jquery的2.0.3版本源码系列(3):96行-283行,给JQ对象,添加一些方法和属性
jquery是面向对象的程序,面向对象就离不开方法和属性。
方法的简化
jQuery.fn=jQuery.prototype={
jquery: 版本
constructor: 修正指向问题
init(): 初始化和参数管理
selector:存储选择字符串
length:this对象的长度
toArray():转数组
get(): 转原生集合
pushStack():JQ对象的入栈
each():遍历集合
ready():DOM加载的接口
slice():集合的截取
first():集合的第一项
last():集合的最后一项
eq():集合的指定项
map():返回新集合
end():返回集合前一个状态
push():(内部使用)
sort():(内部使用)
splice():(内部使用)
};
3.1 jquery属性
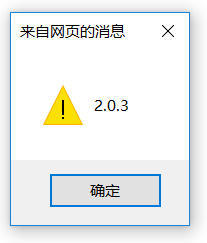
这个属性可以通过jQuery对象来找到版本号。 先要引入jQuery库,alert($().jquery); 代码显示效果
3.2 constructor属性的修正
第一点,原型对象的constructor属性是自动生成的。
首先来看constructor属性其实是原型对象的构造函数。
function Aaa(){
}
//Aaa.prototype.constructor=Aaa;当一个函数创建完成,那么自动会在原型对象上生成constructor属性。
var al=new Aaa();
alert(al.constructor);
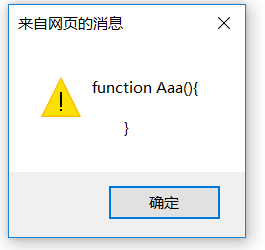
可以看出来,弹出来的内容是这个对象对应的构造函数。其实当写完这个函数,constructor属性就生成了。
Aaa.prototype.constructor=Aaa;当一个函数创建完成,那么自动会在原型对象上生成constructor属性。那么看如下代码。
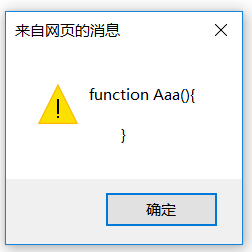
function Aaa(){
}
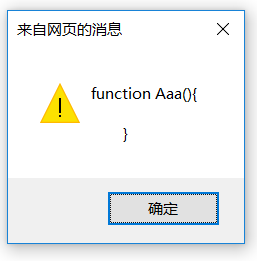
alert(Aaa.prototype.constructor);
显示结果是
第二,需要了解是constructor属性容易被修改。
既然constructor属性是自动生成的,可是为什么要做指定呢?原因在于constructor很容易被修改。
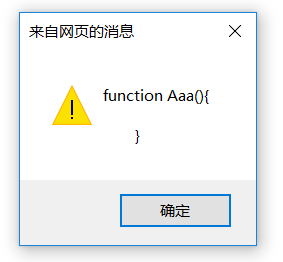
function Aaa(){
}
Aaa.prototype.constructor=Array;//指向constructor属性为数组Array。
alert(Aaa.prototype.constructor)
显示效果是
那么来看两种不同的写法。
(1)通过点语法添加属性。constructor属性没有被修改。
function Aaa(){
}
Aaa.prototype.name="hello";
Aaa.prototype.age="29";
var al=new Aaa();
alert(al.constructor);//返回的是Aaa函数,也就是constructor属性没有被修改。
(2)通过对象字面量覆盖的方式。由于constructor属性没有定义,所以原有的constructor属性就被修改了。
function Aaa(){
}
Aaa.prototype={
"name":"hello",
"age":"29"
};
var al=new Aaa();
alert(al.constructor);
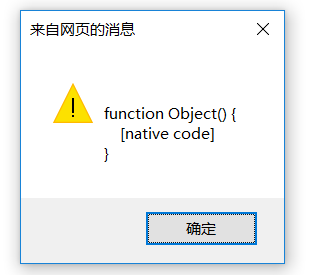
那么修正的方式是添加constructor属性。OK,对了。
function Aaa(){ } Aaa.prototype={ constructor:Aaa, "name":"hello", "age":"29" }; var al=new Aaa(); alert(al.constructor);
3.3 init函数
我们知道,63行,对外提供接口只有$(或者说jquery),最终调用的是jQuery.fn.init。那么就是这里101行的init函数。
首先需要了解的是jQuery操作标签是把原生标签存放到this里。
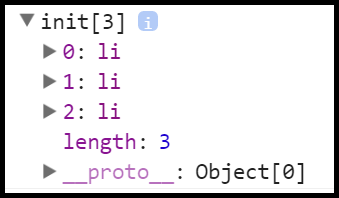
如果是js,它的操作方式是通过原生的方式把li标签存起来。不过在jquery的面向对象的方式里并非如此,因为aLi是局部变量,那么就无法存取,必须通过this对象来共享。
<ul>
<li></li>
<li></li>
<li></li>
</ul>
var aLi=document.getElementsByTagName("li");
for(var i=0;i<aLi.length;i++){
aLi[i].style.background="red";
}
jquery是通过this对象来存储原生标签的。
this ={
0:"li",
1:"li",
2:"li",
length:"3"
}
for(var i=0;i<this.length;i++){
this[i].style.background="red";
}
关于这部分可以通过引入jQuery,来验证this对象里有存储原生标签。 console.log($("li")); 的打印结果如下。那么在for循环里就可以通过下标来访访问了。

当传入错误的内容时,105行
// HANDLE: $(""), $(null), $(undefined), $(false) if ( !selector ) { //当传入的是空字符串,null,undefined,false,那么直接返回 return this; }
传入字符串,110行
当传入HTML字符串时
if ( typeof selector === "string" ) {
if ( selector.charAt(0) === "<" && selector.charAt( selector.length - 1 ) === ">" && selector.length >= 3 ) { //如果字符串的首个字符是小于符号,末位字符是大于符号,那么是HTML,会跳过正则检查。
match = [ null, selector, null ];
//比如,$("<li>")、$("<li></li><li>2</li>"),
//那么进入这个条件,match=[null,"<li>",null],match=[null,"<li>1</li><li>2</li>",null]。
} else { match = rquickExpr.exec( selector );
//如果传入的是$(".box")、$("div"),$("#div1 div.box"),match=null。
//如果传入的是$("#div1"),match=["#div1",null,"div1"]。
//如果传入的是$("<li>hello"),那么match=["<li>hello","<li>",null] } // Match html or make sure no context is specified for #id
//匹配html或者确保没有上下文指定#id。
//如果match存在,并且match[1]存在或者context为空.那么进入这条语句的有:$("<li>")、$("#div1").
if ( match && (match[1] || !context) ) { // HANDLE: $(html) -> $(array) 处理html字符串:$("<li>")。
if ( match[1] ) { context = context instanceof jQuery ? context[0] : context; //instanceof判断传入的context是否是jQuery的实例。
// scripts is true for back-compat
jQuery.merge( this, jQuery.parseHTML( match[1], context && context.nodeType ? context.ownerDocument || context : document, true ) ); // HANDLE: $(html, props) if ( rsingleTag.test( match[1] ) && jQuery.isPlainObject( context ) ) { for ( match in context ) { // Properties of context are called as methods if possible if ( jQuery.isFunction( this[ match ] ) ) { this[ match ]( context[ match ] ); // ...and otherwise set as attributes } else { this.attr( match, context[ match ] ); } } } return this; // HANDLE: $(#id) 这里处理的是$("#div1")之类的。 } else { //XXXXXXX } //XXXXXX
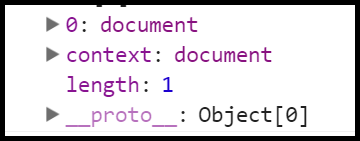
context上下文,要么传入原生的document,要么传入$(document),最终 context instanceof jQuery ? context[0] : context 得到的是原生的document。$(document)对象打印出来的结果是,也就是 console.log($(document)); 。context事实上只能选择document。它跟iframe有关,其实没有太大用处。
parseHTML是用来做什么的?
首先,parseHTML会把传入的HTML字符串转换为数组。
<script src="jquery-2.0.3.min.js"></script>
<script>
var str="<li>1</li><li>2</li><li>3</li>";
var arr=jQuery.parseHTML(str)
console.log(arr);
</script>
打印的结果是一个数组。

