C#继承---理解与分析
在这篇文章中,我们会用示例讨论C#继承。继承是面向对象编程的一项原则,这项原则解决了可扩展性问题。在这篇文章中,我们会讨论以下几点:
1、什么是继承?
2、继承的类型;
3、为什么需要继承?
4、如何在应用程序中使用继承?
一、继承是什么?
从已存在的类中创建一个新类,这样新类就获得了已存在类的所有属性和行为,这一过程就叫做继承。传送属性(或行为)的类,叫做超类或父类或基类,而自超类继承属性或行为的类叫做子类或派生类(derived class)。总之一句话,继承意味着从已经完成或已经现有的可利用的方面取得某些东西。
继承是一种代码可复用性和可改变性为目的的概念。这里所指的可改变性意味着可以重载对象的已有功能或特征,或是给对象添加更多的功能。
C#.NET支持的继承类别
C#.NET将继承划分为两大类:
1、实现继承(Implementation inheritance)
2、接口继承(Interface inheritance)
二、继承的类型
继承分为5种类型,它们分别如下:
1、单一继承(Single Inheritance):当一个类是从单个基类继承而来,这种继承关系叫单一继承;
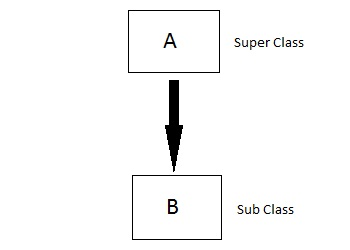
2、多级继承(Multilevel Inheritance):当一个派生类是从另一个派生类创建的,这种继承关系叫多级继承;

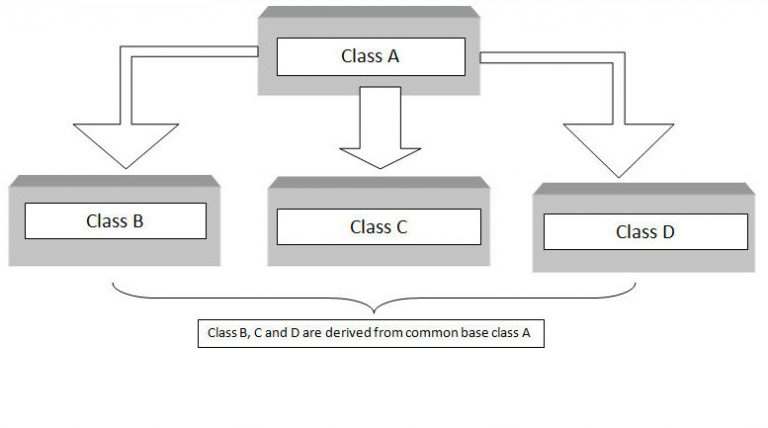
3、同级继承(Hierarchical Inheritance):当多个派生类是从同一基类创建的,这种继承关系叫同级继承;
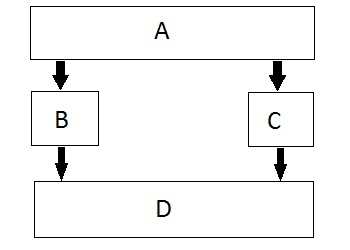
4、混合继承(Hybrid Inheritance):混合继承是任意单继承、同级继承和等级继承的组合;
5、多重继承(Multiple Inheritance):当一个派生类创建于多个基类,这种继承类型叫多重继承。但是在.NET中,类是不能多重继承的,但是接口可以多重继承的。
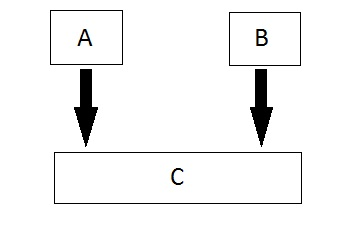
注:处理由多重继承引起的复杂性是非常复杂的,因此在.net中,类是不支持多重继承的,而接口可以支持多重继承。
C#中使用继承需要考虑的规则
规则1:在继承中,对于子类来说,父类的构造函数必须易于访问,否则继承就不成立,因为当我们创建子类对象时,它会运行并调用父类的构造函数,这样父类变量会被初始化,我们就可以在子类中使用它们。
示例如下:
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.Linq; 4 using System.Text; 5 using System.Drawing; 6 using System.Windows.Forms; 7 8 namespace parent_and_child_class 9 { 10 //创建父类Person和子类Student 11 public class Person 12 { 13 public Person() 14 { 15 Console.WriteLine("我是人"); 16 } 17 } 18 19 public class Student : Person 20 { 21 public Student() 22 { 23 Console.WriteLine("我是学生"); 24 } 25 } 26 27 //在客户端通过子类无参构造函数创建子类实例 28 class Program 29 { 30 static void Main(string[] args) 31 { 32 Student student = new Student(); 33 34 Console.ReadKey(); 35 } 36 } 37 }
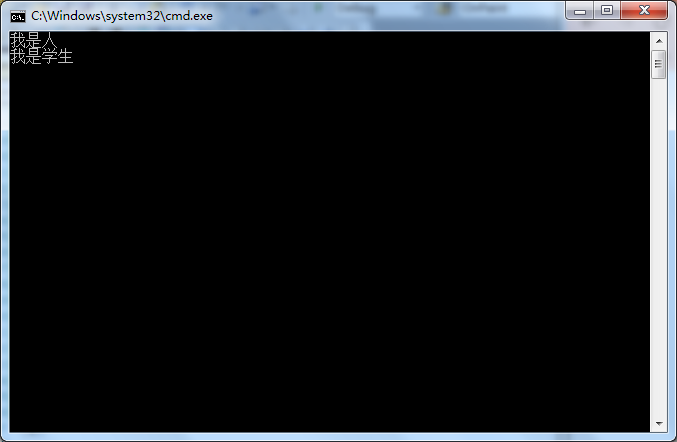
结论:通过调用子类无参构造函数创建子类实例,会默认调用父类无参构造函数。
规则2:在继承中,子类能使用父类成员,但父类不能完全使用在子类中定义的成员。
注: 我们习惯认为,子类对父类是不可见的,或者说父类不知道子类的存在,所以父类是调用不到子类的方法、属性的。
规则3:一个类的对象可以做为引用被分配给同一个类的变量,一个类的对象也可以做为引用分配给父类的变量,这样引用开始分配给它的对象内存,但是现在也可以使用我们控制的引用来访问子类的纯成员。
注:父类对象不能分配给子类变量。通过显式转换,用子类对象创建的父类引用可以转换回子类引用。
为什么我们需要继承?
我们用示例来理解为什么需要继承。假设一家公司有“n”个分支机构,要求将公司分支机构详细信息电脑化,然后我们创建Class Branch类,此类包含data成员BranchCode, BranchName, 和 BranchAddress;还有函数 GetBranchData() 和 DisplayBranchData().。
一段时间后,公司还要求将每个分支机构的雇员详细信息电脑化。然后我们创建了Class Employee,此类包含成员 EmployeeId, EmployeeName, EmployeeAddress, EmployeeAge,还有函数 GetEmployeeData() 和 DisplayEmployeeData().。
如果我们在没有使用继承的情况下创建这两个类,我们需要独立地分别地为每个类创建对象,像下面这样:

Obj1是Class Branch类的对象,Obj2是Employee类的对象。很难分辨哪个employee属于哪个分支机构。所以如果我们从Branch类派生出Employee类,我们再创建派生类Employee的对象,它会代表两个类,会保持对基类和派生类成员的引用。
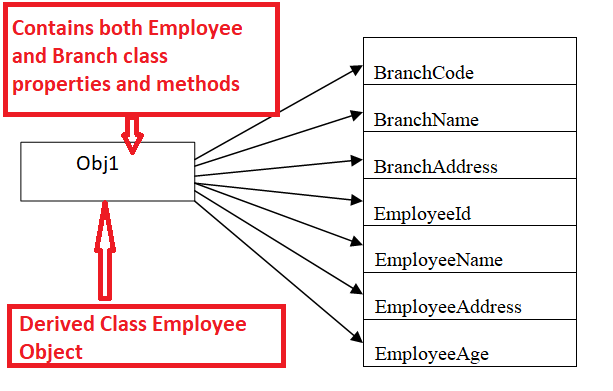
示例:
1 namespace InheritanceDemo 2 { 3 class Branch 4 { 5 int BranchCode; 6 string BranchName, BranchAddress; 7 public void GetBranchData() 8 { 9 Console.WriteLine("ENTER BRANCH DETAILS:"); 10 Console.WriteLine("ENTER BRANCH CODE"); 11 BranchCode = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine()); 12 Console.WriteLine("ENTER BRANCH NAME"); 13 BranchName = Console.ReadLine(); 14 Console.WriteLine("ENTER BRANCH ADDRESS"); 15 BranchAddress = Console.ReadLine(); 16 } 17 public void DisplayBranchData() 18 { 19 Console.WriteLine("BRANCH CODE IS : " + BranchCode); 20 Console.WriteLine("BRANCH NAME IS : " + BranchName); 21 Console.WriteLine("BRANCH ADDRESS IS : " + BranchAddress); 22 } 23 } 24 class Employee : Branch 25 { 26 int EmployeeId, EmployeeAge; 27 string EmployeeName, EmployeeAddress; 28 public void GetEmployeeData() 29 { 30 Console.WriteLine("ENTER EMPLYEE DETAILS:"); 31 Console.WriteLine("ENTER EMPLOYEE ID"); 32 EmployeeId = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine()); 33 Console.WriteLine("ENTER EMPLOYEE AGE"); 34 EmployeeAge = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine()); 35 Console.WriteLine("ENTER EMPLOYEE NAME"); 36 EmployeeName = Console.ReadLine(); 37 Console.WriteLine("ENTER EMPLOYEE ADDRESS"); 38 EmployeeAddress = Console.ReadLine(); 39 } 40 public void DisplayEmployeeData() 41 { 42 Console.WriteLine("EMPLOYEE