nginx
nginx简介
nginx (发音同engine x)是一款轻量级的Web服务器/反向代理服务器及电子邮件(IMAP/POP3)代 理服务器,并在一个BSD-like协议下发行。 nginx 由俄罗斯的程序设计师Igor Sysoev所开发,最初供俄国大型的入口网站及搜寻引擎Rambler使 用。 第一个公开版本0.1.0发布于2004年10月4日。其将源代码以类BSD许可证的形式发布,因它的稳定性、 丰富的功能集、示例配置文件和低系统资源的消耗而闻名。2011年6月1日,nginx 1.0.4发布。 nginx 的特点是占有内存少,并发能力强,事实上 nginx 的并发能力确实在同类型的网页服务器中表现 较好,中国大陆使用 nginx 网站用户有:百度、京东、新浪、网易、腾讯、淘宝等。
nginx的特性
nginx是一个很牛的高性能Web和反向代理服务器,它具有很多非常优越的特性:
- 在高连接并发的情况下,nginx是Apache服务器不错的替代品,能够支持高达50000个并发连接数的响应
- 使用epoll and kqueue作为开发模型
- nginx作为负载均衡服务器:nginx既可在内部直接支持和PHP程序对外进行服务,也可支持作为HTTP代理服务器对外进行服务
- nginx采用C进行编写,不论系统资源开销还是CPU使用效率都比Perlbal要好很多
nginx的优点
- 高并发连接:官方测试能够支撑5万并发连接,在实际生产环境中跑到2-3万并发连接数
- 内存消耗少:在3万并发连接下,开启的10个nginx进程才消耗150M内存(15M*10=150M)
- 配置文件非常简单:风格跟程序一样通俗易懂
- 成本低廉:nginx为开源软件,可以免费使用。而购买F5 BIG-IP、NetScaler等硬件负载均衡交换机则需要十多万至几十万人民币
- 支持Rewrite重写规则:能够根据域名、URL的不同,将HTTP请求分到不同的后端服务器群组
- 内置的健康检查功能:如果Nginx Proxy后端的某台Web服务器宕机了,不会影响前端访问
- 节省带宽:支持GZIP压缩,可以添加浏览器本地缓存的Header头
- 稳定性高:用于反向代理,宕机的概率微乎其微
- 模块化设计:模块可以动态编译
- 外围支持好:文档全,二次开发和模块较多
- 支持热部署:可以不停机重载配置文件
- 支持事件驱动、AIO(AsyncIO,异步IO)、mmap(Memory Map,内存映射)等性能优化
nginx的功能及应用类别
nginx的基本功能
- 静态资源的web服务器,能缓存打开的文件描述符
- http、smtp、pop3协议的反向代理服务器
- 缓存加速、负载均衡
- 支持FastCGI(fpm,LNMP),uWSGI(Python)等
- 模块化(非DSO机制),过滤器zip、SSI及图像的大小调整
- 支持SSL
nginx的扩展功能
- 基于名称和IP的虚拟主机
- 支持keepalive
- 支持平滑升级
- 定制访问日志、支持使用日志缓冲区提高日志存储性能
- 支持URL重写
- 支持路径别名
- 支持基于IP及用户的访问控制
- 支持速率限制,支持并发数限制
nginx的应用类别
- 使用nginx结合FastCGI运行PHP、JSP、Perl等程序
- 使用nginx作反向代理、负载均衡、规则过滤
- 使用nginx运行静态HTML网页、图片
- nginx与其他新技术的结合应用
nginx的模块与工作原理
nginx由内核和模块组成。其中,内核的设计非常微小和简洁,完成的工作也非常简单,仅仅通过查找配置文件将客户端请求映射到一个location block(location是nginx配置中的一个指令,用于URL匹配),而在这个location中所配置的每个指令将会启动不同的模块去完成相应的工作。
nginx的模块分类
nginx的模块从结构上分为核心模块、基础模块和第三方模块
- HTTP模块、EVENT模块和MAIL模块等属于核心模块
- HTTP Access模块、HTTP FastCGI模块、HTTP Proxy模块和HTTP Rewrite模块属于基本模块
- HTTP Upstream模块、Request Hash模块、Notice模块和HTTP Access Key模块属于第三方模块
用户根据自己的需要开发的模块都属于第三方模块。正是有了如此多模块的支撑,nginx的功能才会如此强大
nginx模块从功能上分为三类,分别是:
- Handlers(处理器模块)。此类模块直接处理请求,并进行输出内容和修改headers信息等操作。handlers处理器模块一般只能有一个
- Filters(过滤器模块)。此类模块主要对其他处理器模块输出的内容进行修改操作,最后由nginx输出
- Proxies(代理器模块)。就是nginx的HTTP Upstream之类的模块,这些模块主要与后端一些服务比如fastcgi等操作交互,实现服务代理和负载均衡等功能
nginx模块分为:核心模块、事件模块、标准Http模块、可选Http模块、邮件模块、第三方模块和补丁等
- nginx基本模块:所谓基本模块,指的是nginx默认的功能模块,它们提供的指令,允许你使用定义nginx基本功能的变量,在编译时不能被禁用,包括:
- 核心模块:基本功能和指令,如进程管理和安全。常见的核心模块指令,大部分是放置在配置文件的顶部
- 事件模块:在Nginx内配置网络使用的能力。常见的events(事件)模块指令,大部分是放置在配置文件的顶部
- 配置模块:提供包含机制
具体的指令,请参考nginx的官方文档
nginx的工作原理
nginx的模块直接被编译进nginx,因此属于静态编译方式。
启动nginx后,nginx的模块被自动加载,与Apache不一样,首先将模块编译为一个so文件,然后在配置文件中指定是否进行加载。
在解析配置文件时,nginx的每个模块都有可能去处理某个请求,但是同一个处理请求只能由一个模块来完成。
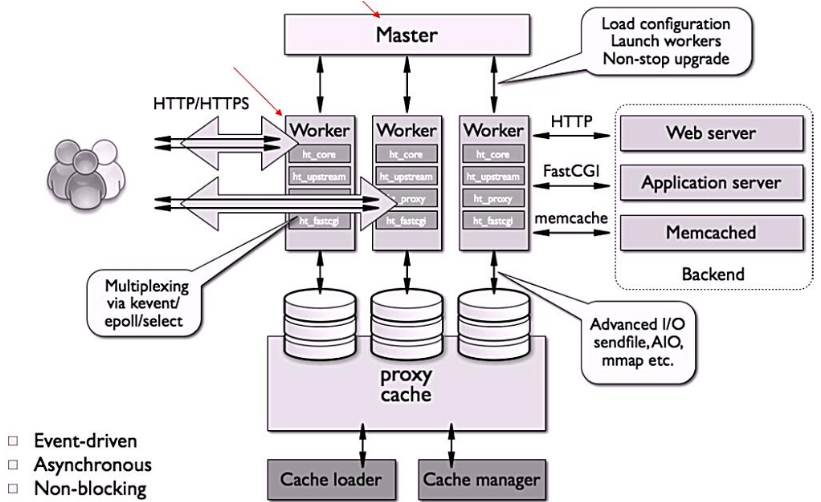
nginx的进程架构:
启动nginx时,会启动一个Master进程,这个进程不处理任何客户端的请求,主要用来产生worker线程,一个worker线程用来处理n个request。
网站访问流程
1.用户通过浏览器输入目标网站网址。
2.本地浏览器自动对网站域名进行解析,包括网站协议(http还是https),网站域名解析就是域名对应的服务器IP地址。
3.浏览器进行ISP通信,先通过网站域名dns解析系统,链接域名根服务器, 并查询该域名的服务器IP地址。
4.当浏览器ISP拿到网站域名对应的服务器的IP地址后,它就会自动请求对应ip地址的网站服务器。
5.当浏览器根据ip地址及服务器端口进行网站服务器访问,就可以进行TCP连接,这时,电脑端的浏览器已经和网站服务器进行了远程连接并进行访问请求。
