单元测试学习
单元测试用法
引用方法
// import { mount } from '@vue/test-utils'
// 和 mount 一样,创建一个包含被挂载和渲染的 Vue 组件的 Wrapper,不同的是被存根的子组件
import { createLocalVue, shallowMount } from '@vue/test-utils'
- createLocalVue 创建测试 vue 环境
模板写法
describe('测试标题', () => {
// todo
it('段落标题', () => {
// todo
})
})
断言使用
toBe
- 判断测试的值是否精确匹配
it('1 + 1 === 2', () => {
expect(1 + 1).toBe(2);
});
toEqual
- 对象、数组里面的 key/value 依次判断是否一致
it('{c: "chen"} === {c: "chen"}', () => {
const obj1 = {c: "chen"};
const obj2 = {c: "chen"}
expect(obj1).toEqual(obj2);
});
toMatch
- 正则匹配字符串
it('/ting/.test("chentingjun") === true', () => {
const reg = new RegExp(/ting/)
const str = 'chentingjun'
expect(str).toMatch(reg)
})
.not
- 测试相反的用例
it('1 + 1 === 2', () => {
expect(1 + 1).not.toBe(3)
});
布尔值匹配器
- toBeNull 只匹配 null
- toBeUndefined 只匹配 undefined
- toBeDefined 与 toBeUndefined 相反,等于 not.toBeUndefined
- toBeTruthy 匹配任何 expect 语句为真
- toBeFalsy 匹配任何 expect 语句为假
test('null', () => {
const n = null;
expect(n).toBeNull();
expect(n).toBeDefined();
expect(n).not.toBeUndefined();
expect(n).not.toBeTruthy();
expect(n).toBeFalsy();
});
test('0', () => {
const z = 0;
expect(z).not.toBeNull();
expect(z).toBeDefined();
expect(z).not.toBeUndefined();
expect(z).not.toBeTruthy();
expect(z).toBeFalsy(); // 0 也是 false
});
test('false', () => {
const b = false;
expect(b).not.toBeNull();
expect(b).toBeDefined();
expect(b).not.toBeUndefined();
expect(b).not.toBeTruthy();
expect(b).toBeFalsy();
});
数字匹配器
- .toBeGreaterThan() - 大于
- .toBeGreaterThanOrEqual() 大于等于
- .toBeLessThan() - 小于
- .toBeLessThanOrEqual() - 小于等于
- .toBeCloseTo() - 浮点数比较
it('.toBeGreaterThan() --> 6 > 5', () => {
expect(6).toBeGreaterThan(5)
})
it('.toBeGreaterThanOrEqual() --> 5 >= 5', () => {
expect(5).toBeGreaterThanOrEqual(5)
})
it('.toBeLessThan() --> 5 < 6', () => {
expect(5).toBeLessThan(6)
})
it('.toBeLessThanOrEqual() --> 5 <= 5', () => {
