Python Django 生产环境部署
在生产上部署Django
Django的部署可以有很多方式,采用nginx+uwsgi的方式是其中比较常见的一种方式。

uwsgi介绍
uWSGI是一个Web服务器,它实现了WSGI协议、uwsgi、http等协议。Nginx中HttpUwsgiModule的作用是与uWSGI服务器进行交换。
要注意 WSGI / uwsgi / uWSGI 这三个概念的区分。
- WSGI是一种Web服务器网关接口。它是一个Web服务器(如nginx,uWSGI等服务器)与web应用(如用Flask框架写的程序)通信的一种规范。
- uwsgi是一种线路协议而不是通信协议,在此常用于在uWSGI服务器与其他网络服务器的数据通信。
- 而uWSGI是实现了uwsgi和WSGI两种协议的Web服务器。
- uwsgi协议是一个uWSGI服务器自有的协议,它用于定义传输信息的类型(type of information),每一个uwsgi packet前4byte为传输信息类型描述,它与WSGI相比是两样东西。
uwsgi性能非常高

uWSGI的主要特点如下
- 超快的性能
- 低内存占用(实测为apache2的mod_wsgi的一半左右)
- 多app管理(终于不用冥思苦想下个app用哪个端口比较好了-.-)
- 详尽的日志功能(可以用来分析app性能和瓶颈)
- 高度可定制(内存大小限制,服务一定次数后重启等)
总而言之uwgi是个部署用的好东东,正如uWSGI作者所吹嘘的:
If you are searching for a simple wsgi-only server, uWSGI is not for you, but if you are building a real (production-ready) app that need to be rock-solid, fast and easy to distribute/optimize for various load-average, you will pathetically and morbidly fall in love (we hope) with uWSGI.
Uwsgi 安装使用
|
1
2
3
4
|
# Install the latest stable release:pip install uwsgi# ... or if you want to install the latest LTS (long term support) release,pip install https://projects.unbit.it/downloads/uwsgi-lts.tar.gz |
基本测试
Create a file called test.py:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
# test.pydef application(env, start_response): start_response('200 OK', [('Content-Type','text/html')]) return [b"Hello World"] # python3 #return ["Hello World"] # python2 |
运行
|
1
|
uwsgi --http :8000 --wsgi-file test.py |
用uwsgi 启动django
|
1
|
uwsgi --http :8000 --module mysite.wsgi |
可以把参数写到配置文件里
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
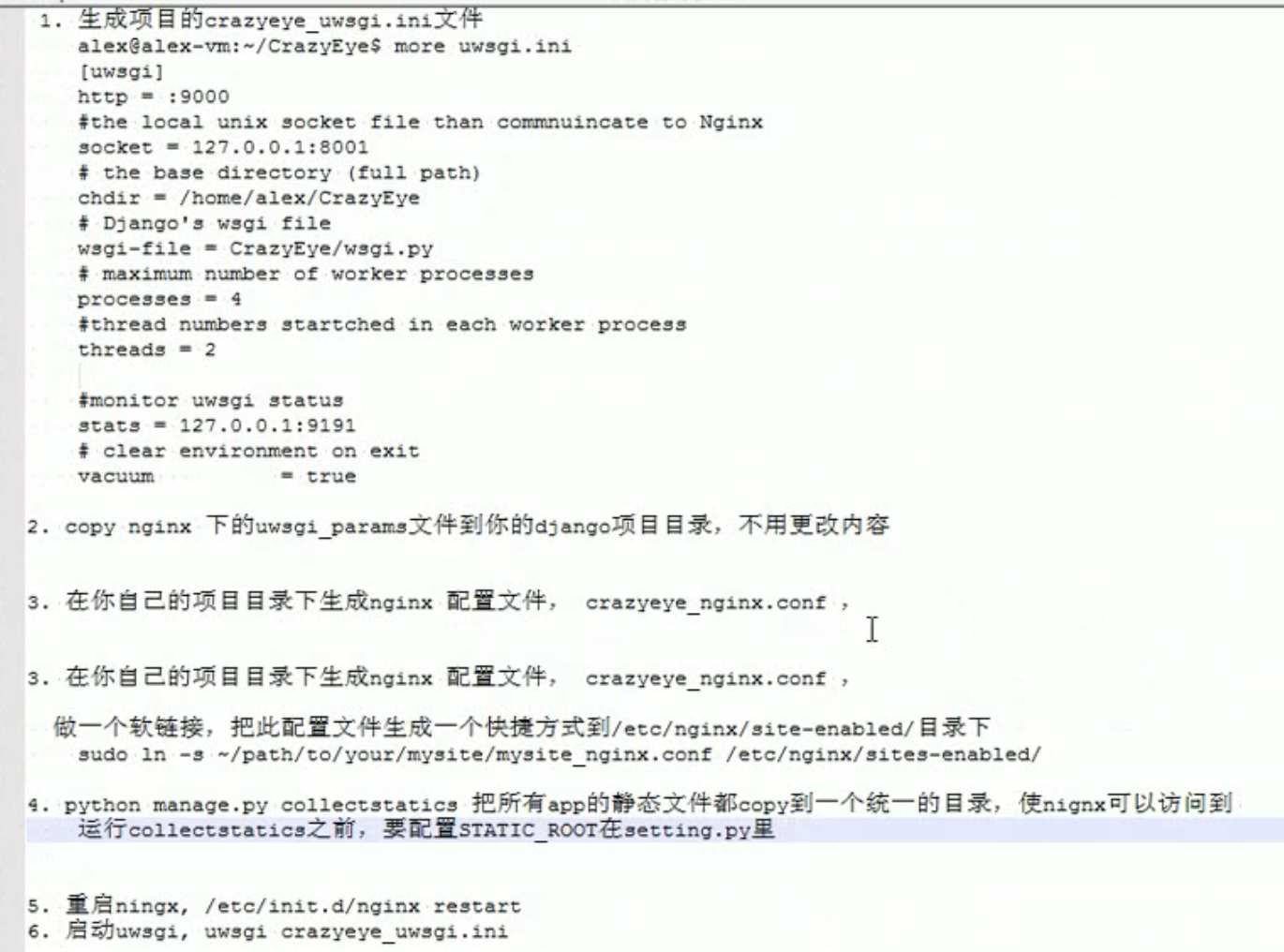
alex@alex-ubuntu:~/uwsgi-test$ more crazye-uwsgi.ini [uwsgi]http = :9000#the local unix socket file than commnuincate to Nginxsocket = 127.0.0.1:8001# the base directory (full path)chdir = /home/alex/CrazyEye # Django's wsgi filewsgi-file = CrazyEye/wsgi.py# maximum number of worker processesprocesses = 4#thread numbers startched in each worker processthreads = 2#monitor uwsgi status stats = 127.0.0.1:9191# clear environment on exitvacuum = true |
启动
|
1
|
/usr/local/bin/uwsgi crazye-uwsgi.ini |
Nginx安装使用
|
1
2
|
sudo apt-get install nginxsudo /etc/init.d/nginx start # start nginx |
为你的项目生成Nginx配置文件
