使用WebApi和Asp.Net Core Identity 认证 Blazor WebAssembly(Blazor客户端应用)
原文:https://chrissainty.com/securing-your-blazor-apps-authentication-with-clientside-blazor-using-webapi-aspnet-core-identity/
由于Blazor框架已经有所更新,翻译中有些内容我根据实际情况做了更改。
设置:创建解决方案
选择Blazor应用
项目名称
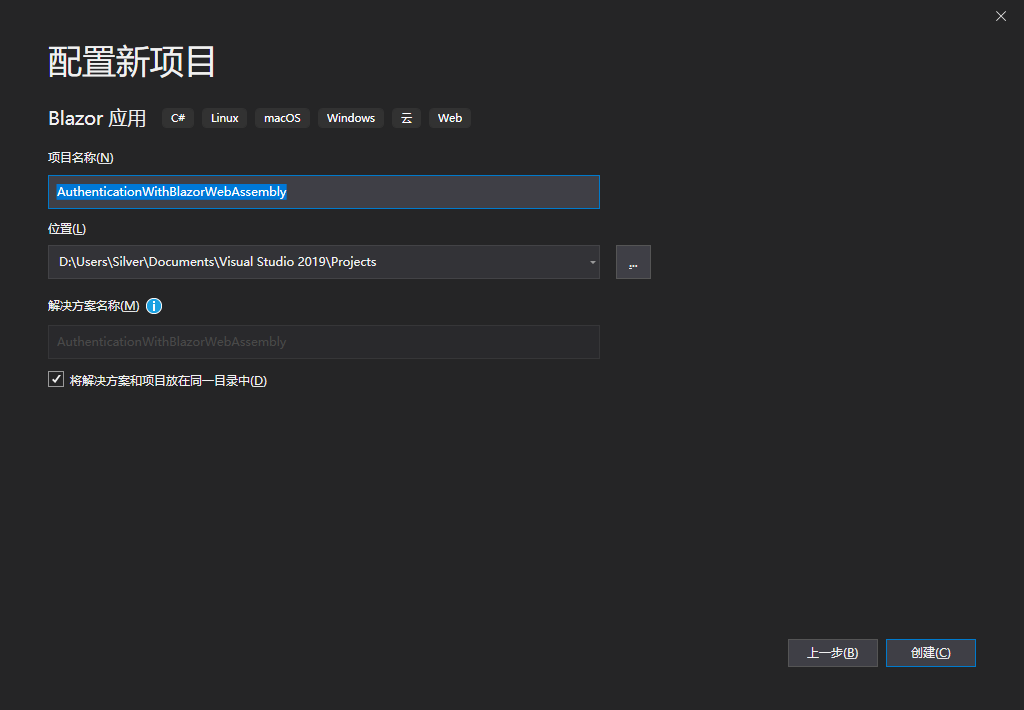
选择Blazor WebAssembly App(这里要勾选Asp.Net Core Host),如果找不到Blazor WebAssembly App,请先在命令行执行以下命令:
dotnet new -i Microsoft.AspNetCore.Blazor.Templates::3.1.0-preview1.19508.20
解决方案创建之后,我们将开始对AuthenticationWithBlazorWebAssembly.Server这个项目进行一些更改。
配置WebAPI
在配置WebAPI之前我先安装一些NuGet包:
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.JwtBearer" Version="3.0.0" /> <PackageReference Include="Microsoft.AspNetCore.Blazor.Server" Version="3.0.0-preview9.19465.2" /> <PackageReference Include="Microsoft.AspNetCore.Diagnostics.EntityFrameworkCore" Version="3.0.0" /> <PackageReference Include="Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity.EntityFrameworkCore" Version="3.0.0" /> <PackageReference Include="Microsoft.AspNetCore.Identity.UI" Version="3.0.0" /> <PackageReference Include="Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer" Version="3.0.0" /> <PackageReference Include="Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools" Version="3.0.0"> <PackageReference Include="Microsoft.VisualStudio.Web.CodeGeneration.Design" Version="3.0.0" />
设置Identity数据库:连接字符串
在进行任何设置之前,数据库方面需要一个连接字符串。这通常是保存在appsettings.json中的,但Blazor托管模版并未提供此文件,所以我们需要手动添加此文件。
在AuthenticationWithBlazorWebAssembly.Server项目右键添加 -> 新建项,然后选择应用设置文件。
{ "ConnectionStrings": { "DefaultConnection": "Server=(localdb)\\MSSQLLocalDB;Database=AuthenticationWithBlazorWebAssembly;Trusted_Connection=True;MultipleActiveResultSets=true" } }
该文件带有一个已经设置好的连接字符串,你可以随时将其指向需要的地方。我们只需要添加一个数据库名就可以了,其余的保持默认值。
设置Identity数据库:DbContext
在AuthenticationWithBlazorWebAssembly.Server项目跟目录创建一个名为Data的目录,然后使用下面代码添加一个名为ApplicationDbContext的类文件。
public class ApplicationDbContext : IdentityDbContext { public ApplicationDbContext(DbContextOptions options) : base(options) { } }
因为我们使用Identity需要将信息存储在数据库中,所以我们不是从DbContext继承,而是从IdentityDbContext继承。IdentityDbContext基类包含EF配置管理Identity数据库表需要的所有配置。
设置Identity数据库:注册服务
在Startup类中,我们需要添加一个构造函数,接收IConfiguration参数和一个属性来存储它。IConfiguration允许我们访问appsettings.json文件,如:连接字符串。
public IConfiguration Configuration { get; } public Startup(IConfiguration configuration) { Configuration = configuration; }
接下来我们将以下代码添加到ConfigureServices方法的顶部。