ID IS : " + EmployeeId); 43 Console.WriteLine("EMPLOYEE NAME IS : " + EmployeeName); 44 Console.WriteLine("EMPLOYEE ADDRESS IS : " + EmployeeAddress); 45 Console.WriteLine("EMPLOYEE AGE IS : " + EmployeeAge); 46 } 47 } 48 class Program 49 { 50 static void Main(string[] args) 51 { 52 Employee obj1 = new Employee(); 53 obj1.GetBranchData(); 54 obj1.GetEmployeeData(); 55 obj1.DisplayBranchData(); 56 obj1.DisplayEmployeeData(); 57 Console.WriteLine("Press any key to exist."); 58 Console.ReadKey(); 59 } 60 } 61 }
在上面的例子中,我们将Branch类的GetEmployeeData() 和 DisplayEmployeeData() 设置为public,是因为外部的Employee类可以访问这些函数。数据字段BranchCode, BranchName, 和 BranchAddress设置为private(默认),这样只有在同一个类内才可以访问。
但是,如果不想让非继承类访问基类成员(在此例子中是Program类),而对于继承类(Employee类)来说可以访问基类,这时我们可以使用protected关键词。
将public更换为protected后,示例如下:
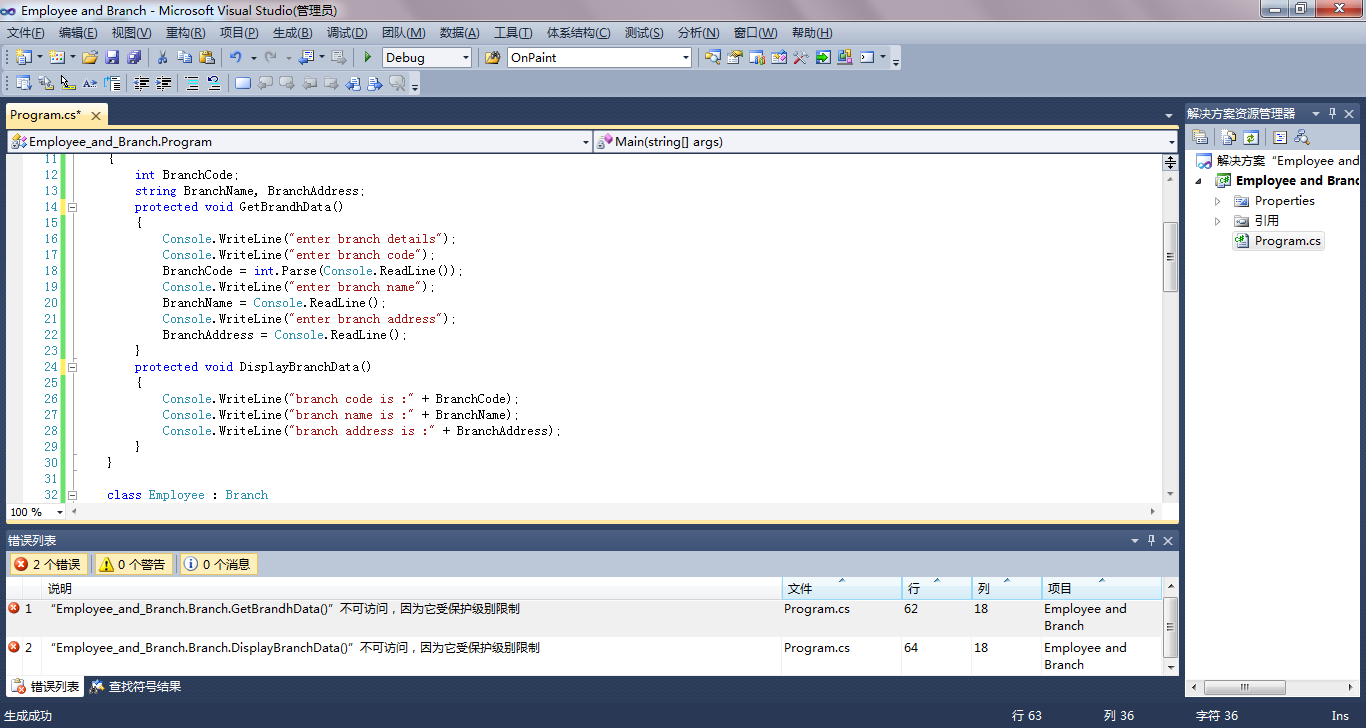
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 using System.Linq; 4 using System.Text; 5 using System.Drawing; 6 using System.Windows.Forms; 7 8 namespace Employee_and_Branch 9 { 10 class Branch 11 { 12 int BranchCode; 13 string BranchName, BranchAddress; 14 protected void GetBrandhData() 15 { 16 Console.WriteLine("enter branch details"); 17 Console.WriteLine("enter branch code"); 18 BranchCode = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine()); 19 Console.WriteLine("enter branch name"); 20 BranchName = Console.ReadLine(); 21 Console.WriteLine("enter branch address"); 22 BranchAddress = Console.ReadLine(); 23 } 24 protected void DisplayBranchData() 25 { 26 Console.WriteLine("branch code is :" + BranchCode); 27 Console.WriteLine("branch name is :" + BranchName); 28 Console.WriteLine("branch address is :" + BranchAddress); 29 } 30 } 31 32 class Employee : Branch 33 { 34 int EmployeeId, EmployeeAge; 35 string EmployeeName, EmployeeAddress; 36 public void GetEmployeeData() 37 { 38 Console.WriteLine("enter emplyee details"); 39 Console.WriteLine("enter employee id"); 40 EmployeeId = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine()); 41 Console.WriteLine("enter employee age"); 42 EmployeeAge = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine()); 43 Console.WriteLine("enter employee name"); 44 EmployeeName = Console.ReadLine(); 45 Console.WriteLine("enter employee address"); 46 EmployeeAddress = Console.ReadLine(); 47 } 48 public void DisplayEmployeeData() 49 { 50 Console.WriteLine("employee id is :" + EmployeeId); 51 Console.WriteLine("employee name is :" + EmployeeName); 52 Console.WriteLine("employee address is :" + EmployeeAddress); 53 Console.WriteLine("employee age is :" + EmployeeAge); 54 } 55 } 56 57 class Program 58 { 59 static void Main(string[] args) 60 { 61 Employee obj1 = new Employee(); 62 obj1.GetBrandhData(); 63 obj1.GetEmployeeData(); 64 obj1.DisplayBranchData(); 65 obj1.DisplayEmployeeData(); 66 Console.WriteLine("press any key to exist."); 67 Console.ReadKey(); 68 } 69 } 70 }
以上代码会报错,具体如下:
1 namespace InheritanceDemo 2 { 3 class Branch 4 { 5 int BranchCode; 6 string BranchName, BranchAddress; 7 protected void GetBranchData() 8 { 9 Console.WriteLine("ENTER BRANCH DETAILS:"); 10 Console.WriteLine("ENTER BRANCH CODE"); 11 BranchCode = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine()); 12 Console.WriteLine("ENTER BRANCH NAME"); 13 BranchName = Console.ReadLine(); 14 Console.WriteLine("ENTER BRANCH ADDRESS"); 15 BranchAddress = Console.ReadLine(); 16 } 17 protected void DisplayBranchData() 18 { 19 Console.WriteLine("BRANCH CODE IS : " + BranchCode); 20 Console.WriteLine("BRANCH NAME IS : " + BranchName); 21 Console.WriteLine("BRANCH ADDRESS IS : " + BranchAddress); 22 } 23 } 24 class Employee : Branch 25 { 26 int EmployeeId, EmployeeAge; 27 string EmployeeName, EmployeeAddress; 28 public void GetEmployeeData() 29 { 30 //to call the base class method use base keyword 31 base.GetBranchData(); 32 Console.WriteLine("ENTER EMPLYEE DETAILS:"); 33 Console.WriteLine("ENTER EMPLOYEE ID"); 