六、Redis事件驱动之Reactor模型
reactor模型应该是redis一道靓丽的风景点,也是面试经常提到的一部分内容。我觉得主要从2方面解答即可:1、reactor模型是什么? 2、redis如何与reactor模型相关联?
一、Reactor模型
Reactor模型就是网络服务器端用来处理高并发网络IO请求的一种编程模型。
不同请求与模型事件的对应关系:
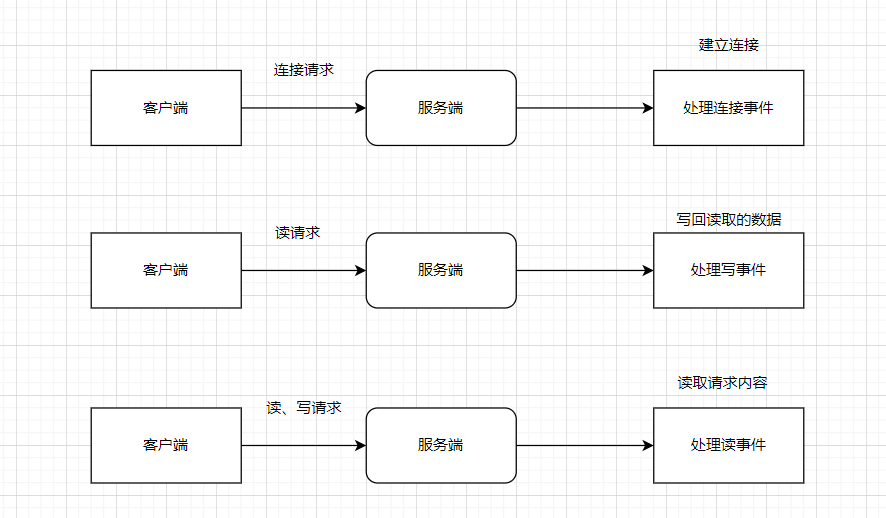
3种角色与事件直接的关系:
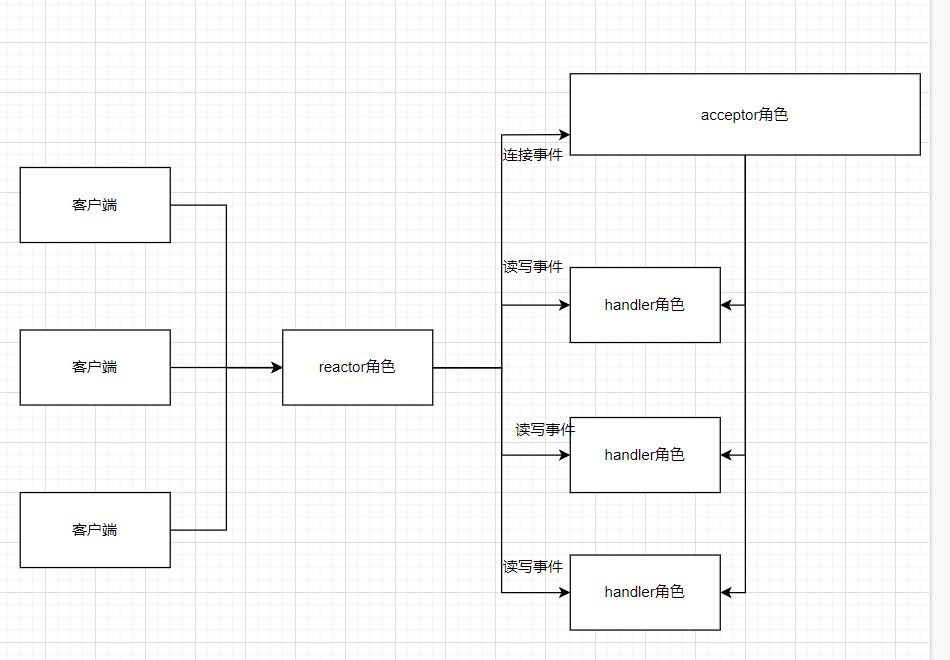
通过上面关系图我们能知道reactor模型的基本工作机制:客户端的不同请求会在服务器端触发连接、读、写三类事件,这三类事件的监听、分发、处理又是由reactor、acceptor、handler三类角色来完成的,然后这三类角色通过事件驱动框架实现交互和事件的处理。
二、Redis对Reactor模型的实现
/* File event structure */ 文件事件结构定义-IO事件 typedef struct aeFileEvent { int mask; /* one of AE_(READABLE|WRITABLE|BARRIER) */ 表示事件类型 aeFileProc *rfileProc; 读事件处理函数 aeFileProc *wfileProc; 写事件处理函数 void *clientData; 客户端私有数据的指针 } aeFileEvent; /* Time event structure */ 时间事件结构定义 typedef struct aeTimeEvent { long long id; /* time event identifier. */时间事件ID long when_sec; /* seconds */ 事件到达的秒级时间 long when_ms; /* milliseconds */ 事件到达的毫秒级时间 aeTimeProc *timeProc; 时间事件触发后的处理函数 aeEventFinalizerProc *finalizerProc; 事件结束后的处理函数 void *clientData; 事件相关的私有数据 struct aeTimeEvent *prev; 时间事件链表的前向指针 struct aeTimeEvent *next; 时间事件链表的后向指针 } aeTimeEvent;
前面redis源码目录结构讲解的时候介绍了一个源码文件对应的功能,那么对于reactor模型的实现主要在ae.c、ae.h文件中,接下来我们熟悉下事件驱动框架的3个主要函数:
一、Redis源码目录结构 - chch213 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
/* Prototypes */ 原型int aeCreateFileEvent(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int fd, int mask, aeFileProc *proc, void *clientData); // 负责事件handler注册
int aeProcessEvents(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int flags); // 事件捕获与分发处理(捕获事件、判断事件类型、调用具体的处理函数)void aeMain(aeEventLoop *eventLoop); // 框架主循环
1、主循环函数aeMain()服务启动时就有调用,详细可以看下: 二、Redis服务启动以及请求流程 - chch213 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
void aeMain(aeEventLoop *eventLoop) { eventLoop->stop = 0; while (!eventLoop->stop) { // 事件循环停止标识,只要不stop一直循环下去 if (eventLoop->beforesleep != NULL) eventLoop->beforesleep(eventLoop); aeProcessEvents(eventLoop, AE_ALL_EVENTS|AE_CALL_AFTER_SLEEP); } }
2、aeProcessEvents()事件捕获分发函数
int aeProcessEvents(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int flags) { int processed = 0, numevents; 1、无事可做吗?尽快返回 if (!(flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS) && !(flags & AE_FILE_EVENTS)) return 0; 2、如果有IO事件发生 或紧急时间事件发生,则开始处理 if (eventLoop->maxfd != -1 || ((flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS) && !(flags & AE_DONT_WAIT))) { int j; aeTimeEvent *shortest = NULL; struct timeval tv, *tvp; if (flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS && !(flags & AE_DONT_WAIT)) shortest = aeSearchNearestTimer(eventLoop); ....../调用aeApiPoll函数,依赖操作系统底层提供的IO多路复用机制,来实现事件捕获。 numevents = aeApiPoll(eventLoop, tvp); /* After sleep callback. */ if (eventLoop->aftersleep != NULL && flags & AE_CALL_AFTER_SLEEP) eventLoop->aftersleep(eventLoop); for (j = 0; j < numevents; j++) { ................ 根据事件类型不同调用不同的函数 processed++; } } 3、检查是否有普通时间事件,若有,则调用函数处理 if (flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS) processed += processTimeEvents(eventLoop); return processed; 返回已经处理的文件或时间 }
ae_evport.c----Solaris系统IO复用函数evport
ae_epoll.c----Linux系统IO复用函数epoll
ae_kqueue.c----macOS\FreeBSD系统IO复用函数kqueue
ae_select.c----Windows系统IO复用函数select
以Linux系统复用函数为例:
static int aeApiPoll(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, struct timeval *tvp) { aeApiState *state = eventLoop->apidata; int retval, numevents = 0; retval = epoll_wait(state->epfd,state->events,eventLoop->setsize, tvp ? (tvp->tv_sec*1000 + tvp->tv_usec/1000) : -1); // 调用epoll_wait监听事件 if (retval > 0) { int j; numevents = retval; 事件数量 for (j = 0; j < numevents; j++) { 循环处理事件 .......保存事件信息 } } return numevents;
3、aeCreateFileEvent()事件注册处理
redis服务器启动会调用initServer函数初始化服务器,过程中就会调用该事件注册函数,从而创建网络连接事件进行监听处理,当然底层也有对IO多了复用函数的封装,以Linux为例,提供了epoll_ctl用于增加新的观察事件。
三、针对reactor模型的使用做个拓展
除了本文讲的Redis使用了Reactor模型,还有几类中间件工具也有使用多路复用:
1、nignx:
nignx是多reactor多进程模型,master进程不处理网络IO,而是初始化socket,每个Worker进程是一个独立的单Reactor单线程模型
2、netty:
通信绝对的王者,默认是多Reactor,主Reactor只负责建立连接,然后把建立好的连接给从Reactor,从Reactor负责IO读写。当然也可以特意调整为单Reactor。
3、kafka:
也是多Reactor,但是因为kafka主要与磁盘IO交互,因此真正的读写数据不是从Reactor处理的,而是有一个worker线程池,专门处理磁盘IO,从Reactor负责网络IO,然后把任务交给worker线程池处理。
本文来自博客园,作者:chch213,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/chch213/p/16272077.html







【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix