二十一、字符串类的创建
1、C语言存在的问题
- C语言不支持真正意义上的字符串
- C语言用字符数组和一组函数实现字符串操作
- C语言不支持自定义类型,无法获得字符串类型
C++可以通过类完成字符串类型的定义,但是原生类型系统并没有包含字符串类型,而是在STL库中。
但是不同的应用中,可能会使用不同的库。
2、字符串类的设计
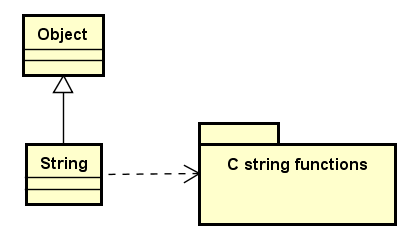
String类继承自顶层父类Object,具体实现时依赖于C语言关于字符串函数的一个包,即关于字符串的函数集。
class String : public Object
{
protected:
char* m_str; // 指向字符串,字符串的具体表现形式就是字符数组
int m_length;
void init(const char *s);
public:
String();
String(const char *s);
String(const String &s);
int length() const;
const char *str() const;
// 比较操作符重载函数
// 加法操作符重载函数
// 赋值操作符重载函数
~String() { }
};
字符串类创建的注意事项:
- 无缝实现
String对象与char*字符串的互操作 - 操作符重载函数要考虑是否支持
const版本 - 通过C语言中的字符串函数实现
String的成员函数
本质:使用面向对象的技术,对C语言中相关字符串函数进行封装
目标:高效地实现代码复用
3、字符串的具体实现
// DTString.h
#ifndef STRING_H
#define STRING_H
#include "Object.h"
namespace DTLib
{
class String : public Object
{
protected:
char *m_str; // 指向字符串,字符串的具体表现形式就是字符数组
int m_length;
void init(const char *s); // 初始化函数
public:
String();
String(char c);
String(const char *s);
String(const String &s);
int length() const;
const char *str() const;
// 比较操作符重载函数
bool operator==(const String &s) const;
bool operator==(const char *s) const; // 针对char*
bool operator!=(const String &s) const;
bool operator!=(const char *s) const; // 针对char*
bool operator>(const String &s) const;
bool operator>(const char *s) const; // 针对char*
bool operator<(const String &s) const;
bool operator<(const char *s) const; // 针对char*
bool operator>=(const String &s) const;
bool operator>=(const char *s) const; // 针对char*
bool operator<=(const String &s) const;
bool operator<=(const char *s) const; // 针对char*
// 加法操作符重载函数
String operator+(const String &s);
String operator+(const char *s);
String operator+=(const String &s);
String operator+=(const char *s);
// 赋值操作符重载函数 3种
String operator=(const String &s);
String operator=(const char *s);
String operator=(char c);
~String();
};
} // namespace DTLib
#endif // !STRING_H
// DTString.cpp
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include "DTString.h"
#include "Exception.h"
using namespace std;
namespace DTLib
{
// 使用参数s来具体产生当前字符串对象中的数据
void String::init(const char *s) // 初始化函数
{
m_str = strdup(s); // 将s复制一份出来
if (m_str)
{ // 复制成功
m_length = strlen(m_str);
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEnoughMemoryException, "No memory to creat String Object...");
}
}
String::String()
{
init("");
}
String::String(const char c)
{
// 字符数组模拟字符串
// 构造字符串
char s[] = {c, '\0'};
init(s);
}
String::String(const char *s)
{
// 防止s是空指针,空指针转换成空字符串
init(s ? s : "");
}
String::String(const String &s)
{
init(s.m_str);
}
int String::length() const
{
return m_length;
}
const char *String::str() const
{
return m_str; // 直接返回成员指针
}
bool String::operator==(const String &s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s.m_str) == 0);
}
bool String::operator==(const char *s) const // 针对char*
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s ? s : "") == 0);
}
bool String::operator!=(const String &s) const
{
return !(*this == s);
}
bool String::operator!=(const char *s) const // 针对char*
{
return !(*this == s);
}
bool String::operator>(const String &s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s.m_str) > 0);
}
bool String::operator>(const char *s) const // 针对char*
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s ? s : "") > 0);
}
bool String::operator<(const String &s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s.m_str) < 0);
}
bool String::operator<(const char *s) const // 针对char*
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s ? s : "") < 0);
}
bool String::operator>=(const String &s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s.m_str) >= 0);
}
bool String::operator>=(const char *s) const // 针对char*
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s ? s : "") >= 0);
}
bool String::operator<=(const String &s) const
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s.m_str) <= 0);
}
bool String::operator<=(const char *s) const // 针对char*
{
return (strcmp(m_str, s ? s : "") <= 0);
}
// 加法
String String::operator+(const String &s)
{
return (*this + s.m_str);
}
String String::operator+(const char *s)
{
String ret;
int len = m_length + strlen(s ? s : "");
char *str = reinterpret_cast<char *>(malloc(len + 1));
if (str)
{
// 调用字符串相关函数
strcpy(str, m_str);
strcat(str, s ? s : "");
// str保存拼接后的结果
free(ret.m_str);
ret.m_str = str;
ret.m_length = len;
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEnoughMemoryException, "No memory to add String values...");
}
return ret;
}
String String::operator+=(const String &s)
{
return (*this = *this + s.m_str);
}
String String::operator+=(const char *s)
{
return (*this = *this + s);
}
// 重载赋值操作符
String String::operator=(const String &s)
{
return (*this = s.m_str);
}
String String::operator=(const char *s)
{
if (m_str != s)
{
char *str = strdup(s ? s : "");
if (str)
{
free(m_str);
m_str = str;
m_length = strlen(str);
}
else
{
THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEnoughMemoryException, "No memory to assign new String value...");
}
}
return *this;
}
String String::operator=(char c)
{
char s[] = {c, '\0'};
return (*this = s);
}
String::~String()
{
free(m_str);
}
} // namespace DTLib
4、小结
C/C++语言本身不支持字符串类类型
C语言通过字符数组和一组函数支持字符串操作
C++通过自定义字符串类型支持字符串操作
字符串类型通过C语言中的字符串函数实现

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号