目标检测数据增强之mosaic
1、技术原理
Mosaic是YOLOV4中提出的新方法,适用于目标检测,主要思想是将四张图片进行拼接到一张图上作为训练样本。由于Mosaic用于目标检测,进行拼接时目标框的坐标也要做相应的变化。Mosaic的主要操作如下:
- 对每一张图进行随机裁剪得到A;crop的目标是选择原图的某一块区域,而不是全图进行后续的拼接;
- 将A进行resize到输出图大小得到B;目标是统一坐标系尺寸,方便后续拼接;坐标框会进行相应的缩放
- 将B随机裁剪一块指定大小的区域C;
- 将C粘贴到输出图相应的位置;此时只需要坐标平移就可以调整坐标框
2、增强图片展示

从图中可以看出,Mosaic合并后的坐标并不是很理想,比如正负样本分配时,往往会将预测框与groundTruth之间的IOU小于一定阈值的视为负样本。而经过Mosaic拼接的训练样本,groundTruth box的大小已经被裁剪,那么原图上为负样本的预测框与裁剪后的groundTruth box之间的IOU可能就满足了IOU阈值条件而被视为正样本。因此,可能存在这么一种情况,同样大小的框,经Mosaic操作被视为正样本,没经Mosaic操作的视为负样本;当然,Mosaic操作的图片都经过了resize,大小在一定程度上都发生了改变,groundTruth box也发生了变化,但这只是相当于将一个原本被视为负样本的box经过resize后就变成了正样本的box。
3、Mosaic算法
Mosaic的源代码已在GitHub上开源,详情可以点击下方卡片查看。
在这里仅展示核心代码。
3.1、主程序

class Yolo_dataset(Dataset): def __init__(self, label_path, cfg, train=True): pass#此处忽略 def __len__(self): return len(self.truth.keys()) def __getitem__(self, index): if not self.train: return self._get_val_item(index) img_path = self.imgs[index] bboxes = np.array(self.truth.get(img_path), dtype=np.float) img_path = os.path.join(self.cfg.dataset_dir, img_path) use_mixup = self.cfg.mixup if random.randint(0, 1): use_mixup = 0 if use_mixup == 3: min_offset = 0.2 # cut_x与cut_y相当于在输出图片上定义一点,然后沿着这点画十字,就将图片分成四个区域了 cut_x = random.randint(int(self.cfg.w * min_offset), int(self.cfg.w * (1 - min_offset))) cut_y = random.randint(int(self.cfg.h * min_offset), int(self.cfg.h * (1 - min_offset))) r1, r2, r3, r4, r_scale = 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 dhue, dsat, dexp, flip, blur = 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 gaussian_noise = 0 out_img = np.zeros([self.cfg.h, self.cfg.w, 3])#定义最后输出的图片(就是上面定义中心点的图片),大小都在配置文件中。 out_bboxes = []#输出的标注框 for i in range(use_mixup + 1): if i != 0: img_path = random.choice(list(self.truth.keys()))#随机抽取一张图片 bboxes = np.array(self.truth.get(img_path), dtype=np.float)#得到改张图片的bboxes img_path = os.path.join(self.cfg.dataset_dir, img_path) img = cv2.imread(img_path) img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) if img is None: continue oh, ow, oc = img.shape#当前图片的shape dh, dw, dc = np.array(np.array([oh, ow, oc]) * self.cfg.jitter, dtype=np.int)#cfg.jitter就是一个缩放因子,限制crop的尺度 #图片增强 dhue = rand_uniform_strong(-self.cfg.hue, self.cfg.hue)#随机色调 dsat = rand_scale(self.cfg.saturation)#随机饱和度 dexp = rand_scale(self.cfg.exposure)#随机曝光 #原图第一次crop的坐标偏移 pleft = random.randint(-dw, dw) pright = random.randint(-dw, dw) ptop = random.randint(-dh, dh) pbot = random.randint(-dh, dh) flip = random.randint(0, 1) if self.cfg.flip else 0#随机翻转 swidth = ow - pleft - pright#当前图片裁剪后的宽,尚未发生裁剪 sheight = oh - ptop - pbot#当前图片裁剪后的高,尚未发生裁剪 #truth就是box的坐标,box坐标经历了两次调整:[1]原图crop后坐标调整;[2]crop后图片放大到(self.cfg.w, self.cfg.h),坐标做相应的调整。 truth, min_w_h = fill_truth_detection(bboxes, self.cfg.boxes, self.cfg.classes, flip, pleft, ptop, swidth, sheight, self.cfg.w, self.cfg.h) #图片增强,原图先crop后resize到(self.cfg.w, self.cfg.h),此时图片才实施裁剪 ai = image_data_augmentation(img, self.cfg.w, self.cfg.h, pleft, ptop, swidth, sheight, flip, dhue, dsat, dexp, gaussian_noise, blur, truth) if use_mixup == 0: out_img = ai out_bboxes = truth if use_mixup == 1: if i == 0: old_img = ai.copy() old_truth = truth.copy() elif i == 1: out_img = cv2.addWeighted(ai, 0.5, old_img, 0.5) out_bboxes = np.concatenate([old_truth, truth], axis=0) elif use_mixup == 3: if flip: pleft,pright = pright,pleft #第二次crop的偏移量,crop的对象是ai left_shift = int(min(cut_x, max(0, (-int(pleft) * self.cfg.w / swidth)))) top_shift = int(min(cut_y, max(0, (-int(ptop) * self.cfg.h / sheight)))) right_shift = int(min((self.cfg.w - cut_x), max(0, (-int(pright) * self.cfg.w / swidth)))) bot_shift = int(min(self.cfg.h - cut_y, max(0, (-int(pbot) * self.cfg.h / sheight)))) #实施随机裁剪并粘贴到预定义的位置 out_img, out_bbox = blend_truth_mosaic(out_img, ai, truth.copy(), self.cfg.w, self.cfg.h, cut_x, cut_y, i, left_shift, right_shift, top_shift, bot_shift) out_bboxes.append(out_bbox) if use_mixup == 3: out_bboxes = np.concatenate(out_bboxes, axis=0)#合并四张图留存下来的坐标 out_bboxes1 = np.zeros([self.cfg.boxes, 5]) out_bboxes1[:min(out_bboxes.shape[0], self.cfg.boxes)] = out_bboxes[:min(out_bboxes.shape[0], self.cfg.boxes)]#只保留一定数量的框 return out_img, out_bboxes1
3.2、裁剪及resize后坐标的调整

def fill_truth_detection(bboxes, num_boxes, classes, flip, dx, dy, sx, sy, net_w, net_h): if bboxes.shape[0] == 0: return bboxes, 10000 np.random.shuffle(bboxes) bboxes[:, 0] -= dx#由于原图被裁剪了,框的坐标当然也要做相应的变化 bboxes[:, 2] -= dx bboxes[:, 1] -= dy bboxes[:, 3] -= dy #被剪后的图片,框的坐标在图片外的进行截断 bboxes[:, 0] = np.clip(bboxes[:, 0], 0, sx)#横坐标不小于0,不大于裁剪后图片的宽 bboxes[:, 2] = np.clip(bboxes[:, 2], 0, sx) bboxes[:, 1] = np.clip(bboxes[:, 1], 0, sy) bboxes[:, 3] = np.clip(bboxes[:, 3], 0, sy) #既然图片被裁剪,那么那些落在被裁剪图片之外的框就应该删除,注意这里使用的是and #对于半边被裁剪的还是留在裁剪后的图片中 out_box = list(np.where(((bboxes[:, 1] == sy) & (bboxes[:, 3] == sy)) | ((bboxes[:, 0] == sx) & (bboxes[:, 2] == sx)) | ((bboxes[:, 1] == 0) & (bboxes[:, 3] == 0)) | ((bboxes[:, 0] == 0) & (bboxes[:, 2] == 0)))[0]) list_box = list(range(bboxes.shape[0])) for i in out_box: list_box.remove(i) # 保留没裁剪图之内的框 bboxes = bboxes[list_box] if bboxes.shape[0] == 0: return bboxes, 10000 #类别肯定是[0,classes] bboxes = bboxes[np.where((bboxes[:, 4] < classes) & (bboxes[:, 4] >= 0))[0]] #限制框的数量,这个在cfg中有配置 if bboxes.shape[0] > num_boxes: bboxes = bboxes[:num_boxes] #对于长宽,取最小的那个 min_w_h = np.array([bboxes[:, 2] - bboxes[:, 0], bboxes[:, 3] - bboxes[:, 1]]).min() #裁剪后的图片变换成输出图片尺寸大小时,各个框的坐标 bboxes[:, 0] *= (net_w / sx) bboxes[:, 2] *= (net_w / sx) bboxes[:, 1] *= (net_h / sy) bboxes[:, 3] *= (net_h / sy) # 翻转就将左右坐标也进行翻转 if flip: temp = net_w - bboxes[:, 0] bboxes[:, 0] = net_w - bboxes[:, 2] bboxes[:, 2] = temp return bboxes, min_w_h
3.3、图片增强

