使用Flask构建机器学习模型API
1. Python环境设置和Flask基础

-
使用“Anaconda”创建一个虚拟环境。如果你需要在Python中创建你的工作流程,并将依赖项分离出来,或者共享环境设置,“Anaconda”发行版是一个不错的选择。
- 安装here
wget https://repo.continuum.io/miniconda/Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.shbash Miniconda3-latest-Linux-x86_64.shsource .bashrcconda create --name <environment-name> python=3.6source activate <environment-name>- 安装必要的Python包:
flask&gunicorn.
-
尝试一个简单的“Flask”Hello-World应用程序,并使用
gunicorn提供服务:-
hello-world.py -
编写代码:
from flask import Flask app = Flask(__name__) @app.route('/users/<string:username>') def hello_world(username=None): return("Hello {}!".format(username)) -
保存
-
gunicorn --bind 0.0.0.0:8000 hello-world:app -
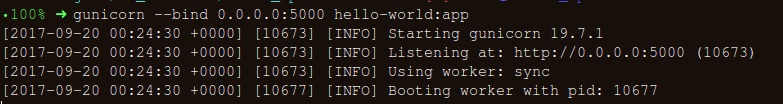
如果你得到了下面的响应,你就走上了正确的道路:
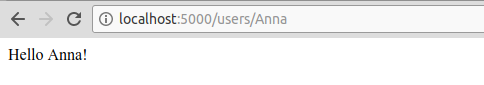
- 在浏览器上访问
https://localhost:8000/users/any-name
-
您编写了第一个Flask应用程序。正如您现在通过几个简单的步骤所体验到的,我们能够创建可以在本地访问的web端点。未来的路也很简单。
使用“Flask”,我们可以很容易地封装我们的机器学习模型,并将它们作为Web api来使用。此外,如果我们想创建更复杂的web应用程序(包括JavaScript ' gasps '),我们只需要进行一些修改。
2. 构建机器学习模型
-
以机器学习比赛为例: Loan Prediction Competition. 主要目标是设置预处理管道和创建ML模型,目标是在部署时简化ML预测。
-
数据:链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1VjqNZxvdKm0G5iBtTs-4TA 提取码:n5ag
import os
import json
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.externals import joblib
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split, GridSearchCV
from sklearn.base import BaseEstimator, TransformerMixin
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
data = pd.read_csv('../data/training.csv')
list(data.columns)
['Loan_ID',
'Gender',
'Married',
'Dependents',
'Education',
'Self_Employed',
'ApplicantIncome',
'CoapplicantIncome',
'LoanAmount',
'Loan_Amount_Term',
'Credit_History',
'Property_Area',
'Loan_Status']
data.shape
(614, 13)
- Finding out the
null/Nanvalues in the columns:
for _ in data.columns:
print("The number of null values in:{} == {}".format(_, data[_].isnull().sum()))
The number of null values in:Loan_ID == 0
The number of null values in:Gender == 13
The number of null values in:Married == 3
The number of null values in:Dependents == 15
The number of null values in:Education == 0
The number of null values in:Self_Employed == 32
The number of null values in:ApplicantIncome == 0
The number of null values in:CoapplicantIncome == 0
The number of null values in:LoanAmount == 22
The number of null values in:Loan_Amount_Term == 14
The number of null values in:Credit_History == 50
The number of null values in:Property_Area == 0
The number of null values in:Loan_Status == 0
- Next step is creating
trainingandtestingdatasets:
pred_var = ['Gender','Married','Dependents','Education','Self_Employed','ApplicantIncome','CoapplicantIncome',\
'LoanAmount','Loan_Amount_Term','Credit_History','Property_Area']
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(data[pred_var], data['Loan_Status'], \
test_size=0.25, random_state=42)
- To make sure that the
pre-processing stepsare followed religiously even after we are done with experimenting and we do not miss them while predictions, we'll create a custom pre-processing Scikit-learnestimator.