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) { services.AddDbContext<ApplicationDbContext>(options => options.UseSqlServer(Configuration.GetConnectionString("DefaultConnection"))); services.AddDefaultIdentity<IdentityUser>() .AddEntityFrameworkStores<ApplicationDbContext>(); //这里省略掉其他代码 }
这里两行代码将ApplicationDbContext添加到服务集合中。然后为ASP.NET Core Identity注册各种服务并通过ApplicationDbContext使用Entity Framework作为数据存储。
设置Identity数据库:创建数据库
现在可以为数据库创建初始迁移。在程序包管理器控制台运行以下命令。
Add-Migration CreateIdentitySchema -o Data/Migations
命令运行完成,你应该能在Data > Migrations文件夹中看到迁移文件。在控制台中运行命令Update-Database将迁移应用到数据库。
在运行迁移命令时遇到任何问题,请确保在程序包管理器中选择AuthenticationWithBlazorWebAssembly.Server项目作为默认项目。
启用身份验证:注册服务
接下来在API中启用身份验证。同样,在ConfigureServices中,在上一节添加的代码之后添加以下代码。
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) { //这里省略到其他代码 services.AddAuthentication(JwtBearerDefaults.AuthenticationScheme) .AddJwtBearer(options => { options.TokenValidationParameters = new TokenValidationParameters { ValidateIssuer = true, ValidateAudience = true, ValidateLifetime = true, ValidateIssuerSigningKey = true, ValidIssuer = Configuration["JwtIssuer"], ValidAudience = Configuration["JwtAudience"], IssuerSigningKey = new SymmetricSecurityKey(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(Configuration["JwtSecurityKey"])) }; });
//这里省略掉其他代码
}
上面代码想服务容器添加和设置一些身份验证所需的服务。然后为JSON Web Tokens(JWT)添加处理程序,并配置接收到的JWTs应该如何验证。你可以根据需求调整这些设置。
启用身份验证:应用程序设置
有一些设置要从appsettings.json文件中加载。
Configuration["JwtIssuer"]Configuration["JwtAudience"]Configuration["JwtSecurityKey"]
我们还未将它们添加到appsettings文件中。现在添加它们并添加一个设置用来控制令牌的持续时间,稍后我们会使用这个设置。
"JwtSecurityKey": "RANDOM_KEY_MUST_NOT_BE_SHARED", "JwtIssuer": "https://localhost", "JwtAudience": "https://localhost", "JwtExpiryInDays": 1,
保证JwtSecurityKey 的安全是非常重要的,因为这是用来对API产生的令牌签名的,如果泄露那么你的应用程序将不在安全。
由于我们在本地运行所有内容,所以我将Issuer和Audience设置为localhost。如果在生产环境使用它,我们需要将Issuer 设置为API运行的域名,将Audience设置为客户端应用程序运行的域名。
启用身份验证:添加中间件
最后,我们需要在Configure 方法中将必要的中间件添加到管道中。这将在API中启用身份验证和授权功能。将以下代码添加到app.UseEndpoints中间件前面。
app.UseAuthentication();
app.UseAuthorization();
这就是Startup类所需要的所有东西。现在API已经启用了身份验证。
你可以通过向WeatherForecastController中的Get方法添加[Authorize]属性来测试一切是否正常。然后启用应用程序并导航到Fetch Data页面,应该不会加载任何数据,应该会在控制台中看到401错误。
添加账户(account)控制器
为了让人们登录到我们的应用程序,他们需要能够注册。我们将添加一个帐户控制器,它将负责创建新帐户。
[Route("api/[controller]")] [ApiController] public class AccountsController : ControllerBase { //private static UserModel LoggedOutUser = new UserModel { IsAuthenticated = false }; private readonly UserManager<IdentityUser> _userManager; public AccountsController(UserManager<IdentityUser> userManager) { _userManager = userManager; } [HttpPost] public async Task<IActionResult> Post([FromBody]RegisterModel model) { var newUser = new IdentityUser { UserName = model.Email, Email = model.Email }; var result = await _userManager.CreateAsync(newUser, model.Password); if (!result.Succeeded) { var errors = result.Errors.Select(x => x.Description); return BadRequest(new RegisterResult { Successful = false, Errors = errors }); } return Ok(new RegisterResult { Successful = true }); } }
Post操作使用ASP.NET Core Identity从RegisterModel来创建系统的新用户。
我们还没用添加注册模型,现在使用以下代码添加到AuthenticationWithBlazorWebAssembly.Shared项目中,稍后我们的Blazor应用程序将会使用到它。
public class RegisterModel { [Required] [EmailAddress] [Display(Name = "Email")] public string Email { get; set; } [Required] [StringLength(100, ErrorMessage = "The {0} must be at least {2} and at max {1} characters long.", MinimumLength = 6)] [DataType(DataType.Password)] [Display(Name = "Password")] public string Password { get; set; } [DataType(DataType.Password)] [Display(Name = "Confirm password")] [Compare("Password", ErrorMessage = "The password and confirmation password do not match.")] public string ConfirmPassword { get; set; } }
如果一切顺利,则会返回一个成功的RegisterResult,否则会返回一个失败的RegisterResult,我们一样将它添加到AuthenticationWithBlazorWebAssembly.Shared项目中。
public class RegisterResult { public bool Successful { get; set; } public IEnumerable<string> Errors { get; set; } }
添加登录(login)控制器
现在我们有了用户注册的方式,我们还需要用户登录方式。
[Route("api/[controller]")] [ApiController] public class LoginController : ControllerBase { private readonly IConfiguration _configuration; private readonly SignInManager<IdentityUser> _signInManager; public LoginController(IConfiguration configuration, SignInManager<IdentityUser> signInManager) { _configuration = configuration; _signInManager = signInManager; } [HttpPost] public async Task<IActionResult> Login([FromBody] LoginModel login) { var result = await _signInManager.PasswordSignInAsync(login.Email, login.Password, false, false); if (!result.Succeeded) return BadRequest(new LoginResult { Successful = false, Error = "Username and password are invalid." }); var claims = new[] { new Claim(ClaimTypes.Name, login.Email) }; var key = new SymmetricSecurityKey(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(_configuration["JwtSecurityKey"])); var creds = new SigningCredentials(key, SecurityAlgorithms.HmacSha256); var expiry = DateTime.Now.AddDays(Convert.ToInt32(_configuration["JwtExpiryInDays"])); var token = new JwtSecurityToken( _configuration["JwtIssuer"], _configuration["JwtAudience"], claims, expires: expiry, signingCredentials: creds ); return Ok(new LoginResult { Successful = true, Token = new JwtSecurityTokenHandler().WriteToken(token) }); } }
登录控制器(login controller)使用ASP.NET Core Identity SignInManger验证用户名和密码。如果它们都正确,则生成一个新的JSON Web Token并在LoginResult返回给客户端。
像之前一样,我们需要将LoginModel和LoginResult添加到AuthenticationWithBlazorWebAssembly.Shared项目中。
public class LoginModel { [Required] public string Email { get; set; } [Required] public string Password { get; set; } public bool RememberMe { get; set; } }
public class LoginResult { public bool Successful { get; set; } public string Error { get; set; } public string Token { get; set; } }
这就是API需要的所有东西。我们现在已经将其配置为通过JSON web tokens进行身份验证。接下来我们需要为Blazor WebAssembly(客户端)应用程序添加注册新用户和登录控制器。
配置Blazor客户端
接下来我们关注Blazor。首先需要安装Blazored.LocalStorage,我们稍后将需要它在登录时从API中持久化验证令牌。
我们还需要在App组件中使用AuthorizeRouteView组件替换RouteView组件(这里需要使用Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components.Authorization NuGet包并在_Imports.razor添加@using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components.Authorization)。
<Router AppAssembly="@typeof(Program).Assembly"> <Found Context="routeData"> <AuthorizeRouteView RouteData="@routeData" DefaultLayout="@typeof(MainLayout)" /> </Found> <NotFound> <LayoutView Layout="@typeof(MainLayout)"> <p>Sorry, there's nothing at this address.</p> </LayoutView> </NotFound> </Router>
此组件提供类型为Task<AuthenticationState>的级联参数。AuthorizeView通过使用它来确定当前用户的身份验证状态。
但是任何组件都可以请求参数并使用它来执行过程逻辑,例如:
@page "/" <button @onclick="@LogUsername">Log username</button> @code { [CascadingParameter] private Task<AuthenticationState> authenticationStateTask { get; set; } private async Task LogUsername() { var authState = await authenticationStateTask; var user = authState.User; if (user.Identity.IsAuthenticated) { Console.WriteLine($"{user.Identity.Name} is authenticated."); } else { Console.WriteLine("The user is NOT authenticated."); } } }
创建自定义AuthenticationStateProvider
因为我们使用Blazor WebAssembly,所以我们需要为AuthenticationStateProvider提供自定义实现。因为在客户端应用程序有太多的选项,所以无法设计一个适用于所有人的默认类。
我们需要重写GetAuthenticationStateAsync方法。在此方法中,我们需要确定当前用户是否经过身份验证。我们还将添加两个辅助方法,当用户登录或注销时,我们将使用这些方法更新身份验证状态。