6.在浏览器请求网站页面过程中,浏览器会根据服务器连接情况,返回对应的连接状态码,比如404就是网站页面不存在,50*就代表服务器端故障或拒绝访问,200就代表连接成功,可以实现网站访问。
7.浏览器和网站服务器连接成功建立后,就可以进行网站所有数据的请求,包括图片,文字,视频及超文本协议语言。
8.浏览器获取网站资料字后,就会根据获取的内容自动进行网站页面的渲染,最终将网页呈现在界面中。
9.当浏览器完成加载网站所有资源之后,就会与远程服务器断开连接
下图展示了nginx 模块一次常规的HTTP请求和响应的过程
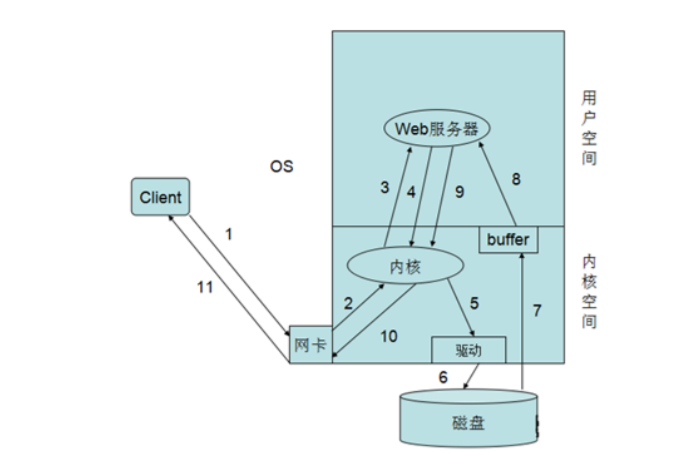
基本流程解释:
用户建立连接,和nginx内核空间建立接连,nginx服务器处理并响应请求,nginx会访问自己的的存储资源池,并且复制一份内存缓存 成为进程缓存,然后构建响应,然后返回到内核空间,通过搭建的网卡链路将数据返回给用户。
具体流程解释:
1.首先我们客户端发送一个请求到Web服务器,请求首先是到网卡。
2.网卡将请求交由内核空间的内核 处理,其实就是拆包了,发现请求的是80端口。
3.内核便将请求发给了在用户空间的Web服务器,Web 服务器接受到请求发现客户端请求的index.html页面。
4.Web服务器便进行系统调用将请求发给内核。
5.内核发现在请求的是一页面,便调用磁盘的驱动程序,连接磁盘。
6.内核通过驱动调用磁盘取得的页 面文件。
7.内核将取得的页面文件保存在自己的缓存区域中便通知Web进程或线程来取相应的页面文 件。
8.Web服务器通过系统调用将内核缓存中的页面文件复制到进程缓存区域中。
9.Web服务器取得页 面文件来响应用户,再次通过系统调用将页面文件发给内核。
10.内核进程页面文件的封装并通过网卡发 送出去。
11.当报文到达网卡时通过网络响应给客户端 简单来说就是:用户请求-->送达到用户空间-->系统调用-->内核空间-->内核到磁盘上读取网页资源->返 回到用户空间->响应给用户。上述简单的说明了一下,客户端向Web服务请求过程,在这个过程中,有 两个I/O过程,一个就是客户端请求的网络I/O,另一个就是Web服务器请求页面的磁盘I/O。
nginx的配置文件详解
主配置文件:/usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
- 默认启动nginx时,使用的配置文件是:安装路径/conf/nginx.conf文件
- 可以在启动nginx时通过-c选项来指定要读取的配置文件
nginx常见的配置文件及其作用
| 配置文件 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| nginx.conf | nginx的基本配置文件 |
| mime.types | MIME类型关联的扩展文件 |
| fastcgi.conf | 与fastcgi相关的配置 |
| proxy.conf | 与proxy相关的配置 |
| sites.conf | 配置nginx提供的网站,包括虚拟主机 |
nginx.conf配置详解
nginx.conf的内容分为以下几段:
- main配置段:全局配置段。其中main配置段中可能包含event配置段
- event {}:定义event模型工作特性
- http {}:定义http协议相关的配置
配置指令:要以分号结尾,语法格式如下:
derective value1 [value2 ...];
支持使用变量:
- 内置变量:模块会提供内建变量定义
- 自定义变量:
set var_name value
nginx的安装与配置
nginx的安装
//创建系统用户nginx [root@localhost ~]# useradd -r -M -s /sbin/nologin nginx //安装依赖环境 [root@localhost ~]# yum -y install pcre-devel openssl openssl-devel gd-devel gcc gcc-c++ make [root@localhost ~]# yum -y groups mark install 'Development Tools' //创建用户和创建日志存放目录 [root@localhost ~]# useradd -r -M -s /sbin/nologin nginx [root@localhost ~]# mkdir -p /var/log/nginx [root@localhost ~]# chown -R nginx.nginx /var/log/nginx //下载nginx [root@localhost ~]# wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.20.0.tar.gz //编译安装 [root@localhost ~]# tar xf nginx-1.20.0.tar.gz [root@localhost ~]# cd nginx-1.20.0 [root@localhost nginx-1.20.0]# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-debug --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_realip_module --with-http_image_filter_module --with-http_gunzip_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-http_stub_status_module --http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log --error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log [root@localhost nginx-1.20.0]# make && make install //配置环境变量 [root@localhost nginx-1.20.0]# echo 'export PATH=/usr/local/nginx/sbin:$PATH' > /etc/profile.d/nginx.sh [root@localhost nginx-1.20.0]# . /etc/profile.d/nginx.sh //启动服务 [root@localhost nginx-1.20.0]# nginx [root@localhost nginx-1.20.0]# ss -antl State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 0 128 [::]:22
