单列集合
单列集合
Collection:用于存储一系列符合某种规则的元素,它有三个子接口分别为List和Set和Queue
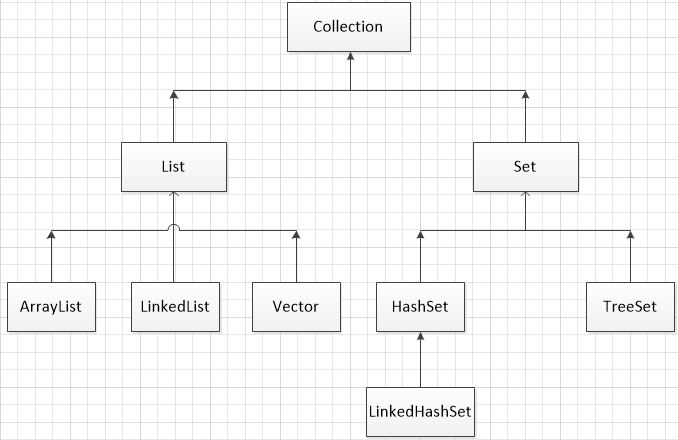
关系图
一.List集合
List的特点:所有元素是以一种线性方式进行存储,元素有序,可重复(存入顺序和取出顺序一致)
1.ArrayList集合
(1)ArrayList介绍
ArrayList是List接口的实现类,在ArrayList内部封装了一个长度可变的数组对象,当存入的元素超过数组的长度时,ArrayList会在内存中分配一个更大的数组来存储这些元素。
(2)优缺点:
ArrayList集合底层是使用一个数组来保存元素的,在增加或删除指定位置的元素时,会导致创建新的数组,效率低,不适合大量的增删操作。
但这种数组的结构允许程序通过索引的方式来访问元素,使用ArrayList集合查找元素方便。
(3)ArrayList集合的遍历
1 public class Test { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>(); 4 list.add("Hello"); 5 list.add("China"); 6 list.add("Hello"); 7 //1.foreach遍历ArrayList集合 8 for(String s:list) { 9 System.out.println(s); 10 } 11 //2.迭代器遍历ArrayList集合 12 Iterator<String> it = list.iterator(); 13 while(it.hasNext()) { 14 String s = it.next(); 15 System.out.println(s); 16 } 17 //3.将list转化成数组进行遍历 18 String[] arr = new String[list.size()]; 19 list.toArray(arr); 20 for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { 21 System.out.println(arr[i]); 22 } 23 } 24 }
2.LinkedList集合
(1)LinkedList介绍
LinkedList是List的实现类,它通过双向循环链表存储元素,链表中的每一个元素都使用引用的方式记住它前一个元素和后一个元素,并将所有的元素彼此连接起来。
(2)优缺点:
LinkedList使用双向循环链表存储元素,便于元素的添加和删除,但需要分配空间存储元素的前驱和后继指针浪费存储空间
二.Set接口
Set的特点:元素无序,不重复,可以用来去重
1.HashSet集合
(1)HashSet介绍
HashSet类用散列表方法存储元素,它根据对象的哈希值来确定元素在集合中的存储位置,因此具有良好的存取和查找性能
(2)HashSet去重原理
当向HashSet集合中添加一个元素时,首先会调用hashCode()方法来计算元素的哈希值,经过运算,算出元素在哈希表中的存储位置。
情况1:如果算出元素的存储位置目前没有任何元素存储,那么该元素就可以直接存储到该位置上。
情况2:如果算出该元素的存储位置目前已经存在其它的元素了,那么再调用对象的equals()方法与该位置的元素比较,
如果equals返回的是true,元素重复,不允许添加;如果返回false,则进行添加。
(3)HashSet应用
1 class Animal{ 2 private Integer id; 3 private String type; 4 public Animal(Integer id,String type) { 5 this.id = id; 6 this.type = type; 7 } 8 //重写toString方法 9 public String toString() { 10 return id+":"+type; 11 } 12 //重写hashCode方法 13 public int hashCode() { 14 return id.hashCode(); 15 } 16 //重写equals方法 17 public boolean equals(Object obj) { 18 //判断是否是一个对象 19 if (this==obj) { 20 return true; 21 } 22 //判断对象是否是Animal类型 23 if (!(obj instanceof Animal)) { 24 return false; 25 } 26 Animal animal = (Animal)obj; 27 //判断id是否相等 28 boolean b = this.id.equals(animal.id); 29 return b; 30 } 31 } 32 public class Test { 33 public static void main(String[] args) { 34 HashSet hs = new HashSet(); 35 Animal a = new Animal(1, "cat"); 36 Animal b = new Animal(2, "dog"); 37 Animal c = new Animal(2, "dog"); 38 hs.add(a); 39 hs.add(b); 40 hs.add(c); 41 System.out.println(hs); 42 } 43 }

2.TreeSet集合
(1)TreeSet介绍
TreeSet()是使用红黑树(二叉树)的原理对新添加的对象按照指定的顺序排序,每添加一个对象都会进行排序,将对象存储到二叉树中,存储原则左小右大
(2)ThreeSet应用
——自然排序:
————Integer和String对象都可以进行默认的TreeSet排序
1 public class Test { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 TreeSet ts = new TreeSet(); 4 ts.add(200); 5 ts.add(100); 6 ts.add(120); 7 ts.add(180); 8 ts.add(80); 9 Iterator it = ts.iterator(); 10 while (it.hasNext()) { 11 System.out.println(it.next()); 12 } 13 } 14 }

————自定义的类必须实现Comparable<T>接口,重写Comparable接口的compareTo方法
1 class Animal implements Comparable<Animal>{ 2 private Integer id; 3 private String type; 4 public Animal(Integer id,String type) { 5 this.id = id; 6 this.type = type; 7 } 8 public Integer getId() { 9 return id; 10 } 11 12 public void setId(Integer id) { 13 this.id = id; 14 } 15 16 public String getType() { 17 return type; 18 } 19 20 public void setType(String type) { 21 this.type = type; 22 } 23 24 @Override 25 public int compareTo(Animal o) { 26 //return -1;表示存放到二叉树的左边,即逆序存储 27 //return 1;表示存放到二叉树的右边,即顺序存储 28 //return 0;表示元素相同,仅存第一个元素多余的去除 29 int n = this.id-o.id; 30 int i=(n==0)?this.id.compareTo(o.id):n; 31 int t=(i==0)?(this.type.length()-o.type.length()):i; 32 return t; 33 } 34 } 35 public class Test { 36 public static void main(String[] args) { 37 TreeSet<Animal> ts = new TreeSet<Animal>(); 38 ts.add(new Animal(12, "cat")); 39 ts.add(new Animal(1, "tiger")); 40 ts.add(new Animal(5, "pig")); 41 ts.add(new Animal(2, "dog")); 42 ts.add(new Animal(2, "dog")); 43 for(Animal animal:ts) { 44 System.out.println(animal.getId()+":"+animal.getType()); 45 } 46 } 47 }

——比较器排序:
————自定义类实现Comparetor<T>接口,重写compare方法
1 class Animal{ 2 private Integer id; 3 private String type; 4 public Animal(Integer id,String type) { 5 this.id = id; 6 this.type = type; 7 } 8 public Integer getId() { 9 return id; 10 } 11 12 public void setId(Integer id) { 13 this.id = id; 14 } 15 16 public String getType() { 17 return type; 18 } 19 20 public void setType(String type) { 21 this.type = type; 22 } 23 24 } 25 public class Test { 26 public static void main(String[] args) { 27 TreeSet<Animal> ts = new TreeSet<Animal>(new Comparator<Animal>() { 28 @Override 29 public int compare(Animal o1, Animal o2) { 30 //主要条件id 31 int n = o1.getId()-o2.getId(); 32 int i=(n==0)?o1.getId().compareTo(o2.getId()):n; 33 int t=(i==0)?(o1.getType().length()-o2.getType().length()):i; 34 return t; 35 } 36 }); 37 ts.add(new Animal(12, "cat")); 38 ts.add(new Animal(1, "tiger")); 39 ts.add(new Animal(5, "pig")); 40 ts.add(new Animal(2, "dog")); 41 ts.add(new Animal(2, "dog")); 42 for(Animal animal:ts) { 43 System.out.println(animal.getId()+":"+animal.getType()); 44 } 45 } 46 }




