包装类
1 包装类 & 装箱与拆箱
1.1 基本数据类型 & 包装器
- 基本数据类型及其包装器:

- 拆箱与装箱: 自动装箱是将基本数据类型转换为其包装类, 自动拆箱是将包装类调用其方法转换为基本数据类型
2. int类型的拆箱与装箱
2.1 实例
1 @Test 2 public void testEquals() { 3 int int1 = 12; 4 int int2 = 12; 5 6 Integer integer1 = new Integer(12); 7 Integer integer2 = new Integer(12); 8 Integer integer3 = new Integer(127); 9 10 Integer a1 = 127; //或者写成Integer a1 = Integer.valueOf(127); 11 Integer a2 = 127; //或者写成Integer a2 = Integer.valueOf(127); 12 13 Integer a = 128; 14 Integer b = 128; 15 16 System.out.println("int1 == int2 -> " + (int1 == int2)); // true 17 System.out.println("int1 == integer1 -> " + (int1 == integer1)); // true 18 System.out.println("integer1 == integer2 -> " + (integer1 == integer2)); // false 19 System.out.println("integer3 == a1 -> " + (integer3 == a1)); // false 20 System.out.println("a1 == a2 -> " + (a1 == a2)); // true 21 System.out.println("a == b -> " + (a == b)); // false 22 }
看其反汇编(javap -c class全类名)
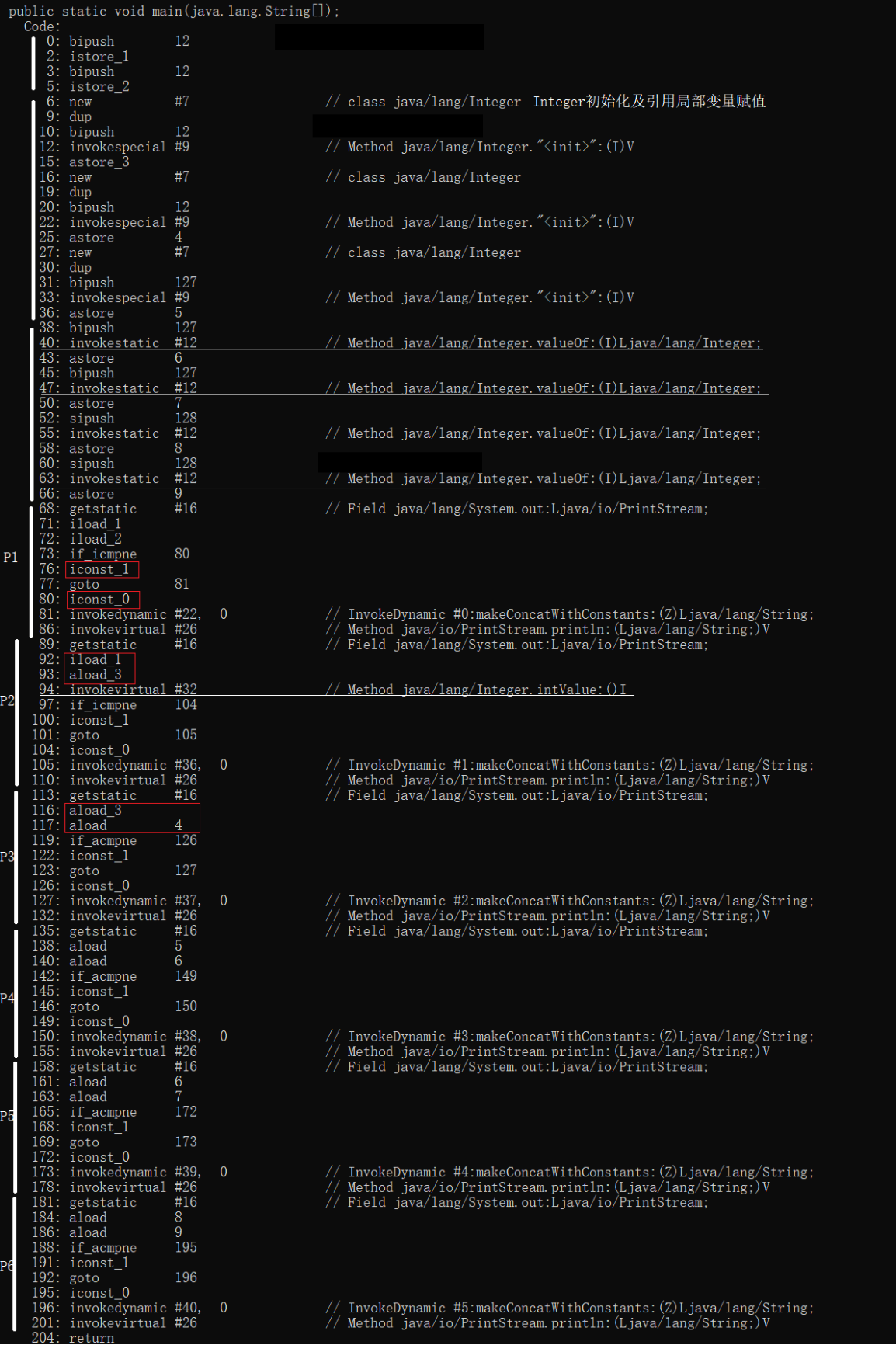
- 主要的汇编指令:
- bipush num: byte型常量num入栈
- istore_index: 栈顶值出栈赋予第index个局部变量(类型为int)
- astore_index: 栈顶值出栈赋予第index个局部变量(类型为引用)
- sipush num: 将short型常量num入栈
- iload_index: 将第index个局部变量入栈(类型为int)
- iconst_num: 将int型常量num入栈
- aload_index: 将第index个局部变量入栈(类型为引用)
2.2 分析
- 6~33行是使用构造函数new Integer(num)创建的,直接调用其构造函数
- 38~66行是直接将int常量值赋予Integer变量,可见编译器处理后变成调用valueOf(num)返回Integer引用,再赋予我们的Integer变量[会在后边说,自己也可先看源码实现]
- P1(第一个println),int类型比较直接比较其值
- P2,int与Integer比较是先调用Integer变量的intValue()获取其int值,再进行ini与int的值比较
- P3,Integer与Integer变量均为引用, 因此比较也是比较引用(是否指向同一个对象)
2.3 解析
构造函数就不说了,不过Integer的有参构造函数被标注在Java9之后全部过时(参数为int或String)
valueOf引用问题, P5同样是比较引用,但却返回true,P6同样是比较引用,而且和P5一样是直接赋予int常量的,却返回false
