DS博客作业02——栈和队列
0.PTA得分截图

1.本周学习总结
1.1 总结栈和队列内容
栈的存储结构及操作

- 栈只能从表的一端存取数据,另一端是封闭的,在栈中,无论是存数据还是取数据,都必须遵循"先进后出"的原则,即最先进栈的元素最后出栈。
2.向栈中添加元素,此过程被称为"进栈"(入栈)。
3.从栈中提取出指定元素,此过程被称为"出栈"。
栈的应用
1.浏览器的"回退"功能
2.括号匹配
3.数值的进制转换
4.逆序输出
......
队列的存储结构及操作
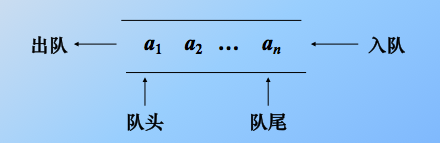
限定在表的一端插入、另一端删除。 插入的那头是队尾,删除的那头是队头。
先进先出 (FIFO结构)。不能在队列中间操作元素,只能在尾部进,在头部出去,类似火车进隧道的过程。(first in first out = FIFO 结构)
链队列
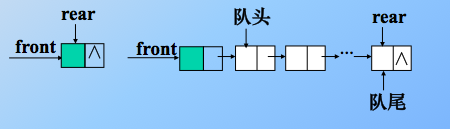
用链表表示的队列,限制仅在表头删除和表尾插入的单链表。
循环队列
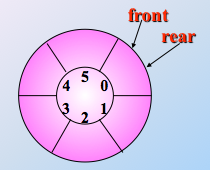
使用循环队列,解决了假溢出问题
使用循环队列,要设置队列的最大长度,否则无法完成判断空
队列应用
1.医院的挂号系统
2.排队
......
1.2 对栈和队列的认识及学习体会。
相同点:
1.插入操作都是限定在表尾进行
2.都可以通过顺序结构和链式结构实现
3.插入与删除的时间复杂度都是O(1),在空间复杂度上两者也一样
不同点:
删除数据元素的位置不同,栈的删除操作在表尾进行,队列的删除操作在表头进行。
栈先进后出。队列后进先出。
学习体会:
栈和队列的结构不同,应用也不同。对于不同的题目而言,栈和队列两者带来的效率截然不同,有时需要两者一起使用。
2.PTA实验作业
2.1 7-2 jmu-字符串是否对称
2.1.1代码截图
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 101
typedef struct
{
char data[MAX];
int top, bottom;
}stack;
int main()
{
int i;
stack *s;
char c[101];
s = new stack;
s->top = -1;
s->bottom = 0;
cin >> c;
for (i = 0; c[i] != '\0'; i++)
{
s->top++;
s->data[s->top] = c[i];
}
while (s->top > 0)
{
if (s->data[s->bottom] != s->data[s->top])
{
cout << "no";
return 0;
}
s->top--;
s->bottom++;
}
cout << "yes";
return 0;
}
2.1.2 本题PTA提交列表说明

2.2 7-6 jmu-报数游戏
2.2.1代码截图
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 101
typedef struct Qnode
{
int data;
struct Qnode*next;
}Qnode;
int main()
{
int i;
Qnode* L,*tail,*p,*q;
q=L = new Qnode;
L->next = NULL;
tail=L;
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
if (m > n)
{
cout << "error!";
return 0;
}
i = 1;
while (i<=n)
{
p = new Qnode;
p->data = i;
tail->next = p;
tail = p;
if (i == 1)
{
q = p;
}
i++;
}
tail->next=q;
p = new Qnode;
p = L;
while (n != 1)
{
for (i = 1; i < m; i++)
{
p = p->next;
}
q = new Qnode;
q = p->next;
cout << q->data<<" ";
p->next = q->next;
free(q);
n--;
}
cout << p->data;
}
2.2.2 PTA提交列表说明

