一个简单的Java web服务器实现
前言
一个简单的Java web服务器实现,比较简单,基于java.net.Socket和java.net.ServerSocket实现;
程序执行步骤
- 创建一个ServerSocket对象;
- 调用ServerSocket对象的accept方法,等待连接,连接成功会返回一个Socket对象,否则一直阻塞等待;
- 从Socket对象中获取InputStream和OutputStream字节流,这两个流分别对应request请求和response响应;
- 处理请求:读取InputStream字节流信息,转成字符串形式,并解析,这里的解析比较简单,仅仅获取uri(统一资源标识符)信息;
- 处理响应:根据解析出来的uri信息,从WEB_ROOT目录中寻找请求的资源资源文件, 读取资源文件,并将其写入到OutputStream字节流中;
- 关闭Socket对象;
- 转到步骤2,继续等待连接请求;
代码实现
服务器实现:
package ex01.pyrmont; import java.net.Socket; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.InetAddress; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.OutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.File; public class HttpServer { /** * WEB_ROOT是HTML和其它文件存放的目录. 这里的WEB_ROOT为工作目录下的webroot目录 */ public static final String WEB_ROOT = System.getProperty("user.dir") + File.separator + "webroot"; // 关闭服务命令 private static final String SHUTDOWN_COMMAND = "/SHUTDOWN"; public static void main(String[] args) { HttpServer server = new HttpServer(); //等待连接请求 server.await(); } public void await() { ServerSocket serverSocket = null; int port = 8080; try { //服务器套接字对象 serverSocket = new ServerSocket(port, 1, InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1")); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); System.exit(1); } // 循环等待一个请求 while (true) { Socket socket = null; InputStream input = null; OutputStream output = null; try { //等待连接,连接成功后,返回一个Socket对象 socket = serverSocket.accept(); input = socket.getInputStream(); output = socket.getOutputStream(); // 创建Request对象并解析 Request request = new Request(input); request.parse(); // 检查是否是关闭服务命令 if (request.getUri().equals(SHUTDOWN_COMMAND)) { break; } // 创建 Response 对象 Response response = new Response(output); response.setRequest(request); response.sendStaticResource(); // 关闭 socket 对象 socket.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); continue; } } } }
Request类:
package ex01.pyrmont; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class Request { private InputStream input; private String uri; public Request(InputStream input) { this.input = input; } //从InputStream中读取request信息,并从request中获取uri值 public void parse() { StringBuffer request = new StringBuffer(2048); int i; byte[] buffer = new byte[2048]; try { i = input.read(buffer); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); i = -1; } for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) { request.append((char) buffer[j]); } System.out.print(request.toString()); uri = parseUri(request.toString()); } /** * * requestString形式如下: * GET /index.html HTTP/1.1 * Host: localhost:8080 * Connection: keep-alive * Cache-Control: max-age=0 * ... * 该函数目的就是为了获取/index.html字符串 */ private String parseUri(String requestString) { int index1, index2; index1 = requestString.indexOf(' '); if (index1 != -1) { index2 = requestString.indexOf(' ', index1 + 1); if (index2 > index1) return requestString.substring(index1 + 1, index2); } return null; } public String getUri() { return uri; } }
Response类:
package ex01.pyrmont; import java.io.OutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.File; /* HTTP Response = Status-Line *(( general-header | response-header | entity-header ) CRLF) CRLF [ message-body ] Status-Line = HTTP-Version SP Status-Code SP Reason-Phrase CRLF */ public class Response { private static final int BUFFER_SIZE = 1024; Request request; OutputStream output; public Response(OutputStream output) { this.output = output; } public void setRequest(Request request) { this.request = request; } public void sendStaticResource() throws IOException { byte[] bytes = new byte[BUFFER_SIZE]; FileInputStream fis = null; try { //将web文件写入到OutputStream字节流中 File file = new File(HttpServer.WEB_ROOT, request.getUri()); if (file.exists()) { fis = new FileInputStream(file); int ch = fis.read(bytes, 0, BUFFER_SIZE); while (ch != -1) { output.write(bytes, 0, ch); ch = fis.read(bytes, 0, BUFFER_SIZE); } } else { // file not found String errorMessage = "HTTP/1.1 404 File Not Found\r\n" + "Content-Type: text/html\r\n" + "Content-Length: 23\r\n" + "\r\n" + "<h1>File Not Found</h1>"; output.write(errorMessage.getBytes()); } } catch (Exception e) { // thrown if cannot instantiate a File object System.out.println(e.toString()); } finally { if (fis != null) fis.close(); } } }
结果测试
访问存在的资源文件(注意存放在工程目录的webroot文件夹里):
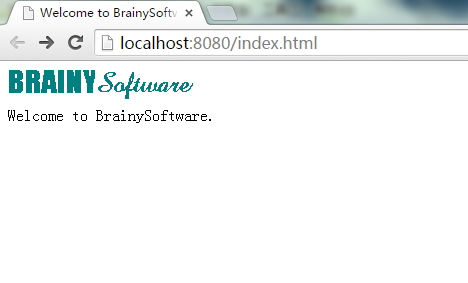
访问不存在的资源文件:
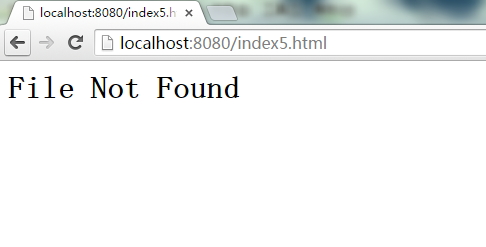
关闭服务器:
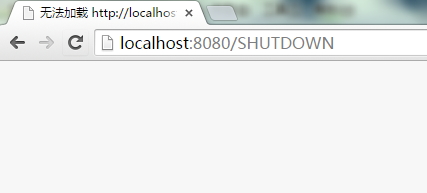
参考资料
《深入剖析Tomcat》


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号