再次,这些原生的标签,可以被追加到某个标签上。
<script src="jquery-2.0.3.min.js"></script>
<script>
var str="<li>1</li><li>2</li><li>3</li>";
var arr=jQuery.parseHTML(str)
$.each(arr,function(i){
$("ul").append(arr[i]);
})
</script>
显示效果如下

最后,第三个参数如果设置为true,是为了让script标签能够执行js代码。默认false禁止js代码执行。
<script src="jquery-2.0.3.min.js"></script>
<script>
var str="<li>1</li><li>2</li><li>3</li><script>alert('4')<\/script>";
var arr=jQuery.parseHTML(str,document,true)
$.each(arr,function(i){
$("ul").append(arr[i]);
})
</script>
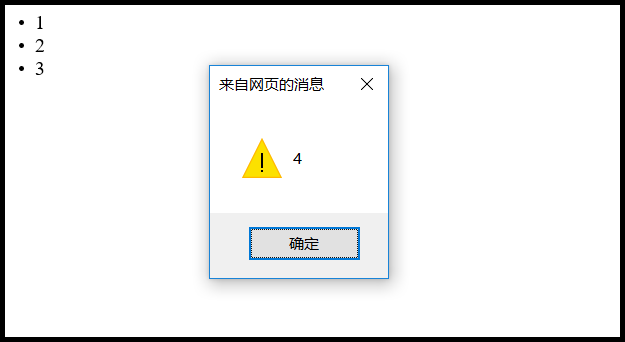
jQuery.merge函数的功能是合并。可以合并数组,也可以合并json。
<script src="jquery-2.0.3.min.js"></script>
<script>
var arr={
0:"a",
1:"b",
length:2
}
var arr2=["c","d"];
console.log($.merge(arr,arr2));
</script>
合并为一个对象,对象的打印结果是