To follow the process on how we ended up with this estimator, read up on this notebook
from sklearn.base import BaseEstimator, TransformerMixin
class PreProcessing(BaseEstimator, TransformerMixin):
"""Custom Pre-Processing estimator for our use-case
"""
def __init__(self):
pass
def transform(self, df):
"""Regular transform() that is a help for training, validation & testing datasets
(NOTE: The operations performed here are the ones that we did prior to this cell)
"""
pred_var = ['Gender','Married','Dependents','Education','Self_Employed','ApplicantIncome',\
'CoapplicantIncome','LoanAmount','Loan_Amount_Term','Credit_History','Property_Area']
df = df[pred_var]
df['Dependents'] = df['Dependents'].fillna(0)
df['Self_Employed'] = df['Self_Employed'].fillna('No')
df['Loan_Amount_Term'] = df['Loan_Amount_Term'].fillna(self.term_mean_)
df['Credit_History'] = df['Credit_History'].fillna(1)
df['Married'] = df['Married'].fillna('No')
df['Gender'] = df['Gender'].fillna('Male')
df['LoanAmount'] = df['LoanAmount'].fillna(self.amt_mean_)
gender_values = {'Female' : 0, 'Male' : 1}
married_values = {'No' : 0, 'Yes' : 1}
education_values = {'Graduate' : 0, 'Not Graduate' : 1}
employed_values = {'No' : 0, 'Yes' : 1}
property_values = {'Rural' : 0, 'Urban' : 1, 'Semiurban' : 2}
dependent_values = {'3+': 3, '0': 0, '2': 2, '1': 1}
df.replace({'Gender': gender_values, 'Married': married_values, 'Education': education_values, \
'Self_Employed': employed_values, 'Property_Area': property_values, \
'Dependents': dependent_values}, inplace=True)
return df.as_matrix()
def fit(self, df, y=None, **fit_params):
"""Fitting the Training dataset & calculating the required values from train
e.g: We will need the mean of X_train['Loan_Amount_Term'] that will be used in
transformation of X_test
"""
self.term_mean_ = df['Loan_Amount_Term'].mean()
self.amt_mean_ = df['LoanAmount'].mean()
return self
- Convert
y_train&y_testtonp.array:
y_train = y_train.replace({'Y':1, 'N':0}).as_matrix()
y_test = y_test.replace({'Y':1, 'N':0}).as_matrix()
We'll create a pipeline to make sure that all the preprocessing steps that we do are just a single scikit-learn estimator.
pipe = make_pipeline(PreProcessing(),
RandomForestClassifier())
pipe
Pipeline(memory=None,
steps=[('preprocessing', PreProcessing()), ('randomforestclassifier', RandomForestClassifier(bootstrap=True, class_weight=None, criterion='gini',
max_depth=None, max_features='auto', max_leaf_nodes=None,
min_impurity_decrease=0.0, min_impurity_split=None,
min_samples_leaf=1, min_samples_split=2,
min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0, n_estimators='warn', n_jobs=None,
oob_score=False, random_state=None, verbose=0,
warm_start=False))])
To search for the best hyper-parameters (degree for PolynomialFeatures & alpha for Ridge), we'll do a Grid Search:
- Defining
param_grid:
param_grid = {"randomforestclassifier__n_estimators" : [10, 20, 30],
"randomforestclassifier__max_depth" : [None, 6, 8, 10],
"randomforestclassifier__max_leaf_nodes": [None, 5, 10, 20],
"randomforestclassifier__min_impurity_split": [0.1, 0.2, 0.3]}
- Running the
Grid Search:
grid = GridSearchCV(pipe, param_grid=param_grid, cv=3)
- Fitting the training data on the
pipeline estimator:
grid.fit(X_train, y_train)
GridSearchCV(cv=3, error_score='raise-deprecating',
estimator=Pipeline(memory=None,
steps=[('preprocessing', PreProcessing()), ('randomforestclassifier', RandomForestClassifier(bootstrap=True, class_weight=None, criterion='gini',
max_depth=None, max_features='auto', max_leaf_nodes=None,
min_impurity_decrease=0.0, min_impu...bs=None,
oob_score=False, random_state=None, verbose=0,
warm_start=False))]),
fit_params=None, iid='warn', n_jobs=None,
param_grid={'randomforestclassifier__n_estimators': [10, 20, 30], 'randomforestclassifier__max_depth': [None, 6, 8, 10], 'randomforestclassifier__max_leaf_nodes': [None, 5, 10, 20], 'randomforestclassifier__min_impurity_split': [0.1, 0.2, 0.3]},
pre_dispatch='2*n_jobs', refit=True, return_train_score='warn',
scoring=None, verbose=0)
- Let's see what parameter did the Grid Search select:
print("Best parameters: {}".format(grid.best_params_))
Best parameters: {'randomforestclassifier__max_depth': None, 'randomforestclassifier__max_leaf_nodes': None, 'randomforestclassifier__min_impurity_split': 0.3, 'randomforestclassifier__n_estimators': 30}
- Let's score:
print("Validation set score: {:.2f}".format(grid.score(X_test, y_test)))
Validation set score: 0.79
3. 保存机器学习模型:序列化和反序列化
# 保存模型
from sklearn.externals import joblib
joblib.dump(grid, 'loan_model.pkl')
['loan_model.pkl']
# 加载模型
grid = joblib.load('loan_model.pkl')
# 读取测试数据
test_df = pd.read_csv('../data/test.csv', encoding="utf-8-sig")
test_df = test_df.head()
test_df
| Loan_ID | Gender | Married | Dependents | Education | Self_Employed | ApplicantIncome | CoapplicantIncome | LoanAmount | Loan_Amount_Term | Credit_History | Property_Area | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | LP001015 | Male | Yes | 0 | Graduate | No | 5720 | 0 | 110.0 | 360.0 | 1.0 | Urban |
| 1 | LP001022 | Male | Yes | 1 | Graduate | No | 3076 | 1500 | 126.0 | 360.0 | 1.0 | Urban |
| 2 | LP001031 | Male | Yes | 2 | Graduate | No | 5000 | 1800 | 208.0 | 360.0 | 1.0 | Urban |
| 3 | LP001035 | Male | Yes | 2 | Graduate | No | 2340 | 2546 | 100.0 | 360.0 | NaN | Urban |
| 4 | LP001051 | Male | No | 0 | Not Graduate | No | 3276 | 0 | 78.0 | 360.0 | 1.0 | Urban |
# 使用模型进行预测
grid.predict(test_df)
array([1, 1, 1, 1, 1], dtype=int64)
4. 使用Flask创建API
我们将保持文件夹结构尽可能简单:
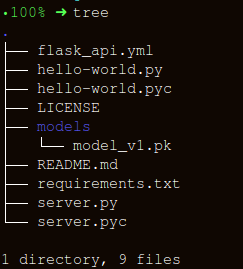
构建包装函数有三个重要部分, apicall():
-
获取请求数据
-
加载模型
-
预测并响应
HTTP消息由头和正文组成。作为标准,发送的主体内容大部分是“json”格式。我们将发送(' POST url-endpoint/ ')传入的数据作为批处理,以获得预测。
(NOTE: 您可以直接发送纯文本、XML、csv或图像,但为了格式的可互换性,建议使用“json”)
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.externals import joblib
from flask import Flask, jsonify, request
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/predict', methods=['POST'])
def apicall():
try:
# 获取test数据,可通过json,也可通过其他方式
test_json = request.get_json()
test = pd.read_json(test_json, orient='records')
test['Dependents'] = [str(x) for x in list(test['Dependents'])]
loan_ids = test['Loan_ID']
# 读取数据库形式
# sql = "select * from data where unif_cust_id=" + unif_cust_id
# conn = create_engine('mysql+mysqldb://test:test@localhost:3306/score_card?charset=utf8')
# data = pd.read_sql(sql, conn)
except Exception as e:
raise e
if test.empty:
return bad_request()
else:
# 加载模型
print("Loading the model...")
