如何在ASP.NET页面中使用异步任务(PageAsyncTask)
在页面加载期间,可能有些操作是要比较耗用时间的(例如调用外部资源,要长时间等待其返回),正常情况下,这个操作将一直占用线程。而大家知道,ASP.NET在服务端线程池中的线程数是有限的,如果一直占用的话,就会导致其他操作需要等待。
在ASP.NET 2.0中,提供了一种异步页的技术。微软有一个专门的文档介绍这个技术
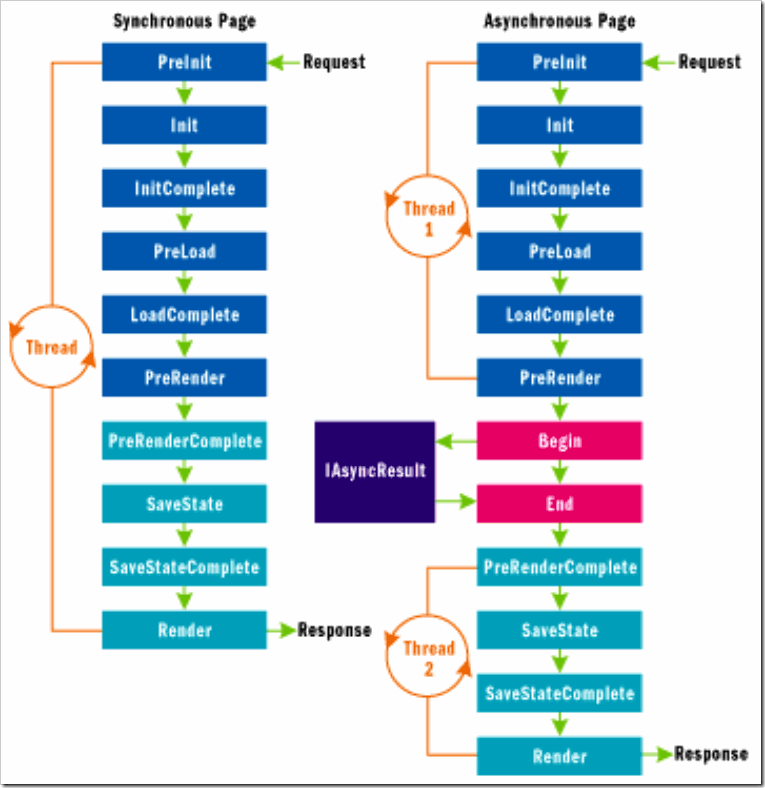
看看下面这个图,很重要
【注意】ASP.NET的异步机制与windows From的异步机制有一个根本区别,就是因为Response不可以分布发送到客户端的,所以,这个异步的效果对客户端来说可能是效果不明显的。也就说客户还是一样等待所有的操作完成之后才能看到页面。但是,使用了异步技术后,服务器端的线程能得到更好的利用,从另外一个层面是提高性能。
下面我用一个简单的例子来演示如何使用该技术
1. 页面需要启用async支持
<%@ Page Language="C#" AutoEventWireup="true" CodeBehind="Default.aspx.cs" Inherits="WebApplication2._Default" Async="true" %>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" >
<head runat="server">
<title></title>
<link rel="Stylesheet" href="default.css" />
</head>
<body>
<form id="form1" runat="server">
<div id="mydiv" runat="server">
</div>
</form>
</body>
</html>
2.通过一个独立的类型(class)定义长时间执行任务的操作
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Web;
using System.Threading;
namespace WebApplication2
{
public class LongTimeTask
{
public string Result = string.Empty;
public HelloWorldHandler handler;
public delegate string HelloWorldHandler();
public string HelloWorld()
{
Thread.Sleep(5000);
return "Hello,world";
}
public IAsyncResult OnBegin(object sender, EventArgs e,
AsyncCallback cb, object extraData)
{
handler = new HelloWorldHandler(this.HelloWorld);
return handler.BeginInvoke(cb, extraData);
}
public void OnEnd(IAsyncResult ar)
{
Result = handler.EndInvoke(ar);
}
public void OnTimeout(IAsyncResult ar)
{
Result = "超时了";
}
}
}
3. 在页面的Page_Load事件中,注册异步任务
LongTimeTask task;
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
task= new LongTimeTask();
PageAsyncTask asynctask = new PageAsyncTask(task.OnBegin, task.OnEnd, task.OnTimeout, null);
RegisterAsyncTask(asynctask);
}
4. 在页面的OnPreRenderComplete的方法里面接收异步任务的结果
protected override void OnPreRenderComplete(EventArgs e)
{
mydiv.InnerHtml = task.Result;
}
【注意】值得一说的是,如果是调用Web Service,也可能会需要比较长时间,但因为Web Service的异步调用有内部的支持。不需要我们像上面这样复杂。
例如,有下面这样一个服务
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.Services;
using System.Threading;
namespace WebApplication2
{
/// <summary>
/// demoService 的摘要说明
/// </summary>
[WebService(Namespace = "http://tempuri.org/")]
[WebServiceBinding(ConformsTo = WsiProfiles.BasicProfile1_1)]
[System.ComponentModel.ToolboxItem(false)]
public class demoService : System.Web.Services.WebService
{
[WebMethod]
public string HelloWorld()
{
Thread.Sleep(5000);
return "Hello World";
}
}
}
添加对其引用之后,我们在页面代码中大致是这样的
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Web;
using System.Web.UI;
using System.Web.UI.WebControls;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading;
namespace WebApplication2
{
public partial class _Default : System.Web.UI.Page
{
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
localhost.demoService proxy = new localhost.demoService();
proxy.HelloWorldCompleted += new WebApplication2.localhost.HelloWorldCompletedEventHandler(proxy_HelloWorldCompleted);//绑定一个完成事件
proxy.HelloWorldAsync();//开始异步调用
}
void proxy_HelloWorldCompleted(object sender, WebApplication2.localhost.HelloWorldCompletedEventArgs e)
{
mydiv.InnerHtml = e.Result;
}
}
}
可以看到,这种方式简单多了。
其他内置支持异步的场景还有IO操作。这里就不一一描述了