MTOM效率测试
MTOM是一种消息编码方式,它的目的是优化SOAP消息的编码,以减小体积,提高传输速度。如果你对其不清楚,可以参考另外一篇文章
http://www.cnblogs.com/chenxizhang/archive/2010/04/09/1708621.html
这一篇,我们主要用实例来看看到底它在性能方面有何表现
我们先做一些准备工作,编写了一个接口和服务
1. 接口
using System.ServiceModel; namespace Services { [ServiceContract] public interface IHelloService { [OperationContract] byte[] GetData(); } }
2.服务 namespace Services { public class HelloWorldService:IHelloService { #region IHelloService 成员 byte[] IHelloService.GetData() { return new byte[10000]; } #endregion } }
注意,我们这里的服务很简单,就是直接返回一个长度为10000的字节数组。
接下来编写宿主和客户端
3.宿主
using System; using System.ServiceModel; using Services; namespace Host { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { using (ServiceHost host = new ServiceHost(typeof(HelloWorldService))) { host.Open(); Console.WriteLine("服务器已经准备好"); Console.Read(); } } } }
宿主的配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <configuration> <system.serviceModel> <services> <service name="Services.HelloWorldService"> <host> <baseAddresses> <add baseAddress="http://localhost:8080/HelloService"/> </baseAddresses> </host> <endpoint address="" contract="Services.IHelloService" binding="basicHttpBinding" bindingConfiguration="mtom"></endpoint> </service> </services> <bindings> <basicHttpBinding> <binding name="mtom" messageEncoding="Mtom"></binding> </basicHttpBinding> </bindings> </system.serviceModel> </configuration>
4. 客户端
using System; using System.ServiceModel; using Services; namespace TestClient { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { IHelloService proxy = (new ChannelFactory<IHelloService>("local")).CreateChannel(); byte[] buffer=proxy.GetData(); Console.WriteLine(buffer.Length); Console.Read(); } } }
客户端的配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <configuration> <system.diagnostics> <sources> <source name="System.ServiceModel.MessageLogging" switchValue="Verbose"> <listeners> <add name="xml" type="System.Diagnostics.XmlWriterTraceListener" initializeData="c:\logs\client.svclog" /> </listeners> </source> </sources> <trace