2022.6.7———HZOI【2022高考集训2】差点爆零记
仍然是成绩综述
 (喵喵qwq
(喵喵qwq
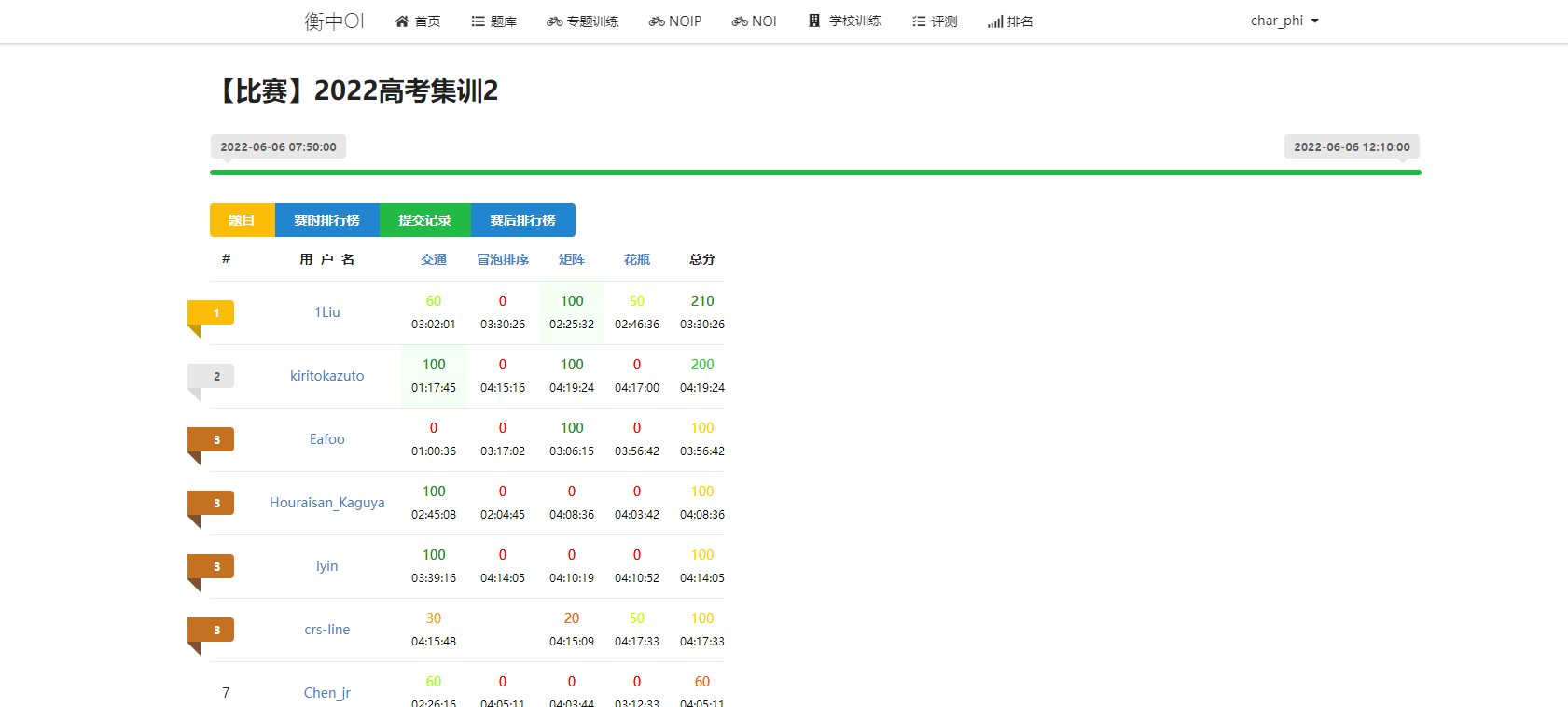
哇塞1Liu大佬太强了啦
kkksc03【kkkzuto】发挥稳定巨巨巨
Eafoo也好强!!!
蓬莱山Kaguya && 老殷 && crs-line笞人朔大佬都好巨!!!
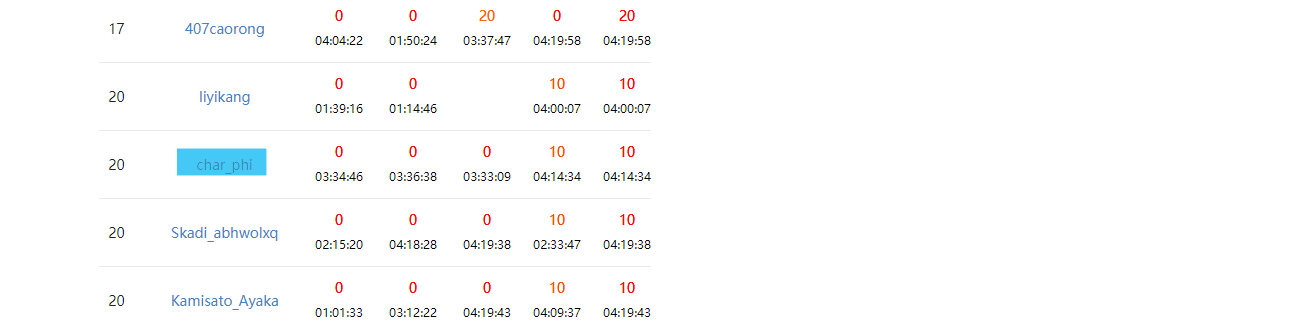
我还是一如既往的菜阿qAq
等等,你这名次怎么这么高,不是一共有44个oier参加吗
没错,我也没想到10分就这么高,因为出现了集体爆零。。。。
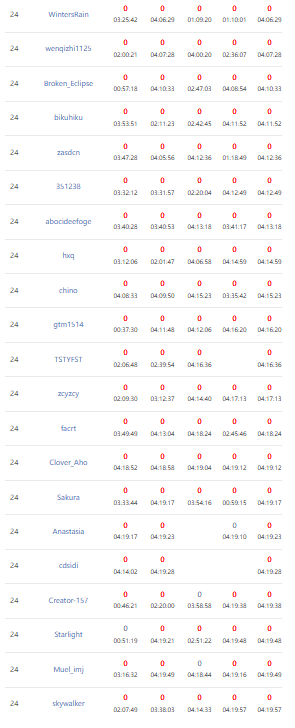
!!!dalao们虽败犹荣!!!肯定是因为打正解但是因为subtask被搞了才爆0的!!