@HotSpotIntrinsicCandidate public static Integer valueOf(int i) { if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high) return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)]; return new Integer(i); }
valueOf并不是直接返回Integer引用,而是先在缓存里找一找,如果有,则返回已存在的引用,否则返回新对象,IntegerCache是一个static内部类
private static class IntegerCache { static final int low = -128; static final int high; // 在low与high范围内通过valueOf创建的会被缓存 static final Integer[] cache; // 指向archivedCache static Integer[] archivedCache; //缓存数组,初始化块里就会将low~high的Integer对象创建并存储 // 不明白为什么有两个cache,archivedCache并没有使用private修饰
high的大小,根据源码来说应该是在启动之前配置的,可以通过jdk.internal.misc.VM.getSavedProperty("java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high");获得,返回String,但是报以下错误
cannot access class jdk.internal.misc.VM (in module java.base) because module java.base does not export jdk.internal.misc to unnamed module @0x2ff4acd0
可以编译通过,上述错误是运行时报的错误。那就只能使用反射来获取了
Class integerClass = Integer.class; Class[] classes = integerClass.getDeclaredClasses(); Field hight = classes[0].getDeclaredField("high"); hight.setAccessible(true); System.out.println(hight.get(null));
注:异常啥的为了方便不处理了
2.4 对象池
上述的对象缓存的问题叫做对象池(参考别人博客的),只有Float和Double没有对象池(可以理解),Integer的对象池默认-128~127, Boolean的对象池为true & false,Byte、Short、Long对象池-128~127,Character为0~127
3. Integer源码分析
3.1 继承链
public final class Integer extends Number implements Comparable<Integer>, Constable, ConstantDesc
注:常用不可被继承类(final修饰):基本数据类型的包装类、String & StringBuilder & StringBuffer、
常用可继承的类:集合类
继承了Comparable<Integer>,可以进行比较
3.2 分析
参考
Java基本数据类型包装类 by 滑稽的命运
Integer装箱拆箱,参数传递 by 宓筱
JDK12 jdk.internal包不可见 by 张伯毅 [虽然并没有解决]
jvm 指令集代码 by zhangpan19910604
Integer装箱拆箱,参数传递 by 宓筱
JDK12 jdk.internal包不可见 by 张伯毅 [虽然并没有解决]
jvm 指令集代码 by zhangpan19910604
未完待续


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号