3.阅读代码
3.1 有序队列
给出了一个由小写字母组成的字符串 S。然后,我们可以进行任意次数的移动。
在每次移动中,我们选择前 K 个字母中的一个(从左侧开始),将其从原位置移除,并放置在字符串的末尾。
返回我们在任意次数的移动之后可以拥有的按字典顺序排列的最小字符串。
示例 1:
输入:S = "cba", K = 1
输出:"acb"
解释:
在第一步中,我们将第一个字符(“c”)移动到最后,获得字符串 “bac”。
在第二步中,我们将第一个字符(“b”)移动到最后,获得最终结果 “acb”。
示例 2:
输入:S = "baaca", K = 3
输出:"aaabc"
解释:
在第一步中,我们将第一个字符(“b”)移动到最后,获得字符串 “aacab”。
在第二步中,我们将第三个字符(“c”)移动到最后,获得最终结果 “aaabc”。
提示:
1 <= K <= S.length <= 1000
S 只由小写字母组成。
char * orderlyQueue(char * S, int K)
{
int len = strlen(S);
char *ret = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char)*(strlen(S)+1));
strcpy(ret, S);
if (K == 1 && strlen(S) > 0)
{
char *cur = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char)*(strlen(S)+1));
strcpy(cur, &S[1]);
cur[len-1] = S[0];
cur[len] = 0;
while (strcmp(cur, S))
{
if (strcmp(cur, ret) < 0)
strcpy(ret, cur);
char c = cur[0];
for (int i=0; i<len; i++) cur[i] = cur[i+1];
cur[len-1] = c;
}
free(cur);
}
else
{
int *hash = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*26);
memset(hash, 0, sizeof(int)*26);
for (int i=0; i<len; i++) hash[S[i]-'a']++;
int p = 0;
for (int i=0; i<26; i++) {
for (int j=0; j<hash[i]; j++) ret[p++] = i+'a';
}
ret[p] = 0;
free(hash);
}
return ret;
}
3.1.1 该题的设计思路
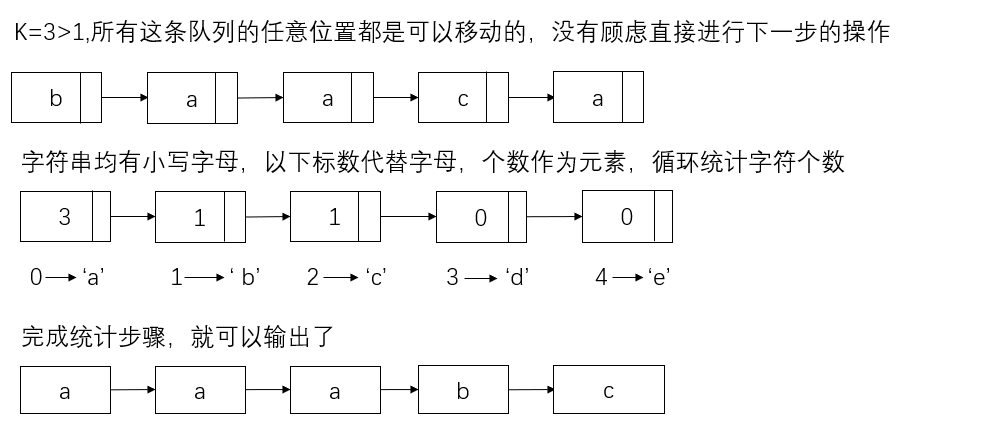
当K>1时:
利用一层循环统计每一个小写字母的个数
两层循环,外循环为二十六的小写字母,内层循环是字母的个数,按照从0开始输出的顺序
当K=1时
暴力解法,将第一个字符移到队尾形成一个新的队列,再将新队列和旧队列进行strcmp(new,S)比较,如果是小于,old=new,new在按照之前的方式形成新的队列。
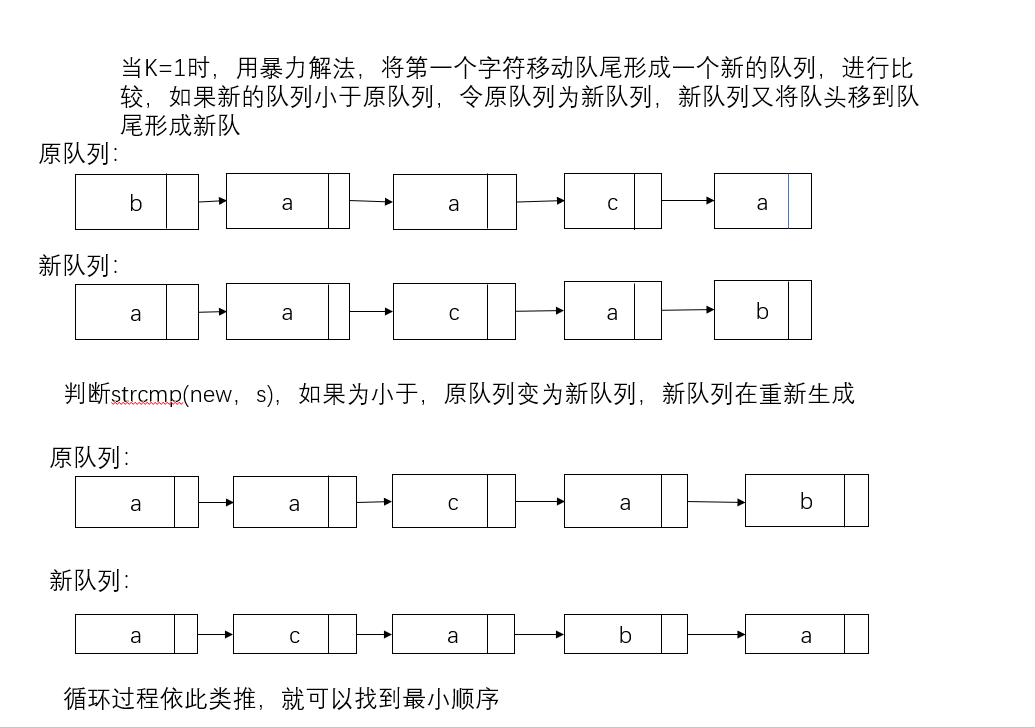
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(n)
3.1.2 伪代码
char * orderlyQueue(char * S, int K)
{
定义整型变量len = strlen(S)记录数组长度
定义字符串ret[MAXSIZE]
定义字符串cur[MAXSIZE]
定义数组hash[MAXSIZE]存放字母个数
将S字符串复制到ret中
if(k为1并且字符串长度大于0)
将字符串第一个元素移到队尾形成一个新的字符串放在cur中
while(strcmp(cur,S))
if(strcmp(cur,ret)<0)
将cur字符串复制到ret中
end if
将cur第一个元素移到队尾形成一个新的cur
end
else
for int i=0 to len do i++
将字母转成下标存进hash数组中
int p=0;
for int i=0 to 26 do i++
for int j=0 to hash[i] do j++
ret[p++]=i+'a' //ret[]数组就是新的最小顺序的可输出数组
end if
}
3.1.3 运行结果

3.1.4 分析该题目解题优势及难点
优势
算法的优化,将时间复杂度降到了O(n)
对K=1的处理
难点
题目难理解
时间复杂度如何降低
3.2 根据身高重建队列
#define PEOPLE_LEN 2
typedef struct node
{
int high;
int pos;
struct node *next;
} Linklist;
Linklist *create()
{
Linklist *head;
head = (Linklist *)malloc(sizeof(Linklist));
head->next=NULL;
return head;
}
void destroy(Linklist *head)
{
Linklist *p, *q;
p = head;
while (p)
{
q = p->next;
free(p);
p = q;
}
}
Linklist *fine_node(Linklist *head, Linklist *node)
{
Linklist *p = head->next;
int temp = 0;
while(p)
{
if (p->high >= node->high)
{
temp++;
if (temp == node->pos)
{
return p;
}
}
p = p->next;
}
return head;
}
Linklist *node_insert(Linklist *head, Linklist *node)
{
Linklist *t;
t = fine_node(head, node);
node->next = t->next;
t->next = node;
return head;
}
int cmp(int *ap, int *bp)
{
int *a = *(int**)ap;
int *b = *(int**)bp;
if (a[0] == b[0])
{
return a[1] - b[1];
}
else
{
return b[0] - a[0];
}
}
int** reconstructQueue(int** people, int peopleSize, int* peopleColSize, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes){
int i;
int** res;
Linklist *head = create();
Linklist *node;
if (people == NULL || peopleSize == 0)
{
*returnSize = 0;
*returnColumnSizes = NULL;
return NULL;
}
qsort(people, peopleSize, sizeof(int*), cmp);
for (i = 0; i < peopleSize; i++)
{
node = (Linklist *)malloc(sizeof(Linklist));
node->high = people[i][0];
node->pos = people[i][1];
node->next = NULL;
head = node_insert(head, node);
}
i = 0;
node = head->next;
res = (int **)malloc(sizeof(int *) * peopleSize);
while (node)
{
res[i] = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * PEOPLE_LEN);
res[i][0] = node->high;
res[i][1] = node->pos;
i++;
node = node->next;
}
destroy(head);
*returnSize = peopleSize;
*returnColumnSizes = peopleColSize;
return res;
}
3.2.1 该题的设计思路
1、先排序(身高相等则比较K,否则直接比身高,从高到矮);
2、借助链表插入(效率高一些)
3、输出处理
时间复杂度:O(n)
空间复杂度:O(n)
3.2.2 该题的伪代码
#define PEOPLE_LEN 2
typedef struct node
{
int high;
int pos;
struct node *next;
} Linklist;
Linklist *create()
{
创建链表,带头结点
}
void destroy(Linklist *head)
{
销毁链表
}
Linklist *fine_node(Linklist *head, Linklist *node) {
Linklist *p = head->next;
int temp = 0;
while(p) {
if (p->high >= node->high) {
temp++;
if (temp == node->pos) {
return p;
}
}
p = p->next;
}
return head;
}
Linklist *node_insert(Linklist *head, Linklist *node)
{
插入的元素排在后面
}
int cmp(int *ap, int *bp) {
int *a = *(int**)ap;
int *b = *(int**)bp;
if (a[0] == b[0]) {
return a[1] - b[1];
} else {
return b[0] - a[0];
}
}
int** reconstructQueue(int** people, int peopleSize, int* peopleColSize, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes){
int i;
int** res;
Linklist *head = create();
Linklist *node;
if (people == NULL || peopleSize == 0) {
*returnSize = 0;
*returnColumnSizes = NULL;
return NULL;
}
qsort(people, peopleSize, sizeof(int*), cmp);//排序
for (i = 0; i < peopleSize; i++)
{
按pos序号插入
}
输出
destroy(head);
*returnSize = peopleSize;
*returnColumnSizes = peopleColSize;
return res;
}
3.2.3 运行结果

3.2.4 分析该题目解题优势及难点
优势
使用链表插入提高效率
难点
如何高效排序


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号