34 EmployeeId = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine()); 35 Console.WriteLine("ENTER EMPLOYEE AGE"); 36 EmployeeAge = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine()); 37 Console.WriteLine("ENTER EMPLOYEE NAME"); 38 EmployeeName = Console.ReadLine(); 39 Console.WriteLine("ENTER EMPLOYEE ADDRESS"); 40 EmployeeAddress = Console.ReadLine(); 41 } 42 public void DisplayEmployeeData() 43 { 44 base.DisplayBranchData(); 45 Console.WriteLine("EMPLOYEE ID IS : " + EmployeeId); 46 Console.WriteLine("EMPLOYEE NAME IS : " + EmployeeName); 47 Console.WriteLine("EMPLOYEE ADDRESS IS : " + EmployeeAddress); 48 Console.WriteLine("EMPLOYEE AGE IS : " + EmployeeAge); 49 } 50 } 51 class Program 52 { 53 static void Main(string[] args) 54 { 55 Employee obj1 = new Employee(); 56 //Here we cannot access the Branch class method as they are now protected 57 // obj1.GetBranchData(); //Will give Compile time error 58 obj1.GetEmployeeData(); 59 // obj1.DisplayBranchData(); // will give compile time error 60 obj1.DisplayEmployeeData(); 61 Console.WriteLine("Press any key to exist."); 62 Console.ReadKey(); 63 } 64 } 65 }
以上是正确的示例代码。
一般地,当我们开发应用程序的时候,遵循以下过程:
1、识别与应用程序相关联的实体;
2、识别与应用程序相关联的特性;
3、现在,按层次顺序分离每个实体的属性,而不存在任何重复项;
4、将这些实体转换为类;
示例:
我们用一个运行时的例子来了解一下继承。假设我们正在为学校开发应用程序,实体的属性如下所示:
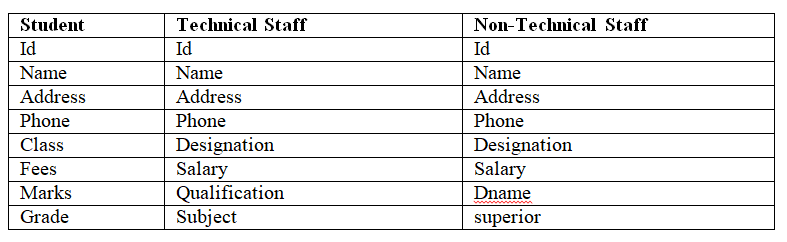
现在,基于以下层级关系来分离实体的属性。
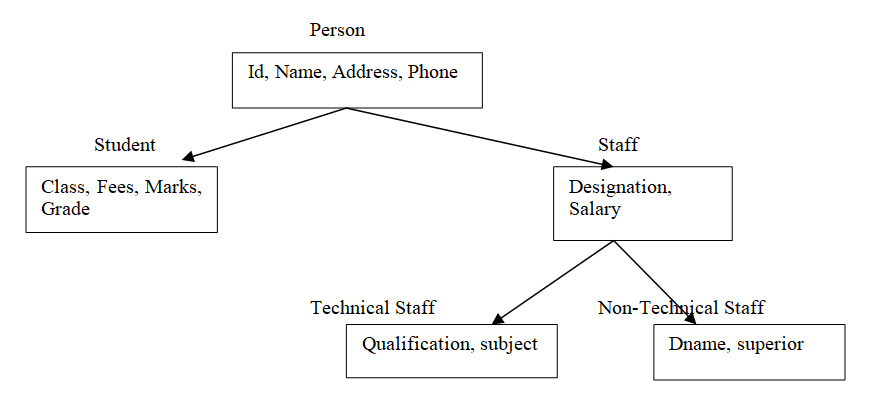
现在定义表示实体的类,如下所示
1 namespace InheritanceDemo 2 { 3 public class Person 4 { 5 int Id; 6 string Name; 7 string Address; 8 string Phone; 9 } 10 public class Student : Person 11 { 12 string Class; 13 string Fees; 14 string Marks; 15 string Grade; 16 } 17 public class Staff : Person 18 { 19 string Designation; 20 double Salary; 21 } 22 public class Technical : Staff 23 { 24 string Qualification; 25 string Subject; 26 } 27 public class NonTechnical : Staff 28 { 29 string Dname; 30 string Superior; 31 } 32 }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号