Ocelot网关+IdentityServer4实现API权限认证
Ocelot是一个用.NET Core实现并且开源的API网关,它功能强大,包括了:路由、请求聚合、服务发现、认证、鉴权、限流熔断、并内置了负载均衡器与Service Fabric、Butterfly Tracing集成。这些功能只都只需要简单的配置即可完成。
本文主要向大家简单介绍一下如何结合Ocelot网关和IdentityServer4鉴权服务实现API接口权限认证。关于IdentityServer4大家可以看下我之前的文章。
好了,下面开始进入正题。我们需要搭建两个API项目+一个IdentityServer4鉴权服务+一个Ocelot网关服务。本文以.NetCore2.2为例。
第一步,快速搭建两个WebAPI项目。
1.新建第一个WebApi项目:

2.配置API端口:6000
1)配置文件appsettings.json中增加端口配置节点。
{ "Http": { "Port": 6000 }, "Logging": { "LogLevel": { "Default": "Warning" } }, "AllowedHosts": "*" }
2)主程序Program.cs中添加端口监听:
1 public static IWebHostBuilder CreateWebHostBuilder(string[] args) => 2 WebHost.CreateDefaultBuilder(args) 3 .ConfigureKestrel(options => 4 { 5 //监听端口 6 var config = options.ApplicationServices.GetRequiredService<IConfiguration>(); 7 var port = config.GetValue<int>("Http:Port"); 8 options.ListenAnyIP(port); 9 }) 10 .UseStartup<Startup>();
3.启动项目
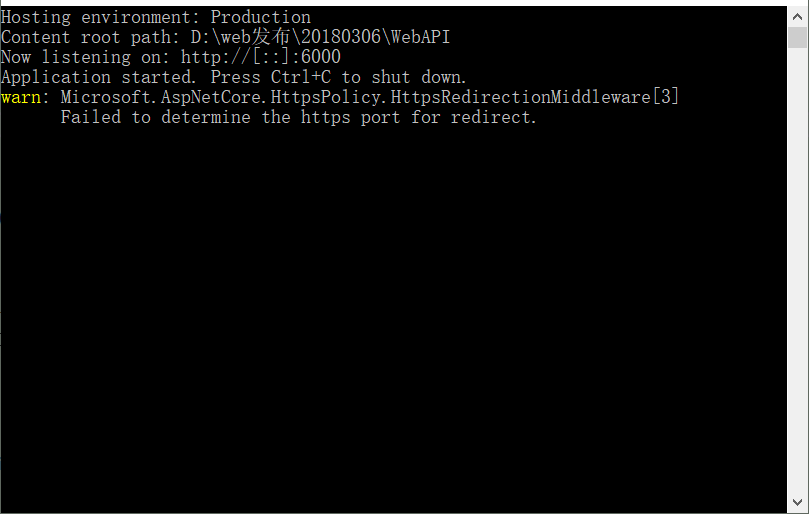
4.新建第二个WebAPI2项目,操作步骤同上,监听端口6002。
第二步,搭建IdentityServer4鉴权服务
1.新增项目Identity4
2.添加IdentityServer4 Nuget程序包。版本大家根据实际开发环境选择。
3.添加IdentityServer配置类
public class Config { /// <summary> /// 定义API资源 /// </summary> /// <returns></returns> public static IEnumerable<ApiResource> GetApiResources() { return new List<ApiResource> { new ApiResource("api1","测试API"), new ApiResource("api2","测试API2") }; } /// <summary> /// 定义客户端 /// </summary> /// <returns></returns> public static IEnumerable<Client> GetClients() { return new List<Client> { new Client{ ClientId="client", //授权方式为客户端验证,类型可参考GrantTypes枚举 AllowedGrantTypes=GrantTypes.ClientCredentials, //秘钥 ClientSecrets= { new Secret("secret".Sha256()) }, AllowedScopes=new []{ "api1" } }, new Client{ ClientId="client2", //授权方式为用户密码验证,类型可参考GrantTypes枚举 AllowedGrantTypes=GrantTypes.ResourceOwnerPassword, //秘钥 ClientSecrets= { new Secret("secret2".Sha256()) }, AllowedScopes=new []{ "api2", IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.OpenId, IdentityServerConstants.StandardScopes.Profile } } }; } /// <summary> /// 定义身份资源 /// </summary> /// <returns></returns> public static IEnumerable<IdentityResource> GetIdentityResources() { return new IdentityResource[] { new IdentityResources.OpenId(), new IdentityResources.Profile() }; } }
这里我们定义了两个API资源(就是我们上面创建的两个API项目):
a.第一个api我们授权client以客户端模式访问
b.第二个api我们授权client2以用户密码模式访问
4.针对用户密码访问模式,我们这里使用了自定义用户认证。(数据库用户密码校验)
我们实现接口:IResourceOwnerPasswordValidator,并通过实现接口方法ValidateAsyn()完成用户认证。
数据库访问我这里使用的SqlSugar ORM框架,在这里不多做介绍,感兴趣的同学可以去了解一下。
public class UserPasswordValidator : IResourceOwnerPasswordValidator { private readonly IDBContext dbcontext; public UserPasswordValidator(IDBContext _context) { dbcontext = _context; } public async Task ValidateAsync(ResourceOwnerPasswordValidationContext context) {
//通过sqlsugar ORM框架实现数据库访问 var user = await dbcontext.DB.Queryable<User>().Where(x => x.USER_NAME == context.UserName && x.PASSWORD == context.Password).FirstAsync(); if (user != null) { context.Result = new GrantValidationResult(subject: context.UserName, authenticationMethod: GrantType.ResourceOwnerPassword, claims: GetUserClaims(user)); } else context.Result = new GrantValidationResult(TokenRequestErrors.InvalidGrant, "账号或密码错误"); } /// <summary> /// 获取用户声明项 /// </summary> /// <returns></returns> private List<Claim> GetUserClaims(User user) { List<Claim> list = new List<Claim>(); list.Add(new Claim(JwtClaimTypes.Name, user.USER_NAME)); list.Add(new Claim(JwtClaimTypes.Id, user.USER_ID));
return list; } }
5.注册IdentityServer4服务并添加中间件。这里使用的就是我们上方定义的配置类以及自定义用户认证类
添加授权客户端:AddInMemoryClients(Config.GetClients())
添加API资源:AddInMemoryApiResources(Config.GetApiResources())
添加身份资源:AddInMemoryIdentityResources(Config.GetIdentityResources())
添加自定义用户认证:AddResourceOwnerValidator<UserPasswordValidator>();
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) { //注册服务 services.AddIdentityServer() .AddDeveloperSigningCredential() .AddInMemoryClients(Config.GetClients()) .AddInMemoryApiResources(Config.GetApiResources()) .AddInMemoryIdentityResources(Config.GetIdentityResources()) .AddResourceOwnerValidator<UserPasswordValidator>(); //添加数据库配置 