def image_data_augmentation(mat, w, h, pleft, ptop, swidth, sheight, flip, dhue, dsat, dexp, gaussian_noise, blur, truth): try: img = mat oh, ow, _ = img.shape pleft, ptop, swidth, sheight = int(pleft), int(ptop), int(swidth), int(sheight) # crop src_rect = [pleft, ptop, swidth + pleft, sheight + ptop] # x1,y1,x2,y2 img_rect = [0, 0, ow, oh] new_src_rect = rect_intersection(src_rect, img_rect) # 交集 dst_rect = [max(0, -pleft), max(0, -ptop), max(0, -pleft) + new_src_rect[2] - new_src_rect[0], max(0, -ptop) + new_src_rect[3] - new_src_rect[1]] # cv2.Mat sized if (src_rect[0] == 0 and src_rect[1] == 0 and src_rect[2] == img.shape[0] and src_rect[3] == img.shape[1]): sized = cv2.resize(img, (w, h), cv2.INTER_LINEAR) else: #裁剪及resize cropped = np.zeros([sheight, swidth, 3]) cropped[:, :, ] = np.mean(img, axis=(0, 1)) cropped[dst_rect[1]:dst_rect[3], dst_rect[0]:dst_rect[2]] = \ img[new_src_rect[1]:new_src_rect[3], new_src_rect[0]:new_src_rect[2]] # resize sized = cv2.resize(cropped, (w, h), cv2.INTER_LINEAR) # flip if flip: # cv2.Mat cropped sized = cv2.flip(sized, 1) # 0 - x-axis, 1 - y-axis, -1 - both axes (x & y) # HSV augmentation # cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV, cv2.COLOR_RGB2HSV, cv2.COLOR_HSV2BGR, cv2.COLOR_HSV2RGB if dsat != 1 or dexp != 1 or dhue != 0: if img.shape[2] >= 3: hsv_src = cv2.cvtColor(sized.astype(np.float32), cv2.COLOR_RGB2HSV) # RGB to HSV hsv = cv2.split(hsv_src) hsv[1] *= dsat hsv[2] *= dexp hsv[0] += 179 * dhue hsv_src = cv2.merge(hsv) sized = np.clip(cv2.cvtColor(hsv_src, cv2.COLOR_HSV2RGB), 0, 255) # HSV to RGB (the same as previous) else: sized *= dexp if blur: if blur == 1: dst = cv2.GaussianBlur(sized, (17, 17), 0) # cv2.bilateralFilter(sized, dst, 17, 75, 75) else: ksize = (blur / 2) * 2 + 1 dst = cv2.GaussianBlur(sized, (ksize, ksize), 0) if blur == 1: img_rect = [0, 0, sized.cols, sized.rows] for b in truth: left = (b.x - b.w / 2.) * sized.shape[1] width = b.w * sized.shape[1] top = (b.y - b.h / 2.) * sized.shape[0] height = b.h * sized.shape[0] roi(left, top, width, height) roi = roi & img_rect dst[roi[0]:roi[0] + roi[2], roi[1]:roi[1] + roi[3]] = sized[roi[0]:roi[0] + roi[2], roi[1]:roi[1] + roi[3]] sized = dst if gaussian_noise: noise = np.array(sized.shape) gaussian_noise = min(gaussian_noise, 127) gaussian_noise = max(gaussian_noise, 0) cv2.randn(noise, 0, gaussian_noise) # mean and variance sized = sized + noise except: print("OpenCV can't augment image: " + str(w) + " x " + str(h)) sized = mat return sized
3.4、第二次crop并粘贴到指定区域

def blend_truth_mosaic(out_img, img, bboxes, w, h, cut_x, cut_y, i_mixup, left_shift, right_shift, top_shift, bot_shift): #第二次crop的偏移坐标 left_shift = min(left_shift, w - cut_x) top_shift = min(top_shift, h - cut_y) right_shift = min(right_shift, cut_x) bot_shift = min(bot_shift, cut_y) # 随机选取一块指定大小的块,然后粘贴到相应的区域 #img的图片格式是[h,w] if i_mixup == 0:#左上角 bboxes = filter_truth(bboxes, left_shift, top_shift, cut_x, cut_y, 0, 0) out_img[:cut_y, :cut_x] = img[top_shift:top_shift + cut_y, left_shift:left_shift + cut_x] if i_mixup == 1:#右上角 bboxes = filter_truth(bboxes, cut_x - right_shift, top_shift, w - cut_x, cut_y, cut_x, 0) out_img[:cut_y, cut_x:] = img[top_shift:top_shift + cut_y, cut_x - right_shift:w - right_shift] if i_mixup == 2:#左下角 bboxes = filter_truth(bboxes, left_shift, cut_y - bot_shift, cut_x, h - cut_y, 0, cut_y) out_img[cut_y:, :cut_x] = img[cut_y - bot_shift:h - bot_shift, left_shift:left_shift + cut_x] if i_mixup == 3:#右下角 bboxes = filter_truth(bboxes, cut_x - right_shift, cut_y - bot_shift, w - cut_x, h - cut_y, cut_x, cut_y) out_img[cut_y:, cut_x:] = img[cut_y - bot_shift:h - bot_shift, cut_x - right_shift:w - right_shift] return out_img, bboxes
4、实验效果
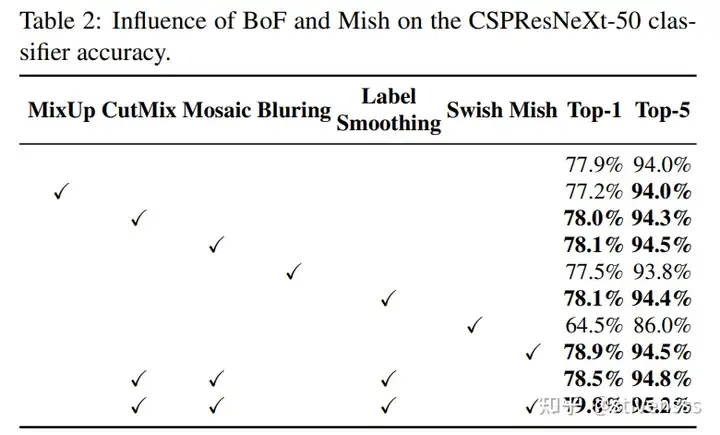
从Table2中可以看出,Mosaic数据增强比其他数据增强方式效果更好。不过也可以看出,Mish激活函数效果更加明显,由Swish转换成Mish就增加了15个百分点。
前言
在Yolo-V4、Yolo-V5中,都有一个很重要的技巧,就是Mosaic数据增强,这种数据增强方式简单来说就是把4张图片,通过随机缩放、随机裁减、随机排布的方式进行拼接。Mosaic有如下优点:
(1)丰富数据集:随机使用4张图片,随机缩放,再随机分布进行拼接,大大丰富了检测数据集,特别是随机缩放增加了很多小目标,让网络的鲁棒性更好;
(2)减少GPU显存:直接计算4张图片的数据,使得Mini-batch大小并不需要很大就可以达到比较好的效果。
mosaic python实现
思路:随机选择四张图,取其部分拼入该图,如下图所示,四种颜色代表四张样本图,超出的部分将被舍弃。
具体做法如下:
step1:新建mosaic画布,并在mosaic画布上随机生成一个点

im_size = 640 mosaic_border = [-im_size // 2, -im_size // 2] s_mosaic = im_size * 2 mosaic = np.full((s_mosaic, s_mosaic, 3), 114, dtype=np.uint8) yc, xc = (int(random.uniform(-x, s_mosaic + x)) for x in mosaic_border)

step2:围绕随机点 (x_c, y_c) 放置4块拼图
(1)左上位置
画布放置区域: (x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a)
case1:图片不超出画布,画布放置区域为 (x_c - w , y_c - h , x_c, y_c)
case2:图片超出画布,画布放置区域为 (0 , 0 , x_c, y_c)
综合case1和case2,画布区域为:
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = max(x_c - w, 0), max(y_c - h, 0), x_c, y_c

