前十周编程练习总结
------------恢复内容开始------------
一、练习涉及的主要知识点概况以及题量和难度
1.继承与多态
2.类与对象
3.容器的使用
4.正则表达式
PTA上的题目题量较少,难度中等偏上。
超星学习通的链表练习题题量少,难度中等。
期中考试的题目题量较少,难度中等偏下。
二、题目源码分析
1.链表练习题
源码:
interface DoubleLinkedListImpl<E> { /** * 判断链表是否为空 * @return */ public boolean isEmpty(); /** * 获取当前链表节点数量 * @return 节点数 */ public int getSize(); /** * 获取链表中第index个位置的节点的data值 * @param index:节点在链表中的位置 * @return:返回该节点的data值 */ public E getData(int index); /** * 删除链表最后一个节点 */ public void remove(); /** *删除链表中第index位置的节点 * @param index:节点在链表中的位置 */ public void remove(int index); /** * 在链表的第index个位置之前插入一个节点,值为theElement,index∈[1,size] * @param index:插入节点在链表中的位置 * @param theElement:新插入节点的data值 */ public void add(int index, E theElement); /** * 在链表尾插入节点,插入节点data值为element * @param element */ public void add(E element); /** * 输出链表 */ public void printList(); /** * 获取第一个节点的data值 * @return */ public E getFirst(); /** * 获取链表最后一个节点的data值 * @return */ public E getLast(); } class DoubleLinkedList<E> implements DoubleLinkedListImpl<E> { private Node<E> head;//头结点,非第一个节点 private Node<E> curr;//当前节点 private Node<E> tail;//最后一个节点 private int size;//当前链表节点数 public DoubleLinkedList(){ size=0; head=null; tail=head; } @Override public boolean isEmpty() { return head == null && tail == null; } @Override public int getSize() { return size; } @Override public E getData(int index) { int k = 0; while (k != index) { curr = curr.getNext (); k++; } return curr.getData (); } @Override public void remove() { if(head==null){ System.out.println ("链表为空,无需删除"); } else if(head.getNext () == null) { head = null; size--; }else { tail.getPrevious ().setNext (null); size--; } tail=tail.getPrevious (); } @Override public void remove(int index) { curr = head; if (index > getSize () || index < 1) { System.out.println ("超出索引范围"); } else if (index == 1) { head.getNext ().setPrevious (null); head = head.getNext (); size--; } else if (index == getSize ()) { remove (); } else { int k = 2; while (k != index) { curr = curr.getNext (); k++; } curr.setNext (curr.getNext ().getNext ()); curr.getNext ().setPrevious (curr); size--; } } @Override public void add(int index, E theElement) { Node<E> node = new Node<> (theElement); curr = head; if (index > getSize () || index < 1) { System.out.println ("超出索引范围"); } else if (index == 1) { node.setNext (head); head.setPrevious (node); head = node; size++; } else { int k=2; while (k!=index) { curr=curr.getNext (); k++; } node.setNext (curr.getNext ()); curr.getNext ().setPrevious (node); curr.setNext (node); node.setPrevious (curr); size++; } } @Override public void add(E element) { Node<E> node = new Node<> (element); if (isEmpty ()) { head = node; } else { node.setPrevious (tail); tail.setNext (node); } tail=node; size++; } @Override public void printList() { curr=head; while ( curr!= null ) { System.out.print (curr.getData ()); System.out.print (" "); curr = curr.getNext (); } // curr=tail; //反向的遍历链表,测试自用 // while ( curr!= null ) { // System.out.print (curr.getData ()); // System.out.print (" "); // curr = curr.getPrevious (); // } } @Override public E getFirst() { return head.getData (); } @Override public E getLast() { return tail.getData (); } } class Node<E> { private E data;//数据域,类型为泛型E private Node<E> next;//后继引用(指针) private Node<E> previous;//前驱引用(指针) public Node(E data) { this.data = data; } Node(){ } public Node<E> getPrevious() { return previous; } public E getData() { return data; } public Node<E> getNext() { return next; } public void setData(E data) { this.data = data; } public void setNext(Node<E> next) { this.next = next; } public void setPrevious(Node<E> previous) { this.previous = previous; } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { DoubleLinkedList doubleLinkedList = new DoubleLinkedList (); for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) { doubleLinkedList.add (i); } doubleLinkedList.printList (); System.out.println (" "); doubleLinkedList.add (2,9); doubleLinkedList.printList (); System.out.println (" "); doubleLinkedList.remove (); doubleLinkedList.printList (); System.out.println (" "); doubleLinkedList.remove (2); doubleLinkedList.printList (); } }
使用ideaProject生成的类图如下:
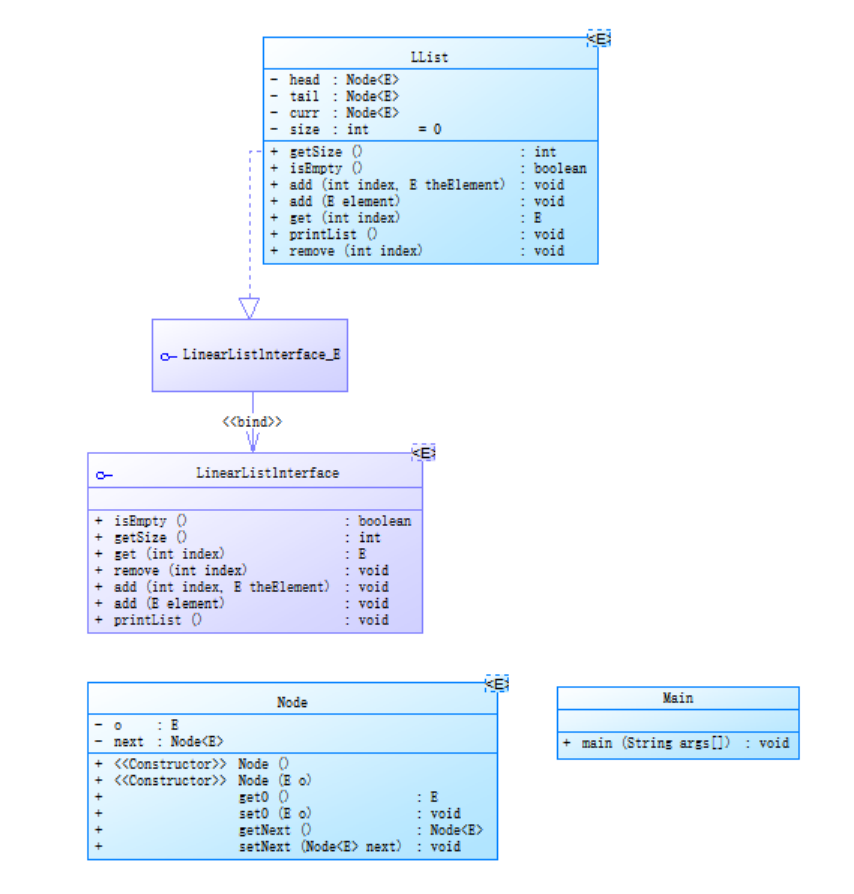
从类来看关键的结构是创建了一个接口,在实现功能的LList类中对接口里的方法进行了重写。
设计思路:
本题的难点在于节点的增、删,下面重点对双向链表的增、删进行分析。
首先分析不输入下标只带元素的add(E element)函数,先判断链表是否为空,为空的话,将要插入的节点作为头节点,此时头和尾是同一个节点。
若是不为空,因为此函数是将节点插到末尾,所以让尾节点里的next节点指向要插入的节点,再让插入的节点的previous节点指向尾节点,最后让插入的节点成为为节点,以此类推。
然后是带下标和元素的add(int index,E element)函数。因该函数在尾部田添加节点的操作与上面相同,现在分两种情况讨论。
在插入和删除之前,都要判断输入的下标是否越界,即是否小于0或者大于链表的长度+1。
1.下标为1,就是让插入的节点成为新的尾节点。具体操作为,将当前head节点的previous节点指向要插入的节点,再将要插入的节点的next节点指向当前head节点,最后让插入的节点成为head节点。
2.下标介于1和链表长度之间,先找到对应下标前一个的节点m,即index-1对应的节点,要在这个节点和这个节点的m.next节点之间插入新节点,具体操作为,先将m.next节点的previous节点设置为插入的节点,将插入节点的next节点设置为m.next,将插入节点的Previou节点设置为m,将m节点的next节点设置为m节点。
最后是删除节点,分三种情况。
1.下标为1,将头节点的下一节点的previous节点设置为null,并将此节点设置为head节点。
.2.下标介于1和链表长度之间,先找到对应下标前一个的节点m,即index-1对应的节点,将m的下一个节点设置为m.next.next,再把m.next.next的previou节点设置为m节点.
3.下标为链表长度,将tail.previous.next设置为null,再把tauk.previous设置为tail节点.
踩坑心得:因添加尾节点需输入下标大小为链表长度加1,删除节点需输入下标大小为链表长度,一开始我将两者都设置为链表长度加1,导致删除尾节点出现如下图错误
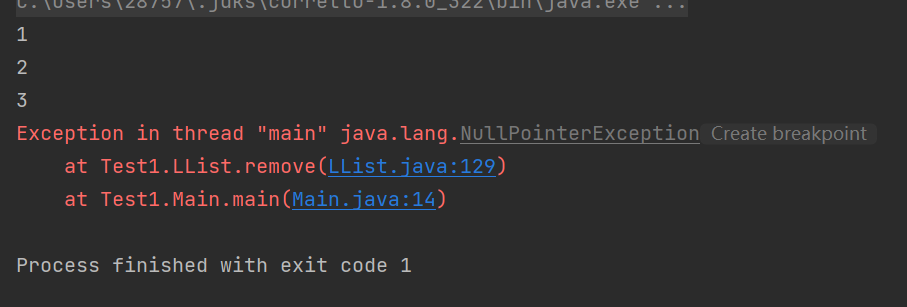
即越界错误。
二.PTA题目集
1.题目集4-7-1

源码:
import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.regex.Matcher; import java.util.regex.Pattern; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int n = -1; double[] a = new double[4]; String content = input.nextLine(); String regStr = "([+|-])?([0-9])+[\\.]?[0-9]?"; Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regStr); Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(content); if (B(content)) { while (matcher.find()) { n++; a[n] = Double.parseDouble(matcher.group(0)); } if(n!=0) { A juli = new A(a[0], a[1], a[2], a[3]); juli.jl(); System.out.print(juli.getD()); } } else { while (matcher.find()) { n++; if (n > 3) { System.out.print("wrong number of points"); n=0; break; } } if(n!=0) System.out.print("Wrong Format\n"); } } public static boolean B(String s) { String regex=("[+-]?(0|[1-9](\\d+)?)(\\.\\d+)?,[+-]?(0|[1-9](\\d+)?)(\\.\\d+)?[\\s][+-]?(0|[1-9](\\d+)?)(\\.\\d+)?,[+-]?(0|[1-9](\\d+)?)(\\.\\d+)?"); if(s.matches(regex)) return true; return false; } } class A{ private double x1; private double y1; private double x2; private double y2; private double d=0; public A(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2) { this.x1=x1; this.y1 =y1; this.x2= x2; this.y2=y2; } void jl(){ d=Math.sqrt(Math.pow(x1-x2,2)+Math.pow(y1-y2,2)); } public double getD() { return d; } }
题目分析:
本题难点不在于计算,难点在于输入格式的正误的判断和截取数据,为了简化代码,我在本题使用了正则表达式,
1.截取数据:因为本题数据的基本格式都是+或者-加数字,或者只有数字,使用正则表达式可以方便的截取数字,可以创建一个数组或容器储存截取的数据,使用Double.parseDouble(String s)将截取的字符串变成浮点数进行计算。
2.判断输入点的数量:在判断输入的点的数量是否符合要求时,可以通过存在数组或则容器里的数据的数量来判断。
3.判断输入格式:同样的,判断输入格式也可以使用正则表达式,使用string.match()返回的bollean值判断输入格式是否符合所写的正则表达式的值。
2.题目集4-7-2

源码:
import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.regex.Matcher; import java.util.regex.Pattern; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int n = -1; double[] a = new double[8]; String content = input.nextLine(); String regStr = "([+|-])?([0-9]+)+[.]?[0-9]?"; Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regStr); Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(content.substring(2,content.length())); if (B(content)) { int m=Integer.parseInt(content.substring(0,1)); while (matcher.find()) { n++; if(n>7){ break; } a[n] = Double.parseDouble(matcher.group(0)); } if(m==1){ if(n!=3){ System.out.println("wrong number of points"); } else{ if(a[0]==a[2]&&a[1]==a[3]){ System.out.println("points coincide"); } else if(a[0]==a[2]&&a[1]!=a[3]){ System.out.println("Slope does not exist"); } else if(a[0]!=a[2]&&a[1]==a[3]) System.out.println("0"); else System.out.println(XL(a[0],a[1],a[2],a[3])); } } else if(m==2){ if(n!=5){ System.out.println("wrong number of points"); } else{ if((a[0]==a[2]&&a[1]==a[3])||(a[0]==a[4]&&a[1]==a[7])||(a[2]==a[4]&&a[3]==a[7])){ System.out.println("points coincide"); } else{ System.out.println(JL(a[0],a[1],a[2],a[3],a[4],a[5])); } } } else if(m==3){ if (n != 5) { System.out.println("wrong number of points"); } else{ if((a[0]==a[2]&&a[1]==a[3])||(a[0]==a[4]&&a[1]==a[5])||(a[2]==a[4]&&a[3]==a[5])){ System.out.println("points coincide"); } else if(JL(a[0],a[1],a[2],a[3],a[4],a[5])==0){ System.out.println("true"); } else{ System.out.println("false"); } } } else if(m==4){ if(n!=7){ System.out.println("wrong number of points"); } else { if((a[0]==a[2]&&a[1]==a[3])||(a[0]==a[4]&&a[1]==a[5])||(a[0]==a[6]&&a[1]==a[7])||(a[2]==a[4]&&a[3]==a[5])||(a[2]==a[6]&&a[3]==a[7])||(a[4]==a[6]&&a[5]==a[7])){ System.out.println("points coincide"); } else{ System.out.println(PX(a[0],a[1],a[2],a[3],a[4],a[5],a[6],a[7])); } } } else if(m==5){ if(n!=7){ System.out.println("wrong number of points"); } else{ if((a[0]==a[2]&&a[1]==a[3])||(a[0]==a[4]&&a[1]==a[5])||(a[0]==a[6]&&a[1]==a[7])||(a[2]==a[4]&&a[3]==a[5])||(a[2]==a[6]&&a[3]==a[7])||(a[4]==a[6]&&a[5]==a[7])){ System.out.println("points coincide"); } else{ if(PX(a[0],a[1],a[2],a[3],a[4],a[5],a[6],a[7]).equals("true")){ System.out.println("is parallel lines,have no intersection point"); } else{ System.out.println(JD(a[0],a[1],a[2],a[3],a[4],a[5],a[6],a[7])); } } } } } else{ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } } public static boolean B (String s){ String regex = ("[1-5]{1}\\:(([+-]?(0|[1-9](\\d+)?)(\\.\\d+)?,[+-]?(0|[1-9](\\d+)?)(\\.\\d+)?[\\s])+)[+-]?(0|[1-9](\\d+)?)(\\.\\d+)?,[+-]?(0|[1-9](\\d+)?)(\\.\\d+)?"); if(s.matches(regex)) return true; return false; } public static double XL(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2){ double XL=0; XL=(y1-y2)/(x1-x2); return XL; } public static double JL(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2,double x3,double y3){ double jl=0; if(x2==x3){ jl=Math.abs(x1-x2); } else if(y2==y3){ jl=Math.abs(y1-y2); } else{ jl=Math.abs((-(y3-y2)/(x3-x2))*x1+y1-y2+((y3-y2)/(x3-x2))*x2)/Math.sqrt(Math.pow((y3-y2)/(x3-x2),2)+1); } return jl; } public static String PX(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2,double x3,double y3,double x4, double y4){ double k1 = (y2-y1)/(x2-x1); double k2 =(y4-y3)/(x4-x3); if(k1==k2){ return "true"; } else return "false"; } public static String JD(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2,double x3,double y3,double x4, double y4){ double max1,max2,min1,min2; max1=x1; min1=x2; max2=x3; min2=x4; if(x2>x1){ max1=x2; min1=x1; } if(x3>x4){ max2=x3; min2=x4; } double k1 = (y2-y1)/(x2-x1); double k2 =(y4-y3)/(x4-x3); double x5=0; double y5=0; if(x1==x2){ x5=x1; y5=k2*x1-k2*x3+y3; } else if(x3==x4){ x5=x3; y5=k1*x3-k1*x1+y1; } else { x5 = (k1 * x1 - k2 * x3 - y1 + y3) / (k1 - k2); y5 = k1 * x5 - k1 * x1 + y1; } if(x5>min1&&x5<max1) { String m = String.valueOf(x5); String n = String.valueOf(y5); return m + "," + n + " true"; } else{ String m = String.valueOf(x5); String n = String.valueOf(y5); return m + "," + n + " false"; } } }
题目重难点分析:
1.输入数据的判断:输入数据的储存使用和判断与第一题类似,以下题目不再赘述。
2.交点是否在线段内部:这个问题的我第一次并没有做出来,在后面做凸四边形的题目时才顺便把这个问题解决,解决思路时用向量的叉乘来判断方向,设有两条线段的两个线段的两个端点分别是A、C和B、D,以及交点E,计算向量AC与AB和AC与AD的叉乘,设其分别为x1,x2,计算向量BD与BC和BD与BA的叉乘,设其分别为x3,x4,,如果x1,x2相乘小于0,说明B,D在直线AC两侧,X3,X4相乘小于0,说明A,C在B,D两侧,两则同时满足,并且交点不在端点处时,说明交点在线段内。
3.题目集4-7-3

import java.text.DecimalFormat; import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.regex.Matcher; import java.util.regex.Pattern; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int n = -1; double[] a = new double[10]; String content = input.nextLine(); String regStr = "([+|-])?([0-9]+)+[.]?[0-9]?"; Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regStr); Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(content.substring(2,content.length())); if (B(content)) { int m=Integer.parseInt(content.substring(0,1)); while (matcher.find()) { n++; if(n>9){ break; } a[n] = Double.parseDouble(matcher.group(0)); } if(m==1){ if(n!=5){ System.out.println("wrong number of points"); } else { if (CD(a[0], a[1], a[2], a[3]) == 0 || CD(a[0], a[1], a[4], a[5]) == 0 || CD(a[4], a[5], a[2], a[3]) == 0 || JL(a[0], a[1], a[2], a[3], a[4], a[5]) == 0) { System.out.println("data error"); } else { if (CD(a[0], a[1], a[2], a[3]) == CD(a[0], a[1], a[4], a[5]) || CD(a[0], a[1], a[2], a[3]) == CD(a[2], a[3], a[4], a[5]) || CD(a[2], a[3], a[4], a[5]) == CD(a[0], a[1], a[4], a[5])) { System.out.print("true "); } else System.out.print("false"); if (CD(a[0], a[1], a[2], a[3]) == CD(a[0], a[1], a[4], a[5]) && CD(a[0], a[1], a[2], a[3]) == CD(a[2], a[3], a[4], a[5])) { System.out.print("true"); } else { System.out.print("false"); } } } } else if(m==2){ if(n!=5){ System.out.println("wrong number of points"); } else{ if(CD(a[0],a[1],a[2],a[3])==0||CD(a[0],a[1],a[4],a[5])==0||CD(a[4],a[5],a[2],a[3])==0||JL(a[0],a[1],a[2],a[3],a[4],a[5])==0){ System.out.println("data error"); } else{ A two = new A(a[0],a[1],a[2],a[3],a[4],a[5]); two.Zx(); two.S(); System.out.println(Sswr(CD(a[0],a[1],a[2],a[3])+CD(a[0],a[1],a[4],a[5])+CD(a[4],a[5],a[2],a[3]))+" "+Sswr(two.getMj())+" "+Sswr(two.getX6())+","+Sswr(two.getY6())); } } } else if(m==3){ if (n != 5) { System.out.println("wrong number of points"); } else{ if(CD(a[0],a[1],a[2],a[3])==0||CD(a[0],a[1],a[4],a[5])==0||CD(a[4],a[5],a[2],a[3])==0||JL(a[0],a[1],a[2],a[3],a[4],a[5])==0){ System.out.println("data error"); } else { B three = new B(CD(a[0],a[1],a[2],a[3]),CD(a[0],a[1],a[4],a[5]),CD(a[4],a[5],a[2],a[3])); three.cos(); if(three.getCosA()<0||three.getCosB()<0||three.getCosC()<0){ System.out.println("true false false"); } else if(three.getCosA()==0||three.getCosB()==0||three.getCosC()==0){ System.out.println("false true false"); } else System.out.println("false false true"); } } } else if(m==4){ if(n!=9){ System.out.println("wrong number of points"); } else { if((a[0]==a[2]&&a[1]==a[3])||(a[0]==a[4]&&a[1]==a[5])||(a[0]==a[6]&&a[1]==a[7])||(a[2]==a[4]&&a[3]==a[5])||(a[2]==a[6]&&a[3]==a[7])||(a[4]==a[6]&&a[5]==a[7])){ System.out.println("points coincide"); } else{ System.out.println(PX(a[0],a[1],a[2],a[3],a[4],a[5],a[6],a[7])); } } } else if(m==5){ if(n!