题
T1 交通
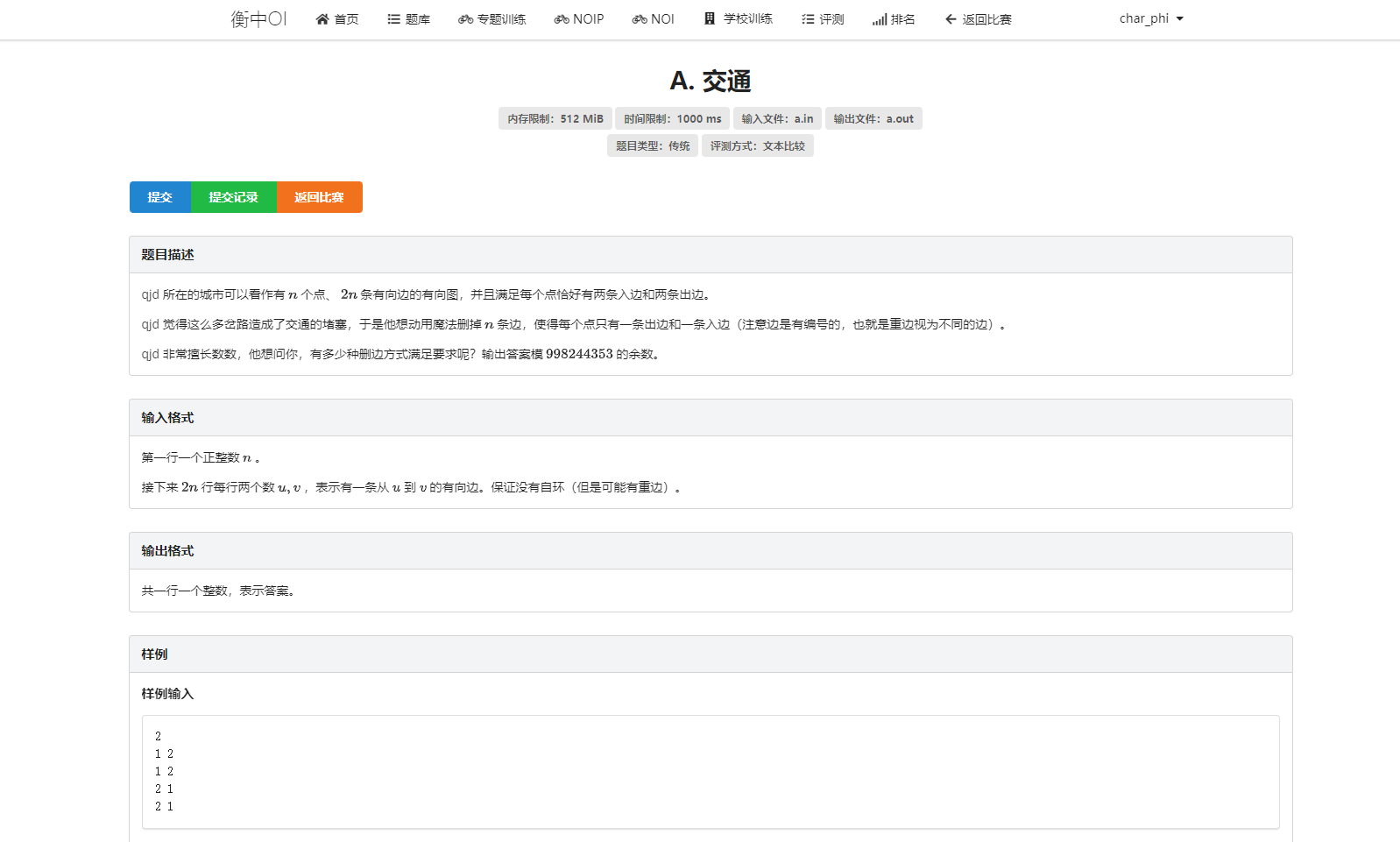
赛时想的是这玩意答案好像是2n,然后镁妙爆零
对每一个点的一对出边连无向边(没错,把边当成点来连),一对入边也是,然后判一下环(可以用并查集,也可以用tarjan(应该行,我一会试一下),floyd就算了吧。。。),答案就是2环数,用快速幂搞
为啥要这么干???
因为题目说了,每个点必须要保留一个出边和一个入边,所以我们对他的一对出边作为点连边和一对入边作为点连边,表示这两个边只能删掉一个
然后最后就会变成几个环,因为新图中每个点恰好度数是二,所以一定还是个偶环
那么为什么答案就是2环数呢?
对于任意一个偶环
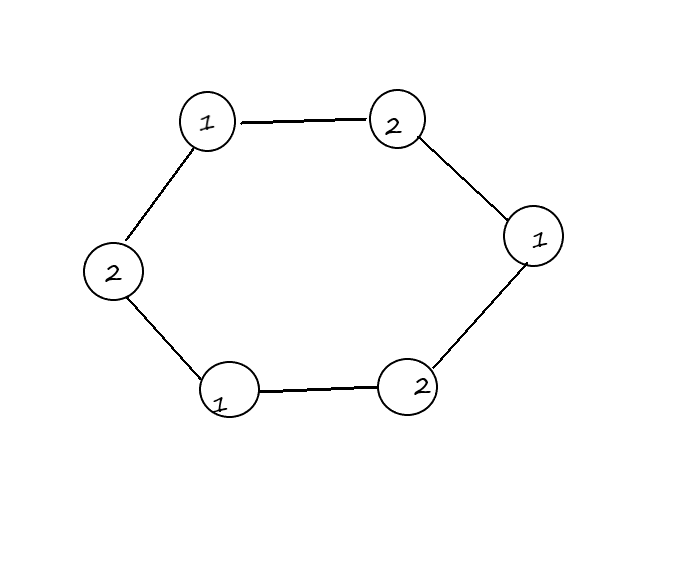 (小画一波
(小画一波
(这是新建的图)
如图所标,1是第一种删边的方案,2是第二种删边的方案
每一个点代表原图中一条边,两个点连起来代表这两个"边"同为某一个点的一对出边或入边,只能删去他俩其中之一
又因为可能存在森林,所以是2环数
T1
/*#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cctype>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#define ll long long
#define mem(x,y) memset(x,y,sizeof(x))
#define re register int
#define iwh printf("我永远爱文虎")
#define ot(x) printf("%d",x)
#define lot(x) printf("%lld",x)
#define MARK printf("~~~")
#define _MARK printf("###")
#define LMARK printf("@@@@@@")
#define SLEEP printf("??")
#define SLEEPER printf("(~﹃~)~zZ")
#define STUDY printf("??")
#define _ putchar(' ')
#define endl putchar('\n')
#define char_phi signed
#define MIN(a,b) ((a < b) ? (a) : (b))
#define MAX(a,b) ((a > b) ? (a) : (b))
#define P 998244353
#define N 100005
using namespace std;
ll n;
int star_cnt, tarjan_id, strong_num, top, toper;
bool inside[N];
int head[N<<2], dfn[N], low[N], st[N];
struct star{
int v,nxt;
}e[N<<2];
int p[N][5];
inline int read(){
int x = 0; char c;
while(!isdigit(c = getchar()));
do{
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (c & 15);
}while(isdigit(c = getchar()));
return x;
}
inline ll readd(){
ll x = 0; char c;
while(!isdigit(c = getchar()));
do{
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (c & 15);
}while(isdigit(c = getchar()));
return x;
}
ll res;
inline ll ksm(ll a,ll b){
res = 1;
while(b){
if(b & 1) res = (res * a) % P;
b >>= 1;
a = (a*a) % P;
}
return res;
}
inline void star_add(int uu,int vv){
e[++ star_cnt].v=vv, e[star_cnt].nxt = head[uu], head[uu] = star_cnt;
}
void tarjan(int x){//我踏马经典tarjan判环
dfn[x] = low[x] = ++ tarjan_id;
st[++ top] = x, inside[x] = true;
for(re i = head[x] ; i ; i = e[i].nxt){
if(dfn[e[i].v] == 0){
tarjan(e[i].v);
low[x] = MIN(low[x],low[e[i].v]);
}
else if(inside[e[i].v] == true){
low[x] = MIN(low[x],dfn[e[i].v]);
}
}
if(dfn[x] == low[x]){
++ strong_num;
do{
toper = st[top], top--, inside[toper] = false;
}while(toper != x);
}
}
inline void work(){
//数论?图论?
//这题好难造数据
//等等,他说的"自环"指的是...自己指向自己?
//也就是说图中可能有环存在?
//欸这不对吧
//每个点都有两个入边和出边,那不就是一个环吗
//还是碳碳双键的环(bushi)
//那么应该就是...
//2^n?
//真nm是这个东西就见了鬼了,但是这样例看不出来啥,打个快速幂直接开T2吧
//太阴险了,是倒是这个,但是,但是!连通图nmd!!!
n = read();
int useless;
for(re i = 1, uu, vv ; i <= (n<<1) ; ++ i){
// useless = read(),useless = read();
// uu = read(), vv = read();
// star_add(uu,vv);
p[uu][++p[uu][0]] = vv;
}
// if(n == 859 && useless == 470){
// puts("32");
// exit(0);
// }
for(re i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++ i){
if(dfn[i] == 0){
tarjan(i);
}
}
printf("%lld",ksm(2,strong_num));
}
char_phi main(){
freopen("a.in","r",stdin);
freopen("a.out","w",stdout);
work();
return 0;
}*/
//重构一波
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cctype>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#define ll long long
#define mem(x,y) memset(x,y,sizeof(x))
#define re register int
#define iwh printf("我永远爱文虎")
#define ot(x) printf("%d",x)
#define lot(x) printf("%lld",x)
#define MARK printf("~~~")
#define _MARK printf("###")
#define LMARK printf("@@@@@@")
#define SLEEP printf("💤")
#define SLEEPER printf("(~﹃~)~zZ")
#define STUDY printf("📕")
#define _ putchar(' ')
// #define endl putchar('\n')
#define char_phi signed
#define MIN(a,b) ((a < b) ? (a) : (b))
#define MAX(a,b) ((a > b) ? (a) : (b))
#define P 998244353
#define N 100005
using namespace std;
ll n;
int star_cnt, ider, final_ans;
bool vis[N<<1];//这里RE了,因为边啊是点的二倍...
int fa[N<<1];
int r[N][5], c[N][5];
inline int read(){
int x = 0; char c;
while(!isdigit(c = getchar()));
do{
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (c & 15);
}while(isdigit(c = getchar()));
return x;
}
inline ll readd(){
ll x = 0; char c;
while(!isdigit(c = getchar()));
do{
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (c & 15);
}while(isdigit(c = getchar()));
return x;
}
ll res;
inline ll ksm(ll a,ll b){
res = 1;
while(b){
if(b & 1) res = (res * a) % P;
b >>= 1;
a = (a*a) % P;
}
return res;
}
int find(int x){
if(fa[x] == x) return x;
return fa[x] = find(fa[x]);
}
inline void uniter(int x, int y){
x = find(x), y = find(y);
// cout << x << "?" << endl;
if(x != y){
fa[x] = y;
}
}
void work(){
/*
懂辽!
对于每个点,只能删掉他的两个入边之一和两个出边之一,所以要把两个入边作为两个点相连,两个出边作为两个点相连,表示这两个边不能同时删掉
比如一个三角形,三个顶点之间有两条有向边连接(一正一反),把边们连起来之后变为:
这样一个样子:
1 — 2
/ \
6 3
\ /
5 — 4
这个【环】囊括了两种情况,只能删1,3,5这三条边或者删2,4,6这三条边
所以要找重新建图后环的个数,再快速幂
然而除了tarjan我不会别的找环。。
并查集找环什么东西
我肯定tarjan啊~
Update:你奈奈无向图不能跑tarjan
*/
n = read();
for(re i = 1, uu, vv ; i <= (n << 1) ; ++ i){
uu = read(), vv = read();
r[vv][++ r[vv][0]] = i;
c[uu][++ c[uu][0]] = i;
// cout << r[vv][r[vv][0]] << "干嘛了" << c[uu][c[uu][0]] << endl;
}
//经典 并查集没有初始化
for(re i = 1 ; i <= (n << 1) ; ++ i){
fa[i] = i;
}
// cout << ider << endl;
for(re i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++ i){
// cout << "入:" << r[i][1] << "📕" << r[i][2] << endl;
// cout << "出:" << c[i][1] << "📕" << r[i][2] << endl;
uniter(r[i][1], r[i][2]);
uniter(c[i][1], c[i][2]);
}
for(re i = 1,sigma ; i <= (n << 1) ; ++ i){
sigma = find(i);
// cout << "??" << sigma << endl;
if(vis[sigma] == false){
vis[sigma] = true;
++ final_ans;
}
}
printf("%lld",ksm(2,final_ans));
}
char_phi main(){
freopen("a.in","r",stdin);
freopen("a.out","w",stdout);
work();
return 0;
}T2 冒泡排序
这个题光是读入就很难搞懂,这题我也没懂,等懂了再来补(逃
T2
//这题真神奇阿
//从头开始打一次
//话说这个编辑器又有dev的简洁又有vscode的快捷键还能兼容表情
//舒爽
//但是这道题还是不会,只能理解一点
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cctype>
#define char_phi signed
#define re register int
#define ll long long
#define MARK "###"
#define SLEEP "💤"
#define _ " "
#define ot(x) printf("%d",x)
#define lot(x) printf("%lld",x)
#define lowbit(x) ((x) & (-x))
#define P 1000000007
#define N 5005
using namespace std;
int n, final_ans;
int num[N], C1[N], C2[N], s1[N], s2[N];
int f[N][N];
inline int read(){
int x(0); char c; bool f(false);
while(!isdigit(c = getchar())){
if(c == '-'){
c = getchar(), f = true;
break;
}
}
do{
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (c & 15);
}while(isdigit(c = getchar()));
if(f == true) return -x;
return x;
}
inline void update(int k, int data, int who[]){
while(k <= n){
who[k] += data;
k += lowbit(k);
}
}
inline int ask(int k, int which){
if(which == 1) return C1[k] + s1[k - lowbit(k)];
else return C2[k] + s2[k - lowbit(k)];
}
inline void prework(){
n = read();
for(re i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++ i){
num[i] = read()+1;//For 树状数组
if(num[i] == i){
goto CHAR_PHI;
}
else if(num[i] > i){//小差分一波
update(i, 1, C1);
update(num[i]-1, -1, C1);
}
else {
update(num[i], 1, C2);
update(i-1, -1, C2);
}
}
for(re i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++ i){
s1[i] = ask(i, 1), s2[i] = ask(i, 2);//?
if(s1[i] != 0 && s2[i] != 0){
goto CHAR_PHI;
}
}
s1[0] = s2[0] = s1[n] = s2[n] = 0;
return;
CHAR_PHI:{
puts("0");
exit(0);
}
}
inline void dp(){
f[1][1] = 1;
for(re i = 2, j = 1 ; i < n ; j = i, ++ i){//这个j就相当于i的前一个
if(s1[j] != 0){
for(re k = 2 ; k <= i ; ++ k){
f[i][k] = (f[i][k-1] + f[j][k-1]) % P;
}
}
else if(s2[j] != 0){
for(re k = j ; k >= 1 ; -- k){
f[i][k] = (f[i][k+1] + f[j][k]) % P;
}
}
else{
for(re k = 1 ; k <= j ; ++ k){
f[i][1] = (f[i][1] + f[j][k]) % P;
}
for(re k = 2 ; k <= i ; ++ k){
f[i][k] = f[i][k-1];
}
}
}
for(re i = 1 ; i <= n-1 ; ++ i){
final_ans = (final_ans + f[n-1][i]) % P;
}
ot(final_ans);
}
inline void work(){
prework();
dp();
}
char_phi main(){
freopen("mp.in","r",stdin);
freopen("mp.out","w",stdout);
work();
return 0;
}
T3 矩阵
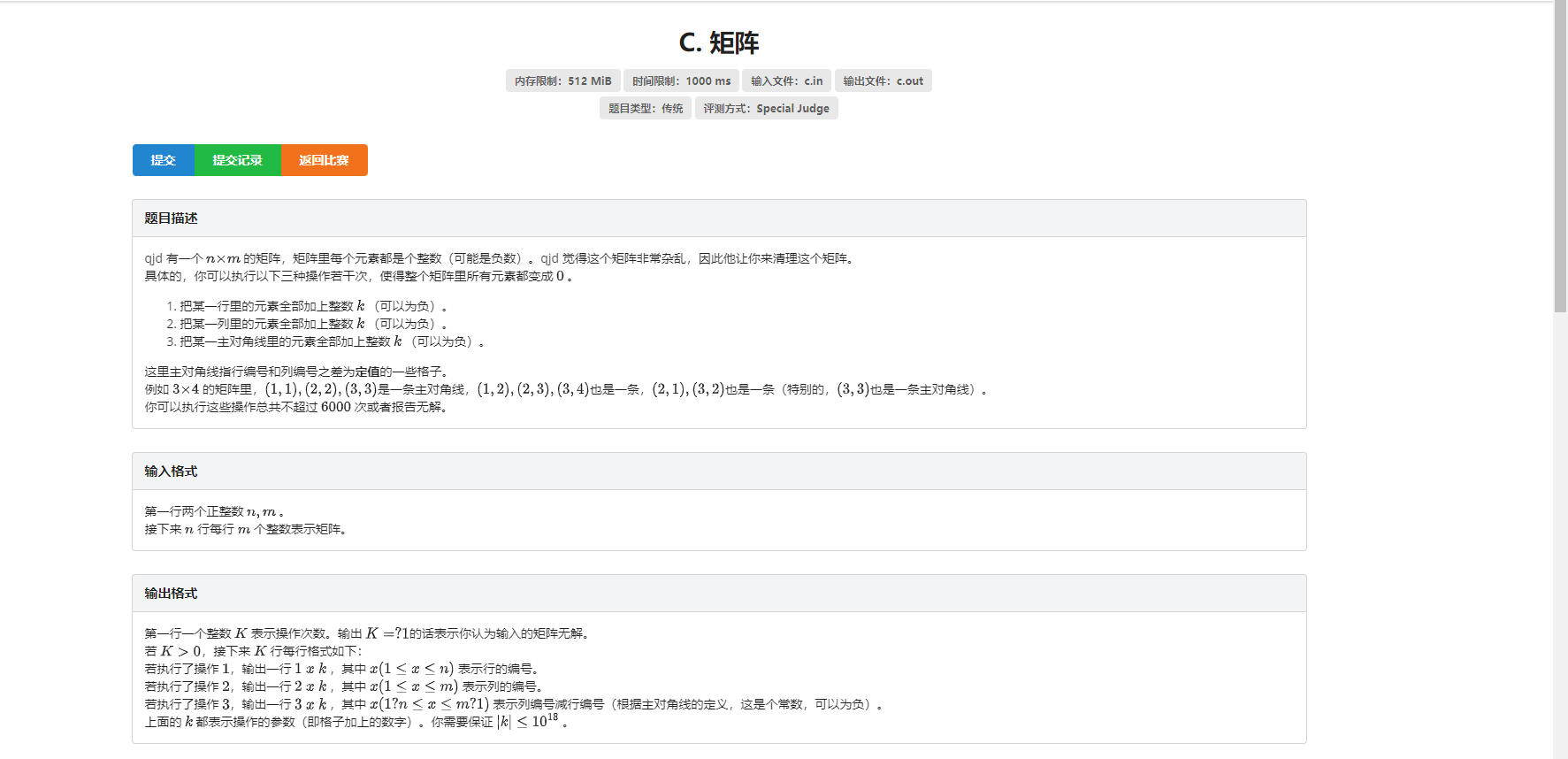
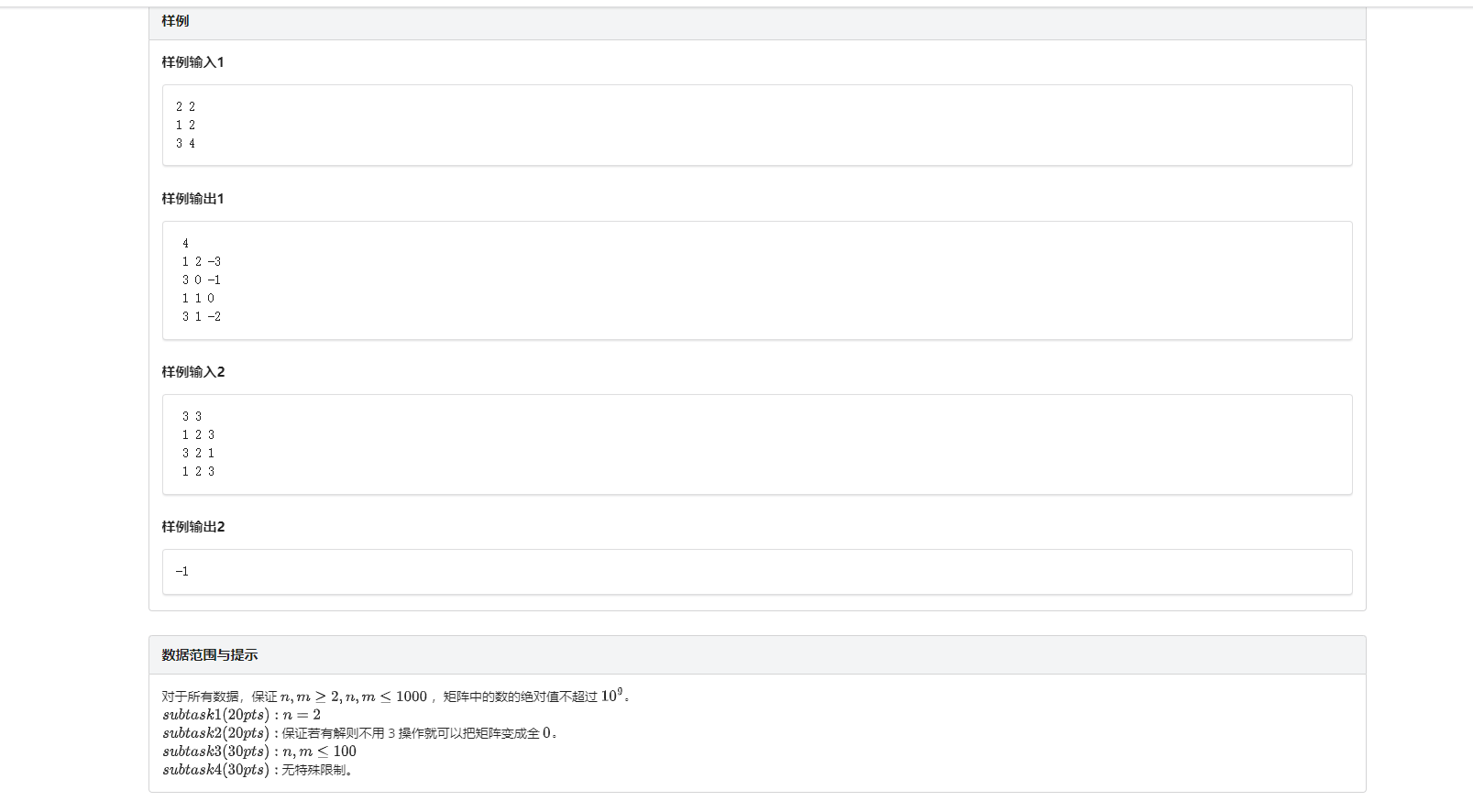
一个牛题阿!!!同机房的都说CDsidi写得好
我也来凑凑热闹
首先来整一个3×3的矩阵
(俺就用excel画图吧。。。
a - b - c = e - f - g + φ(φ是一个常数)(好像是?)
在一个可以全部消为0的矩阵里,φ = 0
证明:
假设他成立.
如果使用行操作(加上一个值为k)在第一行:
a +k - (b+k) - c = a + k - b - k - c = a - b - c 仍然= e - f - g
其他行同理
如果使用列操作(加上一个值为k)在第一列:
a + k - b - (c+k) = a + k - b - c - k = a - b -c 仍然= e - f - g
其他列同理
如果使用对角线操作(加上一个值为k)在a和e的对角线:
左式 = a + k - b - c , 右式 = e + k - f - g
a + k - b - c = e + k - f - g
两边共同消去一个k
仍为 a - b - c = e - f - g
"证毕"
那如何搞推广到大矩阵呢?
先把前两行和前两列都消为0(一会用)
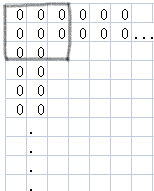
看图:
假设黑框框那个3×3的矩阵的右下角为θ
根据之前那个a - b - c = e - f - g
如果这个矩阵能消:
0 - 0 - 0 = θ - 0 - 0
θ = 0
同理:
刚才那个点确定为0后,往下移,新的黑框框的右下角那个点同理也是0了
别的同理
然后如果是2×2这种矩阵,直接特判就行
Source:
具体做法不想码字了,还得画图去,简单说两句
算了我还是画个图吧 要不真的难看懂我这个语文渣的描述
(像这么着消,把同是一个黑线的变成靠左上的那个元素的值
先消第二列,用行操作强制把当前点变成他左上角那个点(一会对角线操作用)
再消第二行,用列操作强制把当前点变成他左上角那个点(也是一会对角线操作用)
矩阵的最最最左下角和最最最右上角可以承担一切,因为他俩是特殊的对角线,可以自己变成0
然后这两步都搞完之后就用对角线操作,把刚才变成同一个值的那个东西所在的对角线减去他俩的值
