YOLOX之backbone-PAFPN解读
1、前置知识
FPN:Feature pyramid network,特征金字塔网络。
PAN: Path Aggregation network,路径聚合网络。
关于FPN和PAN可以参考:
https://www.cnblogs.com/chentiao/p/16425098.html
YOLO的骨干网主要是借助PA-FPN的结构将不同层次的特状图进行高效融合。
PA(Path Aggregation)的策略使得不同层次的特征在传递时需要“穿越”的网络层次数量大大减少。
关于基本的网络blocks和作用的解释:
Focus模块:
CSP模块:将feature map拆成两个部分,一部分进行卷积操作,另一部分和上一部分卷积操作的结果进行concate。
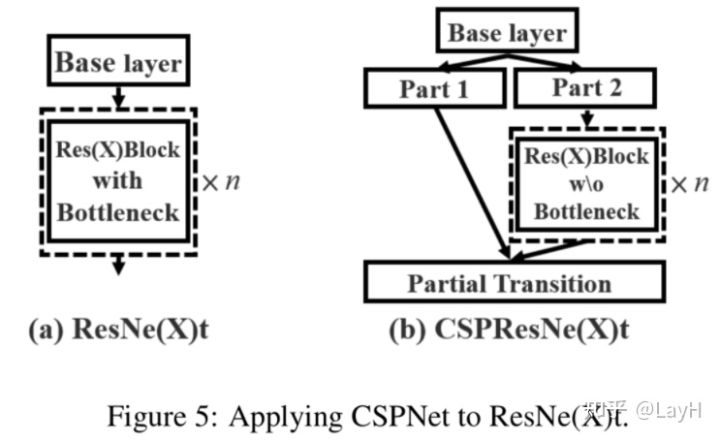
YOLO的CSP层包括了Bottleneck层,
下文网络结构的Conv是指Depthwise Separable Conv,深度可分离卷积。
关于Bottleneck和Depthwise Separable Conv的详细说明:
2、YOLO-PAFPN的网络结构
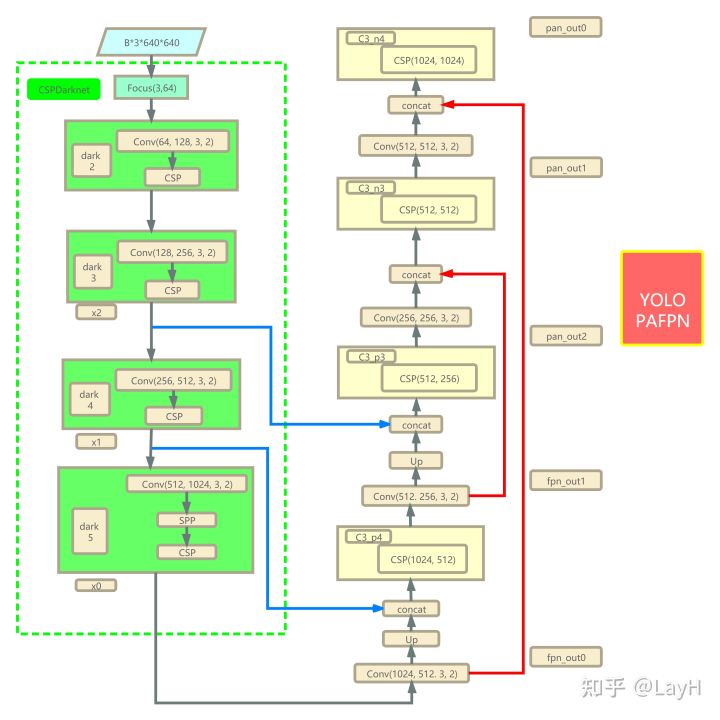
YOLOX的backbone结构图
输入是Batch*3*640*640尺寸的图像。
输出是经过PAFPN网络之后的不同层次的特征图: (pan_out2, pan_out1, pan_out0)。
左边绿色的CSPDarknet,右边红色的线表示Path Aggregation。
具体的代码如下:
class YOLOPAFPN(nn.Module):
"""
YOLOv3 model. Darknet 53 is the default backbone of this model.
"""
def __init__(
self,
depth=1.0,
width=1.0,
in_features=("dark3", "dark4", "dark5"),
in_channels=[256, 512, 1024],
depthwise=False,
act="silu",
):
super().__init__()
self.backbone = CSPDarknet(depth, width, depthwise=depthwise, act=act)
self.in_features = in_features
self.in_channels = in_channels
Conv = DWConv if depthwise else BaseConv
self.upsample = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode="nearest")
self.lateral_conv0 = BaseConv(
int(in_channels[2] * width), int(in_channels[1] * width), 1, 1, act=act
)
self.C3_p4 = CSPLayer(
int(2 * in_channels[1] * width),
int(in_channels[1] * width),
round(3 * depth),
False,
depthwise=depthwise,
act=act,
) # cat
self.reduce_conv1 = BaseConv(
int(in_channels[1] * width), int(in_channels[0] * width), 1, 1, act=act
)
self.C3_p3 = CSPLayer(
int(2 * in_channels[0] * width),
int(in_channels[0] * width),
round(3 * depth),
False,
depthwise=depthwise,
act=act,
)
# bottom-up conv
self.bu_conv2 = Conv(
int(in_channels[0] * width), int(in_channels[0] * width), 3, 2, act=act
)
self.C3_n3 = CSPLayer(
int(2 * in_channels[0] * width),
int(in_channels[1] * width),
round(3 * depth),
False,
depthwise=depthwise,
act=act,
)
# bottom-up conv
self.bu_conv1 = Conv(
int(in_channels[1] * width), int(in_channels[1] * width), 3, 2, act=act
)
self.C3_n4 = CSPLayer(
int(2 * in_channels[1] * width),
int(in_channels[2] * width),
round(3 * depth),
False,
depthwise=depthwise,
act=act,
)
def forward(self, input):
"""
Args:
inputs: input images.
Returns:
Tuple[Tensor]: FPN feature.
"""
# backbone
out_features = self.backbone(input)
features = [out_features[f] for f in self.in_features]
[x2, x1, x0] = features
fpn_out0 = self.lateral_conv0(x0) # 1024->512/32
f_out0 = self.upsample(fpn_out0) # 512/16
f_out0 = torch.cat([f_out0, x1], 1) # 512->1024/16
f_out0 = self.C3_p4(f_out0) # 1024->512/16
fpn_out1 = self.reduce_conv1(f_out0) # 512->256/16
f_out1 = self.upsample(fpn_out1) # 256/8
f_out1 = torch.cat([f_out1, x2], 1) # 256->512/8
pan_out2 = self.C3_p3(f_out1) # 512->256/8
p_out1 = self.bu_conv2(pan_out2) # 256->256/16
p_out1 = torch.cat([p_out1, fpn_out1], 1) # 256->512/16
pan_out1 = self.C3_n3(p_out1) # 512->512/16
p_out0 = self.bu_conv1(pan_out1) # 512->512/32
p_out0 = torch.cat([p_out0, fpn_out0], 1) # 512->1024/32
pan_out0 = self.C3_n4(p_out0) # 1024->1024/32
outputs = (pan_out2, pan_out1, pan_out0)
return outputs
本文来自博客园,作者:海_纳百川,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/chentiao/p/16425019.html,如有侵权联系删除


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号