTranslation(task, sql, sqlEx, false); |
60 | return new PermissionDeniedDataAccessException(buildMessage(task, sql, sqlEx), sqlEx); |
62 | else if(Arrays.binarySearch(this.sqlErrorCodes.getDataAccessResourceFailureCodes(), errorCode) >= 0) { |
63 | logTranslation(task, sql, sqlEx, false); |
64 | return new DataAccessResourceFailureException(buildMessage(task, sql, sqlEx), sqlEx); |
66 | else if(Arrays.binarySearch(this.sqlErrorCodes.getTransientDataAccessResourceCodes(), errorCode) >= 0) { |
67 | logTranslation(task, sql, sqlEx, false); |
68 | return new TransientDataAccessResourceException(buildMessage(task, sql, sqlEx), sqlEx); |
70 | else if(Arrays.binarySearch(this.sqlErrorCodes.getCannotAcquireLockCodes(), errorCode) >=0) { |
71 | logTranslation(task, sql, sqlEx, false); |
72 | return new CannotAcquireLockException(buildMessage(task, sql, sqlEx), sqlEx); |
74 | else if(Arrays.binarySearch(this.sqlErrorCodes.getDeadlockLoserCodes(), errorCode) >= 0) { |
75 | logTranslation(task, sql, sqlEx, false); |
76 | return new DeadlockLoserDataAccessException(buildMessage(task, sql, sqlEx), sqlEx); |
78 | else if(Arrays.binarySearch(this.sqlErrorCodes.getCannotSerializeTransactionCodes(), errorCode) >= 0) { |
79 | logTranslation(task, sql, sqlEx, false); |
80 | return new CannotSerializeTransactionException(buildMessage(task, sql, sqlEx), sqlEx); |
85 | // We couldn't identify it more precisely - let's hand it over to the SQLState fallback translator. |
86 | if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { |
88 | if (this.sqlErrorCodes != null &&this.sqlErrorCodes.isUseSqlStateForTranslation()) { |
89 | codes = "SQL state '" + sqlEx.getSQLState() + "', error code '" + sqlEx.getErrorCode(); |
92 | codes = "Error code '" + sqlEx.getErrorCode() + "'"; |
94 | logger.debug("Unable to translate SQLException with " + codes + ", will now try the fallback translator"); |
可知假如该方法返回的是null,translate方法会调用SQLExceptionSubclassTranslator或者SQLStateSQLExceptionTranslator的translate的方法转译这个异常。
在SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator转译异常的过程中,我们可以在两个地方插入自定义的转译异常:
1、在customTranslate(String task, String sql, SQLException sqlEx)方法中,通过子类化SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator,重写该方法。
2、在classpath下提供sql-error-codes.xml文件。
下面是使用这两种方式进行自定义转译的具体实施情况。
1、扩展SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator
该方法最直接有效,却不够方便,需要子类化并且覆写它的customTranslate方法,
01 | package com.google.spring.jdbc; |
03 | import java.sql.SQLException; |
05 | import org.springframework.dao.DataAccessException; |
06 | import org.springframework.dao.UncategorizedDataAccessException; |
07 | import org.springframework.jdbc.support.SQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator; |
09 | public class SimpleSQLErrorCodeSQLExceptinTranslator extendsSQLErrorCodeSQLExceptionTranslator |
12 | protected DataAccessException customTranslate(String task, String sql, SQLException sqlEx) |
14 | if(sqlEx.getErrorCode()==111) |
16 | StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(); |
17 | builder.append("unexpected data access exception raised when executing "); |
19 | builder.append(" with SQL>"); |
21 | return newUnknownUncategorizedDataAccessException(builder.toString(),sqlEx); |
26 | private class UnknownUncategorizedDataAccessException extendsUncategorizedDataAccessException |
28 | public UnknownUncategorizedDataAccessException(String msg, Throwable cause) { |
1 | ApplicationContext applicationContext = newClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext2.xml"); |
2 | JdbcTemplate jdbc = (JdbcTemplate)applicationContext.getBean("jdbc"); |
3 | DataSource dataSource = (DataSource)applicationContext.getBean("dataSource"); |
4 | SimpleSQLErrorCodeSQLExceptinTranslator simpleSQLErrorCodeSQLExceptinTranslator =new SimpleSQLErrorCodeSQLExceptinTranslator(); |
5 | simpleSQLErrorCodeSQLExceptinTranslator.setDataSource(dataSource); |
6 | jdbc.setExceptionTranslator(simpleSQLErrorCodeSQLExceptinTranslator); |
实际上,它就是一个基本的基于DTD的Spring IOC容器的配置文件,只不过class是固定的。该配置文件对每个数据库类型均提供了一个org.springframework.jdbc.support.SQLErrorCodes的定义。假若我们有另外一个数据库AnotherDb,要扩展该转译,我们有两种方式:
1、
01 | <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> |
02 | <!DOCTYPE beans PUBLIC "-//SPRING//DTD BEAN 2.0//EN" "http://www.springframework.org/dtd/spring-beans-2.0.dtd"> |
06 | <bean id="AnotherDB" class="org.springframework.jdbc.support.SQLErrorCodes"> |
07 | <property name="databaseProductName"> |
08 | <value>AnotherDB*</value> |
10 | <property name="badSqlGrammarCodes"> |
13 | <property name="dataIntegrityViolationCodes"> |
16 | <property name="dataAccessResourceFailureCodes"> |
17 | <value>0031,0032</value> |
19 | <property name="transientDataAccessResourceCodes"> |
22 | <property name="deadlockLoserCodes"> |
23 | <value>0051,0052</value> |
01 | <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> |
02 | <!DOCTYPE beans PUBLIC "-//SPRING//DTD BEAN 2.0//EN" "http://www.springframework.org/dtd/spring-beans-2.0.dtd"> |
06 | <bean id="AnotherDB" class="org.springframework.jdbc.support.SQLErrorCodes"> |
07 | <property name="databaseProductName"> |
08 | <value>AnotherDB*</value> |
10 | <property name="customTranslations"> |
12 | <beanclass="org.springframework.jdbc.support.CustomSQLErrorCodesTranslation"> |
13 | <property name="errorCodes">111</property> |
14 | <property name="exceptionClass"> |
15 | org.springframework.dao.IncorrectResultSizeDataAccessException |