You will need the uwsgi_params file, which is available in the nginx directory of the uWSGI distribution, or from https://github.com/nginx/nginx/blob/master/conf/uwsgi_params
Copy it into your project directory. In a moment we will tell nginx to refer to it.
Now create a file called mysite_nginx.conf, and put this in it:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
# mysite_nginx.conf# the upstream component nginx needs to connect toupstream django { # server unix:///path/to/your/mysite/mysite.sock; # for a file socket server 127.0.0.1:8001; # for a web port socket (we'll use this first)}# configuration of the serverserver { # the port your site will be served on listen 8000; # the domain name it will serve for server_name .example.com; # substitute your machine's IP address or FQDN charset utf-8; # max upload size client_max_body_size 75M; # adjust to taste # Django media location /media { alias /path/to/your/mysite/media; # your Django project's media files - amend as required } location /static { alias /path/to/your/mysite/static; # your Django project's static files - amend as required } # Finally, send all non-media requests to the Django server. location / { uwsgi_pass django; include /path/to/your/mysite/uwsgi_params; # the uwsgi_params file you installed }} |
This conf file tells nginx to serve up media and static files from the filesystem, as well as handle requests that require Django’s intervention. For a large deployment it is considered good practice to let one server handle static/media files, and another handle Django applications, but for now, this will do just fine.
Symlink to this file from /etc/nginx/sites-enabled so nginx can see it:
|
1
|
sudo ln -s ~/path/to/your/mysite/mysite_nginx.conf /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/ |
Deploying static files
Before running nginx, you have to collect all Django static files in the static folder. First of all you have to edit mysite/settings.py adding:
|
1
|
STATIC_ROOT = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, "static/") |
and then run
|
1
|
python manage.py collectstatic |
此时启动Nginx 和Uwsgi,你的django项目就可以实现高并发啦


https://www.cnblogs.com/chenice/p/6921727.html
https://blog.csdn.net/nghuyong/article/details/54025761
部署到云
https://www.jianshu.com/p/55c3fc8ea9b0
使用 Nginx 和 Gunicorn 部署 Django 博客
https://www.zmrenwu.com/post/20/



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号