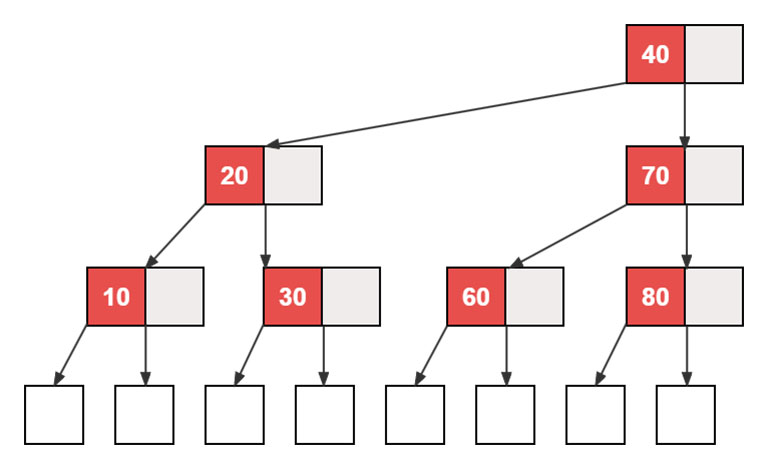
2-3树
定义
一棵 2-3 树是一棵查找树,该查找树要么为空要么满足以下性质(令 left、middle、right 为 2-3 树结点的孩子指针;dl, dr为 2-3 树结点元素):
- 每个内部结点或者是一个2结点,或者是一个3结点。一个2结点存放一个元素,而一个3结点存放两个元素。
- 每个结点的 dl 值大于 left 指向子树所有结点内元素的值 且 小于 middle 指向子树所有结点的元素值。
- 每个结点的 dr 值大于 middle 指向子树所有结点的元素值 且 小于 right 指向子树的所有结点的元素值。
- 所有外部结点都在同一层。
根据定义,可以看出,2-3 树本身就是一个自平衡树。对于高度为 h 的一棵 2-3 树,其上的元素个数介于 2h - 1 到 3h - 1 之间。一棵包含 n 个结点的 2-3 树,其高度在 log2(n+1) 和 log3(n + 1) 之间。
类型定义
结点Java 定义
1 public class TwoThreeNode<T extends Comparable<T>> { 2 private T dataLeft; 3 private T dataRight; 4 private TwoThreeNode left; 5 private TwoThreeNode middle; 6 private TwoThreeNode right; 7 private TwoThreeNode parent; 8 }
树Java定义
1 public class TwoThreeTree<T extends Comparable<T>> implements Tree<TwoThreeNode<T>, T> { 2 3 private static final int LEFT_TREE = 1; 4 private static final int MIDDLE_TREE = 2; 5 private static final int RIGHT_TREE = 3; 6 private static final int EQ_LEFT = 4; 7 private static final int EQ_RIGHT = 8; 8 9 /** 2 结点 */ 10 private static final int TWO_NODE = 1; 11 /** 3 结点 */ 12 private static final int THREE_NODE = 2; 13 }
比较函数
结点有2个元素,定义一个比较函数,返回值含义:
- 1 为左子树方向
- 2 为中子树方向
- 3 为右子树方向
- 4 为等于左元素
- 8 为等于右元素
查找函数
Java 定义
1 public TwoThreeNode<T> search(T data) { 2 TwoThreeNode<T> node = head; 3 while (node != null) { 4 int r = compare(node, data); 5 switch (r) { 6 case 1: node = node.getLeft(); break; 7 case 2: node = node.getMiddle(); break; 8 case 3: node = node.getRight(); break; 9 case 4: 10 case 8: return node; 11 } 12 } 13 return null; 14 }
插入
插入新元素,必然是插入到叶子结点中,如果是 2 结点的话,直接插入就结束了,但如果是3结点的话,如果向下溢出,则破坏了 2-3 树的平衡,因此需要拆分当前的结点然后向上合并,直到树根,以此保持 2-3 树自身的平衡。
- 如果是空树,则插入一个结点,设置结点为树根。
- 查找插入的结点位置,如果发现元素在树中,则插入失败,否则 定位插入的叶子结点 n 。
- n 结点是 2 结点时,直接插入 e 即可。
- n 结点是 3 结点时,由于插入 e 后,结点变为 4 结点,这时需要对结点 n 进行分裂,定义一个结点变量 q,初始化值为空,具体过程如下:
- 将 4 结点的三个元素的最小值存入 n 的左元素位置
- 以 4 结点的三个元素的最大值构建一个新的 2 结点 qq
- 根据 e 的位置设置 qq 的 left 和 middle 指针:
- 如果 e < n.dl 则 qq.left = n.middle | qq.middle = n.right | n.middle = q
- 如果 n.dl < e < n.dr 则 qq.left = q | qq.middle = n.right
- 如果 n.dr < e 则 qq.left = n.right | qq.middle = q
- 将 qq 赋值给 q,将 n 的父结点 赋值给 n,将 4 结点中中间值赋给 e 继续向上回溯
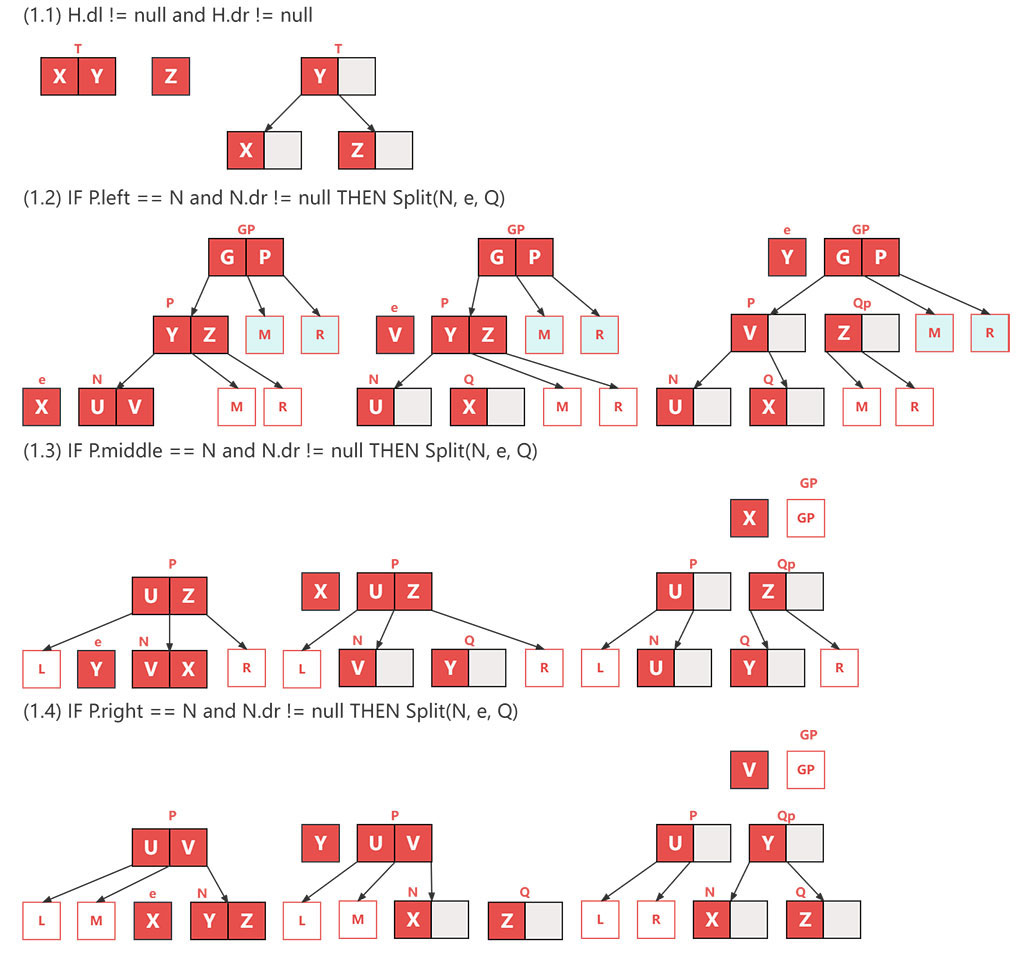
自底向上 拆分3结点
1 private void mergeNode(TwoThreeNode<T> n, T e) { 2 TwoThreeNode<T> q = null; 3 while (n != null) { 4 int dc = dataType(n); 5 if (dc == TWO_NODE) { 6 T dl = n.getDataLeft(); 7 if (e.compareTo(dl) < 0) { 8 n.setDataLeft(e); 9 n.setDataRight(dl); 10 n.setRight(n.getMiddle()); 11 n.setMiddle(q); 12 } else { 13 n.setDataRight(e); 14 n.setRight(q); 15 } 16 break; 17 } else if (dc == THREE_NODE) { 18 TwoThreeNode<T> qq = null; 19 TwoThreeNode<T> temp = null; 20 if (e.compareTo(n.getDataLeft()) < 0) { 21 qq = new TwoThreeNode<>(n.getDataRight()); 22 T tmp = n.getDataLeft(); 23 n.setDataLeft(e); 24 