ArrayList源码的 elementData.getClass() != Object[].class
1. 放出源码
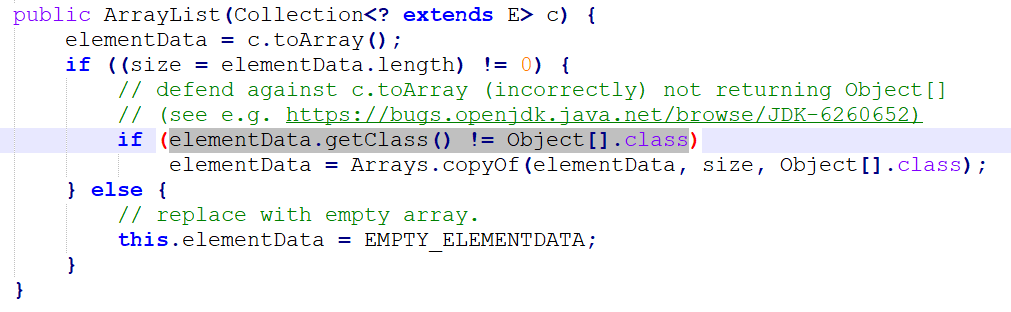
2. elementData与Object[]
elementData的定义如下
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
请看如下代码
package test; public class UserTest2 { public static void main(String[] args) { User[] users = new User[]{ new User(1, "admin", "admin@qq.com"), new User(2, "maco", "maco@qq.com"), new User(3, "kitty", "kitty@163.com") }; Object[] target = users; System.out.println(target.getClass()); // class [Ltest.User; target[0] = new Object(); // java.lang.ArrayStoreException: java.lang.Object } }
显然直接将非Object[]类型数组赋予Object[]类型, 相当于将子类对象赋予父类变量, 这会导致什么问题呢,请看如下代码
List<Object> list = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList("room", "take")); System.out.println(list.getClass()); list.set(0, new Object());
Arrays.asList("room", "take")返回的类型是String[](后面会解释, 注意这个BUG早就被修复了), 上面的代码显然会出错, 且错得莫名其妙, 我定义Object[]还不能存储Object实例了,显然是个BUG
public class UserTest { public static void main(String[] args) { User[] users = new User[]{ new User(1, "admin", "admin@qq.com"), new User(2, "maco", "maco@qq.com"), new User(3, "kitty", "kitty@163.com") }; Object[] objects = users; System.out.println(objects.getClass()); // class [Ltest.User; if(objects.getClass() != Object[].class){ objects = Arrays.copyOf(objects, objects.length, Object[].class); // class [Ljava.lang.Object; } System.out.println(objects.getClass()); } }
如上代码可知, 经过copyOf之后, 返回的类型是Object[], 就不会出现上述所说的错误了
3. Arrays.asList干了什么?
@SafeVarargs @SuppressWarnings("varargs") public static <T> List<T> asList(T... a) { return new ArrayList<>(a); }
其调用的ArrayList不是java.util.ArrayList, 而是其内部类
private static class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E> implements RandomAccess, java.io.Serializable { private final E[] a; ArrayList(E[] array) { a = Objects.requireNonNull(array); } // BUG实现 @Override public Object[] toArray() { return a.clone(); } // jdk-13.0.1的实现 /* @Override public Object[] toArray() { return Arrays.copyOf(a, a.length, Object[].class); } */
可运行以下代码测试
System.out.println(new String[]{}.clone().getClass()); // class [Ljava.lang.String;
4. Arrays.copyOf做了什么
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static <T> T[] copyOf(T[] original, int newLength) {
return (T[]) copyOf(original, newLength, original.getClass());
}
@HotSpotIntrinsicCandidate
public static <T,U> T[] copyOf(U[] original, int newLength, Class<? extends T[]> newType) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T[] copy = ((Object)newType == (Object)Object[].class)
? (T[]) new Object[newLength]
: (T[]) Array.newInstance(newType.getComponentType(), newLength);
System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0,
Math.min(original.length, newLength));
return copy;
}
Class newType = Object[].class; System.out.println(newType.getComponentType()); // class java.lang.Object
数组的class对象的getComponentType()返回其元素组成类型, System.arraycopy进行数组复制(浅复制,复制引用)
public static void main(String[] args) { User[] users = new User[]{ new User(1, "admin", "admin@qq.com"), new User(2, "maco", "maco@qq.com"), new User(3, "kitty", "kitty@163.com") }; Object[] objects = users; System.out.println(objects.getClass()); // class [Ltest.User; objects = new Object[users.length]; System.arraycopy(users, 0, objects, 0, Math.min(users.length, objects.length)); System.out.println(objects.getClass()); // class [Ljava.lang.Object; System.out.println(objects[0] == users[0]); // true }
5. 参考
由ArrayList构造函数源码引出的问题 by zhizhizhiyuan
c.toArray might not return Object[]? by 晚起的虫儿
System.arraycopy()方法详解 by qq_32440951
c.toArray might not return Object[]? by 晚起的虫儿
System.arraycopy()方法详解 by qq_32440951
6.
完






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix