从0到微服务-3 服务发布与订阅
前面小节,我们简单了解了微服务架构以及几个常见的组成部件:
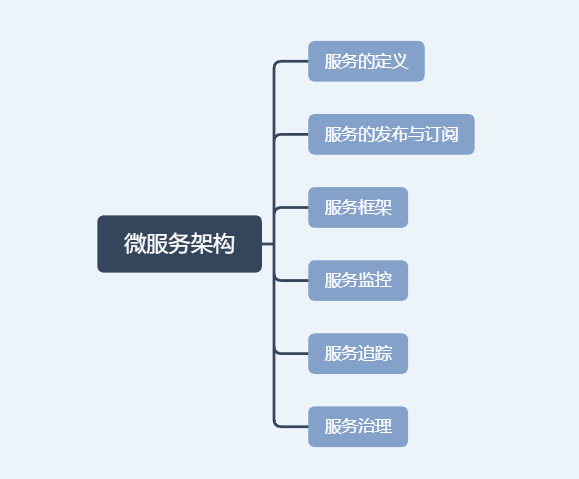
接下来,我们先具体学习下:
一、服务的定义、服务的发布与订阅
服务概念简单来说,就是这个服务的接口名是什么?调用这个服务需要传递哪些参数?接口的返回值是什么类型?以及一些其他接口描述信息。
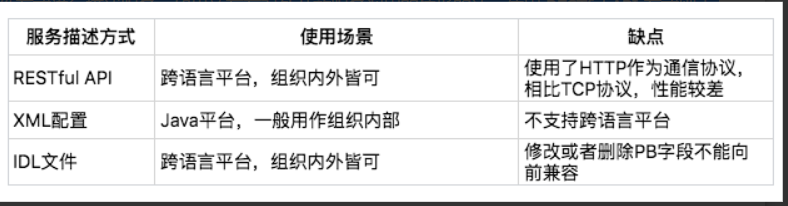
最常见的服务发布和引用的方式有三种:RESTful API 、 XML 配置 、 IDL 文件。
RESTful API
RESTful API 的方式,主要被用作 HTTP 或者 HTTPS 协议的接口定义,即使在非微服务架构体系下,也被广泛采用。
@RequestMapping(path = "/user") @RestController @Api(tags = "用户服务层接口", description = "用户服务层后台交互接口") @Validated public class UserController { @Autowired private final IUserService userService; @PostMapping(path = "/queryUserList") @ApiOperation(value = "查询用户信息", notes = "用于查询用户信息的接口,参数暂不需要", response = UserVO.class) @ApiParam(value = "用户id集合", name = "userIds", required = true) public List<UserVO> queryUserList(@RequestBody @Param("userIds") List<String> userIds) { return userService.queryUserList(userIds); } }
配置service.xml文件,启动服务
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:jaxrs="http://cxf.apache.org/jaxrs" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://cxf.apache.org/jaxrs" > <import resource="classpath:META-INF/cxf/cxf.xml" /> <import resource="classpath:META-INF/cxf/cxf-servlet.xml" /> <jaxrs:server id="apiService" address="/jaxrs"> <jaxrs:serviceBeans> <ref bean="userController"/> </jaxrs:serviceBeans> </jaxrs:server> <bean id="userController" class="com.demo.user.UserController"/> </beans>
具体可参考
XML 配置
这种方式的服务发布和引用主要分三个步骤:
服务提供者定义接口,并实现接口。
服务提供者进程启动时,通过加载 server.xml 配置文件将接口暴露出去,简单点就是提供者需要按一定的编程规范定义一个配置文件,里面包含所有要暴露的接口。
服务消费者进程启动时,通过加载 client.xml 配置文件来订阅要调用的接口,简单点就是消费者需要按一定的编程规范定义一个配置文件,里面包含索要使用的接口。
接下来,我们以微博服务化框架Motan学习下XML配置:
【RPC框架之Motan 介绍】 - 程序员大本营 (pianshen.com)
1、服务提供者
首先,服务提供者定义接口:
public interface IUserService { public String getUserName(String uuid); }
其次,服务提供者实现定义的接口:
public class UserServiceImpl implements IUserService { public String getUserName(String uuid) { return ....; } }
然后,配置server.xml属性文件暴露接口:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:motan="http://api.weibo.com/schema/motan" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://api.weibo.com/schema/motan http://api.weibo.com/schema/motan.xsd"> <!-- service implemention bean --> <bean id="userServiceImpl" class="com.demo.impl.UserServiceImpl" /> <!-- exporting service by Motan --> <motan:service interface="com.demo.IUserService" ref="userServiceImpl" export="8003" /> </beans>
最后,启动提供者微服务,开启端口8003
public class DemoApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:server.xml"); } }
2、服务消费者
配置client.xml属性文件,定义要调用的服务提供者的接口,然后启动服务与服务端一样
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:motan="http://api.weibo.com/schema/motan" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd http://api.weibo.com/schema/motan http://api.weibo.com/schema/motan.xsd"> <!-- reference to the remote service --> <motan:referer id="remoteUserService" interface="com.demo.IUserService" directUrl="http://127.0.0.1:8003"/> </beans>
就这样,通过在服务提供者和服务消费者之间维持一份对等的 XML 配置文件,来保证服务消费者按照服务提供者的约定来进行服务调用。在这种方式下,如果服务提供者变更了接口定义,不仅需要更新服务提供者加载的接口描述文件 server.xml,还需要同时更新服务消费者加载的接口描述文件 client.xml。
一般是私有 RPC 框架会选择 XML 配置这种方式来描述接口,因为私有 RPC 协议的性能要比 HTTP 协议高,所以在对性能要求比较高的场景下,采用 XML 配置的方式比较合适。但这种方式对业务代码侵入性比较高,XML 配置有变更的时候,服务消费者和服务提供者都要更新,所以适合公司内部联系比较紧密的业务之间采用。
IDL 文件
IDL 就是接口描述语言(interface description language)的缩写,通过一种中立的方式来描述接口,使得在不同的平台上运行的对象和不同语言编写的程序可以相互通信交流。比如你用 Java 语言实现提供的一个服务,也能被 PHP 语言调用。
也就是说 IDL 主要是用作跨语言平台的服务之间的调用,有两种最常用的 IDL:一个是 Facebook 开源的 Thrift 协议,另一个是 Google 开源的 gRPC 协议。无论是 Thrift 协议还是 gRPC 协议,它们的工作原理都是类似的。
gRPC协议使用了ProtoBuf,Proto文件来定义接口名、调用参数以及返回类型。ProtoBuf 是由 Google 开发的一种数据序列化协议,它的压缩和传输效率极高,语法也简单。
总结
服务描述最常见的三种方式:RESTful API、XML 配置以及 IDL 文件。具体采用哪种服务描述方式是根据实际情况决定的,通常情况下,如果只是企业内部之间的服务调用,并且都是 Java 语言的话,选择 XML 配置方式是最简单的。如果企业内部存在多个服务,并且服务采用的是不同语言平台,建议使用 IDL 文件方式进行描述服务。如果还存在对外开放服务调用的情形的话,使用 RESTful API 方式则更加通用。
本文来自博客园,作者:chch213,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/chch213/p/16293725.html







【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 写一个简单的SQL生成工具
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探