services.AddDBContext(Configuration.GetValue<string>("ConnectionStrings:DB")); services.AddMvc().SetCompatibilityVersion(CompatibilityVersion.Version_2_2); } public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env) { if (env.IsDevelopment()) { app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage(); } //添加IdentityServer中间件 app.UseIdentityServer(); }
6.配置API端口:7000
1)配置文件appsettings.json中增加端口配置节点。
{
"Http": {
"Port": 7000
},
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Warning"
}
},
"AllowedHosts": "*"
}
2)主程序Program.cs中添加端口监听:
1 public static IWebHostBuilder CreateWebHostBuilder(string[] args) =>
2 WebHost.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
3 .ConfigureKestrel(options =>
4 {
5 //监听端口
6 var config = options.ApplicationServices.GetRequiredService<IConfiguration>();
7 var port = config.GetValue<int>("Http:Port");
8 options.ListenAnyIP(port);
9 })
10 .UseStartup<Startup>();
7.启动项目
第三步,搭建Ocelot网关服务
1.新建GateWay项目
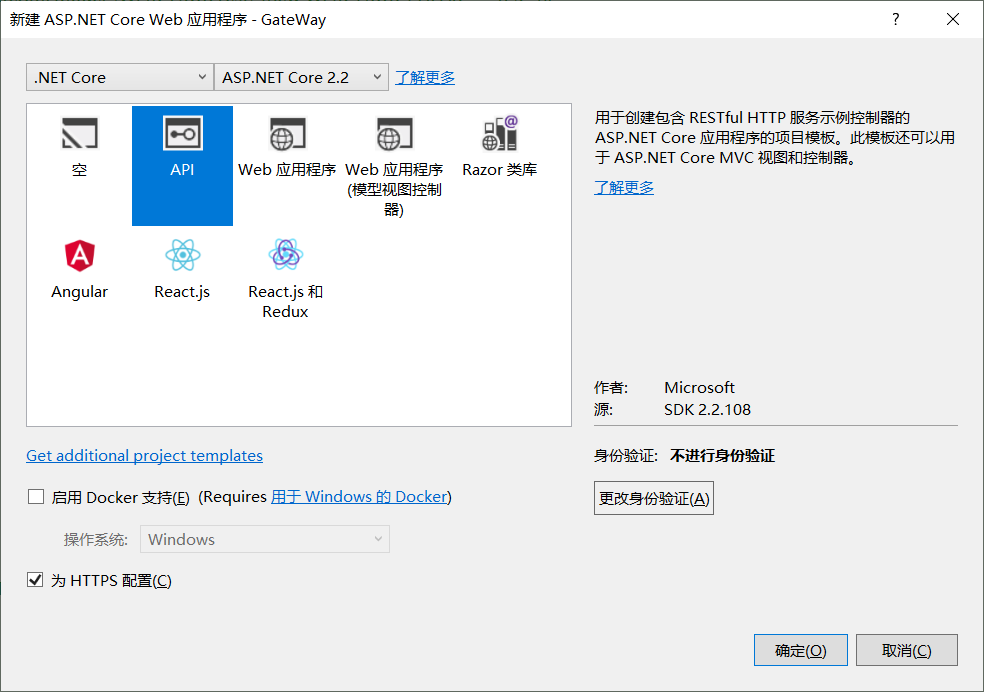
2.添加NuGet依赖包:Ocelot、Ocelot.Provider.Polly(服务质量与熔断配置需引用Polly)、IdentityServer4.AccessTokenValidation


3.添加网关配置文件ocelot.json(配置文件名称可自定义)。
路由是API网关最基本也是最核心的功能、ReRoutes下就是由多个路由节点组成。