setChild(qq, n.getMiddle(), LEFT_TREE); 25 setChild(qq, n.getRight(), MIDDLE_TREE); 26 setChild(n, q, MIDDLE_TREE); 27 e = tmp; 28 } else if (e.compareTo(n.getDataRight()) > 0) { 29 qq = new TwoThreeNode<>(e); 30 e = n.getDataRight(); 31 setChild(qq, n.getRight(), LEFT_TREE); 32 setChild(qq, q, MIDDLE_TREE); 33 } else { 34 qq = new TwoThreeNode<>(n.getDataRight()); 35 setChild(qq, q, LEFT_TREE); 36 setChild(qq, n.getRight(), MIDDLE_TREE); 37 } 38 n.setRight(null); 39 n.setDataRight(null); 40 q = qq; 41 if (n == head) { 42 head = new TwoThreeNode<>(e); 43 setChild(head, n, LEFT_TREE); 44 setChild(head, q, MIDDLE_TREE); 45 break; 46 } 47 } 48 n = n.getParent(); 49 } 50 }
插入函数
1 private boolean insert1(T data) { 2 if (head == null) { 3 head = new TwoThreeNode<>(data); 4 return true; 5 } 6 /* 找到待插入元素的叶子结点 */ 7 TwoThreeNode<T> n = head; 8 while (n != null) { 9 int r = compare(n, data); 10 TwoThreeNode<T> next = null; 11 switch (r) { 12 case LEFT_TREE: next = n.getLeft();break; 13 case MIDDLE_TREE: next = n.getMiddle(); break; 14 case RIGHT_TREE: next = n.getRight(); break; 15 default: return false; //find true 16 } 17 if (next == null) break; 18 n = next; 19 } 20 mergeNode(n, data); 21 return true; 22 }
删除
找到待删除元素所在结点 n,如果 n 不是叶子结点,用它的直接前驱(左子树的最大元素)或者直接后继(右子树的最小元素)替换,进而转换为对叶子结点的删除。
- 如果被删除的是 3结点,直接删除即可。
- 如果被删除的是 2结点,删除后,结点元素为空(零元素)。如果删除结点,则2-3树自身平衡被破坏,因此需要从父节点 parent 和 兄弟节点 sibling 进行借元素进行合并:
-
- 如果 兄弟结点 sibling 为 3结点时,需要从父结点借一个元素过来,填充当前结点,而父结点的被借的元素位置需要从 sibling 的借一个元素过来。
- 如果 兄弟节点 sibling 为 2结点时,需要从父节点借一个元素过来 和 兄弟结点的的元素合并,组成一个3结点,兄弟结点得到释放。
- 如果 父节点处理后,结点元素为空(零元素),则继续向上回溯;否则退出。
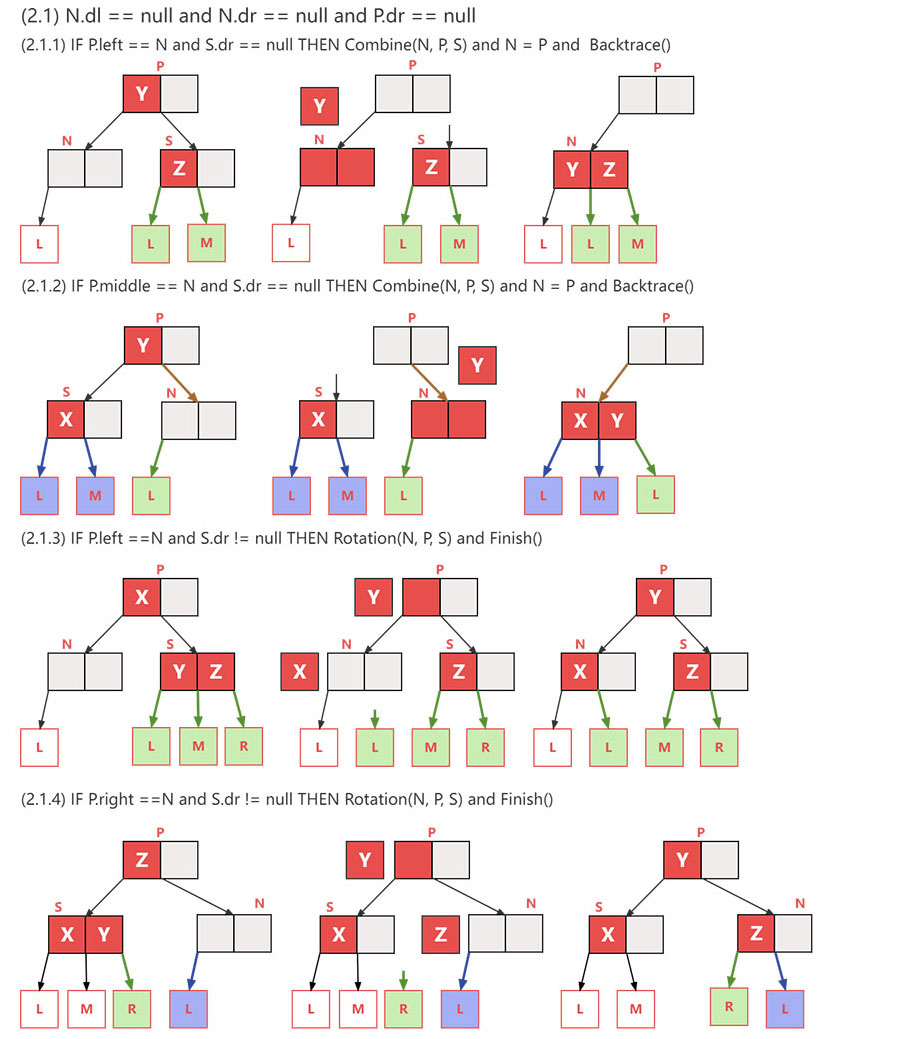
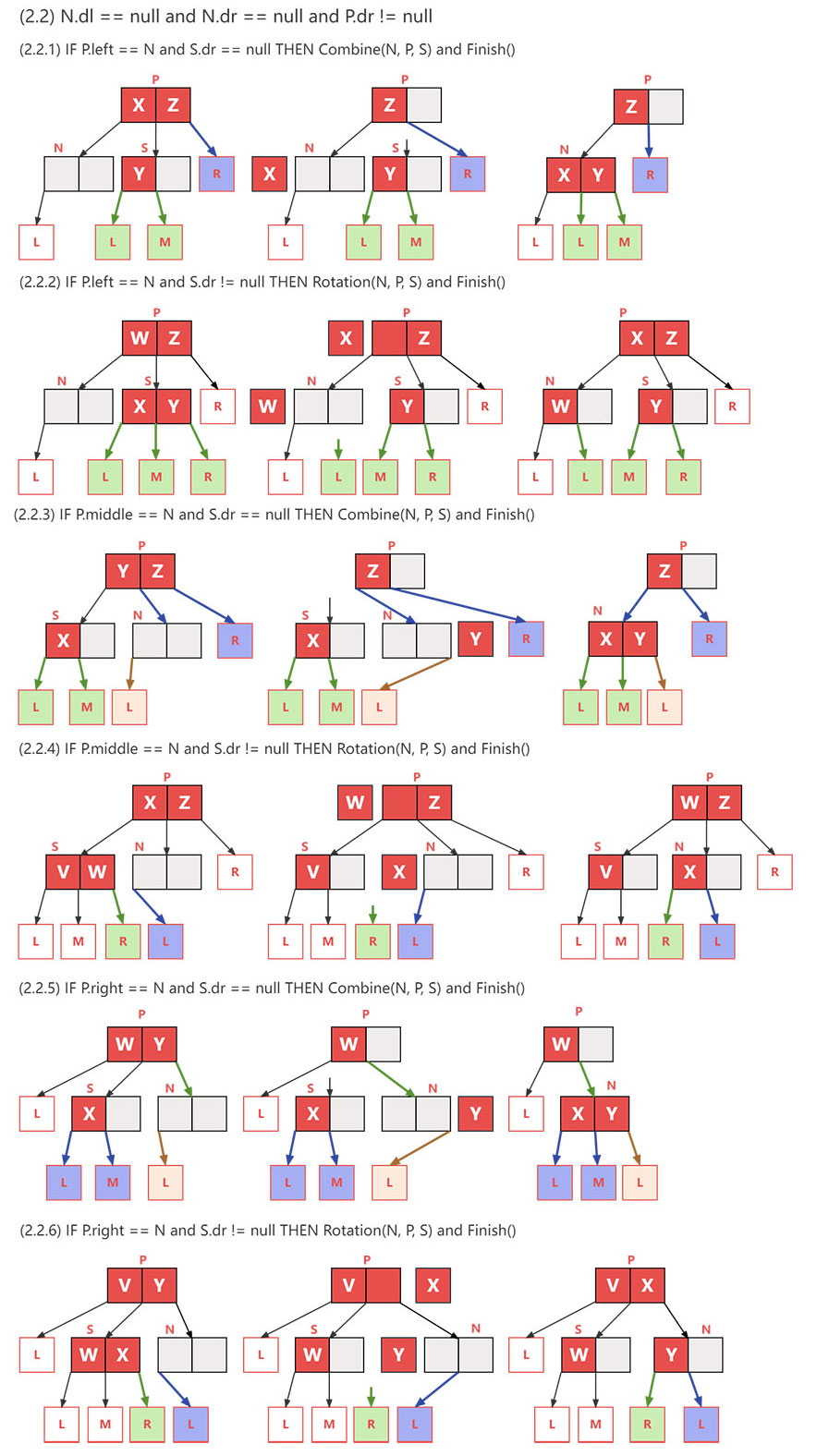
自底向上删除
1 public void remove(T data) { 2 if (head == null) return; 3 TwoThreeNode<T> n = head; 4 int cr = -1; 5 // STEP 1. 找到待删除元素所在结点 n 6 while (n != null) { 7 cr = compare(n, data); 8 if (cr == EQ_LEFT || cr == EQ_RIGHT) break; 9 TwoThreeNode<T> next = null; 10 switch (cr) { 11 case LEFT_TREE: next = n.getLeft();break; 12 case MIDDLE_TREE: next = n.getMiddle();break; 13 case RIGHT_TREE: next = n.getRight(); break; 14 } 15 n = next; 16 } 17 /* 没找到 */ 18 if (n == null) return; 19 // STEP 2. 交换元素,使叶子结点成为删除元素的结点。一般用待删除元素所在结点的 20 // 左子树最大元素 或者 右子树的最小元素与待删除元素进行交换后,删除叶 21 // 子的待删除元素。如果不为空则结束删除操作,如果为空要进行后续的旋转 22 // 或者 合并操作。 23 if ((n = exchange(n, cr)) == null) return; 24 // STEP 3. 叶子结点(n) 零元素时 进行旋转 或者 合并操作 25 // (a) n 结点的兄弟结点为3结点时旋转->结束 26 // (b) n 结点的兄弟结点为2结点时组合->回溯 27 while (n.getDataLeft() == null) { 28 TwoThreeNode<T> p = n.getParent(); 29 TwoThreeNode<T> s = null; 30 if (p.getLeft() == n) { 31 s = p.getMiddle(); 32 cr = LEFT_TREE; 33 } else if (p.getMiddle() == n) { 34 s = p.getLeft(); 35 cr = MIDDLE_TREE; 36 } else if (p.getRight() == n) { 37 s = p.getMiddle(); 38 cr = RIGHT_TREE; 39 } 40 if (dataType(s) == THREE_NODE) { 41 rotate(p, n, s, cr); 42 break; 43 } else { 44 combine(p, n, s, cr); 45 } 46 if (p == head) { 47 head = p.getLeft(); 48 head.setParent(null); 49 break; 50 } else { 51 n = p; 52 } 53 } 54 }