autoflush="true" /> </system.diagnostics> <system.serviceModel> <diagnostics> <messageLogging logEntireMessage="true" maxMessagesToLog="300" logMessagesAtServiceLevel="false" logMalformedMessages="true" logMessagesAtTransportLevel="true" /> </diagnostics> <client> <endpoint address="http://localhost:8080/HelloService" binding="basicHttpBinding" contract="Services.IHelloService" name="local" bindingConfiguration="mtom"></endpoint> </client> <bindings> <basicHttpBinding> <binding name="mtom" messageEncoding="Mtom"></binding> </basicHttpBinding> </bindings> </system.serviceModel> </configuration>
说明,上面的配置文件中,已经配置好了messageEncoding为Mtom. 但我们在运行程序时会分两次运行,一次是标准的编码,一次则是Mtom编码
我们通过下面的日志文件可以比较出来MTOM编码的效率优势
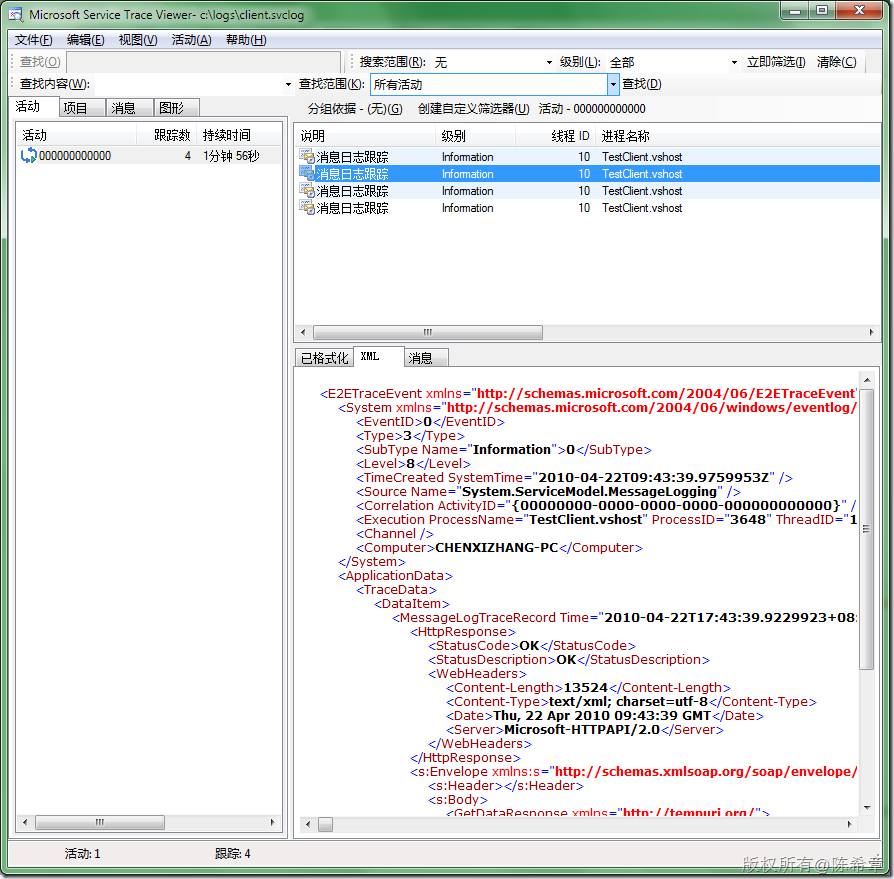
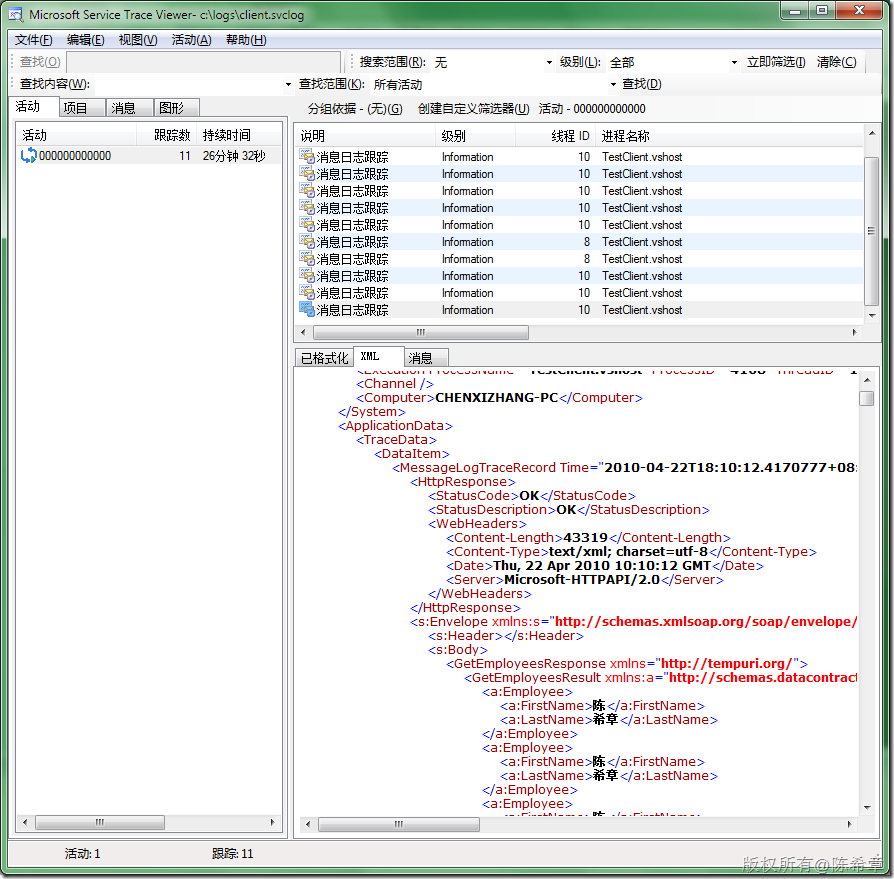
下图是标准编码的结果,请注意Content-length为13524
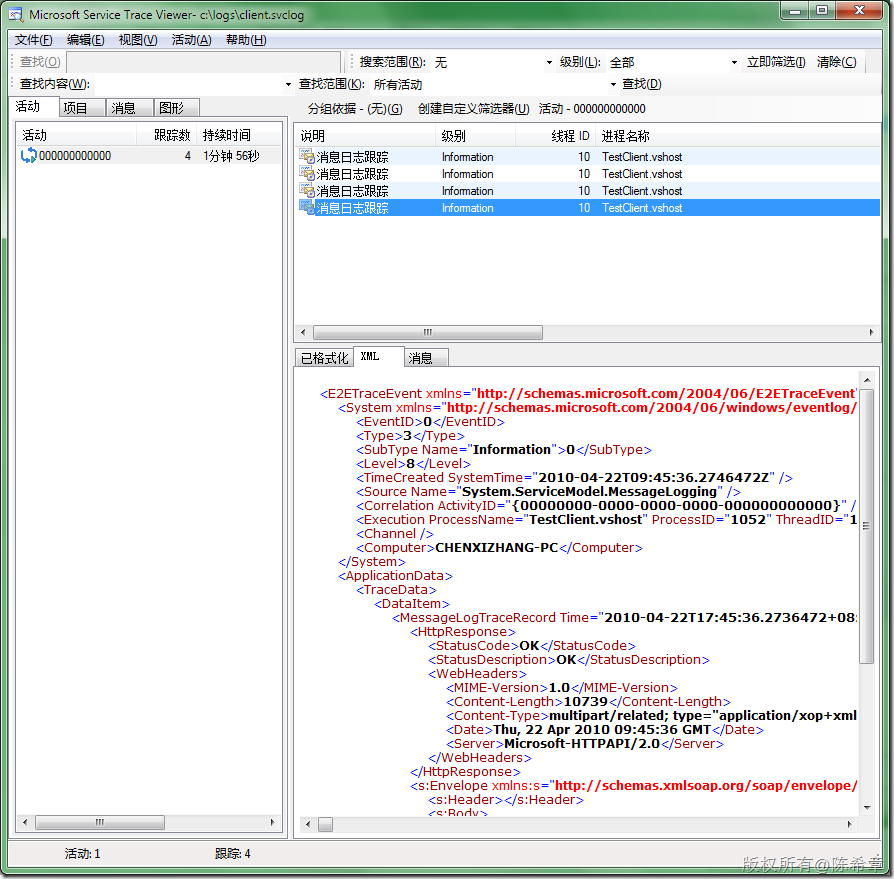
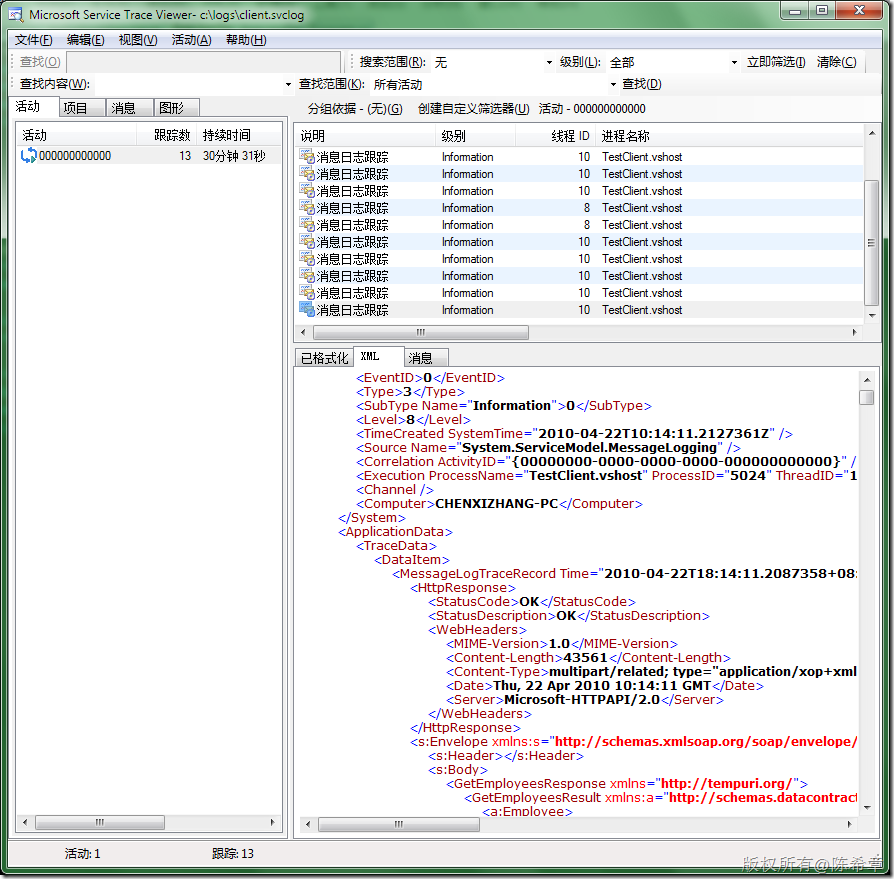
下图是Mtom编码的结果,请注意Content-Length为10739