loaded_model = joblib.load('loan_model.pkl')
# 预测
print("The model has been loaded...doing predictions now...")
predictions = loaded_model.predict(test)
# 将预测结果存入DataFrame中
prediction_series = list(pd.Series(predictions))
final_predictions = pd.DataFrame(list(zip(loan_ids, prediction_series)))
# 返回接口响应
responses = jsonify(predictions=final_predictions.to_json(orient="records"))
responses.status_code = 200
return responses
@app.errorhandler(400)
def bad_request(error=None):
message = {
'status': 400,
'message': 'Bad Request: ' + request.url + '--> Please check your data payload...',
}
resp = jsonify(message)
resp.status_code = 400
return resp
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run()
* Serving Flask app "__main__" (lazy loading)
* Environment: production
WARNING: Do not use the development server in a production environment.
Use a production WSGI server instead.
* Debug mode: off
* Running on http://127.0.0.1:5000/ (Press CTRL+C to quit)
Loading the model...
The model has been loaded...doing predictions now...
127.0.0.1 - - [11/Nov/2019 10:05:09] "[37mPOST /predict HTTP/1.1[0m" 200 -
请求API
如果使用jupyter,请另启一个页面进行请求。
import json
import requests
import pandas as pd
"""Setting the headers to send and accept json responses
"""
header = {'Content-Type': 'application/json', \
'Accept': 'application/json'}
"""Reading test batch
"""
df = pd.read_csv('../data/test.csv', encoding="utf-8-sig")
df = df.head()
"""Converting Pandas Dataframe to json
"""
data = df.to_json(orient='records')
data
'[{"Loan_ID":"LP001015","Gender":"Male","Married":"Yes","Dependents":"0","Education":"Graduate","Self_Employed":"No","ApplicantIncome":5720,"CoapplicantIncome":0,"LoanAmount":110.0,"Loan_Amount_Term":360.0,"Credit_History":1.0,"Property_Area":"Urban"},{"Loan_ID":"LP001022","Gender":"Male","Married":"Yes","Dependents":"1","Education":"Graduate","Self_Employed":"No","ApplicantIncome":3076,"CoapplicantIncome":1500,"LoanAmount":126.0,"Loan_Amount_Term":360.0,"Credit_History":1.0,"Property_Area":"Urban"},{"Loan_ID":"LP001031","Gender":"Male","Married":"Yes","Dependents":"2","Education":"Graduate","Self_Employed":"No","ApplicantIncome":5000,"CoapplicantIncome":1800,"LoanAmount":208.0,"Loan_Amount_Term":360.0,"Credit_History":1.0,"Property_Area":"Urban"},{"Loan_ID":"LP001035","Gender":"Male","Married":"Yes","Dependents":"2","Education":"Graduate","Self_Employed":"No","ApplicantIncome":2340,"CoapplicantIncome":2546,"LoanAmount":100.0,"Loan_Amount_Term":360.0,"Credit_History":null,"Property_Area":"Urban"},{"Loan_ID":"LP001051","Gender":"Male","Married":"No","Dependents":"0","Education":"Not Graduate","Self_Employed":"No","ApplicantIncome":3276,"CoapplicantIncome":0,"LoanAmount":78.0,"Loan_Amount_Term":360.0,"Credit_History":1.0,"Property_Area":"Urban"}]'
"""POST <url>/predict
"""
resp = requests.post("http://127.0.0.1:5000/predict", \
data = json.dumps(data),\
headers= header)
resp.status_code
200
resp.json()
{'predictions': '[{"0":"LP001015","1":1},{"0":"LP001022","1":1},{"0":"LP001031","1":1},{"0":"LP001035","1":1},{"0":"LP001051","1":1}]'}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号