CompletableFuture处理任务
日常开发中,我们都会用到线程池,一般会用execute()和submit()方法提交任务。但是当你用过CompletableFuture之后,就会发现以前的线程池处理任务有多难用,功能有多简陋,CompletableFuture又是多么简洁优雅。
1. 使用线程池处理任务
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; import java.util.concurrent.*; /** * 功能描述 * * @author ASUS * @version 1.0 * @Date 2022/9/12 */ public class TheatDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { handleTastByTheatPool(); handleTastByTheatPool2(); } // 1 使用线程池处理任务 public static void handleTastByTheatPool() { // 1. 创建线程池 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3); List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3); List<Future<String>> futures = new ArrayList<>(); for (Integer key : list) { // 2. 提交任务 Future<String> future = executorService.submit(() -> { // 睡眠一秒,模仿处理过程 Thread.sleep(1000L); return "结果" + key; }); futures.add(future); } // 3. 获取结果 for (Future<String> future : futures) { try { String result = future.get(); System.out.println(result); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } executorService.shutdown(); } // 2 使用线程池处理任务 public static void handleTastByTheatPool2() { /** * int corePoolSize, * int maximumPoolSize, * long keepAliveTime, * TimeUnit unit, * BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, * ThreadFactory threadFactory, * RejectedExecutionHandler handler */ // 1. 创建线程池 int cpuCore = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors(); ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(cpuCore * 2, cpuCore * 200, 60000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(200)); List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3); List<Future<String>> futures = new ArrayList<>(); for (Integer key : list) { // 2. 提交任务 Future<String> future = threadPoolExecutor.submit(() -> { // 睡眠二秒,模仿处理过程 Thread.sleep(2000L); return "结果" + key; }); futures.add(future); } // 3. 获取结果 for (Future<String> future : futures) { try { String result = future.get(); System.out.println("Future:" + result); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } threadPoolExecutor.shutdown(); } }
输出结果:
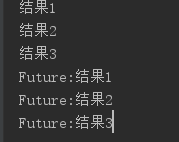
一般大家都会这样使用线程池,但是有没有思考过这样使用有没有什么问题?
反正我发现两个比较严重的问题:
- 获取结果时,调用的future.get()方法,会阻塞当前线程,直到返回结果,大大降低性能
- 有一半的代码在写怎么使用线程,其实我们不应该关心怎么使用线程,更应该关注任务的处理
2. 使用CompletableFuture重构任务处理
// 2. 使用CompletableFuture重构任务处理 public static void handleTaskByCompletableFuture() { // 1. 创建线程池 int cpuCore = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors(); ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(cpuCore * 2, cpuCore * 200, 50000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(200)); List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3); for (Integer key : list) { // 2. 提交任务 CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { // 睡眠一秒,模仿处理过程 try { Thread.sleep(1000L); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } return "结果" + key; }, threadPoolExecutor).whenCompleteAsync((result, exception) -> { // 3. 获取结果 System.out.println(result); }); } threadPoolExecutor.shutdown(); // 由于whenCompleteAsync获取结果的方法是异步的,所以要阻塞当前线程才能输出结果 try { Thread.sleep(2000L); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
输出结果:

代码中使用了CompletableFuture的两个方法,
supplyAsync()方法作用是提交异步任务,有两个传参,任务和自定义线程池。
whenCompleteAsync()方法作用是异步获取结果,也有两个传参,结果和异常信息。
代码经过CompletableFuture改造后,是多么的简洁优雅。
提交任务也不用再关心线程池是怎么使用了,获取结果也不用再阻塞当前线程了。
如果你比较倔强,还想同步获取结果,可以使用whenComplete()方法,或者单独调用join()方法。
join()方法配合Stream流是这样用的:
// 2. 使用CompletableFuture重构任务处理 public static void handleTaskByCompletableFuture2() { // 1. 创建线程池 int cpuCore = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors(); ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(cpuCore * 2, cpuCore * 200, 30000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(200)); // 2. 处理任务 List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3); List<String> results = list.stream().map(key -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { // 睡眠一秒,模仿处理过程 try { Thread.sleep(1000L); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } return "结果" + key; }, threadPoolExecutor)) .map(CompletableFuture::join).collect(Collectors.toList()); threadPoolExecutor.shutdown(); // 3. 获取结果 System.out.println(results); }
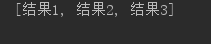
输出结果:
3. CompletableFuture更多妙用
3.1 等待所有任务执行完成
如果让你实现等待所有任务线程执行完成,再进行下一步操作,你会怎么做?
我猜你一定会使用 线程池+CountDownLatch,像下面这样:
/** * @author yideng * @apiNote 线程池和CountDownLatch使用示例 */ public class ThreadDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { // 1. 创建线程池 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3); List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3); CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(list.size()); for (Integer key : list) { // 2. 提交任务 executorService.execute(() -> { // 睡眠一秒,模仿处理过程 try { Thread.sleep(1000L); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } System.out.println("结果" + key); countDownLatch.countDown(); }); } executorService.shutdown(); // 3. 阻塞等待所有任务执行完成 try { countDownLatch.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } } }
Low不Low?十年前可以这样写,Java8都已经发布7年了,你还不会用Java8的写法?看一下使用CompletableFuture是怎么重构的:
/** * @author yideng * @apiNote CompletableFuture.allOf()方法使用示例 */ public class ThreadDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { // 1. 创建线程池 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3); List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3); // 2. 提交任务,并调用join()阻塞等待所有任务执行完成 CompletableFuture .allOf( list.stream().map(key -> CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> { // 睡眠一秒,模仿处理过程 try { Thread.sleep(1000L); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } System.out.println("结果" + key); }, executorService)) .toArray(CompletableFuture[]::new)) .join(); executorService.shutdown(); } }
代码看着有点乱,其实逻辑很清晰。
- 遍历list集合,提交CompletableFuture任务,把结果转换成数组
- 再把数组放到CompletableFuture的allOf()方法里面
- 最后调用join()方法阻塞等待所有任务执行完成
CompletableFuture的allOf()方法的作用就是,等待所有任务处理完成。
这样写是不是简洁优雅了许多?
3.2 任何一个任务处理完成就返回
如果要实现这样一个需求,往线程池提交一批任务,只要有其中一个任务处理完成就返回。
该怎么做?如果你手动实现这个逻辑的话,代码肯定复杂且低效,有了CompletableFuture就非常简单了,只需调用anyOf()方法就行了。
/** * @author yideng * @apiNote CompletableFuture.anyOf()方法使用示例 */ public class ThreadDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { // 1. 创建线程池 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3); List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3); long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 2. 提交任务 CompletableFuture<Object> completableFuture = CompletableFuture .anyOf( list.stream().map(key -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { // 睡眠一秒,模仿处理过程 try { Thread.sleep(1000L); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } return "结果" + key; }, executorService)) .toArray(CompletableFuture[]::new)); executorService.shutdown(); // 3. 获取结果 System.out.println(completableFuture.join()); } }
3.3 一个线程执行完成,交给另一个线程接着执行
有这么一个需求:
一个线程处理完成,把处理的结果交给另一个线程继续处理,怎么实现?
你是不是想到了一堆工具,线程池、CountDownLatch、Semaphore、ReentrantLock、Synchronized,该怎么进行组合使用呢?AB组合还是BC组合?
别瞎想了,你写的肯定没有CompletableFuture好用,看一下CompletableFuture是怎么用的:
/** * @author yideng * @apiNote CompletableFuture线程接力处理示例 */ public class ThreadDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { // 1. 创建线程池 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2); // 2. 提交任务,并调用join()阻塞等待任务执行完成 String result2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { // 睡眠一秒,模仿处理过程 try { Thread.sleep(1000L); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } return "结果1"; }, executorService).thenApplyAsync(result1 -> { // 睡眠一秒,模仿处理过程 try { Thread.sleep(1000L); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } return result1 + "结果2"; }, executorService).join(); executorService.shutdown(); // 3. 获取结果 System.out.println(result2); } }
代码主要用到了CompletableFuture的thenApplyAsync()方法,作用就是异步处理上一个线程的结果。
是不是太方便了?
这么好用的CompletableFuture还有没有其他功能?当然有。
4. CompletableFuture常用API
4.1 CompletableFuture常用API说明
-
提交任务
supplyAsync
runAsync -
接力处理
thenRun thenRunAsync
thenAccept thenAcceptAsync
thenApply thenApplyAsync
handle handleAsync
applyToEither applyToEitherAsync
acceptEither acceptEitherAsync
runAfterEither runAfterEitherAsync
thenCombine thenCombineAsync
thenAcceptBoth thenAcceptBothAsync
API太多,有点眼花缭乱,很容易分类。
带run的方法,无入参,无返回值。
带accept的方法,有入参,无返回值。
带supply的方法,无入参,有返回值。
带apply的方法,有入参,有返回值。
带handle的方法,有入参,有返回值,并且带异常处理。
以Async结尾的方法,都是异步的,否则是同步的。
以Either结尾的方法,只需完成任意一个。
以Both/Combine结尾的方法,必须所有都完成。
- 获取结果
join 阻塞等待,不会抛异常
get 阻塞等待,会抛异常
complete(T value) 不阻塞,如果任务已完成,返回处理结果。如果没完成,则返回传参value。
completeExceptionally(Throwable ex) 不阻塞,如果任务已完成,返回处理结果。如果没完成,抛异常。
4. CompletableFuture常用API使用示例
用最常见的煮饭来举例:
4.1 then、handle方法使用示例
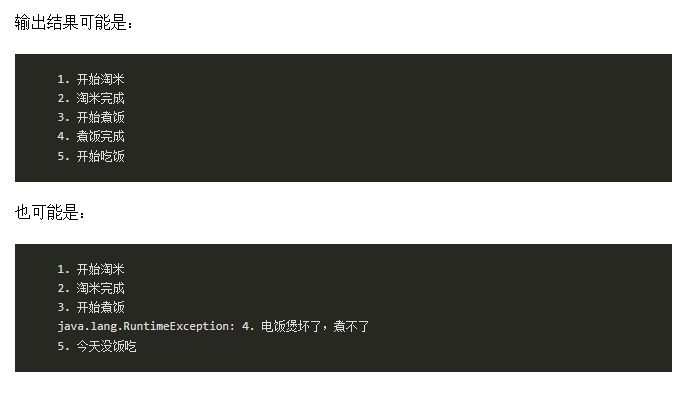
/** * @author yideng * @apiNote then、handle方法使用示例 */ public class ThreadDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { System.out.println("1. 开始淘米"); return "2. 淘米完成"; }).thenApplyAsync(result -> { System.out.println(result); System.out.println("3. 开始煮饭"); // 生成一个1~10的随机数 if (RandomUtils.nextInt(1, 10) > 5) { throw new RuntimeException("4. 电饭煲坏了,煮不了"); } return "4. 煮饭完成"; }).handleAsync((result, exception) -> { if (exception != null) { System.out.println(exception.getMessage()); return "5. 今天没饭吃"; } else { System.out.println(result); return "5. 开始吃饭"; } }); try { String result = completableFuture.get(); System.out.println(result); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
4.2 complete方法使用示例
/** * @author yideng * @apiNote complete使用示例 */ public class ThreadDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { return "饭做好了"; }); //try { // Thread.sleep(1L); //} catch (InterruptedException e) { //} completableFuture.complete("饭还没做好,我点外卖了"); System.out.println(completableFuture.join()); } }

4.3 either方法使用示例
/** * @author yideng * @apiNote either方法使用示例 */ public class ThreadDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { CompletableFuture<String> meal = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { return "饭做好了"; }); CompletableFuture<String> outMeal = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> { return "外卖到了"; }); // 饭先做好,就吃饭。外卖先到,就吃外卖。就是这么任性。 CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture = meal.applyToEither(outMeal, myMeal -> { return myMeal; }); System.out.println(completableFuture.join()); } }

(43条消息) Java获取CPU数量及线程池怎样设置最大线程数量公式_一个长不胖的程序YUAN的博客-CSDN博客_java获取cpu线程数
Java8已经发布7年了,不会还有人没用过CompletableFuture吧 (qq.com)
本文来自博客园,作者:chch213,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/chch213/p/16685591.html



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号