旋转函数
1 private void rotate(TwoThreeNode<T> p, TwoThreeNode<T> n, TwoThreeNode<T> s, int cr) { 2 if (cr == LEFT_TREE /* n 是 p 的左子树 */){ 3 /* 设置 n 结点的左兄弟 以及 中子树 */ 4 n.setDataLeft(p.getDataLeft()); 5 setChild(n, s.getLeft(), MIDDLE_TREE); 6 /* 设置 p 结点的左元素 */ 7 p.setDataLeft(s.getDataLeft()); 8 /* 移动兄弟结点的右元素到左元素位置 移动 中右子树 到 左中子树 */ 9 s.setDataLeft(s.getDataRight()); 10 setChild(s, s.getMiddle(), LEFT_TREE); 11 setChild(s, s.getRight(), MIDDLE_TREE); 12 s.setDataRight(null); 13 setChild(s, null, RIGHT_TREE); 14 } else if (cr == MIDDLE_TREE /* node 是父结点的中子树 */) { 15 /* 设置 n 结点的左元素 以及 左中子树 */ 16 n.setDataLeft(p.getDataLeft()); 17 setChild(n, n.getLeft(), MIDDLE_TREE); 18 setChild(n, s.getRight(), LEFT_TREE); 19 /* 设置 p 结点 左元素 */ 20 p.setDataLeft(s.getDataRight()); 21 /* 设置 s 结点的右元素为空 右子树为空 */ 22 s.setDataRight(null); 23 setChild(s, null, RIGHT_TREE); 24 } else if (cr == RIGHT_TREE /* node 是父结点的右子树 */) { 25 /* 设置 n 结点的左元素 以及 左中子树 */ 26 n.setDataLeft(p.getDataRight()); 27 setChild(n, n.getLeft(), MIDDLE_TREE); 28 setChild(n, s.getRight(), LEFT_TREE); 29 /* 设置 p 结点的右元素为 s 结点的右元素 */ 30 p.setDataRight(s.getDataRight()); 31 /* 设置 s 结点的右元素为空 以及 右子树为空 */ 32 s.setDataRight(null); 33 setChild(s, null, RIGHT_TREE); 34 } 35 }