=7){ System.out.println("wrong number of points"); } else{ if((a[0]==a[2]&&a[1]==a[3])||(a[0]==a[4]&&a[1]==a[5])||(a[0]==a[6]&&a[1]==a[7])||(a[2]==a[4]&&a[3]==a[5])||(a[2]==a[6]&&a[3]==a[7])||(a[4]==a[6]&&a[5]==a[7])){ System.out.println("points coincide"); } else{ if(PX(a[0],a[1],a[2],a[3],a[4],a[5],a[6],a[7]).equals("true")){ System.out.println("is parallel lines,have no intersection point"); } else{ // System.out.println(JD(a[0],a[1],a[2],a[3],a[4],a[5],a[6],a[7])); } } } } } else{ System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } } public static boolean B (String s){ String regex = ("[1-5]{1}\\:(([+-]?(0|[1-9](\\d+)?)(\\.\\d+)?,[+-]?(0|[1-9](\\d+)?)(\\.\\d+)?[\\s])+)[+-]?(0|[1-9](\\d+)?)(\\.\\d+)?,[+-]?(0|[1-9](\\d+)?)(\\.\\d+)?"); if(s.matches(regex)) return true; return false; } public static double CD(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2){ double cd= Math.sqrt(Math.pow(x1-x2,2)+Math.pow(y1-y2,2)); return cd; } public static double XL(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2){ double XL=0; XL=(y1-y2)/(x1-x2); return XL; } public static double JL(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2,double x3,double y3){ double jl=0; if(x2==x3){ jl=Math.abs(x1-x2); } else if(y2==y3){ jl=Math.abs(y1-y2); } else{ jl=Math.abs((-(y3-y2)/(x3-x2))*x1+y1-y2+((y3-y2)/(x3-x2))*x2)/Math.sqrt(Math.pow((y3-y2)/(x3-x2),2)+1); } return jl; } public static String PX(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2,double x3,double y3,double x4, double y4){ double k1 = (y2-y1)/(x2-x1); double k2 =(y4-y3)/(x4-x3); if(k1==k2){ return "true"; } else return "false"; } public static double Sswr(double n){ int count=0; String s = String.valueOf(n); char []a = s.toCharArray(); count =s.length()-1; while(a[count]!='.'){ count--; } if(s.length()-1-count>6){ n= Double.parseDouble(new DecimalFormat("#.######").format(n)); } return n; } } class A{ private double x1, y1, x2, y2, x3,y3; private double x6,y6,mj; public A(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2, double x3, double y3) { this.x1 = x1; this.y1 = y1; this.x2 = x2; this.y2 = y2; this.x3 = x3; this.y3 = y3; } void Zx(){ this.x6=(x1+x2+x3)/3; this.y6=(y1+y2+y3)/3; } void S(){ mj=(x1*y2-x1*y3+x2*y3-x2*y1+x3*y1-x2*y2)/2; } public double getX6() { return x6; } public double getY6() { return y6; } public double getMj() { return mj; } } class B{ private double a,b,c; private double cosA,cosB,cosC; public B(double a, double b, double c) { this.a = a; this.b = b; this.c = c; } public void cos(){ cosA = (Math.pow(b,2)+Math.pow(c,2)-Math.pow(a,2))/(2*b*c); cosB = (Math.pow(a,2)+Math.pow(c,2)-Math.pow(b,2))/(2*a*c); cosC = (Math.pow(a,2)+Math.pow(b,2)-Math.pow(c,2))/(2*b*a); } public double getCosA() { return cosA; } public double getCosB() { return cosB; } public double getCosC() { return cosC; } }
题目重难点分析:
1.输出数据的四舍五入:先将初始数据转化为字符串,再将字符串转化为字符数组,根据字符数组最后一位的下标和小数点的小标判断小数是否超过六位,如果超过则使用 n= Double.parseDouble(new DecimalFormat("#.######").format(n)),进行四舍五入。
2..周长、面积计算:用两点距离公式将三条边距离计算出来相加即可,面积的可以由任意两条边表示的向量的叉乘的二分之一得出。
3.判断三角形的类型:可以使用余弦定理计算三个角的余弦值,任意一个小于0,则为钝角三角形,任意一个为0则为直角三角形,否则为锐角三角形。
4.题目集6-7-2


源码:
import jdk.nashorn.internal.parser.DateParser; import java.awt.geom.Line2D; import java.text.DecimalFormat; import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.regex.Matcher; import java.util.regex.Pattern; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { int i,j; Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int n = -1; double[] a = new double[12]; String content = input.nextLine().trim(); String regStr = "([\\+|\\-]?\\d+)(\\.\\d+)?"; Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regStr); Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(content.substring(2)); if (formatIsTrue(content)) { int m = Integer.parseInt(content.substring(0, 1)); while (matcher.find()) { n++; if (n > 11) { break; } a[n] = Double.parseDouble(matcher.group(0)); } if (m==1){ if (n!=7){ System.out.println("wrong number of points"); } else { Four A = new Four(a[0],a[1],a[2],a[3],a[4],a[5],a[6],a[7]); if (chongHe(a[0],a[1],a[2],a[3])||chongHe(a[0],a[1],a[4],a[5])||chongHe(a[0],a[1],a[6],a[7])||chongHe(a[2],a[3],a[4],a[5])||chongHe(a[2],a[1],a[6],a[7])||chongHe(a[4],a[5],a[6],a[7])){ System.out.println("points coincide"); } else { if(A.isFour()){ System.out.print("true "); } else System.out.print("false "); if (A.isPXin()){ System.out.println("true"); } else { System.out.println("false"); } } } } else if (m==2){ Four A = new Four(a[0], a[1], a[2], a[3], a[4], a[5], a[6], a[7]); if (!A.isFour()){ System.out.println("not a quadrilateral"); } else { if (A.isLinXin()){ System.out.print("true "); } else { System.out.print("false "); } if (A.isJuXin()){ System.out.print("true "); } else { System.out.print("false "); } if (A.isZhengF()){ System.out.println("true"); } else { System.out.println("false"); } } } else if (m==3){ Four A = new Four(a[0], a[1], a[2], a[3], a[4], a[5], a[6], a[7]); if (!A.isFour()){ System.out.println("not a quadrilateral"); }else { if (A.isTu()){ System.out.print("true "); } else { System.out.print("false "); } System.out.print(Sswr(A.ZC())+" "); System.out.print((Sswr(A.area()))); } } else if (m==4){ if (n!=11){ System.out.println("wrong number of points"); } else { if (chongHe(a[0],a[1],a[2],a[3])){ System.out.println("points coincide"); } else { Four A = new Four(a[4], a[5], a[6], a[7], a[8], a[9], a[10], a[11]); if (!A.isFour()){ if (!A.isThree()){ System.out.println("not a quadrilateral or triangle"); } else { A.quRongYu(); if (A.fourPointGx(a[0],a[1], a[2],a[3], A.x2,A.y2,A.x3,A.y3)||A.fourPointGx(a[0],a[1], a[2],a[3], A.x2,A.y2,A.x1,A.y1)||A.fourPointGx(a[0],a[1], a[2],a[3], A.x1,A.y1,A.x3,A.y3)){ System.out.println("The line is coincide with one of the lines"); } else if (A.threePointGx(a[0],a[1], a[2],a[3], A.x2,A.y2)||A.threePointGx(a[0],a[1], a[2],a[3], A.x1,A.y1)||A.threePointGx(a[0],a[1], a[2],a[3], A.x3,A.y3)){ System.out.println("1"); } } } else { if (A.fourPointGx(a[0],a[1], a[2],a[3], A.x2,A.y2,A.x3,A.y3)||A.fourPointGx(a[0],a[1], a[2],a[3], A.x2,A.y2,A.x1,A.y1)||A.fourPointGx(a[0],a[1], a[2],a[3], A.x1,A.y1,A.x4,A.y4)||A.fourPointGx(a[0],a[1], a[2],a[3], A.x3,A.y3,A.x4,A.y4)) { System.out.println("The line is coincide with one of the lines"); } else if (A.threePointGx(a[0],a[1], a[2],a[3], A.x2,A.y2)||A.threePointGx(a[0],a[1], a[2],a[3], A.x1,A.y1)||A.threePointGx(a[0],a[1], a[2],a[3], A.x3,A.y3)||A.threePointGx(a[0],a[1], a[2],a[3], A.x4,A.y4)){ System.out.println("1"); } } } } } else if (m==5){ if (n!=9){ System.out.println("wrong number of points"); } else { Four A = new Four(a[2], a[3], a[4], a[5], a[6], a[7], a[8], a[9]); if (!A.isFour()){ if (!A.isThree()){ System.out.println("not a quadrilateral or triangle"); } else { A.quRongYu(); if ((A.threePointGx(a[0],a[1], A.x1, A.y1,A.x2,A.y2)&&A.onTheMid(a[0],a[1], A.x1, A.y1,A.x2,A.y2))||(A.threePointGx(a[0],a[1], A.x3, A.y3, A.x1,A.y1)&&A.onTheMid(a[0],a[1], A.x3, A.y3, A.x1,A.y1))||(A.threePointGx(a[0],a[1], A.x2, A.y2, A.x3,A.y3)&&A.onTheMid(a[0],a[1], A.x2, A.y2, A.x3,A.y3))){ System.out.println("on the triangle"); } else { double o1=A.x1-a[0]; double p1=A.y1-a[1]; double o2=A.x2-a[0]; double p2=A.y2-a[1]; double o3=A.x3-a[0]; double p3=A.y3-a[1]; double o4=A.x1-A.x2; double p4=A.y1-A.y2; double o5=A.x1-A.x3; double p5=A.y1-A.y3; double s=Math.abs(o1*p2-p1*o2)/2.0+Math.abs(o2*p3-p2*o3)/2.0+Math.abs(o3*p1-p3*o1)/2.0; if (s== Math.abs(o4*p5-p4*o5)/2.0){ System.out.println("in the triangle"); } else { System.out.println("outof the triangle"); } } } } else { if ((A.threePointGx(a[0],a[1], A.x1, A.y1,A.x2,A.y2)&&A.onTheMid(a[0],a[1], A.x1, A.y1,A.x2,A.y2))||(A.threePointGx(a[0],a[1], A.x4, A.y4, A.x1,A.y1)&&A.onTheMid(a[0],a[1], A.x4, A.y4, A.x1,A.y1))||(A.threePointGx(a[0],a[1], A.x2, A.y2, A.x3,A.y3)&&A.onTheMid(a[0],a[1], A.x2, A.y2, A.x3,A.y3))||(A.threePointGx(a[0],a[1], A.x4, A.y4, A.x3,A.y3)&&A.onTheMid(a[0],a[1], A.x4, A.y4, A.x3,A.y3))){ System.out.println("on the quadrilateral"); } else { double o1=A.x1-a[0]; double p1=A.y1-a[1]; double o2=A.x2-a[0]; double p2=A.y2-a[1]; double o3=A.x3-a[0]; double p3=A.y3-a[1]; double o4=A.x4-a[0]; double p4=A.y4-a[1]; double s=Math.abs(o1*p2-p1*o2)/2.0+Math.abs(o2*p3-p2*o3)/2.0+Math.abs(o3*p4-p3*o4)/2.0+Math.abs(o4*p1-p4*o1)/2.0; if (s== A.area()){ System.out.println("in the quadrilateral"); } else { System.out.println("outof the quadrilateral"); } } } } } } else { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } } public static boolean formatIsTrue (String m){ String regex = ("[1-5]\\:[\\+|-]?([0]|([1-9]((\\d)?)+))(\\.\\d+)?\\,([+\\-]?([0]|([1-9]((\\d)?)+)))(\\.\\d+)?(\\s([+\\-]?([0]|([1-9]((\\d)?)+)))(\\.\\d+)?\\,([+\\-]?([0]|([1-9]((\\d)?)+)))(\\.\\d+)?)+"); return m.matches(regex); } public static boolean chongHe(double x1,double y1,double x2, double y2){ if (x1==x2&&y1==y2){ return true; } return false; } public static double Sswr(double n){ int count=0; String s = String.valueOf(n); char []a = s.toCharArray(); count =s.length()-1; while(a[count]!='.'){ count--; } if(s.length()-1-count>3){ n= Double.parseDouble(new DecimalFormat("#.