图片区域 : (x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b)
case1:图片不超出画布,图片不用裁剪,图片区域为 (0 , 0 , w , h)
case2:图片超出画布,超出部分的图片需要裁剪,区域为 (w - x_c , h - y_c , w , h)
综合case1和case2,图片区域为:
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = w - (x2a - x1a), h - (y2a - y1a), w, h
(2)右上位置
画布放置区域: (x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a)
case1:图片不超出画布,画布区域为 (x_c , y_c - h , x_c + w , y_c)
case2:图片超出画布,画布区域为 (x_c , 0 , s_mosaic , y_c)
综合case1和case2,画布区域为:
x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = x_c, max(y_c - h, 0), min(x_c + w, s_mosaic), y_c

图片区域 : (x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b)
case1:图片不超出画布,图片不用裁剪,图片区域为 (0 , 0 , w , h)
case2:图片超出画布,图片需要裁剪,图片区域为 (0 , h - (y2a - y1a) , x2a - x1a , h)
综合case1和case2,图片区域为:
x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = 0, h - (y2a - y1a), min(w, x2a - x1a), h
同理可实现左下和右下的拼图。
step3:更新bbox坐标
4张图片的bbox (n,4),其中n为4张图片中bbox数量,4代表四个坐标值(xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax) ,加上偏移量得到mosaic bbox坐标:
def xywhn2xyxy(x, padw=0, padh=0): # x: bbox坐标 (xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax) x = np.stack(x) y = x.clone() if isinstance(x, torch.Tensor) else np.copy(x) y[:, 0] = x[:, 0] + padw # top left x y[:, 1] = x[:, 1] + padh # top left y y[:, 2] = x[:, 2] + padw # bottom right x y[:, 3] = x[:, 3] + padh # bottom right y return y
mosaic python 完整实现代码如下:

import cv2 import torch import random import os.path import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from camvid import get_bbox, draw_box def load_mosaic(im_files, name_color_dict): im_size = 640 s_mosaic = im_size * 2 mosaic_border = [-im_size // 2, -im_size // 2] labels4, segments4, colors = [], [], [] # mosaic center x, y y_c, x_c = (int(random.uniform(-x, s_mosaic + x)) for x in mosaic_border) img4 = np.full((s_mosaic, s_mosaic, 3), 114, dtype=np.uint8) seg4 = np.full((s_mosaic, s_mosaic), 0, dtype=np.uint8) for i, im_file in enumerate(im_files): # Load image img = cv2.imread(im_file) seg_file = im_file.replace('images', 'labels') name = os.path.basename(seg_file).split('.')[0] seg_file = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(seg_file), name + '_L.png') seg, boxes, color = get_bbox(seg_file, names, name_color_dict) colors += color h, w, _ = np.shape(img) # place img in img4 if i == 0: # top left x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = max(x_c - w, 0), max(y_c - h, 0), x_c, y_c x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = w - (x2a - x1a), h - (y2a - y1a), w, h elif i == 1: # top right x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = x_c, max(y_c - h, 0), min(x_c + w, s_mosaic), y_c x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = 0, h - (y2a - y1a), min(w, x2a - x1a), h elif i == 2: # bottom left x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = max(x_c - w, 0), y_c, x_c, min(s_mosaic, y_c + h) x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = w - (x2a - x1a), 0, w, min(y2a - y1a, h) elif i == 3: # bottom right x1a, y1a, x2a, y2a = x_c, y_c, min(x_c + w, s_mosaic), min(s_mosaic, y_c + h) x1b, y1b, x2b, y2b = 0, 0, min(w, x2a - x1a), min(y2a - y1a, h) img4[y1a:y2a, x1a:x2a] = img[y1b:y2b, x1b:x2b] # place seg in seg4 seg4[y1a:y2a, x1a:x2a] = seg[y1b:y2b, x1b:x2b] # update bbox padw = x1a - x1b padh = y1a - y1b boxes = xywhn2xyxy(boxes, padw=padw, padh=padh) labels4.append(boxes) labels4 = np.concatenate(labels4, 0) for x in labels4[:, 1:]: np.clip(x, 0, s_mosaic, out=x) # clip coord # draw result draw_box(seg4, labels4, colors) return img4, labels4,seg4 if __name__ == '__main__': names = ['Pedestrian', 'Car', 'Truck_Bus'] im_files = ['camvid/images/0016E5_01440.png', 'camvid/images/0016E5_06600.png', 'camvid/images/0006R0_f00930.png', 'camvid/images/0006R0_f03390.png'] load_mosaic(im_files, name_color_dict)

参考
YOLOV5: https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5
本文来自博客园,作者:海_纳百川,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/chentiao/p/17527732.html,如有侵权联系删除




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号