python基础—函数装饰器
python基础—函数装饰器
1、什么是装饰器
装饰器本质上是一个python函数,它可以让其他函数在不需要做任何代码变动的前提下增加额外功能。
装饰器的返回值是也是一个函数对象。
装饰器经常用于有切面需求的场景,比如:插入日志,性能测试,事务处理、缓存、权限校验等场景。装饰器是解决这类问题的绝佳设计,有了装饰器,我们就可以抽离出大量与函数功能无关的雷同代码并继续重用。概括的讲,装饰器的作用就是为已经存在的对象添加额外的功能。
为什么要用装饰器及开放封闭原则
函数的源代码和调用方式一般不修改,但是还需要扩展功能的话就需要在需要扩展的函数的开始使用装饰器。举例:带眼镜
装饰器是任意可调用的对象,本质就是函数
装饰器在python中使用如此方便归因于python的函数能像普通的对象一样能作为参数传递给其他函数,可以被复制给其他变量,可以作为返回值,可以被定义在另一个函数内。
2、 简单的装饰器
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
import timedef timmer(func): def wrapper(*args,**kwargs): start_time=time.time() res=func(*args,**kwargs) stop_time=time.time() print("run time is %s "%(stop_time-start_time)) return wrapper@timmer #等同于 index=timmer(index) , 此后index等同于 wrapper def index(): time.sleep(1) print("welcom ! wen")index() |
输出结果:
|
1
2
|
welcom ! wenrun time is 1.0001096725463867 |
函数timmer就是装饰器,它把执行真正业务方法的func包裹在函数里面,看起来像index被timmer装饰了。
在这个例子中,函数进入和退出时,被称为一个横切面(Aspet),这种编程方式被称为面向切面的编程(Aspet-Oriented Programming)
@符号是装饰器的语法糖,在定义函数的时候,避免再一次赋值操作。
3、装饰器的语法
@timmer
timmer就是一个装饰器
@timmer等同于 被装饰函数名=timmer(被装饰函数名) 被装饰器函数就是紧接@timmer下面的函数
4、无参装饰器
如果多个函数拥有不同的参数形式,怎么共用同样的装饰器?
在Python中,函数可以支持(*args, **kwargs)可变参数,所以装饰器可以通过可变参数形式来实现内嵌函数的签名。
无参装饰器,被装饰函数带参,无返回值
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
import timedef timmer(func): def wrapper(*args,**kwargs): print(func) return wrapper@timmerdef index(): time.sleep(1) print("welcom ! wen")index() |
输出结果:
|
1
|
<function index at 0x000000D132F5AF28> |
多个函数共用一个装饰器:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
import timedef timmer(func): def wrapper(*args,**kwargs): start_time=time.time() func(*args,**kwargs) stop_time=time.time() print("run time is: %s" %(stop_time-start_time)) return wrapper@timmerdef home(name): time.sleep(1) print(" %s home"%name)@timmerdef auth(name,password): time.sleep(1)print(name,password)@timmerdef tell(): time.sleep(1) print("------------------")home("wenyanjie")auth("wen","1234")tell()输出结果为: wenyanjie homerun time is: 1.0002663135528564wen 1234run time is: 1.0000183582305908------------------run time is: 1.0009756088256836 |
无参装饰器,被装饰函数带参,且有返回值
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
import timedef timmer(func): def wrapper(*args,**kwargs): start_time=time.time() res=func(*args,**kwargs) stop_time=time.time() print("run time is: %s" %(stop_time-start_time)) return res return wrapper@timmerdef home(name): time.sleep(1) print(" %s home"%name)@timmerdef auth(name,password): time.sleep(1) print(name,password)@timmerdef tell(): time.sleep(1) print("------------------")@timmerdef my_max(x,y): return x if x > y else yhome("wenyanjie")auth("wen","1234")tell()res=my_max(1,2)print("----->",res) |
输出结果:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
wenyanjie homerun time is: 1.0004072189331055wen 1234run time is: 1.0009665489196777------------------run time is: 1.0001206398010254run time is: 0.0-----> 2 |
5、有参装饰器
装饰器还有更大的灵活性,例如带参数的装饰器:在上面的装饰器调用中,比如@timmer,该装饰器唯一的参数是执行业务的函数。装饰器的语法允许我们在调用时,提供其他参数。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
def auth2(auth_type): def auth(func): def wrapper(*args,**kwargs): if auth_type == "file": name=input("username:") password=input("password") if name=="wen" and password =="123": print("login successful!") res=func(*args,**kwargs) return res else: print("auth error") elif auth_type == "sql": print("sql no learn.....") return wrapper return auth@auth2(auth_type="file")def login(name): print("this is %s index page"%name) return 1flag=login("wenyanjie")print(flag) |
输出结果:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
username:wenpassword123login successful!this is wenyanjie index page1 |
上面例子中的auth2是允许带参数的装饰器。它实际上是对原有装饰器的一个函数封装,并返回一个装饰器。我们可以将他理解为一个含有参数的闭包。当我们使用@auth2(auth_type=”file”)调用的时候,python能够发现这一层的封装,并把参数传递到装饰器的环境中。
上面有参装饰器的执行步骤分解:

6、多个装饰器
装饰器是可以叠加的,那么这就涉及装饰器调用顺序。对于python中的“@”语法糖,装饰器的调用顺序与使用@语法糖的顺序相反。
多个无参装饰器
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
@ccc@bbb@aaadef func(): pass |
#相当与
|
1
2
3
|
func=aaa(func)func=bbb(func)func=ccc(func) |
#相当与
|
1
|
func=ccc(bbb(aaa(func))) |
有参装饰器多个
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
@ccc('c')@bbb('b')@aaa('c')def func(): pass |
#相当与
|
1
2
3
|
func=aaa('a')(func)func=bbb('b')(func)func=ccc('c')(func) |
#相当与
|
1
|
func=ccc('c')(bbb('b')(aaa('a')(func))) |
案例:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
import timecurrent_login={'name':None,'login':False}def timmer(func): def wrapper(*args,**kwargs): start_time=time.time() res=func(*args,**kwargs) stop_time=time.time() print("run time is %s"%(stop_time-start_time)) return res return wrapperdef auth2(auth_type): def auth(func): def wrapper(*args,**kwargs): if current_login['name'] and current_login['login']: res=func(*args,**kwargs) return res if auth_type == "file": name=input("username:") password=input("password:") if name=="wen" and password =="123": print("login successful!") current_login['name']=name current_login['login']=password res=func(*args,**kwargs) return res else: print("auth error") elif auth_type == "sql": print("sql no learn.....") return wrapper return auth@timmer@auth2(auth_type="file")def login(name): print("this is %s index page"%name)login("wenyanjie")login("wenyanjie") |
输出结果:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
username:wenPassword:123login successful!this is wenyanjie index pagerun time is 3.228583812713623this is wenyanjie index pagerun time is 0.0 |
7 eval方法:往文件中放有结构的数据
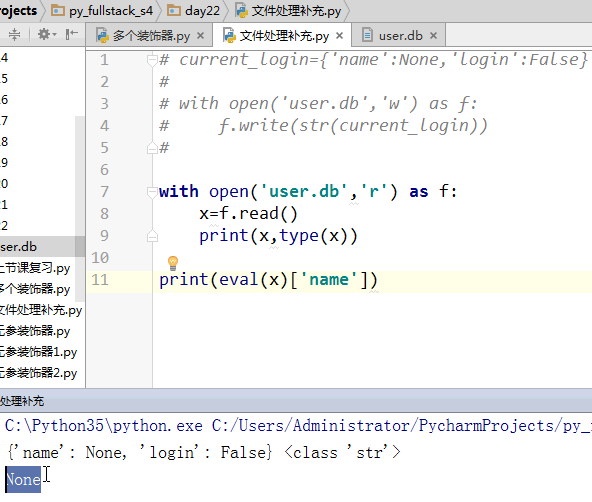
8 被装饰函数将所有注释等自己的定义都传给装饰器
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
import timefrom functools import wrapsdef timmer(func): @wraps(func) def wrapper(*args,**kwargs): "wrapper function" print(func) start_time=time.time() res=func(*args,**kwargs) stop_time=time.time() print("run time is %s "%(stop_time-start_time)) return res return wrapper@timmerdef my_max(x,y): "my_max function" a=x if x>y else y return aprint(help(my_max)) |
输出结果:
|
1
2
|
my_max(x, y) my_max function |