根据之前咱证明那玩意,最后如果矩阵成功全是0了,就输出
有不是0的也就是φ ≠ 0,没法消完,输出-1
T3
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#define STAR "⭐"
#define SLEEP "💤"
#define MARK cout << "###"
#define _MARK "###"
#define re register int
#define ll long long
#define char_phi signed
#define Endl cout << endl
#define _ " "
#define N 1005
using namespace std;
ll n, m, cnth, cntl, cntd;
ll a[N][N];
struct node{
ll id, w;
};
node h[N], l[N], d[N<<1];//行,列,对角线
//shab对角线二倍数组搞得我RE
void debuger(){
cout << STAR; Endl;
for(re i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++ i){
for(re j = 1 ; j <= m ; ++ j){
cout << a[i][j] << _;
}
Endl;
}
cout << STAR; Endl, Endl;
}
void work(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
//发现了奇妙的性质
//写博客里吧
cin >> n >> m;
for(re i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++ i){
for(re j = 1 ; j <= m ; ++ j){
cin >> a[i][j];
}
}
//用行操作来"修改列",用列操作来"修改行"
//用行操作暴力修改第二列
for(re i = 2 ; i <= n ; ++ i){
/*l[++ cntl].id = 2, l[cntl].w = a[i-1][1] - a[i][2];
cout << SLEEP << l[cntl].w << endl;
cout << SLEEP << i << endl;
for(re j = 1 ; j <= m ; ++ j){
a[i][j] += l[cntl].w;
}
cout << "行:" << a[i-1][1] << _ << a[i][2] << endl;
debuger();*/
// cout << a[i-1][1] << _ << a[i][2] << endl << endl << endl;
h[++ cnth].id = i, h[cnth].w = a[i-1][1] - a[i][2];
for(re j = 1 ; j <= m ; ++ j){
a[i][j] += h[cnth].w;
}
// debuger();
}
//修改第二行
for(re j = 3 ; j <= m ; ++ j){
/*h[++ cnth].id = 2, h[cnth].w = a[1][j-1] - a[2][j];
for(re i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++ i){
a[i][j] += h[cnth].w;
}
debuger();*/
l[++ cntl].id = j, l[cntl].w = a[1][j-1] - a[2][j];
for(re i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++ i){
a[i][j] += l[cntl].w;
}
// debuger();
}
//消对角线
for(re st = 1, j ; st <= m-1 ; ++ st){//对角线起点
j = st;
d[++ cntd].id = st-1, d[cntd].w = -a[1][st];
for(re i = 1 ; i <= n && j <= m ; ++ i, ++ j){
a[i][j] += d[cntd].w;
}
// debuger();
}
for(re st = 2, i ; st <= n-1 ; ++ st){
i = st;
d[++ cntd].id = 1-st, d[cntd].w = -a[st][1];
for(re j = 1 ; j <= m && i <= n ; ++ j, ++ i){
a[i][j] += d[cntd].w;
}
// debuger();
}
d[++ cntd].id = m-1, d[cntd].w = -a[1][m];//这里一定记得记录这个操作!!!
d[++ cntd].id = 1-n, d[cntd].w = -a[n][1];
a[n][1] = a[1][m] = 0;
//消完辽?
for(re i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++ i){
for(re j = 1 ; j <= m ; ++ j){
if(a[i][j] != 0){
// cout << i << _ << j << endl;
goto CHAR_PHI;
}
}
}
cout << cnth+cntl+cntd << endl;
// cout << cnth << _ << cntl << _ << cntd << endl;
for(re i = 1 ; i <= cnth ; ++ i){
cout << "1" << _ << h[i].id << _ << h[i].w << endl;
}
for(re i = 1 ; i <= cntl ; ++ i){
cout << "2" << _ << l[i].id << _ << l[i].w << endl;
}
for(re i = 1 ; i <= cntd ; ++ i){
cout << "3" << _ << d[i].id << _ << d[i].w << endl;
}
// debuger();
return;
CHAR_PHI:{
puts("-1");
exit(0);
}
}
char_phi main(){
freopen("c.in","r",stdin);
freopen("c.out","w",stdout);
work();
return 0;
}T4 花瓶
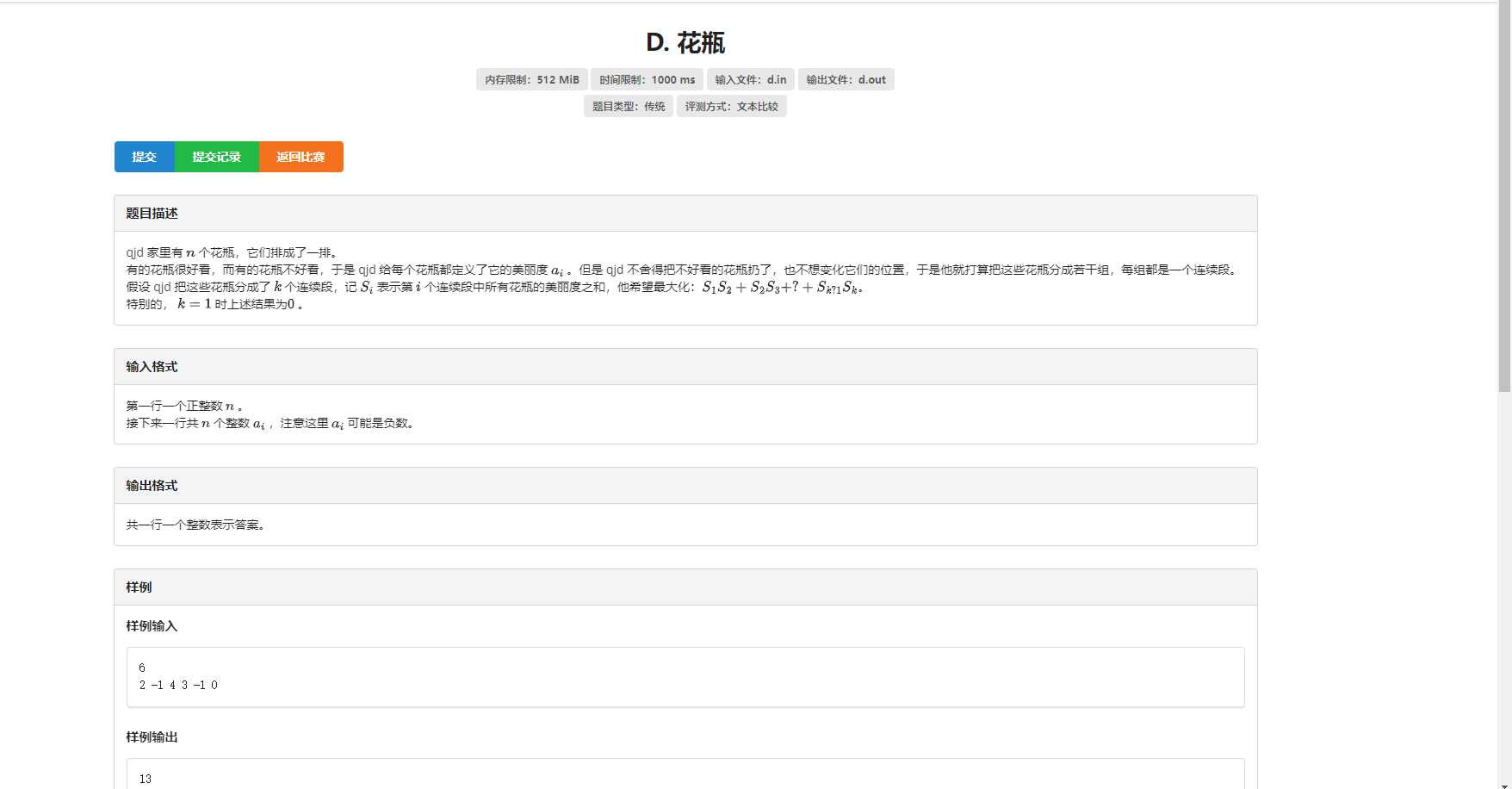
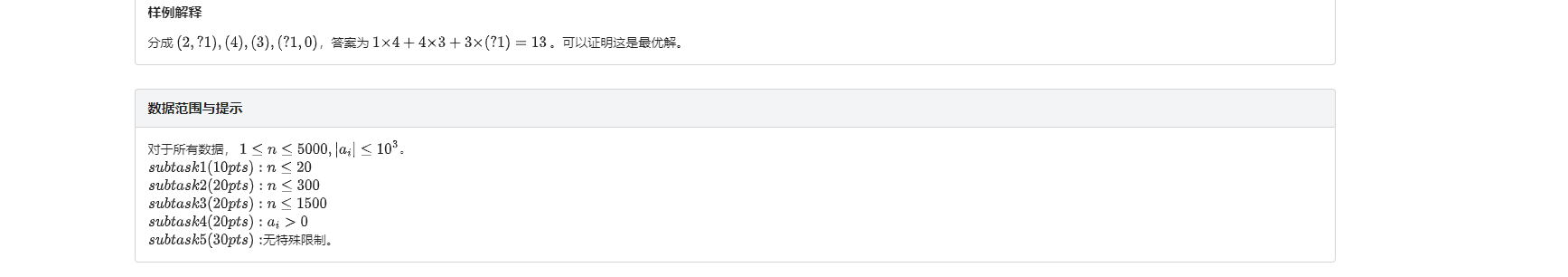
一个很ex的斜率优化dp
我真的不想码字了
唉我还是码一下吧
定义f[i][j]表示现在到了点i,上一个段的终点为j
所以第二维要严格小于第一维
维护一个前缀和数组s[]
k是上一个段的起点
那么有 f[i][j] = max{f[j][k] + (s[i] - s[j]) × (s[j] - s[k])
其中1 <= k < j, 1 <= j <= n
给那max去了,整理,拆开,f[j][k]移项
f[j][k] = (s[i]-s[j]) × s[k] + f[i][j] + s[j] × s[j] - s[i] × s[j]
y = k x + d
一次函数来力!斜率出来力!
然而因为负数的存在,前缀和数组不单调
噔噔咚
?你有嘛病
然后想到了一个东西:
sort
给他前缀和sort一遍强制单调
然后就可以开个队列维护变成了普通的斜率优化了
还有一件事——
维护一个上凸包,因为我们想要的答案是f[i][j],属于截距
不过呢斜率越小截距越大嘛()(),所以上凸包
然后记得刚开始记录每个点的id
然后用好就行了
T4
// {
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#define STAR "⭐"
#define SLEEP "💤"
#define MARK cout << "###"
#define _MARK "###"
#define re register int
#define ll long long
#define char_phi signed
#define Endl cout << endl
#define _ " "
#define MIN(x,y) (((x) < (y)) ? (x) : (y))
#define MAX(x,y) (((x) > (y)) ? (x) : (y))
#define N 5005
using namespace std;
// }