public class ApiAuthenticationStateProvider : AuthenticationStateProvider { private readonly HttpClient _httpClient; private readonly ILocalStorageService _localStorage; public ApiAuthenticationStateProvider(HttpClient httpClient, ILocalStorageService localStorage) { _httpClient = httpClient; _localStorage = localStorage; } public override async Task<AuthenticationState> GetAuthenticationStateAsync() { var savedToken = await _localStorage.GetItemAsync<string>("authToken"); if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(savedToken)) { return new AuthenticationState(new ClaimsPrincipal(new ClaimsIdentity())); } _httpClient.DefaultRequestHeaders.Authorization = new AuthenticationHeaderValue("bearer", savedToken); return new AuthenticationState(new ClaimsPrincipal(new ClaimsIdentity(ParseClaimsFromJwt(savedToken), "jwt"))); } public void MarkUserAsAuthenticated(string token) { var authenticatedUser = new ClaimsPrincipal(new ClaimsIdentity(ParseClaimsFromJwt(token), "jwt")); var authState = Task.FromResult(new AuthenticationState(authenticatedUser)); NotifyAuthenticationStateChanged(authState); } public void MarkUserAsLoggedOut() { var anonymousUser = new ClaimsPrincipal(new ClaimsIdentity()); var authState = Task.FromResult(new AuthenticationState(anonymousUser)); NotifyAuthenticationStateChanged(authState); } private IEnumerable<Claim> ParseClaimsFromJwt(string jwt) { var claims = new List<Claim>(); var payload = jwt.Split('.')[1]; var jsonBytes = ParseBase64WithoutPadding(payload); var keyValuePairs = JsonSerializer.Deserialize<Dictionary<string, object>>(jsonBytes); keyValuePairs.TryGetValue(ClaimTypes.Role, out object roles); if (roles != null) { if (roles.ToString().Trim().StartsWith("[")) { var parsedRoles = JsonSerializer.Deserialize<string[]>(roles.ToString()); foreach (var parsedRole in parsedRoles) { claims.Add(new Claim(ClaimTypes.Role, parsedRole)); } } else { claims.Add(new Claim(ClaimTypes.Role, roles.ToString())); } keyValuePairs.Remove(ClaimTypes.Role); } claims.AddRange(keyValuePairs.Select(kvp => new Claim(kvp.Key, kvp.Value.ToString()))); return claims; } private byte[] ParseBase64WithoutPadding(string base64) { switch (base64.Length % 4) { case 2: base64 += "=="; break; case 3: base64 += "="; break; } return Convert.FromBase64String(base64); } }
这里有很多代码,让我们一步一步来分析。
CascadingAuthenticationState组件调用GetAuthenticationStateAsync方法来确定当前用户是否经过验证。
上面的代码,我们检查local storge是否有验证令牌。如果local storge中没有令牌,那么我们将返回一个新的AuthenticationState,其中包含一个空的ClaimsPrincipal。这就说明当前用户用户没有经过身份验证。
如果有令牌,读取并设置HttpClient的默认Authorization Header,并返回一个包含ClaimsPrincipal新的AuthenticationState的令牌声明。该声明(Claims)使用ParseClaimsFromJwt方法从令牌中提取。此方法解码令牌并返回其中包含的声明。
