yolov5中head修改为decouple head详解
现成的YOLOv5代码真的很香,不管口碑怎么样,我用着反正是挺爽的,下面这篇文章主要给大家介绍了关于yolov5中head修改为decouple head的相关资料,需要的朋友可以参考下
yolov5的head修改为decouple head
yolox的decoupled head结构
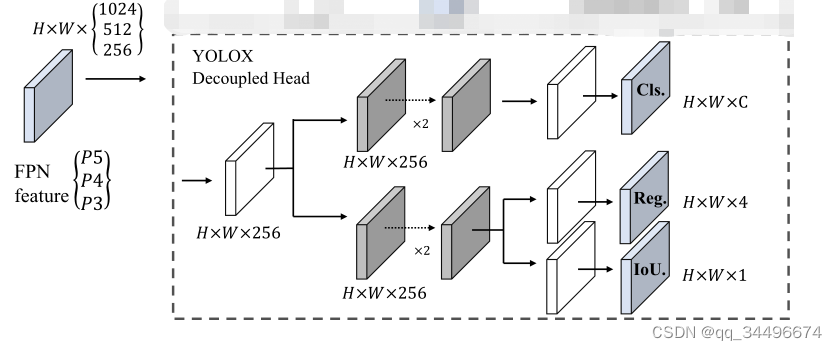
本来想将yolov5的head修改为decoupled head,与yolox的decouple head对齐,但是没注意,该成了如下结构:

感谢少年肩上杨柳依依的指出,如还有问题欢迎指出
1.修改models下的yolo.py文件中的Detect
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
|
class Detect(nn.Module): stride = None # strides computed during build onnx_dynamic = False # ONNX export parameter def __init__(self, nc=80, anchors=(), ch=(), inplace=True): # detection layer super().__init__() self.nc = nc # number of classes self.no = nc + 5 # number of outputs per anchor self.nl = len(anchors) # number of detection layers self.na = len(anchors[0]) // 2 # number of anchors self.grid = [torch.zeros(1)] * self.nl # init grid self.anchor_grid = [torch.zeros(1)] * self.nl # init anchor grid self.register_buffer('anchors', torch.tensor(anchors).float().view(self.nl, -1, 2)) # shape(nl,na,2) # self.m = nn.ModuleList(nn.Conv2d(x, self.no * self.na, 1) for x in ch) # output conv self.m_box = nn.ModuleList(nn.Conv2d(256, 4 * self.na, 1) for x in ch) # output conv self.m_conf = nn.ModuleList(nn.Conv2d(256, 1 * self.na, 1) for x in ch) # output conv self.m_labels = nn.ModuleList(nn.Conv2d(256, self.nc * self.na, 1) for x in ch) # output conv self.base_conv = nn.ModuleList(BaseConv(in_channels = x, out_channels = 256, ksize = 1, stride = 1) for x in ch) self.cls_convs = nn.ModuleList(BaseConv(in_channels = 256, out_channels = 256, ksize = 3, stride = 1) for x in ch) self.reg_convs = nn.ModuleList(BaseConv(in_channels = 256, out_channels = 256, ksize = 3, stride = 1) for x in ch) # self.m = nn.ModuleList(nn.Conv2d(x, 4 * self.na, 1) for x in ch, nn.Conv2d(x, 1 * self.na, 1) for x in ch,nn.Conv2d(x, self.nc * self.na, 1) for x in ch) self.inplace = inplace # use in-place ops (e.g. slice assignment)self.ch = ch def forward(self, x): z = [] # inference output for i in range(self.nl): # # x[i] = self.m[i](x[i]) # convs # print("&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&", i) # print(x[i].shape) # print(self.base_conv[i]) # print("%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%") x_feature = self.base_conv[i](x[i]) # x_feature = x[i] cls_feature = self.cls_convs[i](x_feature) reg_feature = self.reg_convs[i](x_feature) # reg_feature = x_feature m_box = self.m_box[i](reg_feature) m_conf = self.m_conf[i](reg_feature) m_labels = self.m_labels[i](cls_feature) x[i] = torch.cat((m_box,m_conf, m_labels),1) bs, _, ny, nx = x[i].shape # x(bs,255,20,20) to x(bs,3,20,20,85) x[i] = x[i].view(bs, self.na, self.no, ny, nx).permute(0, 1, 3, 4, 2).contiguous() if not self.training: # inference if self.onnx_dynamic or self.grid[i].shape[2:4] != x[i].shape[2:4]: self.grid[i], self.anchor_grid[i] = self._make_grid(nx, ny, i) y = x[i].sigmoid() if self.inplace: y[..., 0:2] = (y[..., 0:2] * 2 - 0.5 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i] # xy y[..., 2:4] = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i] # wh else: # for YOLOv5 on AWS Inferentia https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/pull/2953 xy = (y[..., 0:2] * 2 - 0.5 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i] # xy wh = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i] # wh y = torch.cat((xy, wh, y[..., 4:]), -1) z.append(y.view(bs, -1, self.no)) return x if self.training else (torch.cat(z, 1), x) |
2.在yolo.py中添加
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