expect(5).toBeLessThanOrEqual(5)
})
// 浮点数专用
it('.toBeCloseTo() --> 0.1 + 0.2 === 0.3', () => {
const value = 0.1 + 0.2; // 0.30000000000000004
// expect(value).toBe(0.3); // 这句会报错,因为 js 浮点数有舍入误差
expect(value).toBeCloseTo(0.3); // 这句可以运行
})
数组匹配器
- .toContain(item) - 判断数组是否包含特定子项
- .toContainEqual(item) - 判断数组中是否包含一个特定对象
// 只能用于子项为简单数据类型的数组
it('.toContain() -->["c", "t", "j"].toContain("t")', () => {
expect(["c", "t", "j"]).toContain("t")
})
// 即可用于简单数据类型,也可用于引用数据类型
it('.toContainEqual() -->[{c: "c"}, {t: "t"}, {j: "j"}].toContainEqual({t: "t"})', () => {
expect([{ c: "c" }, { t: "t" }, { j: "j" }]).toContainEqual({ t: "t" })
})
对象匹配器
- .toMatchObject(object) - 判断一个对象嵌套的 key 下面的 value 类型
- .toHaveProperty(keyPath, value) - 判断在指定的 path 下是否有这个属性
const ctj = {
age: 28,
name: 'chentingjun',
isBoy: true,
like: [{ name: 'game', }, { name: '小说' }]
}
it('.toMatchObject(object)', () => {
const other = {
age: 28,
isBoy: true,
}
expect(ctj).toMatchObject(other)
})
// 判断在指定的 path 下是否有这个属性,嵌套的 path 可以用 '.'分割,也可以用数组。
it('.toHaveProperty(keyPath, value)', () => {
expect(ctj).toHaveProperty('isBoy')
expect(ctj).toHaveProperty('isBoy', true)
expect(ctj).not.toHaveProperty('money')
expect(ctj).toHaveProperty('like.0.name', 'game')
expect(ctj).not.toHaveProperty('like.0.name', '小说')
// 也可以拆成数组 deep
expect(ctj).toHaveProperty(['like', '1', 'name'], '小说')
})
自定义匹配器
- 使用expect.extend将自己的匹配器添加到Jest。自定义匹配器需要返回一个包含两个key 的对象
const beloneCtj = [
1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 10
]
// 返回ctj所拥有的且符合条件值
const beloneToCtj = (received, expected) => {
let expectedList = []
if (expected instanceof Array) {
expectedList = [...expected]
} else {
expectedList = [expected]
}
const result = {
pass: false,
message: () => `${received} 必须全部找齐才算对哦~`,
}
const list = []
beloneCtj.forEach(item => {
if (item % received === 0) {
list.push(item)
