scrapy genspider -t crawl --小例子
1.目标
利用链接提取器爬取目标网站简单信息
2.代码
read.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from scrapy.linkextractors import LinkExtractor
from scrapy.spiders import CrawlSpider, Rule
from ..items import ReadbookItem
'''
scrapy genspider -t crawl read www.XXXXX.com
但是这样子我ignore第一页的content,
原因是起始页不正确:false(1107_1.html)true(1107_1.html)
'''
class ReadSpider(CrawlSpider):
name = 'read'
allowed_domains = ['www.dushu.com']
start_urls = ['https://www.dushu.com/book/1107_1.html']
rules = (
Rule(LinkExtractor(allow=r'/book/1107_\d+.html'),
callback='parse_item',
follow=True),
)
def parse_item(self, response):
# 这个结构可以用item+yield代替
# i = {}
# #i['domain_id'] = response.xpath('//input[@id="sid"]/@value').extract()
# #i['name'] = response.xpath('//div[@id="name"]').extract()
# #i['description'] = response.xpath('//div[@id="description"]').extract()
# return i
res = response
img_list = res.xpath('//div[@class="book-info"]//img')
for img in img_list:
# 这里图片用了js懒加载,故而解析data-original
# meanwhile 使用了防盗链,403,没有权限拒加载图片,
# 这个网站直接修改user-agent,或者修改默认请求头,即可解决,
# 他没有校验referer,判断你是否从上一页跳转过来的
pictrue = img.xpath('./@data-original').extract_first()
title = img.xpath('./@alt').extract_first()
#
# print(pictrue)
# print(title)
item = ReadbookItem()
item['title'] = title
item['pictrue'] = pictrue
yield item

pipeline.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Define your item pipelines here
#
# Don't forget to add your pipeline to the ITEM_PIPELINES setting
# See: http://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html
class ReadbookPipeline(object):
def open_spider(self,spider):
self.fp = open('info.json','w+',encoding='utf-8')
def process_item(self, item, spider):
self.fp.write(str(item) )
return item
def close_spider(self , spider):
self.fp.close()
items.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Define here the models for your scraped items
#
# See documentation in:
# http://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/items.html
import scrapy
class ReadbookItem(scrapy.Item):
# define the fields for your item here like:
# name = scrapy.Field()
title = scrapy.Field()
pictrue = scrapy.Field()
3.扩展
follow 是一个布尔(boolean)值,指定了根据该规则从response提取的链接是否需要跟进。 如果callback 为None,follow 默认设置为 True ,添加回调函数callback后为 False,不跟踪
一句话解释:follow可以理解为回调自己的回调函数
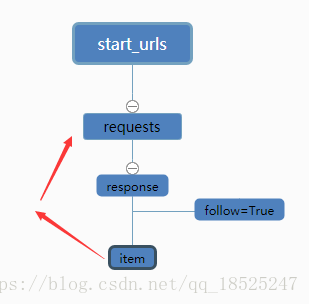
举个例子,如百度百科,从任意一个词条入手,抓取词条中的超链接来跳转,rule会对超链接发起requests请求,如follow为True,scrapy会在返回的response中验证是否还有符合规则的条目,继续跳转发起请求抓取,周而复始,如下图
- 遍历所有的Rule对象, 并使用其link_extractor属性提取链接
- 对于提取到的链接, 我们把它加入到一个集合中
- 使用链接发送一个请求, 并且callback的最终结果是self._parse_response
- 同时在你可以在规则提取里添加多个提取规则作用于下一级URL提取
-
rules = ( Rule(LinkExtractor(allow=r'/book/1107_\d+.html'), callback='parse_item', follow=True), Rule(LinkExtractor(allow=r'XXXXXX'), callback='parse_item', follow=True), Rule(LinkExtractor(allow=r'XXXXX'), callback='parse_item', follow=True), )然后在回调函数里还可以配合scrapy.Request()使用来提取详细信息
上述操作表明, 当我们follow一个链接时, 我们其实是用rules把这个链接返回的response再提取一遍.
所以要注意read.py里的follow的布尔值。
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_18525247/article/details/82743614,https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/25650763



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号