ArrayList
简介
动态扩容数组实现的List(非定容),提供常数时间的元素随机访问能力。
继承体系
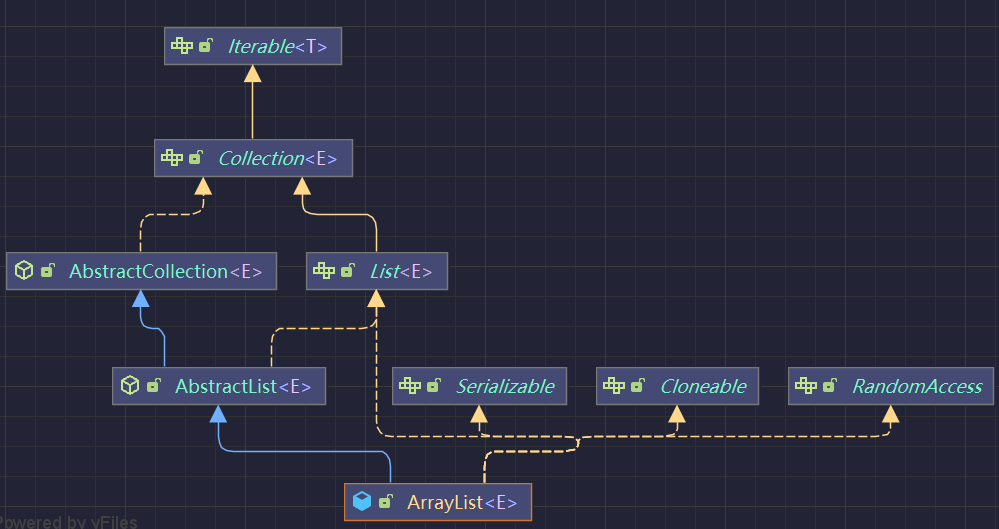
- Serializable:可序列化
- Cloneable:克隆
- RandomAccess:随机访问
问题
- Serializable接口作用?标记接口?什么时候需要继承这个接口?有哪些序列化方式?如何避免/处理类版本不一致导致的序列化问题?
- Cloneable接口作用?什么时候需要重写clone方法?如何重写clone方法?深浅克隆?
- ArrayList和L:inkedList区别?使用场景?(LinkedList作者自己也几乎不使用LinkedList)
- ArrayList/数组为什么存储对象也能实现随机访问?
- 与Vector的区别?
- 如何转换为不可变List?如何快速创建List?如何快速创建单个元素List?如何创建线程安全List(及区别和选择)
- 扩容为什么选择1.5倍扩容?ArrayList扩容平摊时间成本/时间复杂度?如何计算?
- 最大容量为多少?为什么(原理限制)?
- ConcurrentModificationException?fail-fast机制?
- 型变(协变与逆变)?泛型、数组的型变?
- 元素是否有必要重写hashCode和equals方法?如何重写?重写原则?
源码解析
属性
// 默认容量 private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; // 空集合 private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; // 默认容量空集合 private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; // 存储元素的数组. DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA 添加第一个元素时会扩容到 DEFAULT_CAPACITY transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access // 存储的元素个数 private int size;
构造函数
// 默认容量空集合, 添加第一个元素时扩容为默认容量 public ArrayList() { this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) { if (initialCapacity > 0) { this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity]; } else if (initialCapacity == 0) { // 空集合 this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } else { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+ initialCapacity); } } public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) { elementData = c.toArray(); if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) { // c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] // 必须保证数组是 Object[], 为什么 // --> 避免传入 E-SubClass 集合得到 E-SubClass[] 数组, 但是这个数组却无法存储 E 类型元素实例, 导致运行时报错 if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class) elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class); } else { // 空集合 this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } }
添加元素
add(E e)
public boolean add(E e) { // 确保数组足以容纳元素 ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! elementData[size++] = e; return true; } private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) { ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity)); } private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) { // 默认容量空数组则取max(默认容量, 需要的容量) if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); } // 否则取需要的容量 return minCapacity; } // 确保数组容量满足请求容量minCapacity private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) { modCount++; // 不满足则扩容 if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) grow(minCapacity); } private void grow(int minCapacity) { int oldCapacity = elementData.length; // 1.5 倍扩容 int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); // 1.5 倍不够则扩容为请求容量 if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) newCapacity = minCapacity; // 大于允许最大容量 // private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8; if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); // 复制并扩容 elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); }
- 检查是否需要扩容
- 扩容:DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA(默认构造函数)则扩容为max(默认容量 or 需要的容量(集合添加时))
- 尾部添加
add(int index, E element)
public void add(int index, E element) { // 校验索引合法性 rangeCheckForAdd(index); // 同上, 略 ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! // 向后移动元素, 也即将 [index, size - 1] --> [index + 1, size], 元素批量后移 System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, // size - index 是需要移动的元素数量 size - index); // set 元素到合适位置 elementData[index] = element; size++; }
addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) { Object[] a = c.toArray(); int numNew = a.length; // 同样是默认构造函数得到的 DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA, 新增第一个元素和使用元素新增, 扩容的容量可能就不一样 ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount // 尾部新增, 新增索引从size开始, 数量是 numNew System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, size, numNew); size += numNew; return numNew != 0; }
addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c)
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { rangeCheckForAdd(index); Object[] a = c.toArray(); int numNew = a.length; ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount // 要移动的元素数量, 先将这些元素后移 int numMoved = size - index; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew, numMoved); // 复制插入到中间 System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew); size += numNew; return numNew != 0; }
可以看到集合新增时,只有确实插入了元素才会返回 true
移除
remove(int index)
public E remove(int index) { // 校验索引合法性 rangeCheck(index); modCount++; E oldValue = elementData(index); int numMoved = size - index - 1; // 如果是移除了中间的元素, 则需要将后面的元素前移 if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved); // 置 null, 这里到底是否有必要?避免若几乎不写可能会导致内存泄露? elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work return oldValue; }
remove(Object o)
public boolean remove(Object o) { // null 值特殊处理, 因为只需要 == 即可 if (o == null) { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) if (elementData[index] == null) { fastRemove(index); return true; } } else { for (int index = 0; index < size; index++) // equals 比较 if (o.equals(elementData[index])) { fastRemove(index); return true; } } // 确实查找到并移除了元素会返回 true return false; } // 移除某索引处元素, 内部使用, 避免索引合法性校验 private void fastRemove(int index) { modCount++; int numMoved = size - index - 1; if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved); elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work }
注意这里的移除,当我们创建一个 ArrayList<Integer/Short>时,就要注意移除时的参数了(到底是调用的哪个方法) --> 传入基本数据类型就是调用 remove(int index) (不会进行自动包装),传入包装类就是调用 remove(Object o) (不会自动拆箱)
移除元素时整个集合的数组不会缩容。
get & set
get(int index)
get(int index)
public E set(int index, E element) { rangeCheck(index); E oldValue = elementData(index); elementData[index] = element; return oldValue; }
交集差集
retainAll(Collection<?> c)
retain:保留
仅保留同样在集合C中存在的元素
public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) { Objects.requireNonNull(c); // 批量删除, 传入 true 表示删除删除不在集合 c 中的元素 return batchRemove(c, true); } // complement // true: 删除不在集合 c 中的元素 // false: 删除集合 c 中的元素 private boolean batchRemove(Collection<?> c, boolean complement) { final Object[] elementData = this.elementData; // 双指针遍历数组 // r 读取遍历数组 // w 要保留的元素写入此索引 int r = 0, w = 0; boolean modified = false; try { // 遍历当前集合 for (; r < size; r++) // 含或不含进行删除此元素 if (c.contains(elementData[r]) == complement) // 进入这说明保留 r 索引处元素 // true: c 含 r, r 保留, 也就是删除不在集合 c 中的元素 // false: c 不含 r, r 保留, 也就是删除在集合 c 中的元素 elementData[w++] = elementData[r]; } finally { // Preserve behavioral compatibility with AbstractCollection, // even if c.contains() throws. // c.contains() 可能抛出的异常(注意集合c仅保证是集合), 比如集合 c 可能不能存储 null 值, 那么 contains(null) 就可能抛出异常 if (r != size) { // 把未读取到的元素拷贝到写指针之后, 也就是已删除的元素就删除了, 抛出异常之后的元素不继续处理例了 System.arraycopy(elementData, r, elementData, w, size - r); w += size - r; } // 说明有元素被删除了 if (w != size) { // 置 null 帮助 GC for (int i = w; i < size; i++) elementData[i] = null; modCount += size - w; size = w; modified = true; } } return modified; }
removeAll(Collection<?> c)
public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) { Objects.requireNonNull(c); // 仅保留在集合 c 中不存在的元素 return batchRemove(c, false); }
序列化
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s) throws java.io.IOException{ // Write out element count, and any hidden stuff int expectedModCount = modCount; // 先将默认字段进行写入 s.defaultWriteObject(); // Write out size as capacity for behavioural compatibility with clone() // 写入元素数量, 元素数量是否被写入了两次?(上面默认处理一次, 这里一次) s.writeInt(size); // 写入 for (int i=0; i<size; i++) { s.writeObject(elementData[i]); } if (modCount != expectedModCount) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } } private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s) throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException { elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; // 默认读取 s.defaultReadObject(); // 忽略写入的 s.readInt(); // ignored // 读取 if (size > 0) { // be like clone(), allocate array based upon size not capacity int capacity = calculateCapacity(elementData, size); SharedSecrets.getJavaOISAccess().checkArray(s, Object[].class, capacity); ensureCapacityInternal(size); Object[] a = elementData; // Read in all elements in the proper order. for (int i=0; i<size; i++) { a[i] = s.readObject(); } } }
克隆
public Object clone() { try { // 默认克隆是浅克隆, 克隆引用 ArrayList<?> v = (ArrayList<?>) super.clone(); // 自己处理存储元素的数组, 这里也不是复制整个数组 v.elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size); v.modCount = 0; return v; } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { // this shouldn't happen, since we are Cloneable throw new InternalError(e); } }
总结
- 动态扩容数组实现的 List
- 非定容数组
- 常数时间内索引随机访问元素
- 尾部的新增和删除的时间复杂的O(1),非尾部删除的平均时间复杂度O(N)
- 并集addAll、交集retainAll、单向差集removeAll
问题回答






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· AI编程工具终极对决:字节Trae VS Cursor,谁才是开发者新宠?
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!