{
"ReRoutes": [
]
}
注意:16.0版本开始之后,路由使用
Routes,否则会提示找不到路由。
几个主要节点说明:
- DownstreamPathTemplate:下游服务路径(实际接口请求url)
- DownstreamScheme:下游服务http schema
- DownstreamHostAndPorts:下游服务的地址(包含Host:IP地址 、 Port:端口号),如果使用LoadBalancer(负载均衡)的话这里可以填多项
- UpstreamPathTemplate: 上游服务路径(客户端输入的请求Url)
- UpstreamHttpMethod: 上游请求http方法,可使用数组,如:Get,Post等
- AuthenticationOptions:添加此节点表示改路由需要进行权限认证
- QosOptions:熔断,配置什么情况下停止将请求转发到下游服务。
{ "ReRoutes": [ { "DownstreamPathTemplate": "/{url}", "DownstreamScheme": "http", "DownstreamHostAndPorts": [ { "Host": "localhost", "Port": 6000 } ], "UpstreamPathTemplate": "/Service1/{url}", "UpstreamHttpMethod": [ "Get", "Post" ], "AuthenticationOptions": { "AuthenticationProviderKey": "auth", "AllowedScopes": [] }, "QoSOptions": { "ExceptionsAllowedBeforeBreaking": 3, "DurationOfBreak": 5, "TimeoutValue": 10000 } }, { "DownstreamPathTemplate": "/{url}", "DownstreamScheme": "http", "DownstreamHostAndPorts": [ { "Host": "localhost", "Port": 6002 } ], "UpstreamPathTemplate": "/Service2/{url}", "UpstreamHttpMethod": [ "Get", "Post" ], "AuthenticationOptions": { "AuthenticationProviderKey": "auth2", "AllowedScopes": [] }, "QoSOptions": { "ExceptionsAllowedBeforeBreaking": 3, "DurationOfBreak": 5, "TimeoutValue": 10000 } }, { "DownstreamPathTemplate": "/{url}", "DownstreamScheme": "http", "DownstreamHostAndPorts": [ { "Host": "localhost", "Port": 7000 } ], "UpstreamPathTemplate": "/auth/{url}", "UpstreamHttpMethod": [ "Get", "Post" ] } ], "GlobalConfiguration": { "BaseUrl": "", "RateLimitOptions": { "ClientWhitelist": [], "EnableRateLimiting": true, "Period": "1s", "PeriodTimespan": 1, "Limit": 1000 } } }
4.添加启用ocelot.json并配置端口号5000
public static IHostBuilder CreateHostBuilder(string[] args) => Host.CreateDefaultBuilder(args) .ConfigureAppConfiguration((context, builder) => {
//添加启用配置文件
builder.SetBasePath(context.HostingEnvironment.ContentRootPath); builder.AddJsonFile("ocelot.json", optional: true, reloadOnChange: true); }) .UseKestrel(options => { //动态配置默认端口号5000 var config = options.ApplicationServices.GetRequiredService<IConfiguration>(); var httpPort = config["Http:Port"]; options.ListenAnyIP(Convert.ToInt32(httpPort)); }); UseStartup<Startup>();
5.注册ocelot服务和Identity4认证
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) { //注册ocelot服务 services.AddOcelot().AddPolly(); //注册Identity4认证 services.AddAuthentication() .AddIdentityServerAuthentication("auth", option => { option.Authority = "http://localhost:7000"; option.RequireHttpsMetadata = false; option.ApiName = "api1"; }) .AddIdentityServerAuthentication("auth2", option => { option.Authority = "http://localhost:7000"; option.RequireHttpsMetadata = false; option.ApiName = "api2"; }); services.AddControllers(); } public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env) { if (env.IsDevelopment()) { app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage(); } //添加ocelot中间件 app.UseOcelot().Wait(); }
重点说明:
1.这里我们需要注意AddIdentityServerAuthentication中参数值auth和auth2分别对应了ocelot配置文件中两个API路由下鉴权节点AuthenticationOptions:AuthenticationProviderKey。
这里绑定的对应关系,实际上也就是说第一个api启用的auth对应的权限认证,并可以访问api1资源;第二个api启用auth2对应的权限认证,并可访问api2资源。
2.option.ApiName = "api1"这里指定可访问api资源。此处配置的API资源来自我们在IdentityServer4服务中配置类中定义的API资源。
6.启动项目

项目都搭建成功了,下面我们开始使用postman模拟请求,给大家演示一下效果。
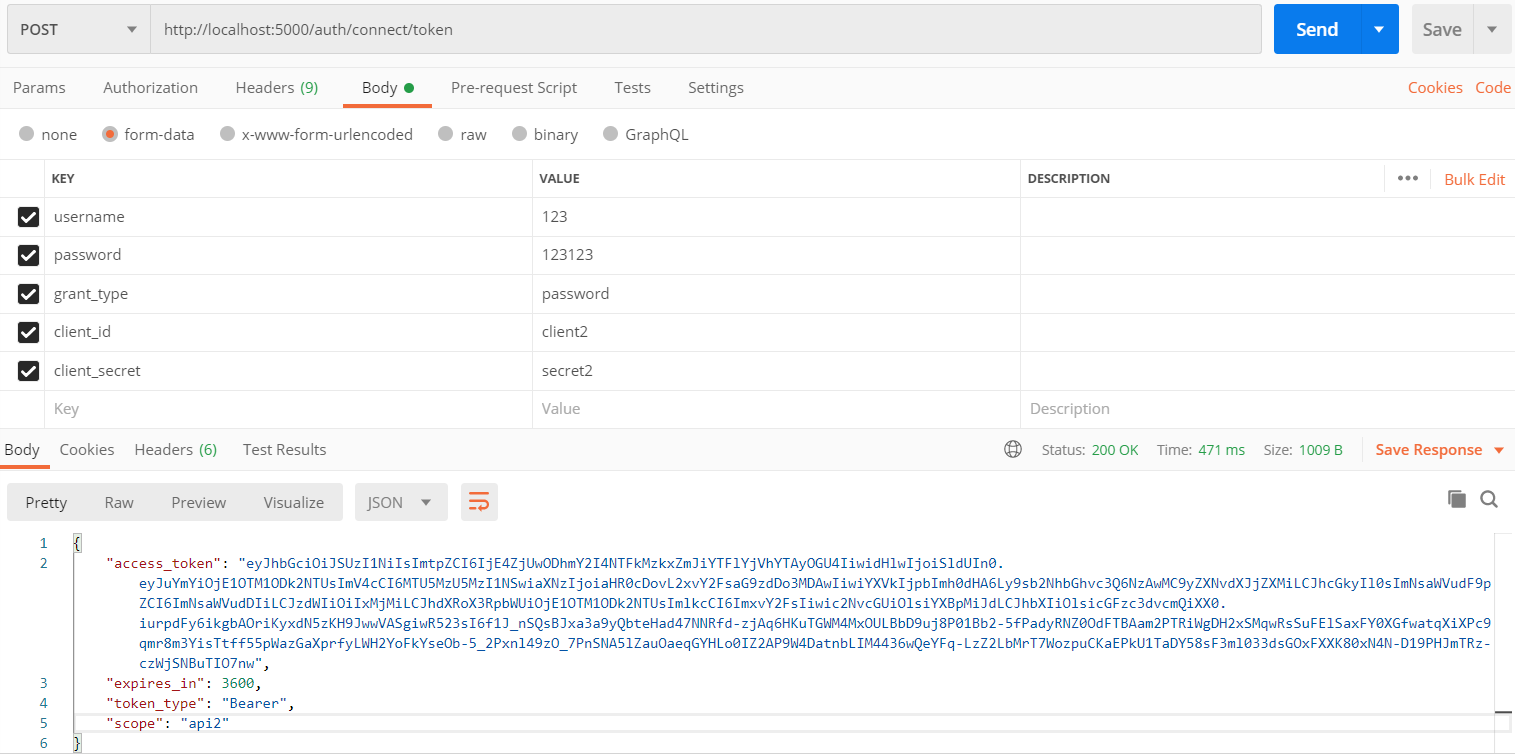
1.首先请求token:IdentityServer4框架为我们开放了token获取接口/connect/token
请求URL:http://locahost:5000/auth/connect/token 根据ocelot配置的路由上游模板auth/{url},此时会触发下游服务:localhost:7000/connect/token 其实也就是我们搭建的IdentityServer4服务接口地址。
第一种方式,客户端验证模式。
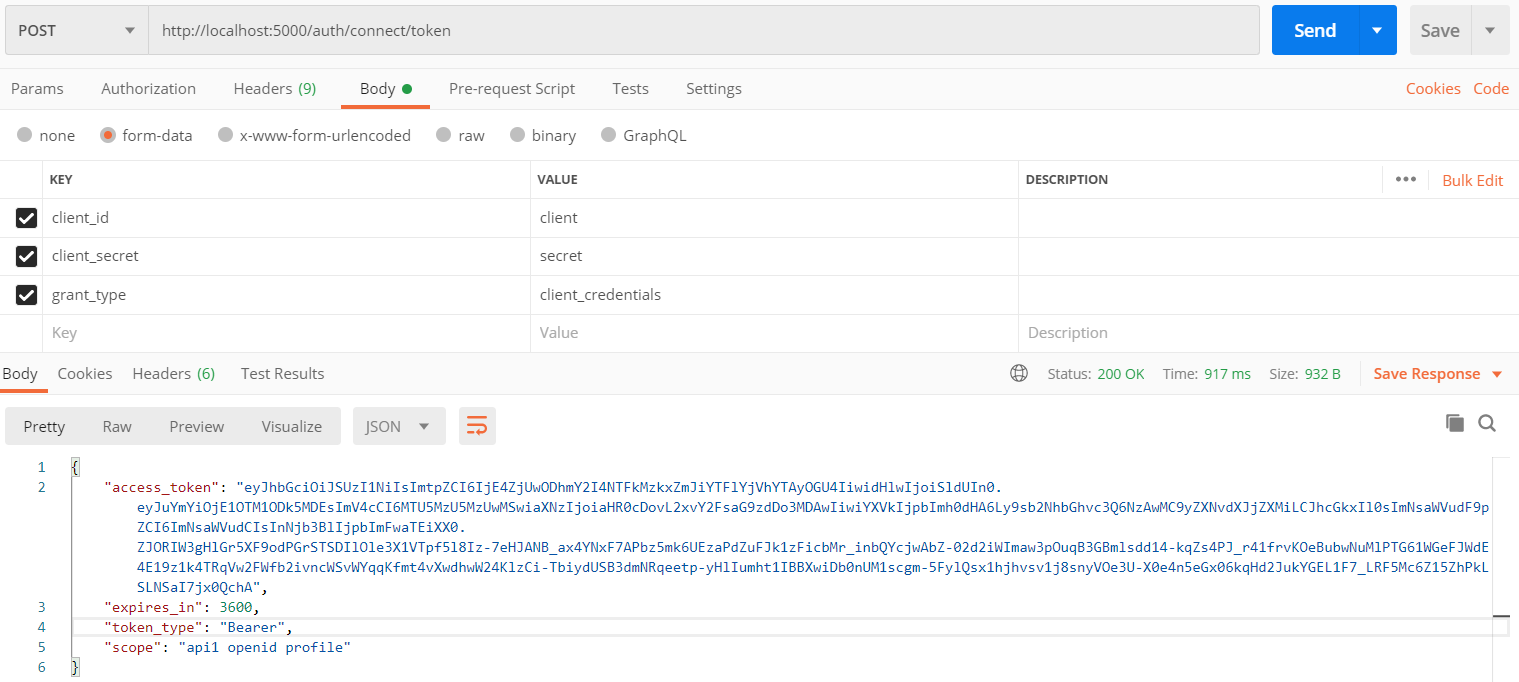
第二种方式,用户名密码模式
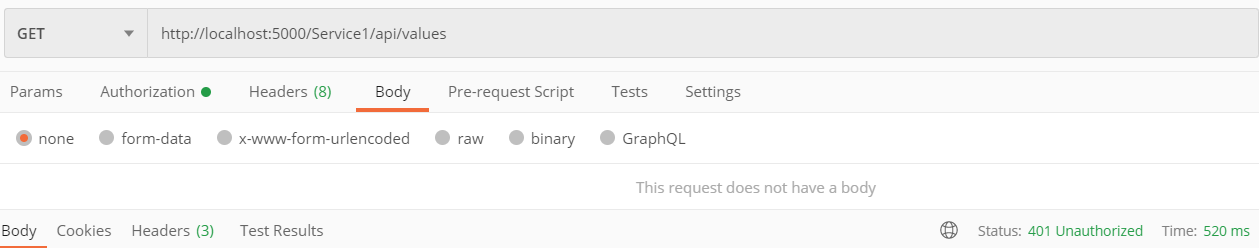
2.请求第一个API项目接口/api/values
请求URL:http://locahost:5000/Service1/api/values 根据ocelot配置的路由上游模板Service1/{url},此时会触发下游服务:localhost:6000/api/values 其实也就是我们搭建的第一个API服务接口地址。
此时,由于我们还没有权限,提示401
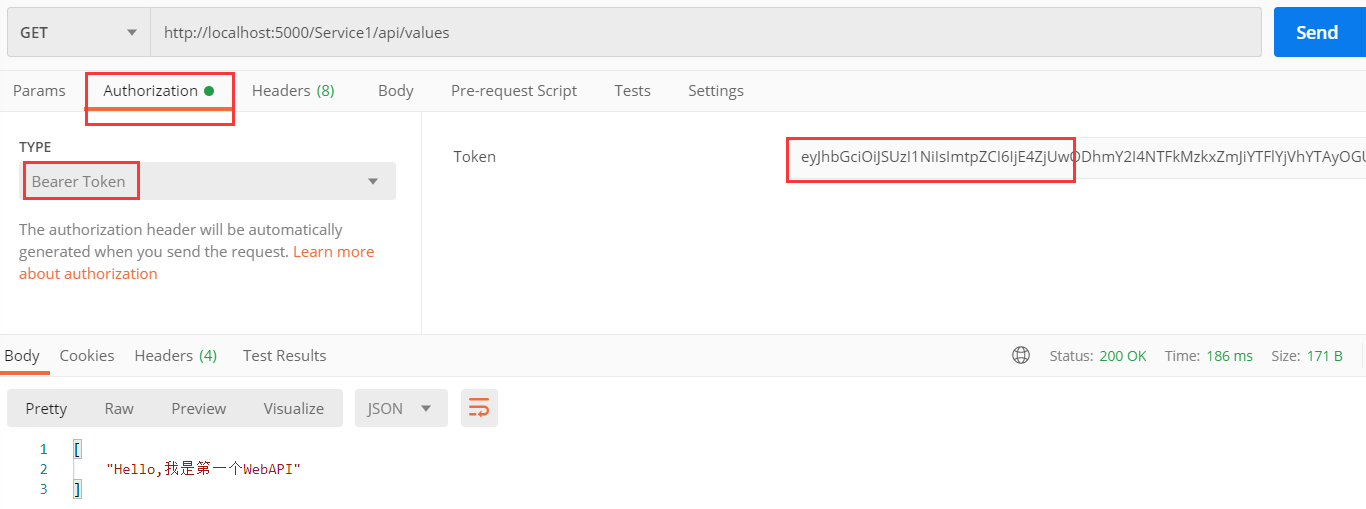
我们在请求头加入client获取的token,再次发起请求,请求成功。
试想一下,如果我们用client2获取的token,再次发起请求,会发生什么。。。可想而知,以失败告终。那这是为什么呢?
