net6 限制访问频率中间件 及 客户端缓存
十年河东,十年河西,莫欺少年穷
学无止境,精益求精
客户端缓存请参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/catcher1994/p/responsecaching.html
接着Json web Token 中间件,今天写了个简单的限速中间件
json web token 中间件地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/chenwolong/p/16444022.html
所谓限速中间件,主要作用用于限制用户频繁访问,防止多次高频率请求造成服务器压力大
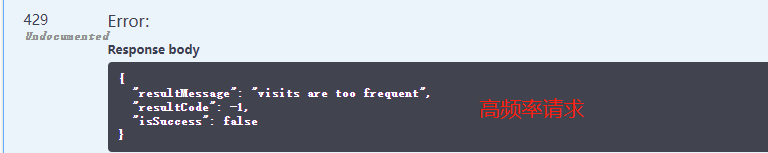
下面演示一个每秒钟同一个IP地址只能访问一次带有JWT授权的Action,一秒内多次访问,直接返回 visits are too frequent
代码如下:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http; using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc; using Microsoft.Extensions.Caching.Memory; using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging; using Newtonsoft.Json; using swapCommon; using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace swap.Middlewares { /// <summary> /// 限制用户频繁访问带有JwtToken授权 的 action中间件,一秒一次 /// </summary> public class LimitActionMiddlewares { private readonly RequestDelegate next; private readonly IHostingEnvironment environment; private readonly IMemoryCache memory; private int milliSeconds = 1000;//一秒 public LimitActionMiddlewares(RequestDelegate next, IHostingEnvironment environment , IMemoryCache memory) { this.next = next; this.environment = environment; this.memory = memory; } public async Task Invoke(HttpContext context) { //正式环境限速 if (environment.IsProduction()) { var ip = context.Connection.RemoteIpAddress.ToString(); string key = $"User_{ip}"; long? lastVisit = memory.Get<long?>(key); // if (context.Items["userdata"] == null) { await next.Invoke(context); } else { if (lastVisit == null || Environment.TickCount64 - lastVisit > milliSeconds) { memory.Set<long>(key, Environment.TickCount64, TimeSpan.FromSeconds(10));//避免长期不访问的用户占用服务器资源 await next.Invoke(context); } else { await Response(context, 429, "visits are too frequent"); } } } else { await next.Invoke(context); } } private async Task Response(HttpContext httpContext, int statusCode, string message) { httpContext.Response.StatusCode = statusCode; httpContext.Response.ContentType = "application/json; charset=utf-8"; var result = CommonBaseResponse.SetResponse(false, message); await httpContext.Response.WriteAsync(JsonConvert.SerializeObject(result)); } } }
服务注册时需引入缓存中间件
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) { services.AddResponseCaching(); //其他代码 }
引用中间件时
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env) { if (env.IsDevelopment()) { app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage(); } //注意中间件的引入顺序,jwt在前,limitAction在后 app.UseMiddleware<JwtMiddlewares>(); app.UseMiddleware<LimitActionMiddlewares>(); app.UseMiddleware<ExceptionMiddlewares>(); }
注意中间件的引入顺序,jwt在前,limitAction在后
代码解读
if(context.Items["userdata"] == null) { await next.Invoke(context); }
context.Items["userdata"] 是通过Jwt中间件进行赋值了,在一次请求中,它可以在各个中间件之间传递。
本中间件作用于需要JWT授权的Action访问,因此需要上述 if 判断
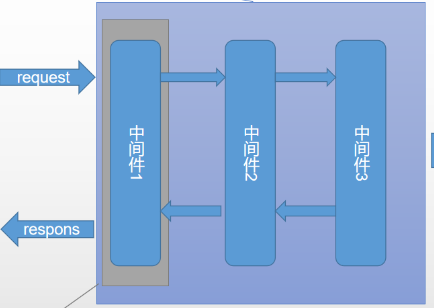
更深次的原因是:
由上图可知,一次请求,每个中间件都会被执行两次,两次执行过程所用时间小于1秒,如果不加上述 if 判断,在swagger初始化时,会报visits are too frequent 异常。
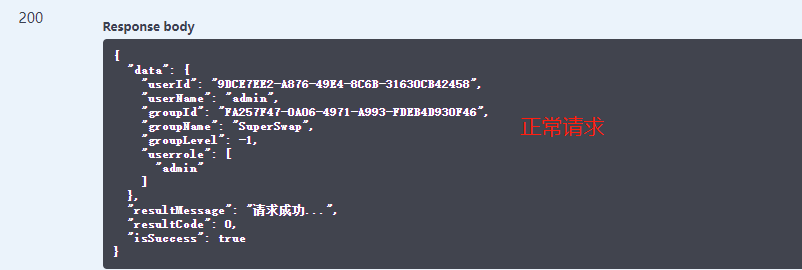
请求示例
@陈卧龙的博客



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号