用于调试、定位问题的配置参数
daemon {on|off}; #是否以守护进程方式运行nginx,调试时应设置为off
master_process {on|off}; #是否以master/worker模型来运行nginx,调试时可以设置为off
error_log 位置 级别; #配置错误日志
正常运行必备的配置参数
user USERNAME [GROUPNAME]; #指定运行worker进程的用户和组 pid /path/to/pid_file; #指定nginx守护进程的pid文件 worker_rlimit_nofile number; #设置所有worker进程最大可以打开的文件数,默认为1024 worker_rlimit_core size; #指明所有worker进程所能够使用的总体的最大核心文件大小,保持默认即可
优化性能的配置参数
worker_processes n; #启动n个worker进程,这里的n为了避免上下文切换,通常设置为cpu总核心数-1或等于总核心数 worker_cpu_affinity cpumask ...; #将进程绑定到某cpu中,避免频繁刷新缓存 #cpumask:使用8位二进制表示cpu核心,如: 0000 0001 #第一颗cpu核心 0000 0010 #第二颗cpu核心 0000 0100 #第三颗cpu核心 0000 1000 #第四颗cpu核心 0001 0000 #第五颗cpu核心 0010 0000 #第六颗cpu核心 0100 0000 #第七颗cpu核心 1000 0000 #第八颗cpu核心 timer_resolution interval; #计时器解析度。降低此值,可减少gettimeofday()系统调用的次数 worker_priority number; #指明worker进程的nice值
事件相关的配置:event{}段中的配置参数
accept_mutex {off|on}; #master调度用户请求至各worker进程时使用的负载均衡锁;on表示能让多个worker轮流地、序列化地去响应新请求
lock_file file; #accept_mutex用到的互斥锁锁文件路径
use [epoll | rtsig | select | poll]; #指明使用的事件模型,建议让nginx自行选择
worker_connections #; #每个进程能够接受的最大连接数
网络连接相关的配置参数
keepalive_timeout number; #长连接的超时时长,默认为65s keepalive_requests number; #在一个长连接上所能够允许请求的最大资源数 keepalive_disable [msie6|safari|none]; #为指定类型的UserAgent禁用长连接 tcp_nodelay on|off; #是否对长连接使用TCP_NODELAY选项,为了提升用户体验,通常设为on client_header_timeout number; #读取http请求报文首部的超时时长 client_body_timeout number; #读取http请求报文body部分的超时时长 send_timeout number; #发送响应报文的超时时长
fastcgi的相关配置参数
LNMP:php要启用fpm模型 配置示例如下: location ~ \.php$ { root html; fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; //定义反向代理 fastcgi_index index.php; fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name; include fastcgi_params; }
常需要进行调整的参数
worker_processes
worker_connections
worker_cpu_affinity
worker_priority
nginx作为web服务器时使用的配置:http{}段的配置参数
http{...}:配置http相关,由ngx_http_core_module模块引入。nginx的HTTP配置主要包括四个区块,结构如下
http { #协议级别 include mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; keepalive_timeout 65; gzip on; upstream { #负载均衡配置 ... } server { #服务器级别,每个server类似于httpd中的一个<VirtualHost> listen 80; server_name localhost; location / { #请求级别,类似于httpd中的<Location>,用于定义URL与本地文件系统的映射关系 root html; index index.html index.htm; } } }
http{}段配置:
server {}:定义一个虚拟主机,示例如下:
server { listen 80; server_name www.xxx.com; root "/vhosts/web"; }
listen:指定监听的地址和端口
listen address[:port];
listen port;
server_name NAME [...];后面可跟多个主机,名称可使用正则表达式或通配符
当有多个server时,匹配顺序如下: 先做精确匹配检查 左侧通配符匹配检查,如*.idfsoft.com 右侧通配符匹配检查,如mail.* 正则表达式匹配检查,如~ ^.*\.idfsoft\.com$ default_server
root path 设置资源路径映射,用于指明请求的URL所对应的资源所在的文件系统上的起始路径
alias path 用于location配置段,定义路径别名
error_page code [...] [=code] URI | @name 根据http响应状态码来指明特用的错误页面,例如 error_page 404 /404_customed.html
[=code]:以指定的响应码进行响应,而不是默认的原来的响应,默认表示以新资源的响应码为其响应码,例如 error_page 404 =200 /404_customed.html
location区段,通过指定模式来与客户端请求的URI相匹配
#功能:允许根据用户请求的URI来匹配定义的各location,匹配到时,此请求将被相应的location配置块中的配置所处理,例如做访问控制等功能
#语法:location [ 修饰符 ] pattern {......}
常用修饰符说明:
| 修饰符 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| = | 精确匹配 |
| ~ | 正则表达式模式匹配,区分大小写 |
| ~* | 正则表达式模式匹配,不区分大小写 |
| ^~ | 前缀匹配,类似于无修饰符的行为,也是以指定模块开始,不同的是,如果模式匹配,那么就停止搜索其他模式了,不支持正则表达式 |
| @ | 定义命名location区段,这些区段客户端不能访问,只可以由内部产生的请求来访问,如try_files或error_page等 |
nginx平滑升级过程:
1.获取之前的编译参数
2.下载新模块
3.重新编译软件,--add-module=新模块的路径
4.编译,替换主程序(原程序先备份)
5.启动新程序
Nginx信号简介
主进程支持的信号
TERM,INT: 立刻退出QUIT: 等待工作进程结束后再退出KILL: 强制终止进程HUP: 重新加载配置文件,使用新的配置启动工作进程,并逐步关闭旧进程。USR1: 重新打开日志文件USR2: 启动新的主进程,实现热升级WINCH: 逐步关闭工作进程
工作进程支持的信号
TERM,INT: 立刻退出QUIT: 等待请求处理结束后再退出USR1: 重新打开日志文件
//平滑升级过程 [root@localhost ~]# wget https://github.com/openresty/echo-nginx-module/archive/refs/heads/master.zip [root@localhost ~]# unzip master.zip [root@localhost ~]# nginx -V nginx version: nginx/1.20.0 built by gcc 8.3.1 20191121 (Red Hat 8.3.1-5) (GCC) built with OpenSSL 1.1.1g FIPS 21 Apr 2020 TLS SNI support enabled configure arguments: --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-debug --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_realip_module --with-http_image_filter_module --with-http_gunzip_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-http_stub_status_module --http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log --error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log [root@localhost ~]# tar -xf nginx-1.20.0.tar.gz [root@localhost nginx-1.20.0]# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-debug --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_realip_module --with-http_image_filter_module --with-http_gunzip_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-http_stub_status_module --http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log --error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log --add-module=../echo-nginx-module-master/ [root@localhost nginx-1.20.0]# make //替换主程序 [root@localhost nginx-1.20.0]# mv /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx /opt/nginx_$(date +%F) [root@localhost nginx-1.20.0]# mv objs/nginx /usr/local/nginx/sbin/ [root@localhost nginx-1.20.0]# kill -USR2 `cat /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid` [root@localhost nginx-1.20.0]# nginx -V nginx version: nginx/1.20.0 built by gcc 8.3.1 20191121 (Red Hat 8.3.1-5) (GCC) built with OpenSSL 1.1.1g FIPS 21 Apr 2020 TLS SNI support enabled configure arguments: --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-debug --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_realip_module --with-http_image_filter_module --with-http_gunzip_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-http_stub_status_module --http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log --error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log --add-module=../echo-nginx-module-master/
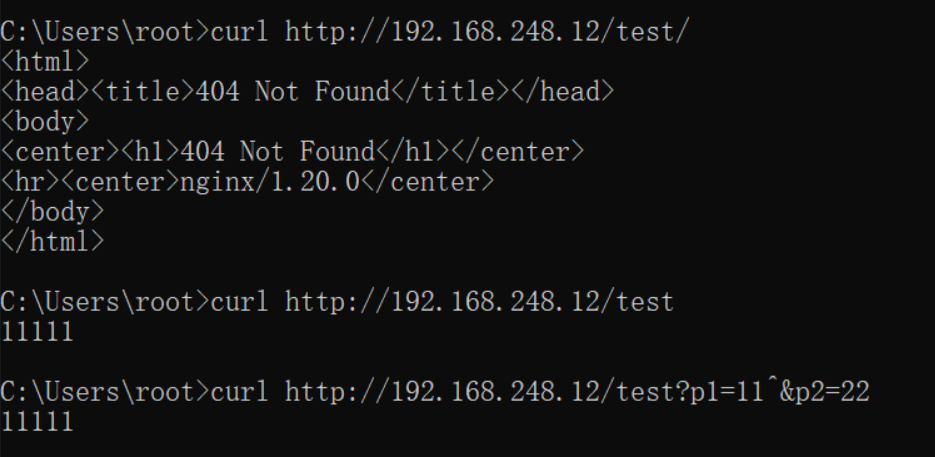
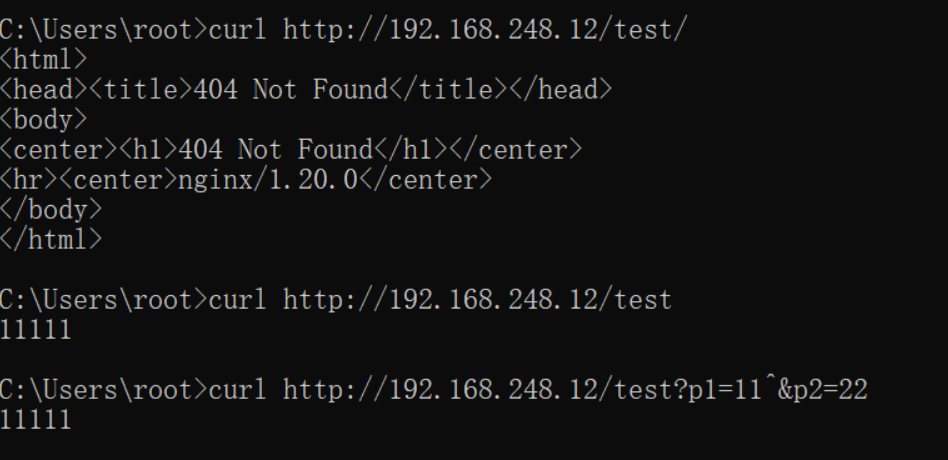
没有修饰符表示必须以指定模式开始 如:
server { listen 80; server_name localhost; location /test { echo "11111"; }
那么有几种正确匹配的方式例如:(其中ip就是指IP地址)
- http://ip/test
- http://ip/test?p1=11?p2=22
- http://ip/test/
=:表示必须与指定的模式精确匹配,如:
server { listen 80; server_name localhost; location = /test { echo "11111"; }
那么如下内容就可正确匹配:
- http://ip/test
- http://ip/test?p1=11?p2=22
~:表示指定的正则表达式要区分大小写,如:
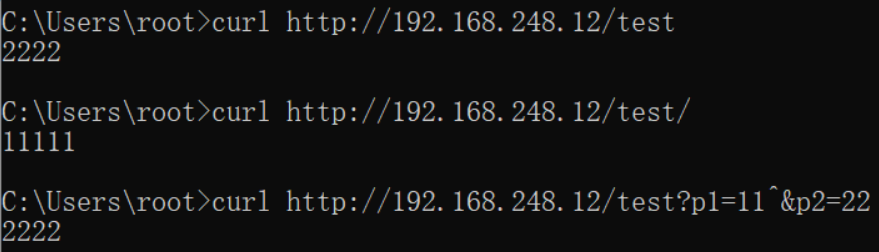
server { listen 80; server_name localhost; location ~ /test$ { echo "2222"; }
那么如下内容就可正确匹配:
- http://ip/test
- http://ip/test?p1=11?p2=22
如下内容则无法匹配:
- http://ip/test/
- http://ip/TEST
- http://ip/testabc
~*:表示指定的正则表达式不区分大小写,如:
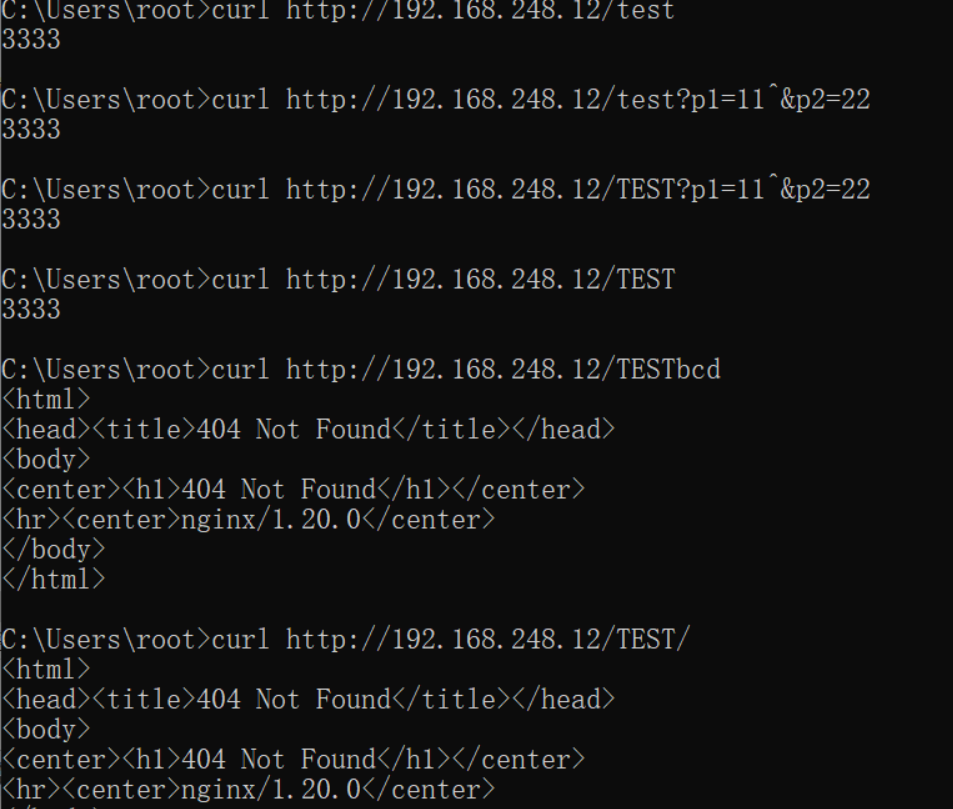
server { listen 80; server_name localhost; location ~* /test$ { echo "3333"; }
那么如下内容就可正确匹配:
- http://ip/test
- http://ip/test?p1=11?p2=22
- http://ip/TEST
如下内容则无法匹配:
- http://ip/test/
- http://ip/testabc
查找顺序和优先级:由高到底依次为
- 带有
=的精确匹配优先 - 正则表达式按照他们在配置文件中定义的顺序
- 带有
^~修饰符的,开头匹配 - 带有
~或~*修饰符的,如果正则表达式与URI匹配 - 没有修饰符的精确匹配
优先级次序如下:
( location = 路径 ) --> ( location ^~ 路径 ) --> ( location ~ 正则 ) --> ( location ~* 正则 ) --> ( location 路径 )
开启状态界面
状态页面信息详解:
| 状态码 | 表示的意义 |
|---|---|
| Active connections 2 | 当前所有处于打开状态的连接数 |
| accepts | 总共处理了多少个连接 |
| handled | 成功创建多少握手 |
| requests | 总共处理了多少个请求 |
| Reading | nginx读取到客户端的Header信息数,表示正处于接收请求状态的连接数 |
| Writing | nginx返回给客户端的Header信息数,表示请求已经接收完成, 且正处于处理请求或发送响应的过程中的连接数 |
| Waiting | 开启keep-alive的情况下,这个值等于active - (reading + writing), 意思就是Nginx已处理完正在等候下一次请求指令的驻留连接 |
用于location段
allow:设定允许哪台或哪些主机访问,多个参数间用空格隔开
deny:设定禁止哪台或哪些主机访问,多个参数间用空格隔开
location /status { stub_status {on | off}; allow 127.0.0.1; #允许本机访问 deny all; }
用于server段
//我只放行了虚拟机IP访问nginx,拒绝了所有其他机器 server { listen 80; server_name localhost; allow 192.168.248.12; deny all; //在虚拟机里访问网站能够成功,但在真机访问会失败 [root@localhost ~]# curl 192.168.248.12 <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>Welcome to nginx!</title> <style> body { width: 35em; margin: 0 auto; font-family: Tahoma, Verdana, Arial, sans-serif;
由此可见,写在location字段里面是针对某个资源,写在server里是针对整个网站
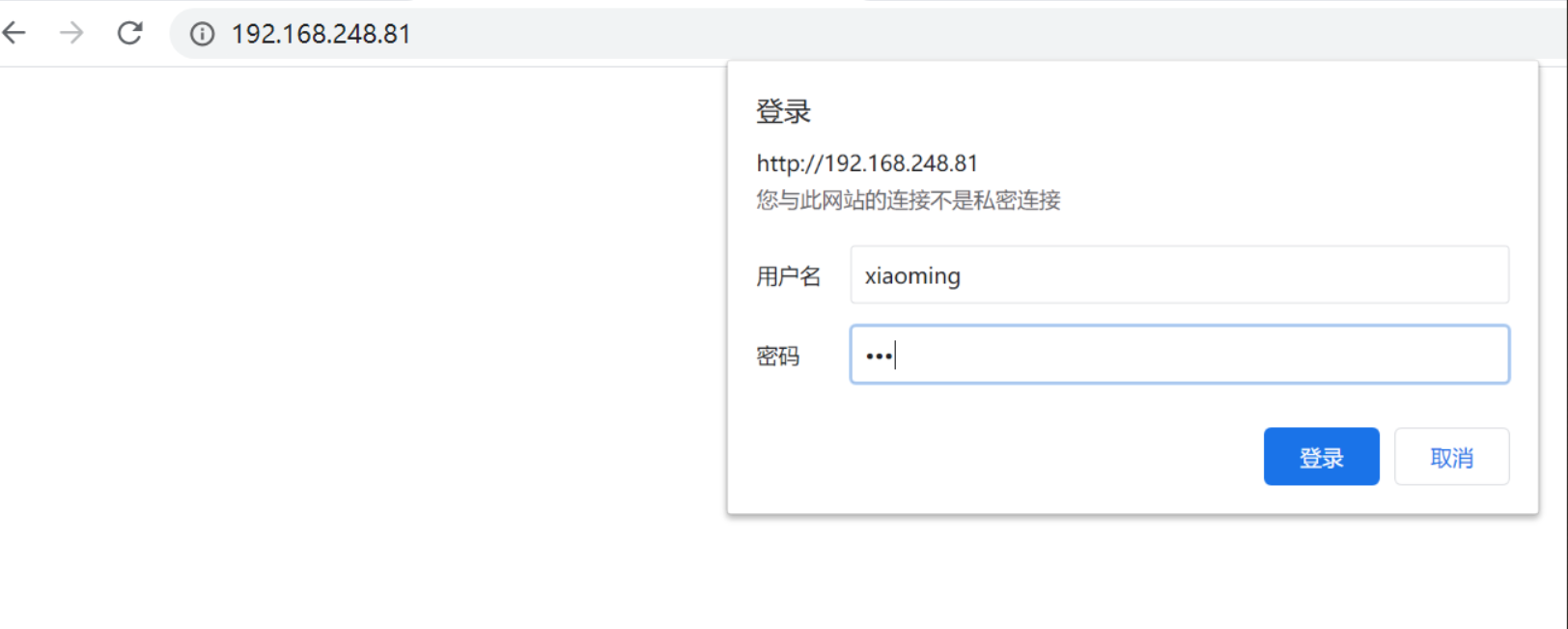
基于用户认证
auth_basic "欢迎信息"; auth_basic_user_file "/path/to/user_auth_file"
user_auth_file内容格式为:
username:password
这里的密码为加密后的密码串,建议用htpasswd来创建此文件:
htpasswd -c -m /path/to/.user_auth_file USERNAME
示例
[root@localhost ~]# htpasswd -c -m /etc/nginx/.auth_user xiaoming New password: Re-type new password: Adding password for user xiaoming [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf .......................... location / { auth_basic "hello"; auth_basic_user_file "/etc/nginx/.auth_user"; } [root@localhost ~]# nginx -s reload
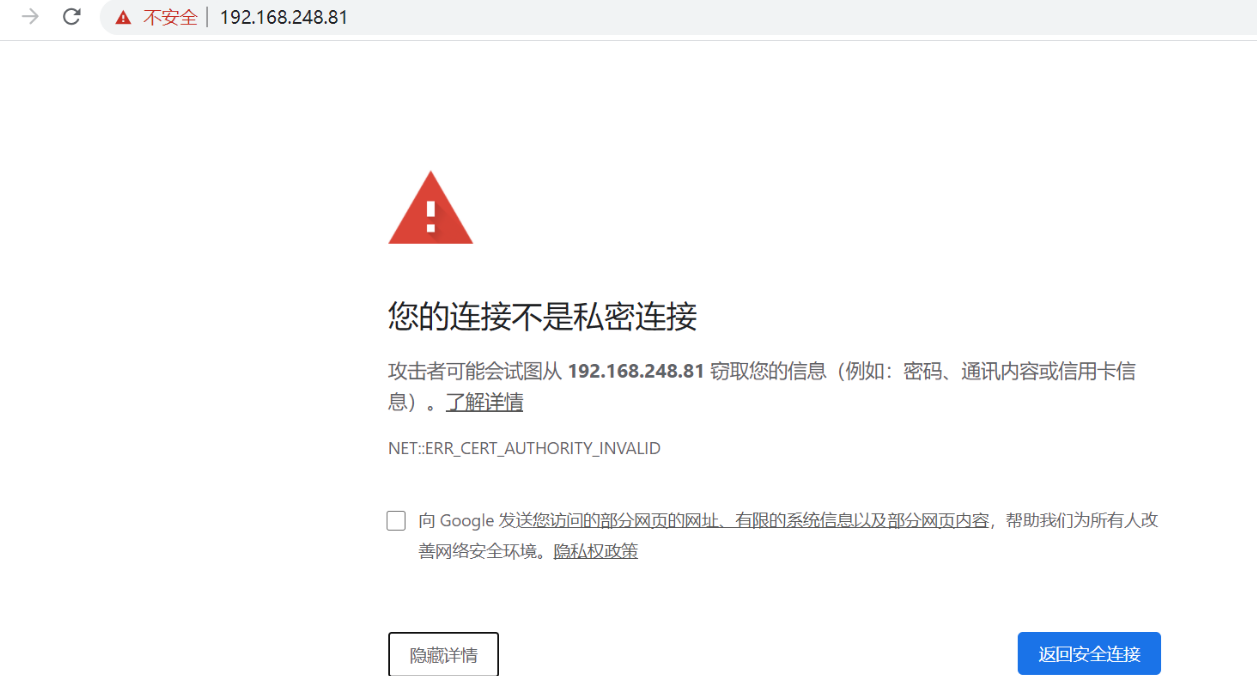
https配置