举个例子方便大家理解:
当我们以client身份获取token之后,访问service1下面的接口,触发Service1配置的auth认证,此认证允许访问资源api1;而刚好IdentityServer4服务允许client访问api1资源,请求成功;诚然,如果以client身份访问Service2则会失败,因为Service2配置的auth2认证,此认证允许访问资源api2,而IdentityServer4服务仅允许client访问api1资源。
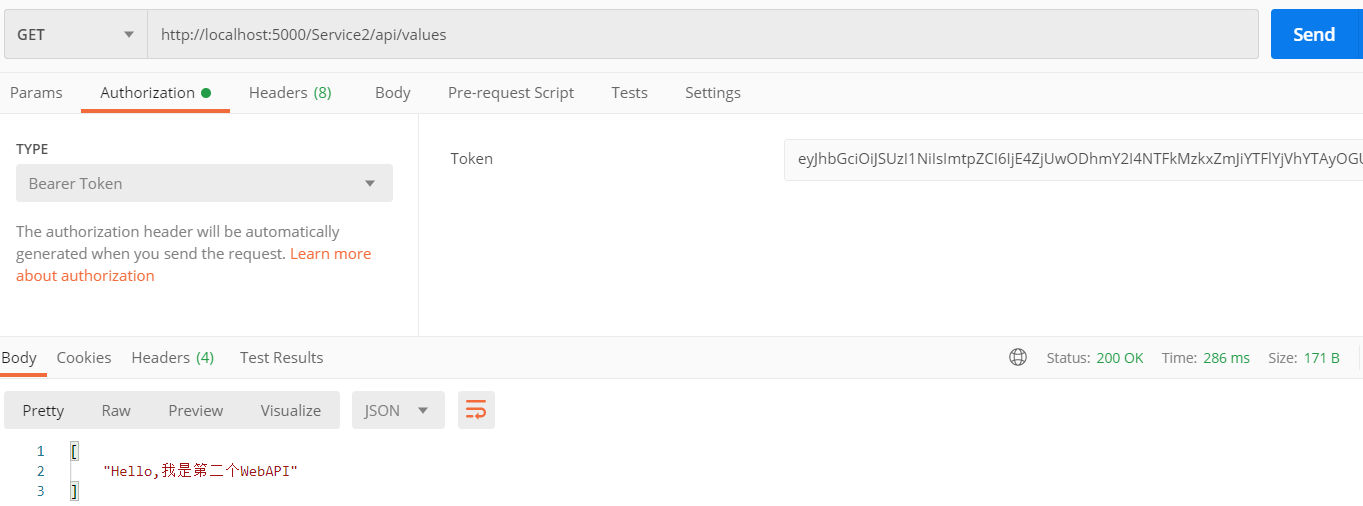
2.请求第一个API项目接口/api/values
请求URL:http://locahost:5000/Service2/api/values 根据ocelot配置的路由上游模板Service2/{url},此时会触发下游服务:localhost:6002/api/values 其实也就是我们搭建的第二个API服务接口地址。
此时,由于我们还没有权限,提示401.
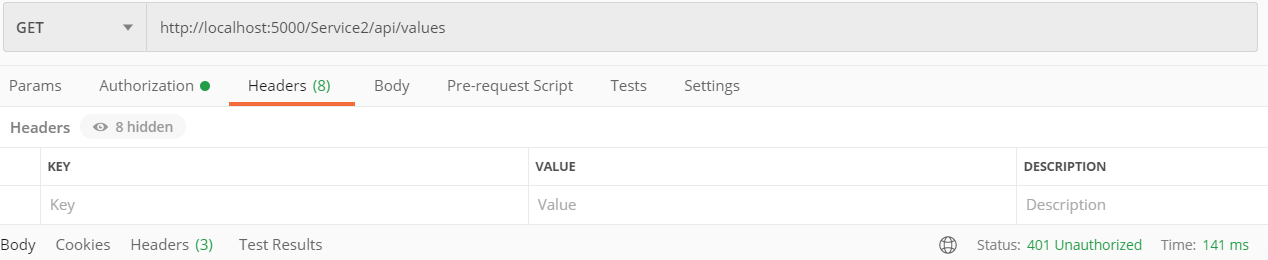
我们用client2获取的token,再次发起请求,请求成功。
想必到了这里,大家一定也有所想,有所言,欢迎大家交流。另外,大家不妨自己动手操作演示一下,或许更容易理解。






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构