C# Using 语句: Dispose and IDisposable
这些C#示例项目会展示using语句的使用。他们处理IDisposable类型。
Using块用于管理资源
从概念上来说,通过指定资源的使用范围来保护整个系统的资源。using语句与实现IDisposable的类型相结合。
Example
刚开始,这个小项目定义了一个叫做SystemResource的类。这个类实现了IDisposable接口和所需的Dispose方法。在Main方法中,我们在using语句中包装了SystemResource实例。
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.Linq; 4 using System.Text; 5 using System.Drawing; 6 using System.Windows.Forms; 7 8 namespace UsingDemo 9 { 10 class Program 11 { 12 static void Main(string[] args) 13 { 14 // Use using statement with class that implements Dispose. 15 using (SystemResource resource = new SystemResource()) 16 { 17 Console.WriteLine(1); 18 } 19 Console.WriteLine(2); 20 } 21 } 22 23 class SystemResource : IDisposable 24 { 25 public void Dispose() 26 { 27 // The implementation of this method not described here. 28 // ... For now, just report the call. 29 Console.WriteLine(0); 30 } 31 } 32 }

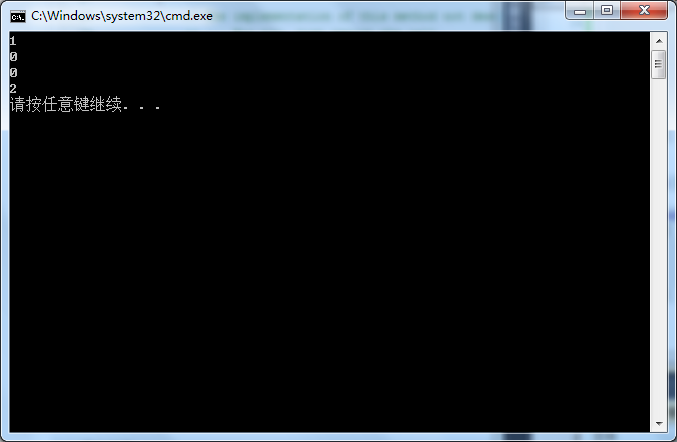
当项目执行的时候会发生什么呢?
首先,SystemResource实例在托管堆上被分配。接下来,“1”被输出;第三,“0”被输出,因为调用了Dispose方法。最后,“2”被打印出来。
然后:如展示的那样,当控制流退出using块时,立即调用Dispose方法。
Using嵌套:
可以一个接一个地嵌套多层using语句。在这种情况下,不需要使用任何花括号。在第二个或更多层次的using语句中,你可以使用在前面的using语句中声明的变量。
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.Linq; 4 using System.Text; 5 using System.Drawing; 6 using System.Windows.Forms; 7 8 namespace UsingDemo 9 { 10 class Program 11 { 12 static void Main(string[] args) 13 { 14 // Use using statement with class that implements Dispose. 15 using (SystemResource resource1 = new SystemResource()) 16 using (SystemResource resource2 = new SystemResource()) 17 { 18 Console.WriteLine(1); 19 } 20 Console.WriteLine(2); 21 } 22 } 23 24 class SystemResource : IDisposable 25 { 26 public void Dispose() 27 { 28 // The implementation of this method not described here. 29 // ... For now, just report the call. 30 Console.WriteLine(0); 31 } 32 } 33 }
最常见的与using一起使用的类型是那些已经在.NET框架中定义好的类型。这些类型包括StreamReader, StreamWriter, BinaryReader, BinaryWriter, 甚至是 DataTable。
为此,只需在using语句中为类型使用资源获取表达式。你不需要实现任何接口。很多类型已经实现了Dispose方法。
Performance性能
using语句会影响到性能。在一些地方,using语句不是必要的,因为这些对象不会接触到托管资源。我们进一步探讨这一点。我们在不需要using语句的对象上使用using语句进行基准测试。
首先:这个函数版本有多层using语句,这个函数接收一个byte数组,这个数组是托管类型。
注:所有的流都是从byte数组创建的,所以它们不能链接到像磁盘这样的非托管资源。
Version with using statements: C# static byte[] Decompress1(byte[] gzip) { using (MemoryStream mem = new MemoryStream(gzip)) using (GZipStream stream = new GZipStream(mem, CompressionMode.Decompress)) { const int size = 4096; byte[] buffer = new byte[size]; using (MemoryStream memory = new MemoryStream()) { int count = 0; do { count = stream.Read(buffer, 0, size); if (count > 0) { memory.Write(buffer, 0, count); } } while (count > 0); return memory.ToArray(); } } }
下面,我们看一个没有三层using语句块嵌套的版本。这是安全的,因为它们不是使用非托管资源创建的。在中间语言中,这消除了许多复杂性和三个try-finally构造。
Version without using statements: C# static byte[] Decompress2(byte[] gzip) { GZipStream stream = new GZipStream(new MemoryStream(gzip), CompressionMode.Decompress); const int size = 4096; byte[] buffer = new byte[size]; MemoryStream memory = new MemoryStream(); int count = 0; do { count = stream.Read(buffer, 0, size); if (count > 0) { memory.Write(buffer, 0, count); } } while (count > 0); return memory.ToArray(); }
C# program that benchmarks using statements using System.IO; using System.IO.Compression; class Program { const int _max = 200000; static void Main() { byte[] array = File.ReadAllBytes("C:\\t2\\_default.gz"); Decompress1(array); Decompress2(array); for (int i = 0; i < _max; i++) { Decompress1(array); } for (int i = 0; i < _max; i++) { Decompress2(array); } } }
Benchmark results Decompress1: Has 3 using statements. Decompress2: Has 0 using statements. Decompress1 Memory: 4852 K, 4804 K, 4852 K Decompress2 Memory: 4768 K, 4752 K, 4784 K
结果:我们看到了试验结果。每个函数耗费了相同数量的时候去执行(9s)。这主要是依据文件大小。然而,Decompress2函数使用了更少的内存消耗。
因此:不必要的using语句最终浪费了内存。这可以通过方法大小膨胀和复杂性增加来解释。
概述:using语句为调用IDisposable接口实现中的Dispose方法提供了一个语法糖。本文没有描述Dispose的有用实现。
https://thedeveloperblog.com/using
using实质
在程序编译阶段,编译器会自动将using语句生成为try-finally语句,并在finally块中调用对象的Dispose方法,来清理资源。所以,using语句等效于try-finally语句,例如:
using (Font f2 = new Font("Arial", 10, FontStyle.Bold))
{
font2.F();
}
被编译器翻译为:
Font f2 = new Font("Arial", 10, FontStyle.Bold);
try
{
font2.F();
}
finally
{
if (f2 != null) ((IDisposable)f2).Dispose();
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号