那么最终就能够合并到我们想要的this数组的形式。
例如
<script src="jquery-2.0.3.min.js"></script>
<script>
console.log($("<li>0</li><li>1</li><li>2</li>"));
</script>
if ( rsingleTag.test( match[1] ) && jQuery.isPlainObject( context ) ) {
for ( match in context ) {
// Properties of context are called as methods if possible
if ( jQuery.isFunction( this[ match ] ) ) {
this[ match ]( context[ match ] );
// ...and otherwise set as attributes
} else {
this.attr( match, context[ match ] );
}
}
}
这是这部分的最后一段儿代码。首先,标签检测是不是单标签,context是不是对象字面量。单标签只有两种类型,要么是类似"<li>",要么是类似"<li></li>"
<script src="jquery-2.0.3.min.js"></script>
<script>
$("<li>",{title:"hello",html:"abcd"}).appendTo("ul");
</script>
显示效果,如下。首先li标签的内容是abcd,然后由于添加了title,所以鼠标移上去会有"hello"的提示。
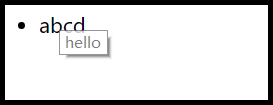
for(match in context)循环要做什么呢? 那么添加一些伪代码,就能够清楚他们都干了什么,context就是第二个参数,this就是$()通过传入参数获得的jQuery对象。
$("<li>",{title:"hello",html:"abcd"}).appendTo("ul");
var context={title:"hello",html:"abcd"};
var thisObject=$("<li>",{title:"hello",html:"abcd"});
for ( match in context ) {
// Properties of context are called as methods if possible
if ( jQuery.isFunction( thisObject[ match ] ) ) {
console.log("if语句"+match);
thisObject[ match ]( context[ match ] );
// ...and otherwise set as attributes
} else {
console.log("else语句"+match);
//this.attr( match, context[ match ] );
}
}
那么传入的 {title:"hello",html:"abcd"} title属性进入else循环,根据142行的代码,使用this.attr添加到元素的属性上。html属性因为是jQuery的函数,也就是html(),那么进行函数调用,就像$().html()一样。
(3)传入id值的处理。
对应的代码是150行到164行,如下代码
} else {
elem = document.getElementById( match[2] );
// Check parentNode to catch when Blackberry 4.6 returns
// nodes that are no longer in the document #6963
if ( elem && elem.parentNode ) {
// Inject the element directly into the jQuery object
this.length = 1;
this[0] = elem;
}
this.context = document;
this.selector = selector;
return this;
}
首先要弄清楚match数组是什么。如果传入的是"#div1",match数组会长成 match=["#div1",null,"div1"]; 那么对于html代码, <div id="div1">div1</div> 。
<script src="jquery-2.0.3.min.js"></script>
<script>
match=["#div1",null,"div1"];
elem = document.getElementById( match[2] );
//<div id="div1">div1</div>
</script>
而下面的代码155行到159行,对于黑莓4.6浏览器的兼容性代码,即使html并没有这个元素,竟然还能够找到。就目前国内的情况黑莓用户很少,可以不用去管它。
if ( elem && elem.parentNode ) {
// Inject the element directly into the jQuery object
this.length = 1;
this[0] = elem;
}
this.context = document; 重置上下文。 this.selector = selector; 则是把selector选择器赋给this对象的seletor属性。
(4)传入复杂标签的处理,比如$("ul li.box"),$(".box")、$("#div1 div.box")。当执行上下文不存在时,走的是这一条路径,都是通过find方法来查找,具体说起来是sizzle引擎的查找。
} else if ( !context || context.jquery ) {
return ( context || rootjQuery ).find( selector );
// HANDLE: $(expr, context)
// (which is just equivalent to: $(context).find(expr)
} else {
return this.constructor( context ).find( selector );
}
如果context不存在,那么返回的是通过rootjQuery也就是$(document)来寻找选择器,也就是复杂标签,相当于 $(document).find("ul li.box"); 。如果存在上下文context, $("ul li.box",document); 对应的是else if语句。
$("ul li.box",$(document)); 对应的是else语句。最终执行的都是 $(document).find("ul li.box"); 。
当传入的是节点,177行

} else if ( selector.nodeType ) { this.context = this[0] = selector; this.length = 1; return this; // HANDLE: $(function) // Shortcut for document ready }
传入节点,处理的是类似$(this),$(document),如果是节点,那么".nodeType"就能做判断,返回1到12的值。可查看DOM节点介绍。既然已经是节点,所以就直接放到this对象的第一个元素里,length归为0,而且节点没有父集的说法,所以上下文直接设为它就好了。这个JSON的特点就是带小标,带length属性。
处理传入的是函数,也就是文档加载,184行

} else if ( jQuery.isFunction( selector ) ) { return rootjQuery.ready( selector ); }
如果是函数,那么返回的是rootjQuery.ready。rootjQuery是$(document)。关于文档加载,有2种方式,$(document).ready(function(){}),$(function(){})。
处理的是传入jquery对象,比如$($("#div1"))

if ( selector.selector !== undefined ) { this.selector = selector.selector; this.context = selector.context; }
那么最终的话是把$($("#div1"))转化为$("#div1")那么重新对应就好了。
处理的是合并参数,193行