组合函数
1 public void combine(TwoThreeNode<T> p, TwoThreeNode<T> n, TwoThreeNode<T> s, int cr) { 2 if (cr == LEFT_TREE /* n 为 p 的左儿子 */) { 3 /* 设置 p 结点 左右元素 以及 中右子树 */ 4 n.setDataLeft(p.getDataLeft()); 5 n.setDataRight(s.getDataLeft()); 6 setChild(n, s.getLeft(), MIDDLE_TREE); 7 setChild(n, s.getMiddle(), RIGHT_TREE); 8 /* 设置父结点左元素以及中子树 */ 9 p.setDataLeft(p.getDataRight()); 10 setChild(p, p.getRight(), MIDDLE_TREE); 11 p.setDataRight(null); 12 setChild(p, null, RIGHT_TREE); 13 } else if (cr == MIDDLE_TREE /* n 为 p 的中儿子 */) { 14 /* 设置 n 结点 左右元素 和 左中右子树 */ 15 n.setDataLeft(s.getDataLeft()); 16 n.setDataRight(p.getDataLeft()); 17 setChild(n, n.getLeft(), RIGHT_TREE); 18 setChild(n, s.getLeft(), LEFT_TREE); 19 setChild(n, s.getMiddle(), MIDDLE_TREE); 20 /* 设置 p 结点 左元素 和 左中子树 */ 21 p.setDataLeft(p.getDataRight()); 22 setChild(p, n, LEFT_TREE); 23 setChild(p, p.getRight(), MIDDLE_TREE); 24 p.setDataRight(null); 25 setChild(p, null, RIGHT_TREE); 26 } else if (cr == RIGHT_TREE /* n 为 p 的右儿子 */) { 27 /* 设置 n 结点 左右元素 以及 左中右子树 */ 28 n.setDataLeft(s.getDataLeft()); 29 n.setDataRight(p.getDataRight()); 30 setChild(n, n.getLeft(), RIGHT_TREE); 31 setChild(n, s.getLeft(), LEFT_TREE); 32 setChild(n, s.getMiddle(), MIDDLE_TREE); 33 /* 设置 p 结点 中子树 置 右元素 和 右子树为空 */ 34 setChild(p, n, MIDDLE_TREE); 35 p.setDataRight(null); 36 setChild(p, null, RIGHT_TREE); 37 } 38 }
无论遇到什么困难、一往直前



