apidoc快速生成在线文档,apidoc生成静态文件的生成规则,原理分析,实践
在老大的指引下,需要将系统的json文件格式转换成apidoc的json格式,也就是json格式的重组,但是这个apidoc的生成格式是不固定的,因为apidoc有自己一套的生成规则,我需要研究一下是怎么生成的。
一、官方基础栗子
二、理解apidoc生成静态文档的结构解读
三、深入理解一下apidoc生成原理以及规则
一、apidoc基础栗子
全局安装apidoc
npm install apidoc -g
1、首先建立文件目录
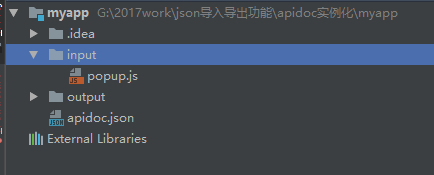
2、需要你在input文件夹里面写上你的js部分
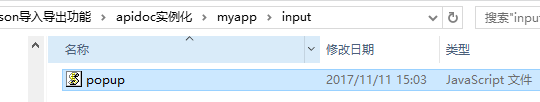
这个是栗子的js部分。
/** @api {get} /user/:id Request User information @apiName GetUser @apiGroup User @apiParam {Number} id Users unique ID. @apiSuccess {String} firstname Firstname of the User. @apiSuccess {String} lastname Lastname of the User. */ /** @api {post} /user/:id Create User information @apiName CreateUser @apiGroup User @apiParam {Number} id Users unique ID. @apiSuccess {String} data @apiSuccess {String} data.firstname Firstname of the User. @apiSuccess {String} data.first.lastname Lastname of the User. @apiSuccessExample {json} Success-Response: * HTTP/1.1 200 OK * { * "firstname": "John", * "lastname": "Doe" * } */
3、新建apidoc.json文件
apidoc.json栗子
{ "name": "example", "version": "0.1.0", "description": "apiDoc basic example", "title": "Custom apiDoc browser title", "url" : "https://api.github.com/v1" }
4、在myapp文件夹下面运行
apidoc -i myapp/ -o apidoc/ -t mytemplate/
官网原文:Creates an apiDoc of all files within dir myapp/, uses template from dir mytemplate/ and put all output to dir apidoc/.
-i 是输入文件的路径 , -o 是输出文件的路径, -t是使用模板的路径(可缺省)
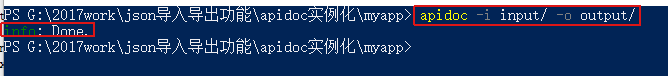
打开output文件夹,发现生成一个apidoc在线文档,直接打开html就可以看到
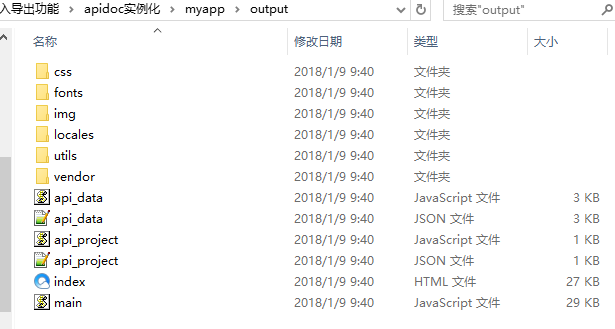
打开html文件
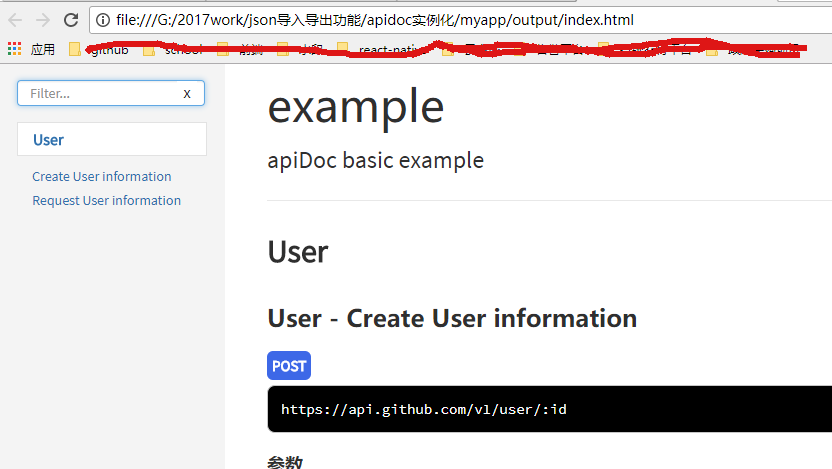
二、理解apidoc生成静态文档的结构解读
一个静态的文档很漂亮的生成了,但是实际控制这个现实的是api_data.js和api_project.js。但是实际上的数据显示是由api_data.json和api_project.json这两个json文件。
所以在支持将其他json格式转换成api_data.json和api_project.json,把apidoc生成的这两个文件进行替换,然后替换js文件,直接生产静态文档。
可以看一下api_data.json格式
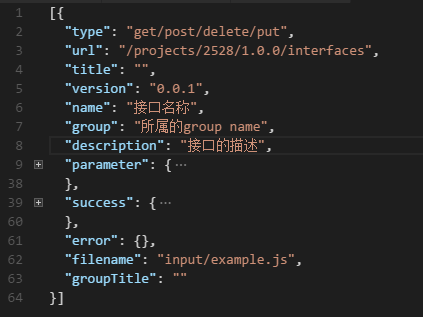
对比一下api_data.js格式
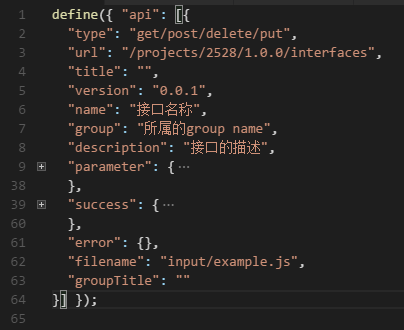
很明显就能看出来,就是在api_data.json的基础上,封装成了一层,加上define({ "api": api_data.json});
api_project.json和api_project.js也是使用相同的方法封装的。
三、深入理解一下apidoc生成原理以及规则
apidoc设计到如下的参数

(1)第一个是@api
@api是必须的,
@api {method} path [title]
比如

method 包括请求的方式:get,post,put,delete,等
path 表示请求的路径。
title (可选项)表示分组的解释,导航。
对应的静态页面
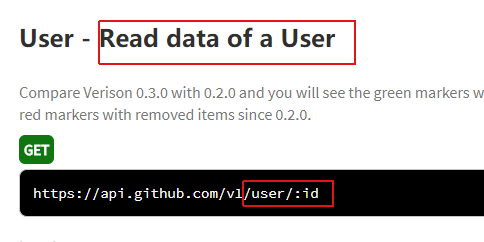
(2)@apiDefine
@apiDefine name [title] [description]
表示的是:嵌入在api块或api中的文档块
没有找到对应的页面
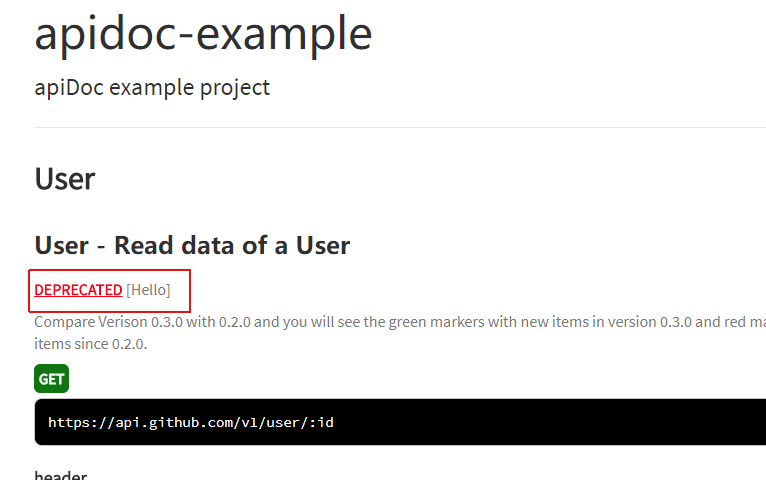
(3)@apiDeprecated
@apiDeprecated [text]
标志位api方法的反对(不对)的地方。
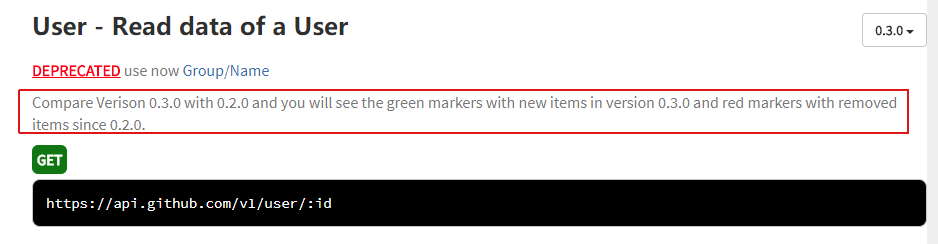
(4)@apiDescription
表示的是描述。
@apiDescription text

页面上显示的是:
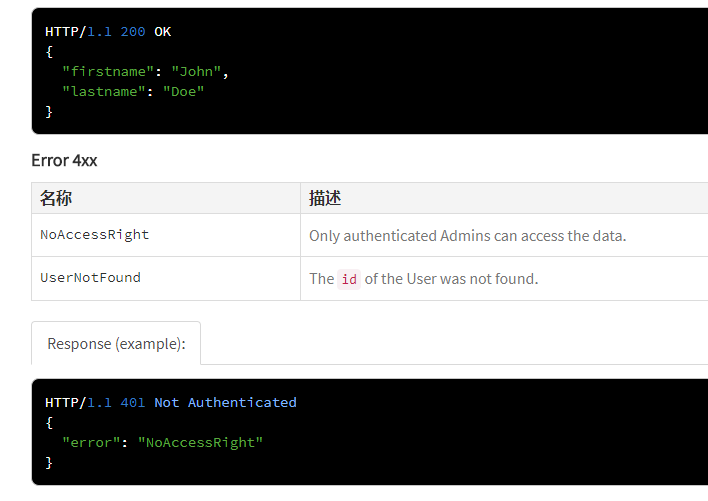
(5)@apiError和@apiErrorExample
表示的错误返回的参数
@apiError [(group)] [{type}] field [description]

页面的显示:
(6)@apiGroup
这个是必填项,表示的分组。
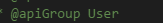
页面显示的是:
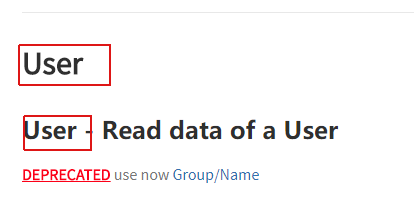
(7)@apiHeader
表示的是:传递给API头部的参数
@apiHeader [(group)] {type} [field=defaultValue] [description]
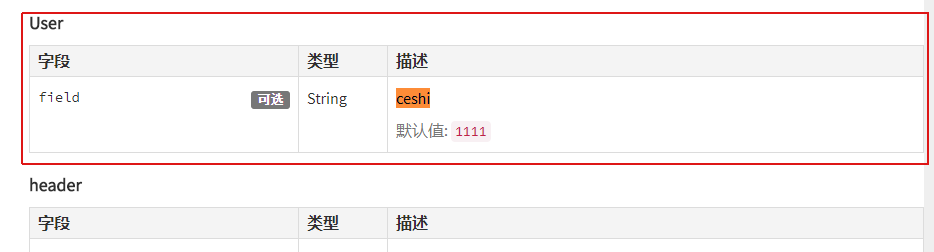
发现:@apiHeader与@apiParam用法显示上很像,但是在生成的api_data.json所在的树形结构不一致。
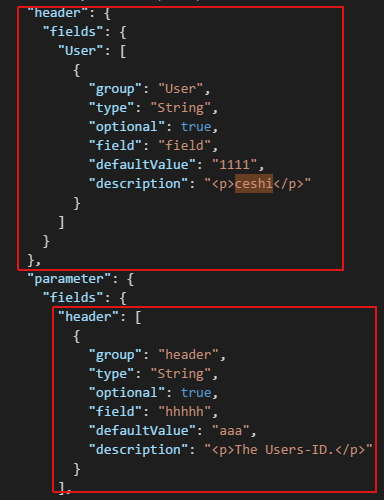 ,上面的红框是@apiHeader生成的,下面的红框是@apiParam生成的。
,上面的红框是@apiHeader生成的,下面的红框是@apiParam生成的。
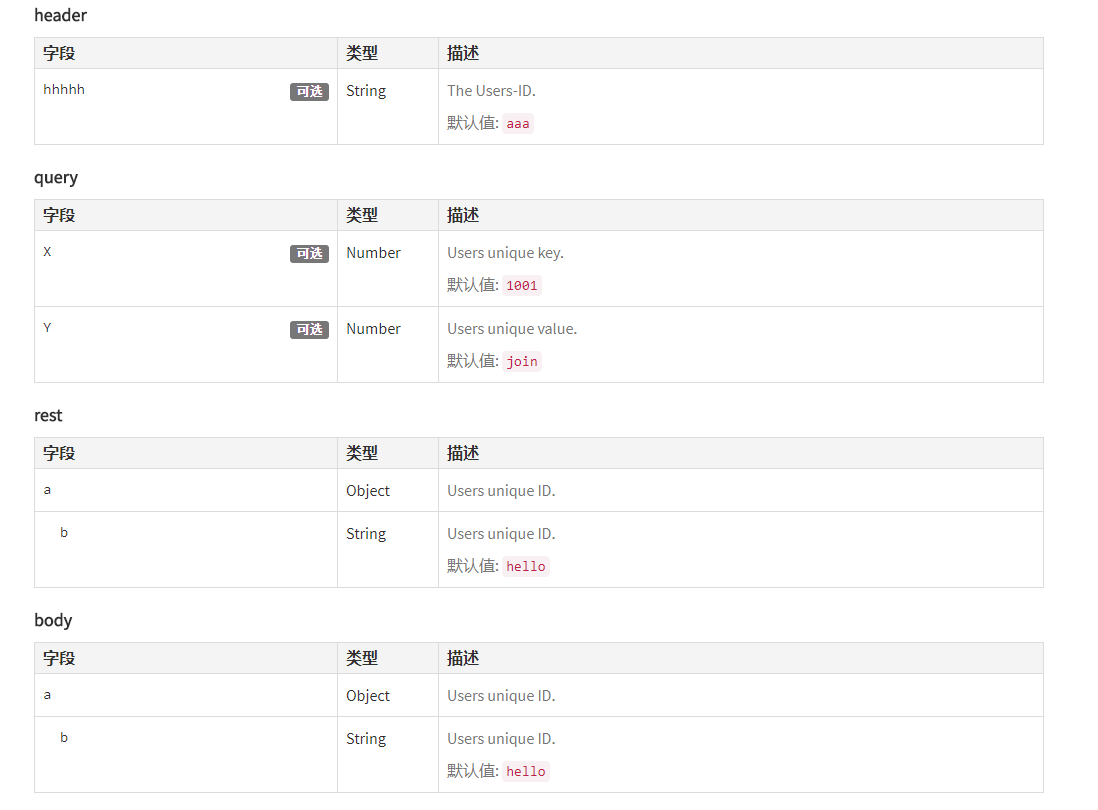
(8)@apiParam
表示的:传递给API方法的参数
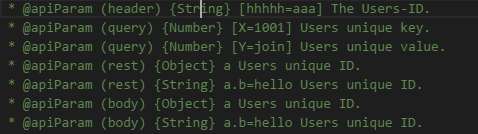
页面显示的是:
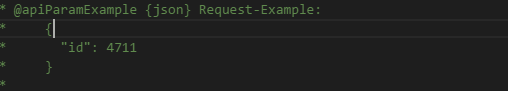
(9)@apiParamExample
表示的是:参数实例
页面上的显示:

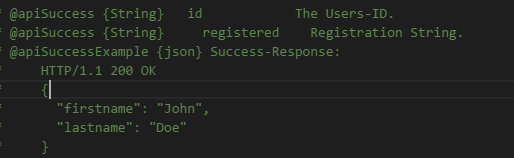
(10)@apiSuccess和@apiSuccessExample
表示的是:成功返回的参数。
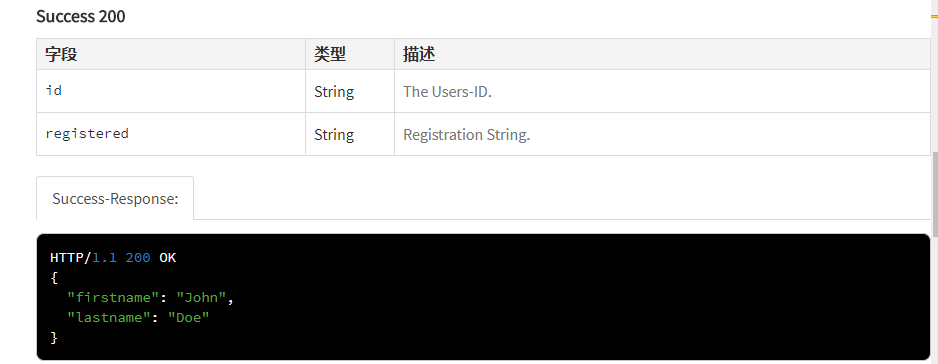
页面上的显示:
目前主要用到了这10多个参数,还是够完成老大要求的任务。
apidoc的输入的js文件
/** * @api {get} /user/:id Read data of a User * @apiVersion 0.3.0 * @apiName GetUser * @apiGroup User * @apiDeprecated use now (#Group:Name) * * @apiDescription Compare Verison 0.3.0 with 0.2.0 and you will see the green markers with new items in version 0.3.0 and red markers with removed items since 0.2.0. * * @apiHeader (User) {String} [field=1111] ceshi * @apiParam (header) {String} [hhhhh=aaa] The Users-ID. * @apiParam (query) {Number} [X=1001] Users unique key. * @apiParam (query) {Number} [Y=join] Users unique value. * @apiParam (rest) {Object} a Users unique ID. * @apiParam (rest) {String} a.b=hello Users unique ID. * @apiParam (body) {Object} a Users unique ID. * @apiParam (body) {String} a.b=hello Users unique ID. * @apiParam (body) {String} a.b.c=world Users unique ID. * @apiParam (body) {String} a.c=ccccc Users unique ID. * @apiParamExample {json} Request-Example: * { * "id": 4711 * } * * @apiSuccess {String} id The Users-ID. * @apiSuccess {String} registered Registration String. * @apiSuccessExample {json} Success-Response: * HTTP/1.1 200 OK * { * "firstname": "John", * "lastname": "Doe" * } * * @apiError NoAccessRight Only authenticated Admins can access the data. * @apiError UserNotFound The <code>id</code> of the User was not found. * * @apiErrorExample Response (example): * HTTP/1.1 401 Not Authenticated * { * "error": "NoAccessRight" * } */ /** * @api {post} /user Create a new User * @apiVersion 0.3.0 * @apiName PostUser * @apiGroup User * * @apiDescription In this case "apiUse" is defined and used. * Define blocks with params that will be used in several functions, so you dont have to rewrite them. * * @apiParam {String} name Name of the User. * * @apiSuccess {String} id The new Users-ID. * * @apiUse CreateUserError */ /** * @api {put} /user/:id Change a new User * @apiVersion 0.3.0 * @apiName PutUser * @apiGroup User * * @apiDescription This function has same errors like POST /user, but errors not defined again, they were included with "apiUse" * * @apiParam {String} name Name of the User. * * @apiUse CreateUserError */
apidoc.json文件
{ "name": "apidoc-example", "version": "0.3.0", "description": "apiDoc example project", "title": "Custom apiDoc browser title", "url" : "https://api.github.com/v1", "order": [ "GetUser", "PostUser" ], "template": { "withCompare": true, "withGenerator": true } }





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 分享 3 个 .NET 开源的文件压缩处理库,助力快速实现文件压缩解压功能!
· Ollama——大语言模型本地部署的极速利器
· [AI/GPT/综述] AI Agent的设计模式综述