return jQuery.makeArray( selector, this );
makeArray可以把集合转换为数组。通过getElementByTagName获得的是集合
<div>1</div>
<div>2</div>
<div>3</div>
<div>4</div>
<div>5</div>
<script src="jquery-2.0.3.min.js"></script>
<script>
$(function(){
var aDiv=document.getElementsByTagName("div");
console.log(aDiv);
})
</script>
对应的结果截图是
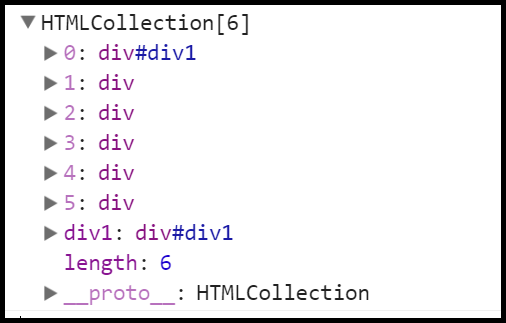
那么现在就可以通过makeArray来构造数组。如果添加了某个json,那么就会合并成为一个json。也就是对应源代码里面的this参数。
var aDiv=document.getElementsByTagName("div");
var aArray=$.makeArray(aDiv);
console.log(aArray);//[ div, div, div, div, div]
var thisObject={0:"li",1:"li",length:2};
var aArray2=$.makeArray(aDiv,thisObject);
console.log(aArray2);
3.4 selector、length属性
seletor、length属性可以被修改,默认为空字符串和0。
3.5 toArray方法、get方法、pushStack方法、end方法、slice方法
toArray: function() {
return core_slice.call( this );
},
// Get the Nth element in the matched element set OR
// Get the whole matched element set as a clean array
get: function( num ) {
return num == null ?
// Return a 'clean' array
this.toArray() :
// Return just the object
( num < 0 ? this[ this.length + num ] : this[ num ] );
},
// Take an array of elements and push it onto the stack
// (returning the new matched element set)
pushStack: function( elems ) {
// Build a new jQuery matched element set
var ret = jQuery.merge( this.constructor(), elems );
// Add the old object onto the stack (as a reference)
ret.prevObject = this;
ret.context = this.context;
// Return the newly-formed element set
return ret;
},
toArray方法的功能是转数组。源代码的core_slice是要操作的数据,然后合并到this的JSON对象里。
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
<div></div>
$("div").toArray();
//$("div"):等于{0,"div";1:"div",2:"div"}。
//toArray():那么就会转化为["div","div","div"]
get方法的功能是转原生集合。那么怎么用呢?
<div>1</div>
<div>2</div>
<div>3</div>
<div>4</div>
$("div").get(0).innerHTML="我是第一个DIV";
//$("div").get(0):获取到第一个div,并转原生标签
//innerHTML:既然是原生标签,那么就可以使用原生的属性来操作
$("div").get();
//不传参,那么返回的就是div的原生集合,[div, div, div, div]
根据源代码,
return num == null ?
// Return a 'clean' array 如果传入的num是null,那么返回是一个数组。
this.toArray() :
// Return just the object如果有传入索引的参数,那么返回一个对象,从索引来取得this对象的某个值。如果是负数,那么加上length长度就可以从后往前找了。
( num < 0 ? this[ this.length + num ] : this[ num ] );
pushStack方法的功能是JQ对象的入栈处理。
首先聊一聊栈的概念。它与队列不一样,队列和火车站排队一样,先排的先买到票,从而先脱离队列。栈的概念就像进电梯,先进的人走到里面,后进的人站在靠外边一点,那么后进的人先出来,先进的人后出来。

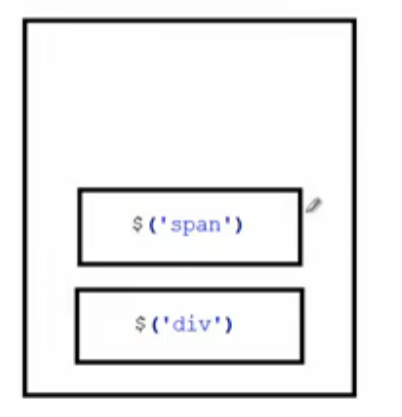
<div id="div1">div1</div>
<span>span</span>
$("#div1").pushStack($("span")).css("background","red");
这里使用pushStack把div和span都入栈,如下图,那么$("#div1").pushStack($("span"))最终css操作的是span。
pushStack: function( elems ) {
// Build a new jQuery matched element set
var ret = jQuery.merge( this.constructor(), elems );
// Add the old object onto the stack (as a reference)
//对应上面的调用例子,就是把$("#div1")挂载到了prevObject。而context就是一个简单的赋值而已。
//下面的栈的操作方法end()就是使用了prevObject。
ret.prevObject = this;
ret.context = this.context;
// Return the newly-formed element set
return ret;
},
$("#div1").pushStack($("span")).end().css("background","yellow");
//这里的end方法会回溯到栈的下一层,那么就是div这个元素了。
271行的end方法的功能是回溯到上一层。
它就是使用了prevObject来操作。pushStack在源代码内部用的比较多。比如slice。
slice方法的功能是截取数组。
它使用了pushStack(入栈)方法来操作。
slice: function() {
return this.pushStack( core_slice.apply( this, arguments ) );
},
<div>div1</div>
<div>div2</div>
<div>div3</div>
<div>div4</div>
<div>div5</div>
$("div").slice(1,3).css("background","red").end().css("color","blue");
//通过slice数组把第2,3个元素截取出来
//因为有入栈的操作,那么通过end来回溯上一层就是$("div")这4个div
//所以字体颜色变化是所有的div颜色变成blue。
入栈的示意图是是slice截取出来的索引为2、3的数组在一开始的4个div上面。

3.6 each方法、ready方法
each: function( callback, args ) {
return jQuery.each( this, callback, args );
},
each方法,它可以通过$("li")之类的实例对象调用,也就是实例方法,同时在源代码里面的each方法是工具方法。
ready: function( fn ) { // Add the callback这里是一个承诺的完成。 jQuery.ready.promise().done( fn ); return this; },
3.7 first方法、last方法、eq方法
first: function() {
return this.eq( 0 );//寻找第一个元素
},
last: function() {
return this.eq( -1 );//寻找最后一个元素
},
eq方法返回集合的指定项。支持传入的是负数哦,比如-1表示倒数第1项,-2表示倒数第2项。
根据源码,对应索引的值以入栈的方式加入到this对象。
var len = this.length,
j = +i + ( i < 0 ? len : 0 );
//len是this的length值,然后把传入的索引赋给j。并对负数参数做了修正
//加一加length长度
return this.pushStack( j >= 0 && j < len ? [ this[j] ] : [] );
//j >= 0 && j < len ? [ this[j] ] : []的意思是当j大于0,小于length,
//那么是合法的数值,就可以返回this对象对应索引的值。
来看一个示例
<div>div1</div>
<div>div2</div>
<div>div3</div>
<div>div4</div>
$("div").eq(2).css("background","yellow"); 对应的是显示效果和入栈示意图。


3.8 map方法、push方法、sort方法、splice方法
map: function( callback ) {
return this.pushStack( jQuery.map(this, function( elem, i ) {
return callback.call( elem, i, elem );
}));
},
map实例方法调用的是jQuery的工具方法,和each很类似。map方法如何使用呢?map的作用是以函数传递元素的方式来进行遍历。
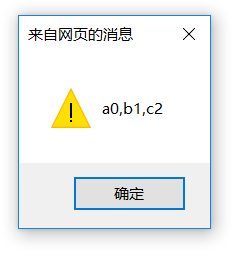
var arr=["a","b","c"];
arr=$.map(arr,function(elem,i){
return elem+i;
})
alert(arr);
浏览器的显示效果为
push、sort、splice是数组的添加、排序、截取,都是内部使用的。