}
})
if (list.sort().join('') === expectedList.sort().join('')) {
result.pass = true
}
return result
}
expect.extend({ beloneToCtj })
it('[2,8,10] is right', () => {
expect(5).beloneToCtj([5, 10])
expect(2).beloneToCtj([2, 8, 10])
})
其他 jest Expect 方法
- toThrow - 要测试的特定函数会在调用时抛出一个错误
- .resolves 和 .rejects - 用来测试 promise
- .toHaveBeenCalled() - 用来判断一个函数是否被调用过
- .toHaveBeenCalledTimes(number) - 判断函数被调用过几次
- .lastCalledWith
- .toBeCalledWith
- .toHaveBeenCalledWith
- .toHaveBeenLastCalledWith
- .toBeInstanceOf
- .toMatchSnapshot
- .toThrowError
- .toThrowErrorMatchingSnapshot
实例
常用资料页面-新增常用资料:
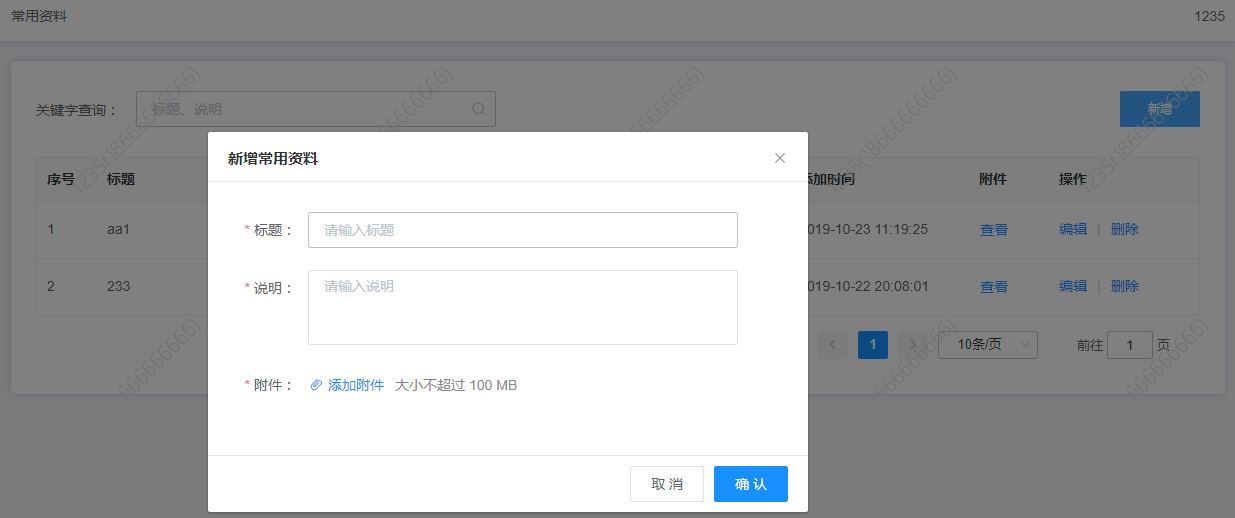

> 创建测试文件 common-data.spec.js
import { createLocalVue, shallowMount } from '@vue/test-utils'
import CommonData from '@/views/pages/common-data'
import beforeTest from './lib/before-test'
describe('新增常用资料', () => {
// todo
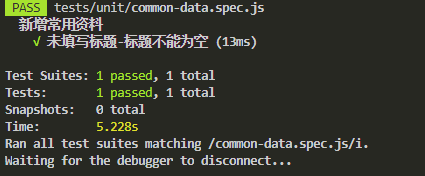
it('未填写标题-标题不能为空', () => {
// todo
})
})
> 标题未填写,应该提示【标题不能为空】
- 准备
// 创建 vue 实例(shallowMount 不会渲染出子组件,mount 会渲染出子组件到父组件上)
const localVue = createLocalVue()
// 安装 vue plugins 及一些加到 vue 实例上的属性
localVue.use(beforeTest)
// 挂载组件,也可以加 store 和 router
const wrapper = shallowMount(CommonData, { localVue })
const { vm } = wrapper
// 弹出对话框
vm.editCommonData()
> ###### shallowMount 渲染的代码【自定义标签未解析渲染】
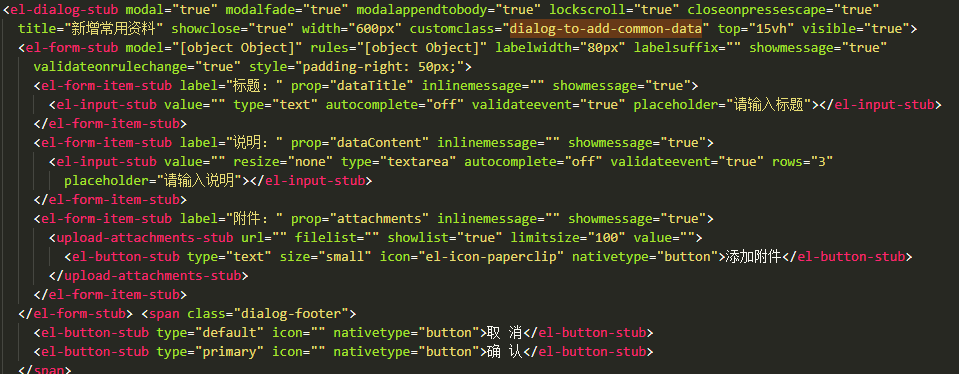
> ####### mount 渲染的代码【已解析到 dom 上】
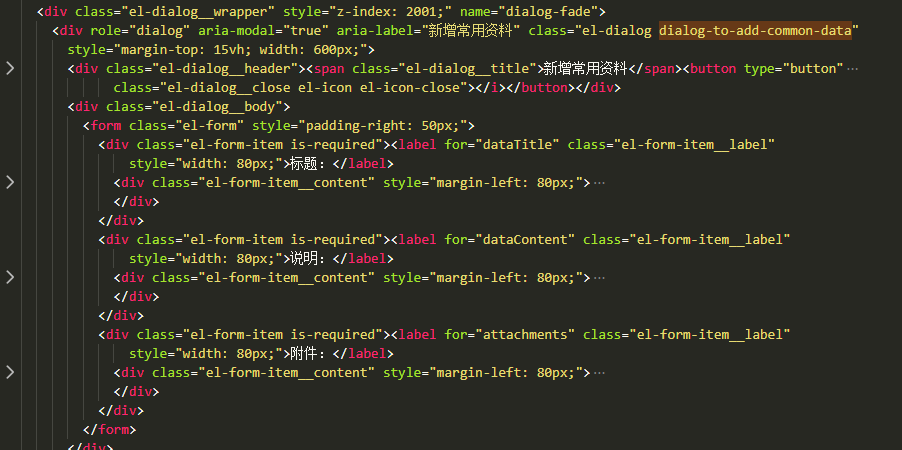
所以如果需要渲染的话,要用 mount 并且一些相关的如 store 或引用的文件也要在测试文件中引入并挂载
const validateTitle = new RegExp(/el-form-item__error.*?>\s*标题不能为空/)
it('未填写标题-标题不能为空', () => {
// todo
const { commonForm } = vm
wrapper.setData({
commonForm: {
...commonForm,
// 标题置空
dataTitle: '',
}
})
vm.$refs.commonForm.validate()
const wrapperHtml = wrapper.html()
// 正则匹配有提示‘标题不能为空’则通过
expect(wrapperHtml).toMatch(validateTitle)
})



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号