最后有一点要提示的是,MTOM编码主要针对二进制结果有优势。原因在于,标准编码(Text)在对二进制数据编码的时候会采取Base64编码,使得数据平白地多出来了1/3左右。
而针对纯文本的数据,则MTOM编码的长度 总是会大于标准编码的长度。
例如我们有如下的一个方法,返回一些字符
public string GetString() { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) { sb.Append("Hello"); } return sb.ToString(); }
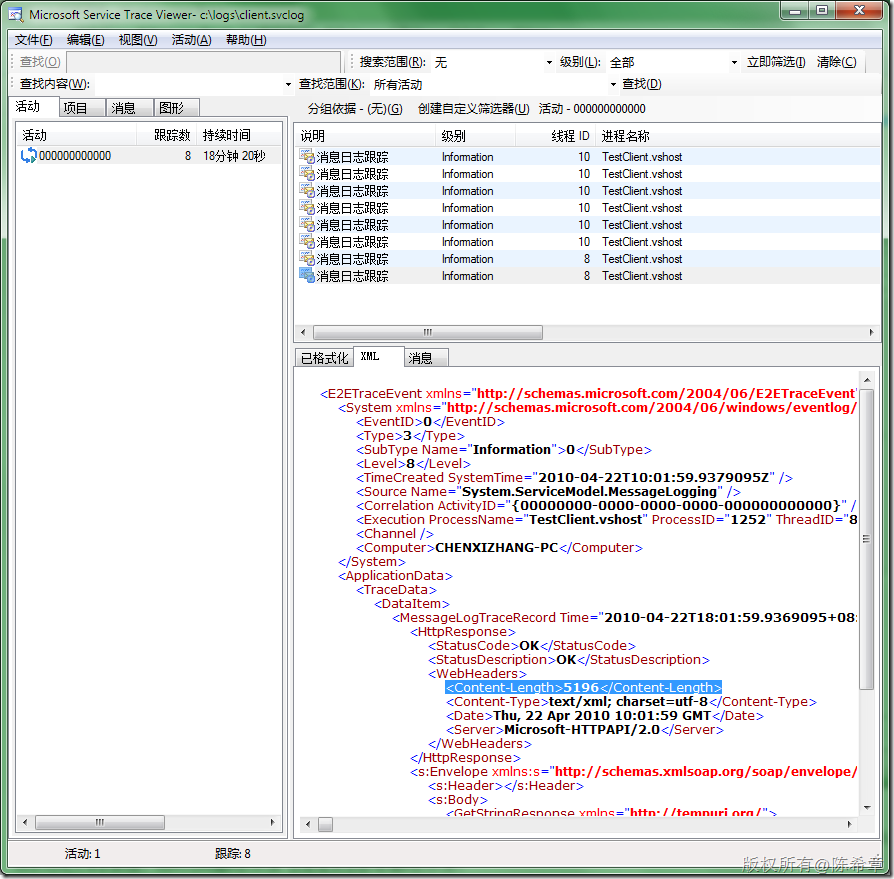
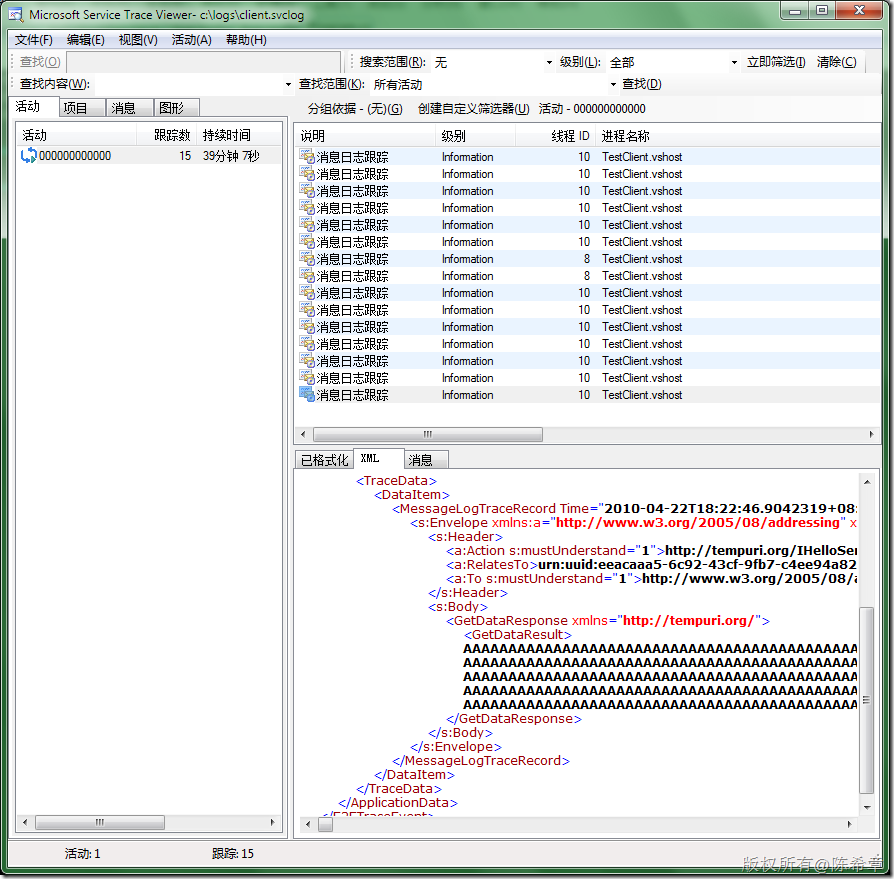
首先看标准编码的长度,为5196
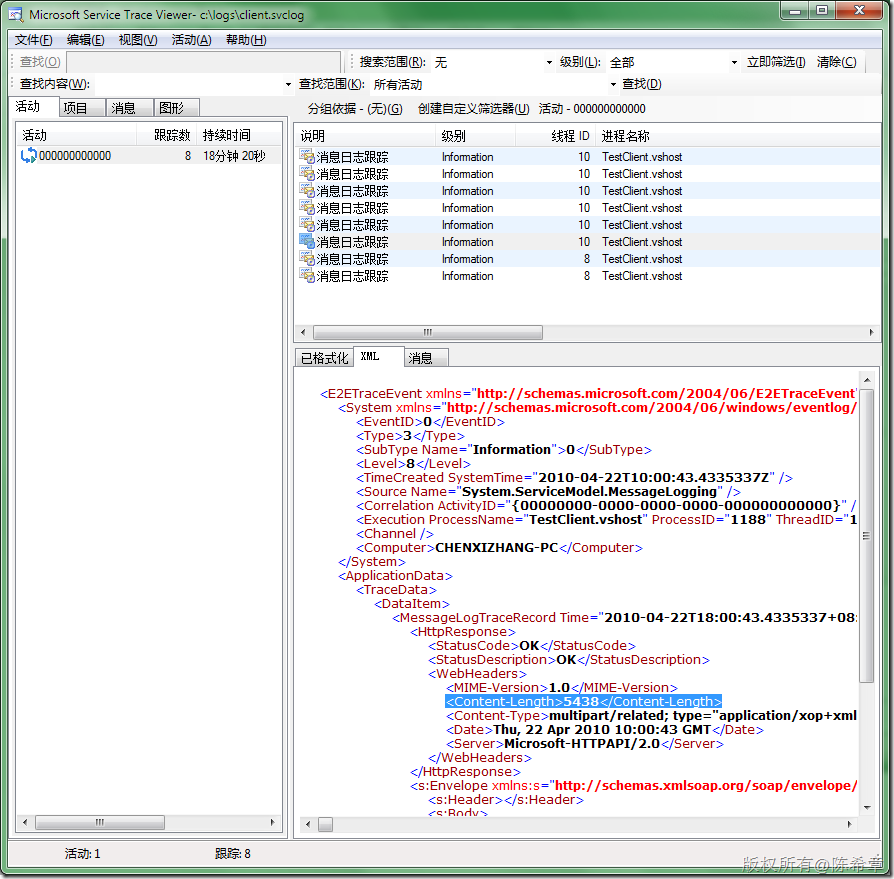
而MTOM编码的长度则为
我们再来测试一下复杂类型的情况。为了演示,我们添加了一个Employee类型在客户端和服务器之间传递。
[DataContract]
public class Employee {
[DataMember]
public string FirstName { get; set; }
[DataMember]
public string LastName { get; set; }
public override string ToString()
{
return string.Format("{0},{1}", FirstName, LastName);
}
}
然后在服务中实现了一个方法
Employee[] IHelloService.GetEmployees()
{
List<Employee> result = new List<Employee>();
for (int i = 0; i < 500; i++)
{
result.Add(new Employee()
{
FirstName = "陈",
LastName = "希章"
});
}
return result.ToArray();
}
我们看到,发送500个员工的数据,如果按照标准编码的话,长度大致需要43319
如果改成mtom呢,长度为43561,还是稍微大一些。这是因为MTOM这种编码本身会有一些额外的开销
好的,这里需要总结一下了
1. MTOM是一个编码方式
2. MTOM是针对较大的二进制数据有优化作用,相比较默认的Text编码,它传输的是接近于数据原本的格式,而Text编码方式则采用了Base64的方式进行编码。
3. 针对标准文本或者对象,MTOM并没有优化作用。
最后,有没有朋友想到了这样一个问题:既然是二进制的数据,能不能直接就采用二进制的方式传递呢?干嘛要去编码成文本呢?
是的,这是一个很好的问题,我们当然也可以直接采用netTcpBinding,它默认就是直接使用二进制编码
我们从下图是看不到长度的
但如果我们真的有兴趣,可以通过下面的代码计算得到不同的编码方式到底会有多长
static void CompareMessageSize(int dataSize) { // Create and buffer a message with a binary payload byte[] binaryData = new byte[dataSize]; Message message = Message.CreateMessage(MessageVersion.Soap12WSAddressing10, "action", binaryData); MessageBuffer buffer = message.CreateBufferedCopy(int.MaxValue); // Print the size of a text encoded copy int size = SizeOfTextMessage(buffer.CreateMessage()); Console.WriteLine("Text encoding with a {0} byte payload: {1}", binaryData.Length, size); // Print the size of an MTOM encoded copy size = SizeOfMtomMessage(buffer.CreateMessage()); Console.WriteLine("MTOM encoding with a {0} byte payload: {1}", binaryData.Length, size); Console.WriteLine(); message.Close(); } static int SizeOfTextMessage(Message message) { // Create a text encoder MessageEncodingBindingElement element = new TextMessageEncodingBindingElement(); MessageEncoderFactory factory = element.CreateMessageEncoderFactory(); MessageEncoder encoder = factory.Encoder; // Write the message and return its length MemoryStream stream = new MemoryStream(); encoder.WriteMessage(message, stream); int size = (int)stream.Length; message.Close(); stream.Close(); return size; } static int SizeOfMtomMessage(Message message) { // Create an MTOM encoder MessageEncodingBindingElement element = new MtomMessageEncodingBindingElement(); MessageEncoderFactory factory = element.CreateMessageEncoderFactory(); MessageEncoder encoder = factory.Encoder; // Write the message and return its length MemoryStream stream = new MemoryStream(); encoder.WriteMessage(message, stream); int size = (int)stream.Length; stream.Close(); message.Close(); return size; }