//创建证书和私钥的目录 [root@localhost ~]# cd /etc/nginx/ [root@localhost ~]# mkdir CA //创建服务器私钥,命令会让你输入一个口令 //注意,centos版本如果是CentOS Linux release 8.0.1905 (Core)版本,私钥长度不能设置成1024位,必须2048位 [root@localhost ~]# cd CA [root@localhost CA]# openssl genrsa -des3 -out server.key 2048 //创建签名请求的证书(CSR),设置信息 [root@localhost CA]# openssl req -new -key server.key -out server.csr //标记证书使用上述私钥和CSR [root@backup CA]# openssl x509 -req -days 365 -in server.csr -signkey server.key -out server.crt //配置nginx [root@backup CA]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf server { listen 443 ssl ; server_name www.xxxx.com; root /usr/share/nginx/html; ssl_certificate "/etc/nginx/CA/server.crt"; ssl_certificate_key "/etc/nginx/CA/server.key"; ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m; ssl_session_timeout 10m; ssl_ciphers PROFILE=SYSTEM; ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on; # Load configuration files for the default server block. include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf; location / { } error_page 404 /404.html; location = /40x.html { } error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = /50x.html { } }
重启服务网页上访问
使用zabbix监控nginx状态
编写监控脚本在从库上运行
[root@node1 ~]# cat /usr/local/etc/zabbix_scripts/nginx_status.sh #!/bin/bash case $1 in Active) /usr/bin/curl -s 127.0.0.1/status | awk 'NR==1 {print $3}' ;; reading) /usr/bin/curl -s 127.0.0.1/status | grep 'Reading'|cut -d" " -f2 ;; Writing) /usr/bin/curl -s 127.0.0.1/status | grep 'Writing'|cut -d" " -f4 ;; Waiting) /usr/bin/curl -s 127.0.0.1/status | grep 'Waiting'|cut -d" " -f6 ;; acceptes) /usr/bin/curl -s 127.0.0.1/status | awk 'NR==3{print $1}' ;; handled) /usr/bin/curl -s 127.0.0.1/status | awk 'NR==3{print $2}' ;; requests) /usr/bin/curl -s 127.0.0.1/status | awk 'NR==3{print $3}' ;; *) echo "Usage: $0 {Active|reading|Writing|Waiting|acceptes|handled|requests}" ;; esac [root@node1 ~]# chmod +x /usr/local/etc/zabbix_scripts/nginx_status.sh //添加键值 [root@node1 ~]# vim /usr/local/etc/zabbix_agentd.conf UnsafeUserParameters=1 UserParameter=nginx_check_status[*],/usr/local/etc/zabbix_scripts/nginx_status.sh $1 [root@node1 ~]# pkill zabbix [root@node1 ~]# zabbix_agentd
测试zabbix获取值
[root@localhost ~]# zabbix_get -s 192.168.248.81 -k 'nginx_check_status[Writing]' 1 [root@localhost ~]# zabbix_get -s 192.168.248.81 -k 'nginx_check_status[requests]' 6 [root@localhost ~]# zabbix_get -s 192.168.248.81 -k 'nginx_check_status[Reading]' 0 [root@localhost ~]# zabbix_get -s 192.168.248.81 -k 'nginx_check_status[Waiting]' 0
在Zabbix的WEB页面添加监控项
添加主机组
添加监控项
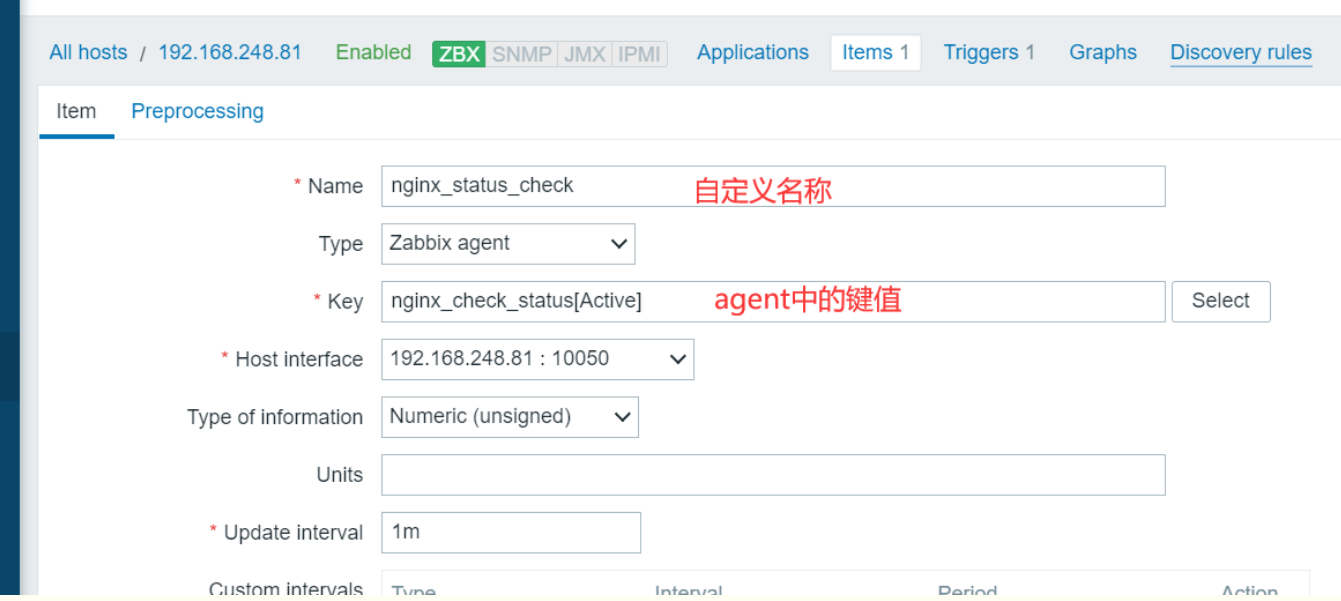
查看监控值
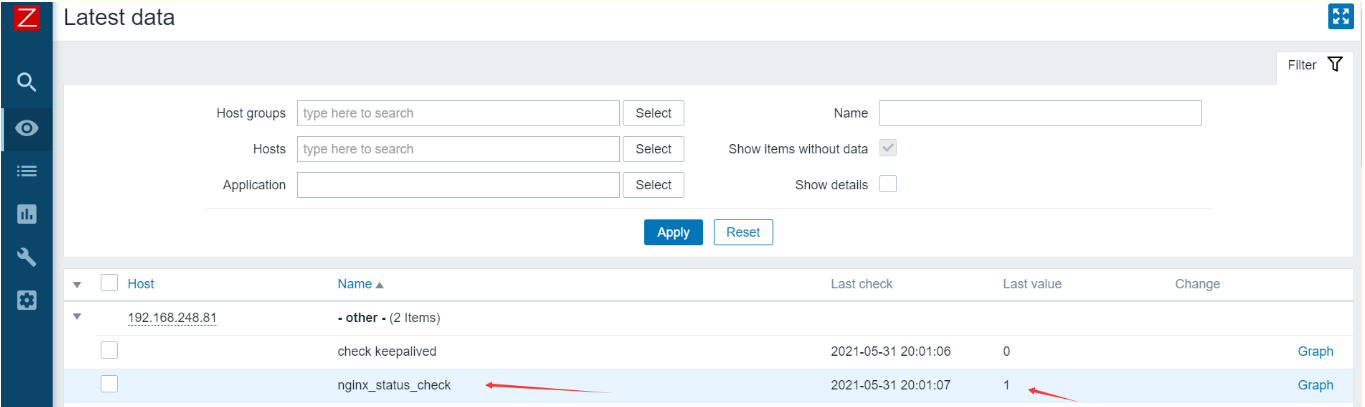
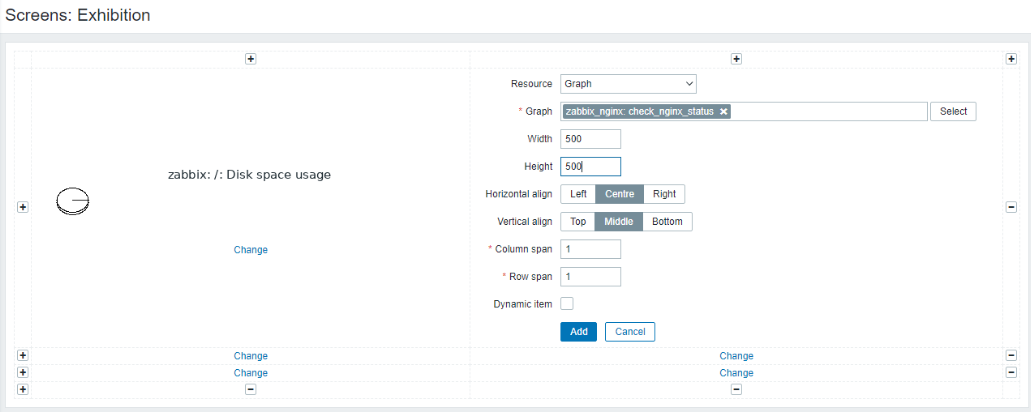
也可以在客户端上添加graph
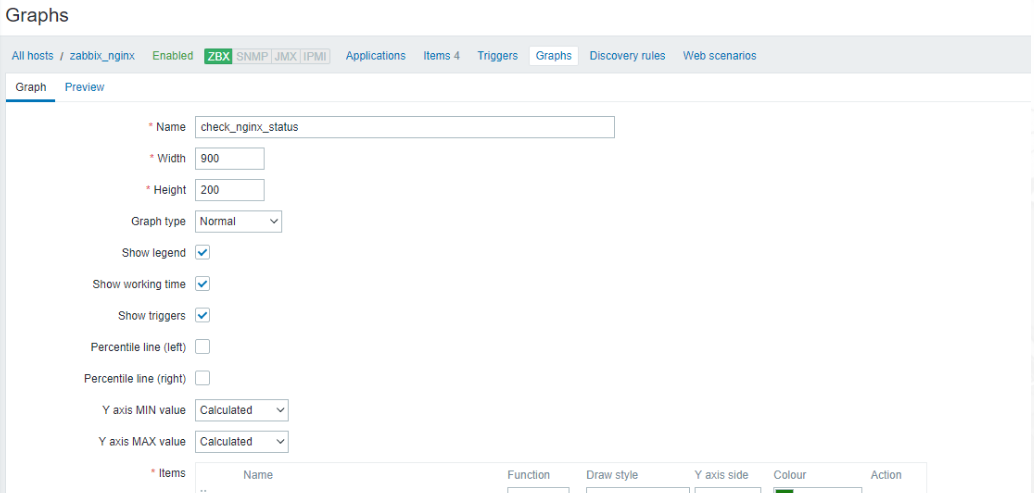
在Screens上添加图表方便监控
rewrite
语法:rewrite regex replacement flag;,如:
将url 开头为/imgs 下所有的以.jpg结尾的文件路径全部转成 /images下所有.jpg结尾的文件
rewrite ^/images/(.*\.jpg)$ /imgs/$1 break; rewrite ^/bbs/(.*)$ http://www.idfsoft.com/index.html redirect;
常见的flag
| flag | 作用 |
|---|---|
| last | 基本上都用这个flag,表示当前的匹配结束,继续下一个匹配,最多匹配10个到20个 一旦此rewrite规则重写完成后,就不再被后面其它的rewrite规则进行处理 而是由UserAgent重新对重写后的URL再一次发起请求,并从头开始执行类似的过程 |
| break | 中止Rewrite,不再继续匹配 一旦此rewrite规则重写完成后,由UserAgent对新的URL重新发起请求, 且不再会被当前location内的任何rewrite规则所检查 |
| redirect | 以临时重定向的HTTP状态302返回新的URL |
| permanent | 以永久重定向的HTTP状态301返回新的URL |
rewrite模块的作用是用来执行URL重定向。这个机制有利于去掉恶意访问的url,也有利于搜索引擎优化(SEO)
nginx使用的语法源于Perl兼容正则表达式(PCRE)库,基本语法如下:
| 标识符 | 意义 |
|---|---|
| ^ | 必须以^后的实体开头 |
| $ | 必须以$前的实体结尾 |
| . | 匹配任意字符 |
| [] | 匹配指定字符集内的任意字符 |
| [^] | 匹配任何不包括在指定字符集内的任意字符串 |
| | | 匹配 | 之前或之后的实体 |
| () | 分组,组成一组用于匹配的实体,通常会有 | 来协助 |
捕获子表达式,可以捕获放在()之间的任何文本,比如:
^(hello|sir)$ //字符串为“hi sir”捕获的结果:$1=hi$2=sir
示例:在nginx网页访问目录下创建一个目录,在里面放入一张图片
[root@localhost ~]# cd /usr/share/nginx/html [root@localhost ~]# mkdir images [root@localhost html]# ls images/ 1.jpg
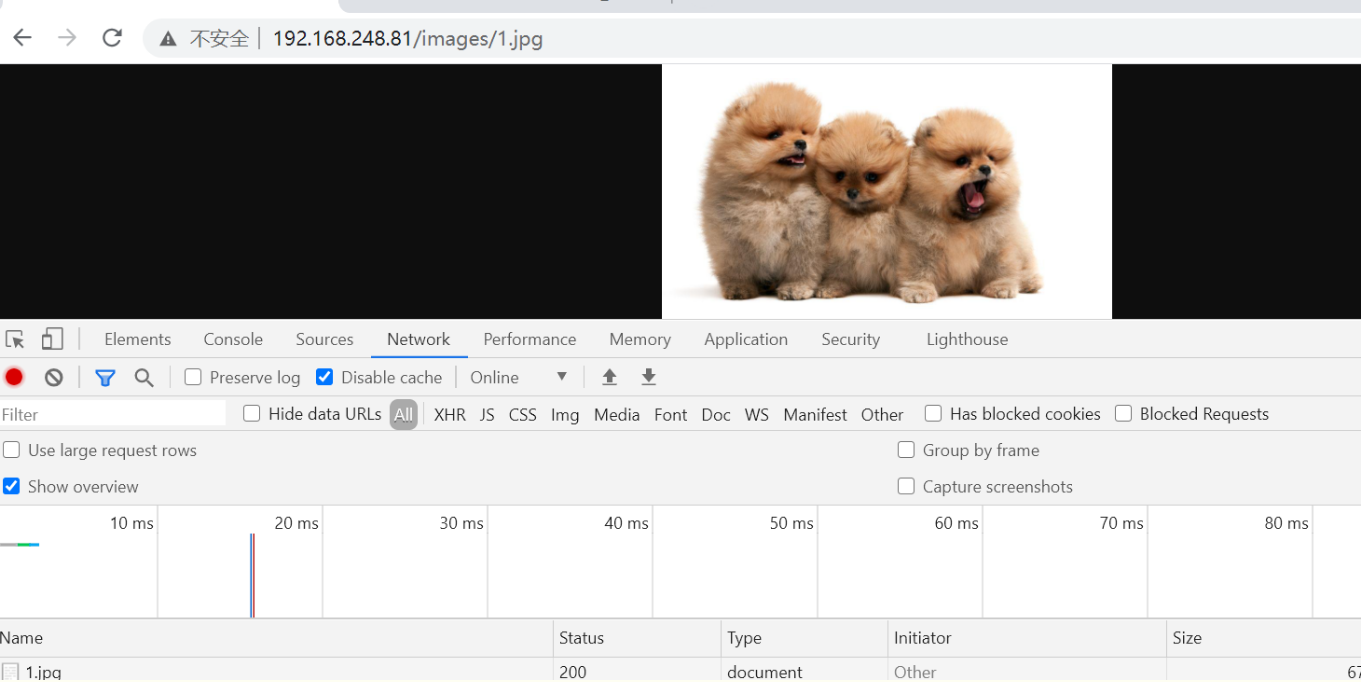
现在需求改变文件目录,但是再访问会发现404,这时我们需要修改配置文件使其访问还是以images/1.jpg访问
[root@localhost ~]# cd /usr/local/nginx/html [root@localhost html]# mkdir imgs [root@localhost html]# mv images/1.jpg imgs/ [root@localhost html]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf ......................... location /images { rewrite ^/images/(.*\.jpg)$ /imgs/$1 permanent; } [root@localhost html]# nginx -t nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful [root@localhost html]# nginx -s reload
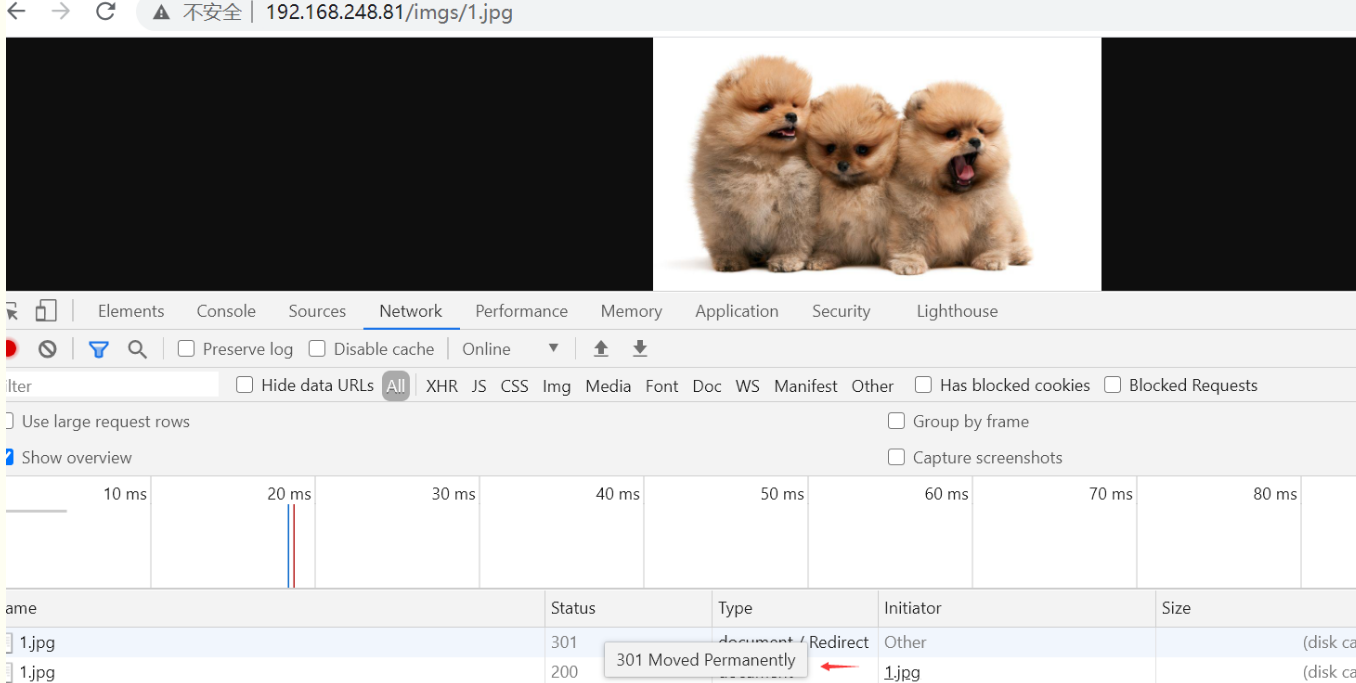
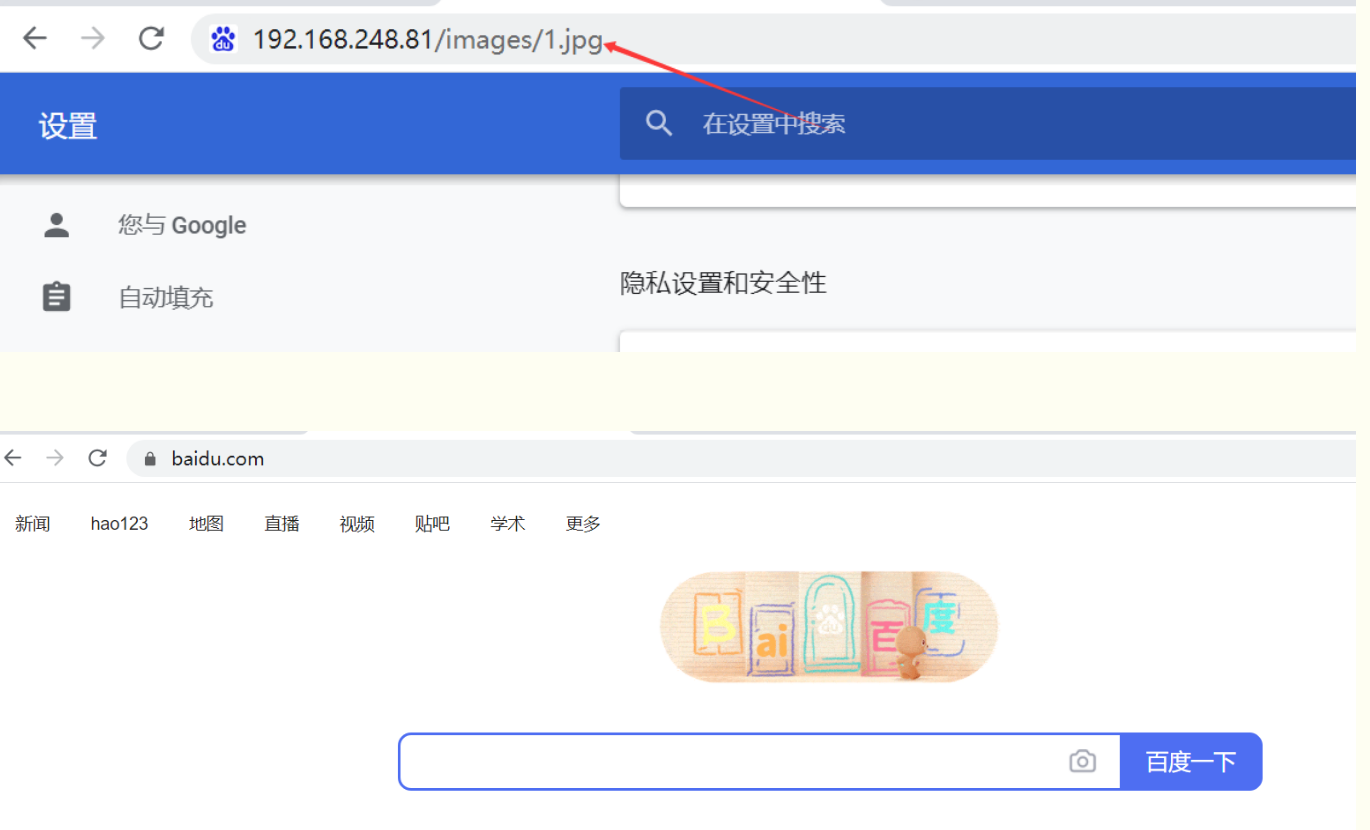
last (这样我们会先访问到图片,刷新后跳转到百度)
[root@localhost html]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf location /images { rewrite ^/images/(.*\.jpg)$ /imgs/$1 last; } location /imgs { rewrite ^/imgs/(.*\.jpg)$ http://www.baidu.com last; }
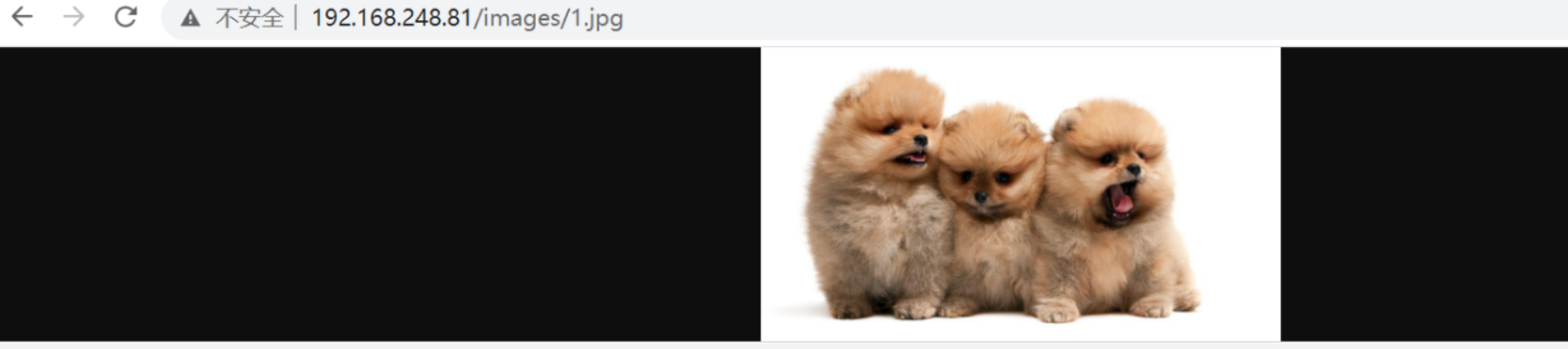
break (当匹配第一个break之后就不会去匹配后面的了)
[root@localhost html]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf location /images { rewrite ^/images/(.*\.jpg)$ /imgs/$1 break; } location /imgs { rewrite ^/imgs/(.*\.jpg)$ http://www.baidu.com last; } [root@localhost html]# nginx -s reload
if
语法:
if (condition) {...}
应用场景:
- server段
- location段
常见的condition
- 变量名(变量值为空串,或者以“0”开始,则为false,其它的均为true)
- 以变量为操作数构成的比较表达式(可使用=,!=类似的比较操作符进行测试)
- 正则表达式的模式匹配操作
- ~:区分大小写的模式匹配检查
- ~*:不区分大小写的模式匹配检查
- !~和!~*:对上面两种测试取反
- 测试指定路径为文件的可能性(-f,!-f)
- 测试指定路径为目录的可能性(-d,!-d)
- 测试文件的存在性(-e,!-e)
- 检查文件是否有执行权限(-x,!-x)
基于浏览器实现分离案例
if ($http_user_agent ~ Firefox) { rewrite ^(.*)$ /firefox/$1 break; } if ($http_user_agent ~ MSIE) { rewrite ^(.*)$ /msie/$1 break; } if ($http_user_agent ~ Chrome) { rewrite ^(.*)$ /chrome/$1 break; }
防盗链案例
location ~* \.(jpg|gif|jpeg|png)$ { valid_referers none blocked www.idfsoft.com; if ($invalid_referer) { rewrite ^/ http://www.idfsoft.com/403.html; }
反向代理与负载均衡
nginx通常被用作后端服务器的反向代理,这样就可以很方便的实现动静分离以及负载均衡,从而大大提高服务器的处理能力。
nginx实现动静分离,其实就是在反向代理的时候,如果是静态资源,就直接从nginx发布的路径去读取,而不需要从后台服务器获取了。
但是要注意,这种情况下需要保证后端跟前端的程序保持一致,可以使用Rsync做服务端自动同步或者使用NFS、MFS分布式共享存储。
Http Proxy模块,功能很多,最常用的是proxy_pass和proxy_cache
如果要使用proxy_cache,需要集成第三方的ngx_cache_purge模块,用来清除指定的URL缓存。这个集成需要在安装nginx的时候去做,如:
./configure --add-module=../ngx_cache_purge-1.0 ......
nginx通过upstream模块来实现简单的负载均衡,upstream需要定义在http段内
在upstream段内,定义一个服务器列表,默认的方式是轮询,如果要确定同一个访问者发出的请求总是由同一个后端服务器来处理,可以设置ip_hash,如:
upstream idfsoft.com { ip_hash; server 127.0.0.1:9080 weight=5; server 127.0.0.1:8080 weight=5; server 127.0.0.1:1111; }
环境:
| 主机名 | IP | 安装的服务 |
| localhost | 192.168.100.145 | nginx |
| node1 | 192.168.100.147 | httpd |
| node2 | 192.168.100.148 | httpd |
准备工作:关闭防火墙selinux
//写一个测试文件到第一台机 [root@node1~]# echo "test1" > /var/www/html/index.html [root@node1 ~]# systemctl start httpd //写一个测试文件到第二台机 [root@node2 ~]# echo "test2" > /var/www/html/index.html [root@node2 ~]# systemctl start httpd [root@localhost ~]# curl 192.168.100.147 test1 [root@loclhost ~]# curl 192.168.100.148 test2 //配置nginx [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf upstream index.html { server 192.168.100.147; server 192.168.100.148; } server { listen 80; server_name localhost; location / { proxy_pass http://index.html; } [root@localhost ~]# nginx -t nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful [root@localhost ~]# nginx -s reload
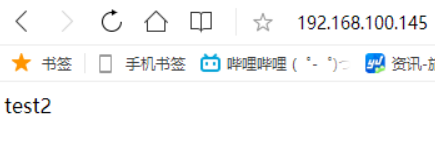
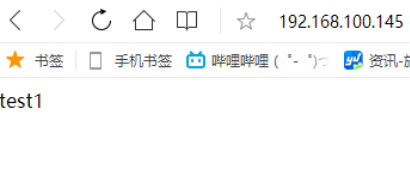
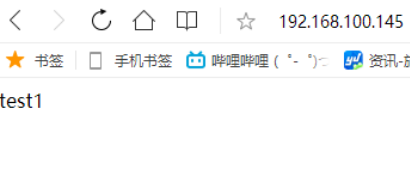
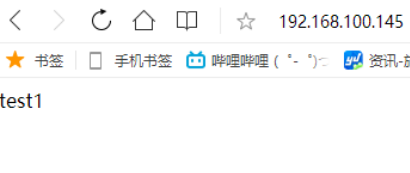
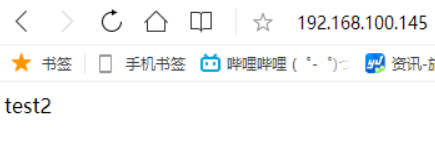
修改配置文件在node1的IP末尾加上weigtht=2,会发现前两次访问的是test1,后一次就是test2了。
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf upstream index.html { server 192.168.100.147 weight=2; server 192.168.100.148; } server { listen 80; server_name localhost; location / { proxy_pass http://index.html; } [root@localhost ~]# nginx -t nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful [root@localhost ~]# nginx -s reload
注:因为他们的端口号都是一致的,所以不用加端口号,不一样的话就需要加上端口号;不然就会触发nginx的健康检查机制
此时我们将第一台机httpd的修改配置监听端口80改成8080
[root@node1 ~]# vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf [root@node1 ~]# systemctl restart httpd [root@node1 ~]# ss -antl State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 0 128 *:8080 *:* LISTEN 0 128 [::]:22 [::]:*
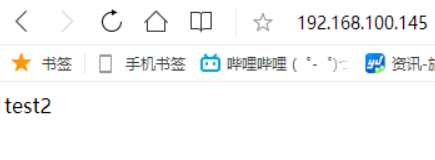
此时就会发现访问的永远是node2,因为他访问不到node1的80端口。
主机间端口如果不一致需要修改配置文件:
//将nginx配置文件中ip后加上端口号就又能访问了 [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf upstream index.html { server 192.168.100.147:8080 weight=2; server 192.168.100.148:80; } [root@localhost ~]# nginx -t nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful [root@localhost ~]# nginx -s reload
ip_hash;一台主机分配一个请求
//加上ip_hash [root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf upstream index.html { ip_hash; server 192.168.100.147:8080 weight=2; server 192.168.100.148:80; } [root@localhost ~]# nginx -t nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful [root@localhost ~]# nginx -s reload [root@node1 ~]# curl 192.168.100.145 test1 [root@node1 ~]# curl 192.168.100.145 test1 [root@node1 ~]# curl 192.168.100.145 test1
此时会发现一直访问的是test1
注意:这个方法本质还是轮询,而且由于客户端的ip可能是不断变化的,比如动态ip,代理,FQ等,因此ip_hash并不能完全保证同一个客户端总是由同一个服务器来处理。
定义好upstream后,需要在server段内添加如下内容:
server { location / { proxy_pass http://index.html; } }


