搜索
在学习的同时也要做一些以前学过的知识,以往打搜索的时候遇到从一个地方到另一个地方瞬间开方向数组来搜索最小路,可多做几道搜索的时候发现dfs寻找最小方法的局限性很小很小,所以今天这篇博客来提醒自己不要单纯就开方向数组来统计一些最小值。

这道题很显然是道搜索于是开始了dfs结果200+行代码下来还没打完,想想不对搜索的策略有问题我总是在加一加一的加,于是百度了一下发现题解给的是如果哪个键管用直接两个键数相减,通过中间的某个值来选取最小值思想很巧妙,这点值得深思。

#include<iostream> #include<cmath> #include<cstring> #include<string> #include<ctime> #include<cstdio> #include<algorithm> #include<map> #include<vector> #include<stack> #include<queue> #include<iomanip> using namespace std; inline int read() { int x=0,f=1;char ch=getchar(); while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')f=-1;ch=getchar();} while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){x=x*10+ch-'0';ch=getchar();} return x*f; } int a[20]; int n,m; const int maxn=10000000; int ans=maxn; int fast(int x,int y) { if(x==y) return 0; if(y/10==0) { if(a[y]==1) return 1; else return maxn; } else { if(a[y%10]==1&&a[y/10]==1&&a[10]==1) { return 3; } else return maxn; } } int slow(int x,int y) { int b=maxn,w=maxn; if(x==y) return 0; if(a[11]==1) { if(y<x)b=100-x+y; else b=y-x; } if(a[12]==1) { if(y<x)w=x-y; else w=x+100-y; } return min(b,w); } int main() { freopen("1.in","r",stdin); a[1]=read();a[2]=read();a[3]=read();a[11]=read(); a[4]=read();a[5]=read();a[6]=read();a[12]=read(); a[7]=read();a[8]=read();a[9]=read();a[10]=read(); a[0]=read(); n=read();m=read(); for(int i=0;i<=99;i++) { ans=min(ans,fast(n,i)+slow(i,m)); } if(ans<maxn)printf("%d\n",ans); else printf("-1\n"); return 0; }
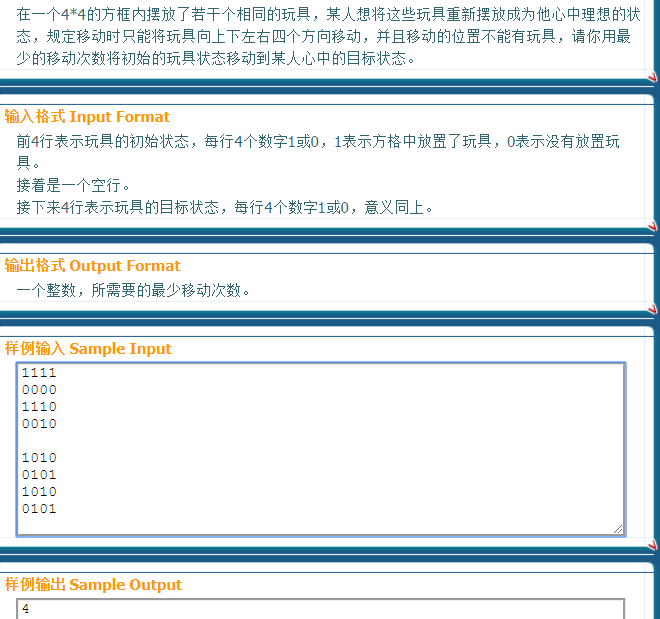
这道题很简单的一道搜索,却被我的方向数组给毁了,原始想法是每个点都找到离自己最近的点找到离自己最近的点后自己和找到的那个点同时消失来进行下个点的寻找,结果80分被打脸辛辛苦苦200+行代码不管用,心酸,看学长的代码发现自己的代码有很大的漏洞,这点一定要注意,学长采取的是曼哈顿距离这样可以把所有情况都搜出来这不就是搜索的本质么,100行不到就a掉了,搜索也很不好打的!搜索的方式一定要在做题之前想好,这样才能快速高效,搜索方式不对不但代码繁杂而且效率极低,50分就很不错了对于一些非模板题的搜索还是需要认真思考搜索的方式。
这是代码。

#include<iostream> #include<iostream> #include<cstring> #include<string> #include<cmath> #include<ctime> #include<cstdio> #include<iomanip> #include<algorithm> #include<vector> #include<stack> #include<queue> #include<map> using namespace std; inline int read() { int x=0,f=1;char ch=getchar(); while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')f=-1;ch=getchar();} while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){x=x*10+ch-'0';ch=getchar();} return x*f; } int a[10][10],b[10][10]; char ch; int vis[1000]; int ans=2000,len=0,len1=0; struct bwy { int x,y; }; bwy t[100],t1[110]; void dfs(int u,int sum) { if(u==len+1){ans=min(ans,sum);return;} for(int i=1;i<=len;i++) { if(vis[i]==1) continue; sum+=abs(t[u].x-t1[i].x)+abs(t[u].y-t1[i].y); vis[i]=1; dfs(u+1,sum); vis[i]=0; sum-=abs(t[u].x-t1[i].x)+abs(t[u].y-t1[i].y); } } int main() { //freopen("1.in","r",stdin); for(int i=1;i<=4;i++) for(int j=1;j<=4;j++) { cin>>ch; if(ch=='1') a[i][j]=1; } for(int i=1;i<=4;i++) for(int j=1;j<=4;j++) { cin>>ch; if(ch=='1') b[i][j]=1; } for(int i=1;i<=4;i++) for(int j=1;j<=4;j++) { if(a[i][j]==b[i][j]) { if(a[i][j]==1) a[i][j]=0,b[i][j]=0; } } for(int i=1;i<=4;i++) for(int j=1;j<=4;j++) { if(a[i][j]==1) { t[++len].x=i; t[len].y=j; } if(b[i][j]==1) { t1[++len1].x=i; t1[len1].y=j; } } dfs(1,0); printf("%d",ans); return 0; }
多情自古空余恨,道是无晴却有晴。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号