###").format(n)); } return n; } } class Four{ double x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3,x4,y4; public Four(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2, double x3, double y3, double x4, double y4) { this.x1 = x1; this.y1 = y1; this.x2 = x2; this.y2 = y2; this.x3 = x3; this.y3 = y3; this.x4 = x4; this.y4 = y4; } public boolean isPXin(){ if ((JL(x1, y1, x2, y2)==JL(x3,y3,x4,y4))&&(JL(x2,y2,x3,y3)==JL(x1, y1, x4, y4))){ return true; } else return false; } public double JL(double x1,double y1,double x2, double y2){ return Math.sqrt(Math.pow(x1-x2,2)+Math.pow(y1-y2,2)); } public boolean hasJiao(){ Line2D line1 = new Line2D.Double(x1,y1,x2,y2); Line2D line2 = new Line2D.Double(x3,y3,x4,y4); Line2D line3 = new Line2D.Double(x1,y1,x4,y4); Line2D line4 = new Line2D.Double(x2,y2,x3,y3); if(line2.intersectsLine(line1)||line3.intersectsLine(line4)){ return true; } else return false; } public boolean notHaiJiao(){ if (!hasJiao()){ return true; } else { return false; } } public boolean gongXian (){ if ((x1==x2&&x1==x3)||(x1==x2&&x1==x4)||(x1==x3&&x1==x4)||(x3==x2&&x3==x4)){ return true; } else if ((y2-y1)/(x2-x1)==(y2-y3)/(x2-x3)||(y2-y1)/(x2-x1)==(y2-y4)/(x2-x4)||(y3-y1)/(x3-x1)==(y4-y3)/(x4-x3)||(y3-y2)/(x3-x2)==(y3-y4)/(x3-x4)){ return true; } else { return false; } } public boolean isFour(){ if (!gongXian()){ if (notHaiJiao()){ return true; } else return false; } return false; } public boolean isLinXin(){ if (isFour()){ if (isPXin()){ if (JL(x1,y1,x2,y2)==JL(x2,y2,x3,y3)){ return true; } } else { return false; } } return false; } public boolean isJuXin(){ if (isFour()){ if (isPXin()){ if ((x2-x1)*(x3-x2)+(y2-y1)*(y3-y2)==0){ return true; } else { return false; } } } return false; } public boolean isZhengF(){ if (isJuXin()){ if (JL(x1,y1,x2,y2)==JL(x2,y2,x3,y3)){ return true; } else { return false; } } return false; } public boolean isTu(){ Line2D line1 = new Line2D.Double(x1,y1,x3,y3); Line2D line2 = new Line2D.Double(x2,y2,x4,y4); if(line2.intersectsLine(line1)){ return true; } else return false; } public double area(){ double S=0.0; double x = x3-x1; double y = y3-y1; double xx = x2-x1; double yy = y2-y1; double xxx = x4-x1; double yyy= y4-y1; double s = (Math.abs(x * yy - y * xx) + Math.abs(x * yyy - y * xxx)) / 2.0; if (isTu()){ S = s; } else { if ((x*yyy-y*xxx)*(x*yy-y*xx)<0){ S = s; } else { double s1 = Math.abs(x * yy - y * xx)/2.0; double s2 = Math.abs(x * yyy - y * xxx)/2.0; if (s1>s2){ S = s1-s2; } else { S = s2 - s1; } } } return S; } public double ZC(){ return JL(x1,y1,x2,y2)+ JL(x2,y2,x3,y3)+ JL(x3,y3,x4,y4)+ JL(x4,y4,x1,y1); } public boolean isThree(){ if ((onTheMid(x2,y2,x1,y1,x3,y3)&&threePointGx(x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3))||(onTheMid(x1,y1,x2,y2,x4,y4)&&threePointGx(x1,y1,x2,y2,x4,y4))||(onTheMid(x4,y4,x1,y1,x3,y3)&&threePointGx(x1,y1,x4,y4,x3,y3))||(onTheMid(x3,y3,x2,y2,x4,y4)&&threePointGx(x4,y4,x2,y2,x3,y3))){ return true; } else { return false; } } public boolean threePointGx(double x5,double y5,double x6,double y6,double x7,double y7){ if (x5==x6&&x5==x7){ return true; } else if ((y5-y6)/(x5-x6)==(y7-y6)/(x7-x6)){ return true; } return false; } public boolean fourPointGx(double x5,double y5,double x6,double y6,double x7,double y7,double x8,double y8){ if (x5==x6&&x5==x7&&x5==x8){ return true; } else if ((y5-y6)/(x5-x6)==(y7-y6)/(x7-x6)&&(y5-y6)/(x5-x6)==(y7-y8)/(x7-x8)){ return true; } return false; } public void quRongYu(){ if (x2>=Math.min(x1,x3)&&x2<=Math.max(x1,x3)&&y2>=Math.min(y1,y3)&&y2<=Math.max(y1,y3)&&threePointGx(x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3)){ x2 = x3; y2=y3; x3=x4; y3=y4; } else if (x1>=Math.min(x2,x4)&&x1<=Math.max(x2,x4)&&y1>=Math.min(y2,y4)&&y1<=Math.max(y2,y4)&&threePointGx(x1,y1,x2,y2,x4,y4)){ x1 = x2; y1=y2; x2=x3; y2=y3; x3=x4; y3=y4; } else if (x3>=Math.min(x2,x4)&&x3<=Math.max(x2,x4)&&y3>=Math.min(y2,y4)&&y3<=Math.max(y2,y4)&&threePointGx(x4,y4,x2,y2,x3,y3)){ x3=x4; y3=y4; } } public boolean onTheMid(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2,double x3,double y3){ if (x1>=Math.min(x2,x3)&&x1<=Math.max(x2,x3)&&y1>=Math.min(y2,y3)&&y1<=Math.max(y2,y3)) return true; else return false; } }
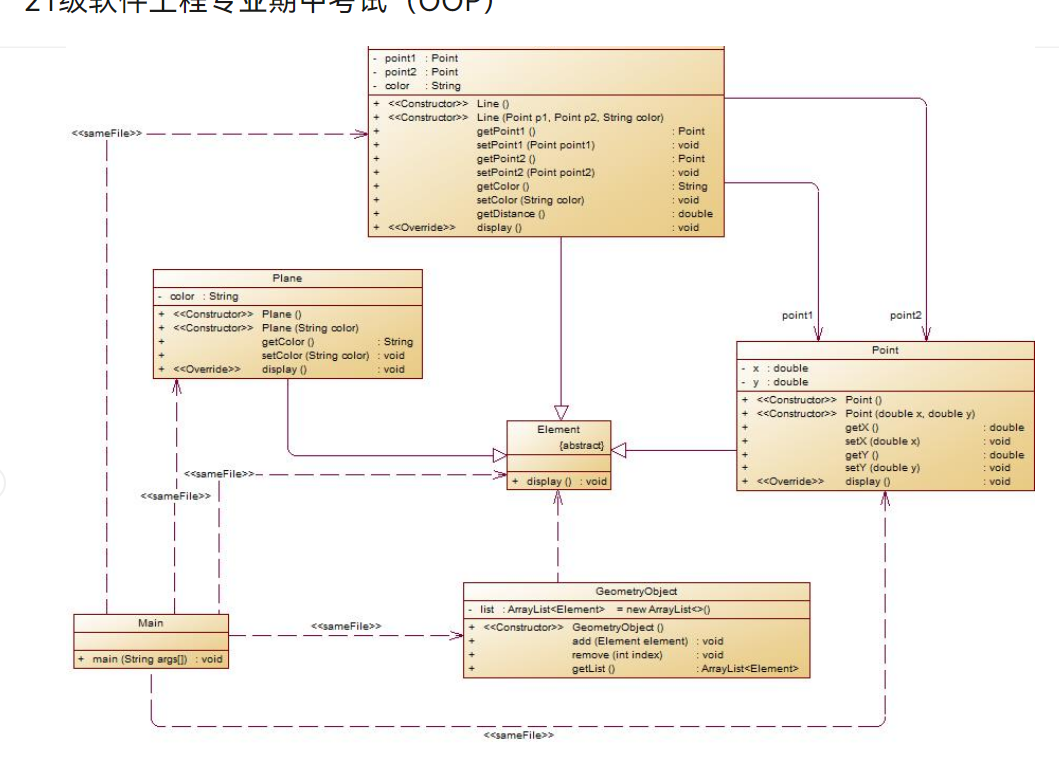
生成的类图如下:

题目重难点分析:
1.四边形的判断:我使用的方法是先保证任意三点不在同一条直线上,又因为输入的点是依次连接的,所以最后再保证,点1、2和点3、4分别构成的线段不会相交,以及点1,4和点2,3分别构成的线段不会相交。
其中判断线段相交是否相交的源码如下:
public boolean hasJiao(){ Line2D line1 = new Line2D.Double(x1,y1,x2,y2); Line2D line2 = new Line2D.Double(x3,y3,x4,y4); Line2D line3 = new Line2D.Double(x1,y1,x4,y4); Line2D line4 = new Line2D.Double(x2,y2,x3,y3); if(line2.intersectsLine(line1)||line3.intersectsLine(line4)){ return true; } else return false; }
2.凹凸四边形的判断:我在纸上画出凸四边形的图形,和凹四边形当凹点为点1、2、3、4时的所有情况,发现凸四边形点1、3和点2,4分别构成的线段必定相交,而凹四边形点1、3和点2,4分别构成的线段必定不相交,所以用与上面类似的方法判断线段相交即可,代码如下:
public boolean isTu(){ Line2D line1 = new Line2D.Double(x1,y1,x3,y3); Line2D line2 = new Line2D.Double(x2,y2,x4,y4); if(line2.intersectsLine(line1)){ return true; } else return false; }
3.凹凸四边形的面积:对于凸四边形,连接1、3,将四边形分割成两个三角形,用1,3边构成的向量作为公共向量,取三角形任意一条向量算叉乘取绝对值再乘二分之一即可得到三角形的面积,将两个三角形面积相加即可。
对于凹四边形同样连接1,3,理解下面的操作你需要需画一个凹四边形的图,不管凹点是哪个你会发现线段13会与2,4中的一个点形成小三角形,与2,4中的一个点形成大三角形。并且小三角形在大三角形内部,凹四边形的面积为大三角形减去小的,所以我们只需把三角形132与三角形134都计算出来(使用叉乘或者其他方法),然后判断哪个更大,用大的减去小的,或者直接算出两者相减的绝对值。
4.四个点构成三角形的判断:根据题目要求,因为点与点之间有连接顺序,所以四个点构成三角形有以下几种:
1:123共线,点2在线段13之间(点二在一三之间要保证横纵坐标都在一三之间,因为不知道点1和点3横纵坐标大小,推荐使用Math.max Math.min.)下同
2.124共线,点1在线段24之间
134共线,点4在线段一3之间
234共线,点3在线段24之间
5.判断点是否在图形内部,图形中,或者图形外,类似上面,如果这个点与图形任意一条边共线并在线段中间,则点在图形中,判断是否在图形内,只需将该点与图形各个端点相连,若在图形内,三角形会被分割成三个小三角形,四边形会分割成四个小三角形,判断这些小三角形相加是否等于原图形面积,相等则在图形内部,否则在图形外。
三、期中测试题:
第一题:

源码:
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args){ Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); Double x1=in.nextDouble(); Double y1=in.nextDouble(); Double x2=in.nextDouble(); Double y2=in.nextDouble(); String color = in.next(); if (x1>0&&x1<=200&&y1>0&&y1<=200&&x2>0&&x2<=200&&y2>0&&y2<=200){ Point point1=new Point(x1,y1); Point point2=new Point(x2,y2); Line line = new Line(point1,point2,color); line.display(); } else { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } } } class Point{ private double x,y; public Point(double x, double y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; } public double getX() { return x; } public void setX(double x) { this.x = x; } public double getY() { return y; } public void setY(double y) { this.y = y; } public void display(){ System.out.println("("+String.format("%.2f", x)+","+String.format("%.2f",y)+")"); } } class Line{ private Point point1; private Point point2; private String color; public Line() { } public Line(Point point1, Point point2, String color) { this.point1 = point1; this.point2 = point2; this.color = color; } public Point getPoint1() { return point1; } public void setPoint1(Point point1) { this.point1 = point1; } public Point getPoint2() { return point2; } public void setPoint2(Point point2) { this.point2 = point2; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; } public Double getDistance(){ double l = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(point1.getX()- point2.getX(),2)+Math.pow(point1.getY()- point2.getY(),2)); return l; } public void display(){ System.out.println("The line's color is:"+color); System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:"); point1.display(); System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:"); point2.display(); System.out.print("The line's length is:"); System.out.println( String.format("%.2f",getDistance())); } }
题目分析:
该题只需注意按照类图写,注意变量的共有私有,方法的返回类型。
第二题:


源码:
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args){ Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); Double x1=in.nextDouble(); Double y1=in.nextDouble(); Double x2=in.nextDouble(); Double y2=in.nextDouble(); String color = in.next(); if (x1>0&&x1<=200&&y1>0&&y1<=200&&x2>0&&x2<=200&&y2>0&&y2<=200){ Point point1=new Point(x1,y1); Point point2=new Point(x2,y2); Line line1 = new Line(point1,point2,color); Plane plane1 = new Plane(color); Element element; Element p1 = (Element)point1; Element p2 = (Element)point2; Element line = (Element)line1; Element plane = (Element)plane1; element = p1;//起点Point element.display(); element = p2;//终点Point element.display(); element = line;//线段 element.display(); element = plane;//面 element.display(); } else { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } } } class Point extends Element { private double x,y; public Point(double x, double y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; } public double getX() { return x; } public void setX(double x) { this.x = x; } public double getY() { return y; } public void setY(double y) { this.y = y; } public void display(){ System.out.println("("+String.format("%.2f", x)+","+String.format("%.2f",y)+")"); } } class Line extends Element{ private Point point1; private Point point2; private String color; public Line() { } public Line(Point point1, Point point2, String color) { this.point1 = point1; this.point2 = point2; this.color = color; } public Point getPoint1() { return point1; } public void setPoint1(Point point1) { this.point1 = point1; } public Point getPoint2() { return point2; } public void setPoint2(Point point2) { this.point2 = point2; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; } public Double getDistance(){ double l = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(point1.getX()- point2.getX(),2)+Math.pow(point1.getY()- point2.getY(),2)); return l; } @Override public void display(){ System.out.println("The line's color is:"+color); System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:"); point1.display(); System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:"); point2.display(); System.out.print("The line's length is:"); System.out.println( String.format("%.2f",getDistance())); } } class Plane extends Element { private String color; public Plane() { } public Plane(String color) { this.color = color; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; } @Override public void display() { System.out.println("The Plane's color is:"+color); } } abstract class Element{ public void Display(){ ; } public abstract void display(); }
题目分析:
该题需根据类图来设计类之间的关系,在调用display方法时,要使用向上造型将子类的对象当成父类的对象然后再调用。
第三题:

源码:
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args){ Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); Double x1; Double y1; Double x2; Double y2; int index; int i; int choice = in.nextInt(); String color ; GeometryObject<Element> geometryObject = new GeometryObject<>(); while (choice!=0) { switch (choice) { case 1://insert Point object into list x1 = in.nextDouble(); y1 = in.nextDouble(); if (x1 <= 0 || x1 > 200 || y1 <= 0 || y1 > 200) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } else { Point point1 = new Point(x1, y1); geometryObject.add(point1); } break; case 2://insert Line object into list x1 = in.nextDouble(); y1 = in.nextDouble(); x2 = in.nextDouble(); y2 = in.nextDouble(); color = in.next(); if (x1 <= 0 || x1 > 200 || y1 <= 0 || y1 > 200 || x2 <= 0 || x2 > 200 || y2 <= 0 || y2 > 200) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } else { Point point1 = new Point(x1, y1); Point point2 = new Point(x2, y2); Line line = new Line(point1, point2, color); geometryObject.add(line); } break; case 3://insert Plane object into list color = in.next(); Plane plane = new Plane(color); geometryObject.add(plane); break; case 4://delete index - 1 object from list index = in.nextInt(); if (index >=1&&index<=geometryObject.getList().size()) { geometryObject.remove(index - 1); } } choice = in.nextInt(); } for (i=0;i<=geometryObject.getList().size()-1;i++){ geometryObject.getList().get(i).display(); } } } class Point extends Element { private double x,y; public Point(double x, double y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; } public double getX() { return x; } public void setX(double x) { this.x = x; } public double getY() { return y; } public void setY(double y) { this.y = y; } public void display(){ System.out.println("("+String.format("%.2f", x)+","+String.format("%.2f",y)+")"); } } class Line extends Element{ private Point point1; private Point point2; private String color; public Line() { } public Line(Point point1, Point point2, String color) { this.point1 = point1; this.point2 = point2; this.color = color; } public Point getPoint1() { return point1; } public void setPoint1(Point point1) { this.point1 = point1; } public Point getPoint2() { return point2; } public void setPoint2(Point point2) { this.point2 = point2; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; } public Double getDistance(){ double l = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(point1.getX()- point2.getX(),2)+Math.pow(point1.getY()- point2.getY(),2)); return l; } @Override public void display(){ System.out.println("The line's color is:"+color); System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:"); point1.display(); System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:"); point2.display(); System.out.print("The line's length is:"); System.out.println( String.format("%.2f",getDistance())); } } class Plane extends Element { private String color; public Plane() { } public Plane(String color) { this.color = color; } public String getColor() { return color; } public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; } @Override public void display() { System.out.println("The Plane's color is:"+color); } } abstract class Element{ public abstract void display(); } class GeometryObject<E>{ private ArrayList<Element> list = new ArrayList<>(); public GeometryObject() { } public void add(Element element){ list.add(element); } public void remove(int index){ list.remove(index); } public ArrayList<Element> getList() { return list; } }
题目分析:
与第二题相比,第三题首先多了一个父类,点,线,面类从父类中继承了并重写了Display方法。新创建了一个泛型容器,类型只能是父类Element,只有这样才能向容器添加子类对象。
总结:
1.使用函数可以达到事倍功半的方法,比如判断两个线段是否相交,调用line方法比使用叉乘判断更加简便。
2.解决问题需要一定的数学知识和运用的数学能力,图形类设计题涉及了大量解析几何的数学知识,运用不熟练会导致很多地方出错。
3.在特定情况下使用继承和多态可以在简化代码的同时,提高代码的复用性。
------------恢复内容结束------------