def get_activation(name="silu", inplace=True): if name == "silu": module = nn.SiLU(inplace=inplace) elif name == "relu": module = nn.ReLU(inplace=inplace) elif name == "lrelu": module = nn.LeakyReLU(0.1, inplace=inplace) else: raise AttributeError("Unsupported act type: {}".format(name)) return moduleclass BaseConv(nn.Module): """A Conv2d -> Batchnorm -> silu/leaky relu block""" def __init__( self, in_channels, out_channels, ksize, stride, groups=1, bias=False, act="silu" ): super().__init__() # same padding pad = (ksize - 1) // 2 self.conv = nn.Conv2d( in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=ksize, stride=stride, padding=pad, groups=groups, bias=bias, ) self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels) self.act = get_activation(act, inplace=True) def forward(self, x): # print(self.bn(self.conv(x)).shape) return self.act(self.bn(self.conv(x))) # return self.bn(self.conv(x)) def fuseforward(self, x): return self.act(self.conv(x)) |
decouple head的特点:
由于训练模型时,应该是channels = 256的地方改成了channels = x(失误),所以在decoupled head的部分参数量比yolox要大一些,以下的结果是在channels= x的情况下得出
比yolov5s参数多,计算量大,在我自己的2.5万的数据量下map提升了3%多
1.模型给出的目标cls较高,需要将conf的阈值设置较大(0.5),不然准确率较低
|
1
|
parser.add_argument('--conf-thres', type=float, default=0.5, help='confidence threshold') |
2.对于少样本的检测效果较好,召回率的提升比准确率多
3.在conf设置为0.25时,召回率比yolov5s高,但是准确率低;在conf设置为0.5时,召回率与准确率比yolov5s高
4.比yolov5s参数多,计算量大,在2.5万的数据量下map提升了3%多
对于decouple head的改进
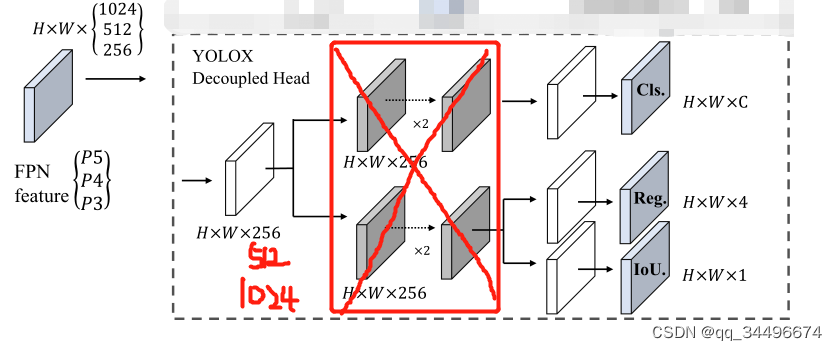
改进:
1.将红色框中的conv去掉,缩小参数量和计算量;
2.channels =256 ,512 ,1024是考虑不增加参数,不进行featuremap的信息压缩
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
class Detect(nn.Module): stride = None # strides computed during build onnx_dynamic = False # ONNX export parameter def __init__(self, nc=80, anchors=(), ch=(), inplace=True): # detection layer super().__init__() self.nc = nc # number of classes self.no = nc + 5 # number of outputs per anchor self.nl = len(anchors) # number of detection layers self.na = len(anchors[0]) // 2 # number of anchors self.grid = [torch.zeros(1)] * self.nl # init grid self.anchor_grid = [torch.zeros(1)] * self.nl # init anchor grid self.register_buffer('anchors', torch.tensor(anchors).float().view(self.nl, -1, 2)) # shape(nl,na,2) self.m = nn.ModuleList(nn.Conv2d(x, self.no * self.na, 1) for x in ch) # output conv self.inplace = inplace # use in-place ops (e.g. slice assignment) def forward(self, x): z = [] # inference output for i in range(self.nl): x[i] = self.m[i](x[i]) # conv bs, _, ny, nx = x[i].shape # x(bs,255,20,20) to x(bs,3,20,20,85) x[i] = x[i].view(bs, self.na, self.no, ny, nx).permute(0, 1, 3, 4, 2).contiguous() if not self.training: # inference if self.onnx_dynamic or self.grid[i].shape[2:4] != x[i].shape[2:4]: self.grid[i], self.anchor_grid[i] = self._make_grid(nx, ny, i) y = x[i].sigmoid() if self.inplace: y[..., 0:2] = (y[..., 0:2] * 2 - 0.5 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i] # xy y[..., 2:4] = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i] # wh else: # for YOLOv5 on AWS Inferentia https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/pull/2953 xy = (y[..., 0:2] * 2 - 0.5 + self.grid[i]) * self.stride[i] # xy wh = (y[..., 2:4] * 2) ** 2 * self.anchor_grid[i] # wh y = torch.cat((xy, wh, y[..., 4:]), -1) z.append(y.view(bs, -1, self.no)) return x if self.training else (torch.cat(z, 1), x) |
特点
1.模型给出的目标cls较高,需要将conf的阈值设置较大(0.4),不然准确率较低
2.对于少样本的检测效果较好,准确率的提升比召回率多
3. 准确率的提升比召回率多,
该改进不如上面的模型提升多,但是参数量小,计算量小少9Gflop,占用显存少
decoupled head指标提升的原因:由于yolov5s原本的head不能完全的提取featuremap中的信息,decoupled head能够较为充分的提取featuremap的信息;
疑问
为什么decoupled head目标的cls会比较高,没想明白
为什么去掉base_conv,召回率要比准确率提升少
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_34496674/article/details/124828868
本文来自博客园,作者:海_纳百川,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/chentiao/p/16425546.html,如有侵权联系删除



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· Docker 太简单,K8s 太复杂?w7panel 让容器管理更轻松!