ll n, l, r, final_ans(-520131420050628);
ll a[N], s[N], q[N], id[N];//s前缀和
ll f[N][N];//f[i][j] 现在到了点i,上一段的终点为j
inline bool comp(ll A, ll B){
return s[A] < s[B];//递增排序(横坐标)
}
inline long double getk(ll i, ll j, ll k){
return ((long double)(f[i][k] - f[i][j]) / (long double)(s[k] - s[j]));//两点确定一条直线【斜率】
}
void work(){
//什么都不能阻止我%%%phigros
//展开后:
//f[j][k] = (s[i]-s[j]) × s[k] + f[i][j]+s[j]×s[j] -s[i]×s[j]
// y = k × x + d
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> n;
for(re i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++ i){
cin >> a[i];
s[i] = s[i-1] + a[i], id[i] = i;
}
for(re i = 1 ; i <= n+1 ; ++ i){
for(re j = 1 ; j <= n+1 ; ++ j){
f[i][j] = -0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
}
}
sort(id, id+n+1, comp);///把x坐标搞成单调的,
for(re i = 1 ; i <= n ; ++ i) f[i][0] = 0;//目前一整个串的都是0(响应题目号召)
for(re j = 1 ; j <= n ; ++ j){//上一个块的终点
l = 1, r = 0;
for(re k = 0 ; k <= n ; ++ k){//k从0开始为啥
if(id[k] < j){//f[j][id[k]],k得小于j吧
while(l < r && getk(j, q[r-1], q[r]) <= getk(j, q[r-1], id[k]))
-- r;
q[++ r] = id[k];
}
}
for(re i = n ; i >= 0 ; -- i){
if(j < id[i]){//f[id[i]][j],j得小于id[i]
while(l < r && getk(j, q[l], q[l+1]) >= (s[id[i]] - s[j]))
++ l;
//s[id[i]] - s[j]是k
f[id[i]][j] = MAX(f[id[i]][j], f[j][q[l]] + (s[id[i]] - s[j]) * (s[j] - s[q[l]]));
}
}
}
for(re i = 0 ; i < n ; ++ i){//0~n,第二维要严格小于第一维
final_ans = MAX(final_ans, f[n][i]);
}
cout << final_ans ;
}
char_phi main(){
freopen("d.in","r",stdin);
freopen("d.out","w",stdout);
work();
return 0;
}这考的都什么神仙题,还带了subtask。。。
Welcome to Phigros.

 T1 交通 | T2 冒泡排序 | T3 矩阵 | T4 花瓶 | 什么也看不到
T1 交通 | T2 冒泡排序 | T3 矩阵 | T4 花瓶 | 什么也看不到


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号