MarkUserAsAuthenticated辅助方法用于登录时调用NotifyAuthenticationStateChanged方法,该方法触发AuthenticationStateChanged事件。这将通过CascadingAuthenticationState组件级联新的身份验证状态。
MarkUserAsLoggedOut用于用户注销时。
Auth Service
Auth Service将在组件中注册用户并登录到应用程序和用户注销使用。
public class AuthService : IAuthService { private readonly HttpClient _httpClient; private readonly AuthenticationStateProvider _authenticationStateProvider; private readonly ILocalStorageService _localStorage; public AuthService(HttpClient httpClient, AuthenticationStateProvider authenticationStateProvider, ILocalStorageService localStorage) { _httpClient = httpClient; _authenticationStateProvider = authenticationStateProvider; _localStorage = localStorage; } public async Task<RegisterResult> Register(RegisterModel registerModel) { var result = await _httpClient.PostJsonAsync<RegisterResult>("api/accounts", registerModel); return result; } public async Task<LoginResult> Login(LoginModel loginModel) { var loginAsJson = JsonSerializer.Serialize(loginModel); var response = await _httpClient.PostAsync("api/Login", new StringContent(loginAsJson, Encoding.UTF8, "application/json")); var loginResult = JsonSerializer.Deserialize<LoginResult>(await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync(), new JsonSerializerOptions { PropertyNameCaseInsensitive = true }); if (!response.IsSuccessStatusCode) { return loginResult; } await _localStorage.SetItemAsync("authToken", loginResult.Token); ((ApiAuthenticationStateProvider)_authenticationStateProvider).MarkUserAsAuthenticated(loginResult.Token); _httpClient.DefaultRequestHeaders.Authorization = new AuthenticationHeaderValue("bearer", loginResult.Token); return loginResult; } public async Task Logout() { await _localStorage.RemoveItemAsync("authToken"); ((ApiAuthenticationStateProvider)_authenticationStateProvider).MarkUserAsLoggedOut(); _httpClient.DefaultRequestHeaders.Authorization = null; } }
Register方法提交registerModel给accounts controller并返回RegisterResult给调用者。
Login 方法类似于Register 方法,它将LoginModel 发送给login controller。但是,当返回一个成功的结果时,它将返回一个授权令牌并持久化到local storge。
最后我们调用ApiAuthenticationStateProvider上的方法MarkUserAsAuthenticated ,设置HttpClient的默认authorization header。
Logout 这个方法就是执行与Login 方法相反的操作。
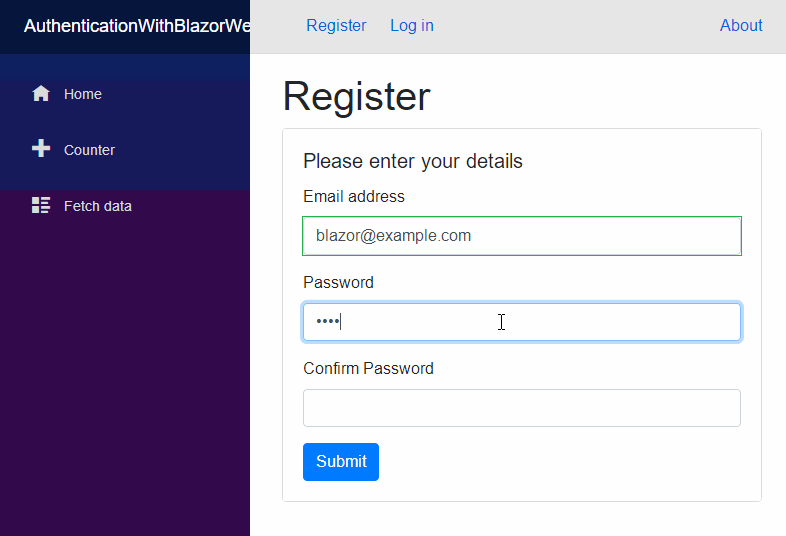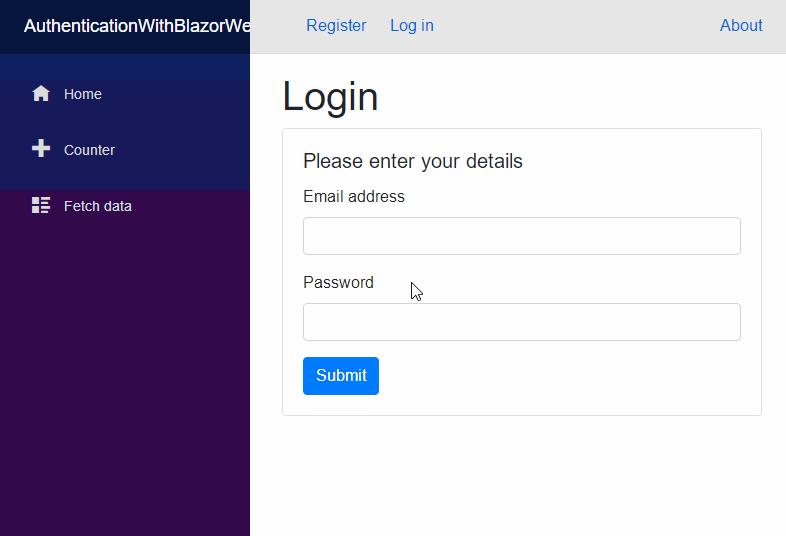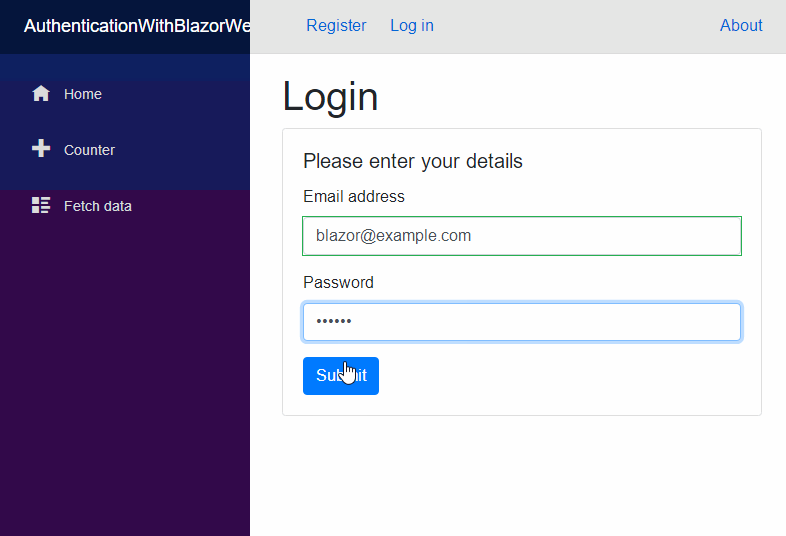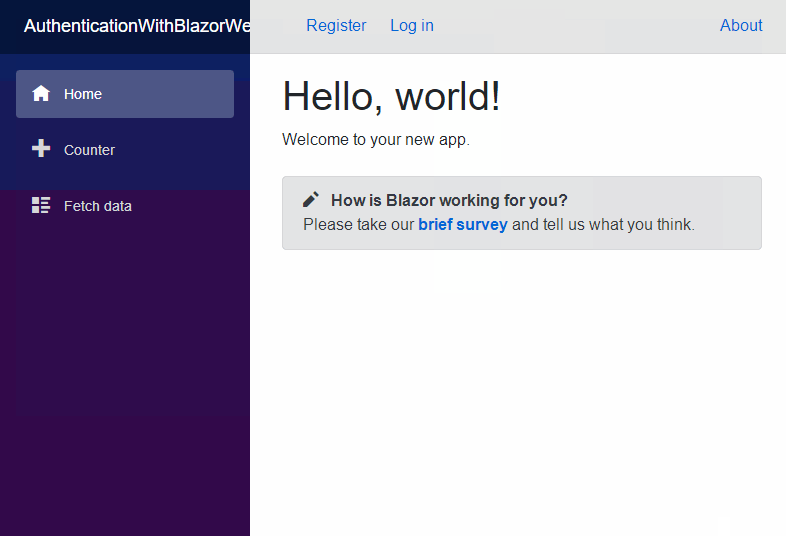
注册组件(Register Component)
我们已经到了最后阶段了。现在我们可以将注意力转向UI,并创建一个允许人们在站点注册的组件。
@page "/register" @inject IAuthService AuthService @inject NavigationManager NavigationManager <h1>Register</h1> @if (ShowErrors) { <div class="alert alert-danger" role="alert"> @foreach (var error in Errors) { <p>@error</p> } </div> } <div class="card"> <div class="card-body"> <h5 class="card-title">Please enter your details</h5> <EditForm Model="RegisterModel" OnValidSubmit="HandleRegistration"> <DataAnnotationsValidator /> <ValidationSummary /> <div class="form-group"> <label for="email">Email address</label> <InputText Id="email" class="form-control" @bind-Value="RegisterModel.Email" /> <ValidationMessage For="@(() => RegisterModel.Email)" /> </div> <div class="form-group"> <label for="password">Password</label> <InputText Id="password" type="password" class="form-control" @bind-Value="RegisterModel.Password" /> <ValidationMessage For="@(() => RegisterModel.Password)" /> </div> <div class="form-group"> <label for="confirmpassword">Confirm Password</label> <InputText Id="confirmpassword" type="password" class="form-control" @bind-Value="RegisterModel.ConfirmPassword" /> <ValidationMessage For="@(() => RegisterModel.ConfirmPassword)" /> </div> <button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Submit</button> </EditForm> </div> </div> @code { private RegisterModel RegisterModel = new RegisterModel(); private bool ShowErrors; private IEnumerable<string> Errors; private async Task HandleRegistration() { ShowErrors = false; var result = await AuthService.Register(RegisterModel); if (result.Successful) { NavigationManager.NavigateTo("/login"); } else { Errors = result.Errors; ShowErrors = true; } } }
注册组件包含一个表单让用户输入他们的电子邮件和密码。提交表单时,会调用AuthService 的方法Register 。如果注册成功那么用户会被导航到登录页,否则,会将错误显示给用户。
登录组件(Login Component)
现在我们可以注册一个新的帐户,我们需要能够登录。登录组件将用于此。
@page "/login" @inject IAuthService AuthService @inject NavigationManager NavigationManager <h1>Login</h1> @if (ShowErrors) { <div class="alert alert-danger" role="alert"> <p>@Error</p> </div> } <div class="card"> <div class="card-body"> <h5 class="card-title">Please enter your details</h5> <EditForm Model="loginModel" OnValidSubmit="HandleLogin"> <DataAnnotationsValidator /> <ValidationSummary /> <div class="form-group"> <label for="email">Email address</label> <InputText Id="email" Class="form-control" @bind-Value="loginModel.Email" /> <ValidationMessage For="@(() => loginModel.Email)" /> </div> <div class="form-group"> <label for="password">Password</label> <InputText Id="password" type="password" Class="form-control" @bind-Value="loginModel.Password" /> <ValidationMessage For="@(() => loginModel.Password)" /> </div> <button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Submit</button> </EditForm> </div> </div> @code { private LoginModel loginModel = new LoginModel(); private bool ShowErrors; private string Error = ""; private async Task HandleLogin() { ShowErrors = false; var result = await AuthService.Login(loginModel); if (result.Successful) { NavigationManager.NavigateTo("/"); } else { Error = result.Error; ShowErrors = true; } } }
与注册组件类似的设计,我们也提供一个表单用于用户输入电子邮件和密码。表单提交时,将调用AuthService的方法Login。如果登录成功,用户将被重定向到主页,否则将显示错误消息。
注销组件(Logout Component)
我们现在可以注册和登录,但我们也需要注销的功能。我用了一个页面组件来做这个,但是你也可以通过点击某个地方的按钮来实现。
@page "/logout" @inject IAuthService AuthService @inject NavigationManager NavigationManager @code { protected override async Task OnInitializedAsync() { await AuthService.Logout(); NavigationManager.NavigateTo("/"); } }
这个组件没有用户界面,当用户导航到它时,将调用AuthService上的方法Logout,然后将用户重定向回主页。
添加一个LoginDisplay组件并更新MainLayout组件
最后的任务是添加一个LoginDisplay组件并更新MainLayout 组件。
LoginDisplay 组件与Blazor Server模版一样,如果未经验证,它将显示登录与注册链接,否则显示电子邮件和注销链接。
<AuthorizeView>
<Authorized>
Hello, @context.User.Identity.Name!
<a href="/logout">Log out</a>
</Authorized>
<NotAuthorized>
<a href="/register">Register</a>
<a href="/login">Log in</a>
</NotAuthorized>
</AuthorizeView>
我们现在只需要更新MainLayout组件。
@inherits LayoutComponentBase <div class="sidebar"> <NavMenu /> </div> <div class="main"> <div class="top-row px-4"> <LoginDisplay /> <a href="http://blazor.net" target="_blank" class="ml-md-auto">About</a> </div> <div class="content px-4"> @Body </div> </div>
注册服务(Registering Services)
最后在Startup类中注册服务。
services.AddBlazoredLocalStorage(); services.AddAuthorizationCore(); services.AddScoped<AuthenticationStateProvider, ApiAuthenticationStateProvider>(); services.AddScoped<IAuthService, AuthService>();
如果一切都按计划进行,那么你应该得到这样的结果。
总结
这篇文章展示了如何WebAPI和ASP.NET Core Identity创建一个带有身份验证的Blazor WebAssembly(Blazor客户端)应用程序。
展示WebAPI如何处理和签发令牌(JSON web tokens)。以及如何设置各种控制器操作来为客户端应用程序提供服务。最后,展示如何配置Blazor来使用API和它签发的令牌来设置应用的身份验证状态。
最后也提供我学习本文跟随作者所写的源码(GITHUB)。




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 记一次 .NET某云HIS系统 CPU爆高分析
· 如果单表数据量大,只能考虑分库分表吗?
· 一文彻底搞懂 MCP:AI 大模型的标准化工具箱
· 电商平台中订单未支付过期如何实现自动关单?
· 用 .NET NativeAOT 构建完全 distroless 的静态链接应用
· 精选 4 款免费且实用的数据库管理工具,程序员必备!
· Cursor:一个让程序员“失业”的AI代码搭子
· MCP开发应用,使用python部署sse模式
· 重生之我是操作系统(七)----内存管理(上)
· 【杭电多校比赛记录】2025“钉耙编程”中国大学生算法设计春季联赛(6)